Abstract
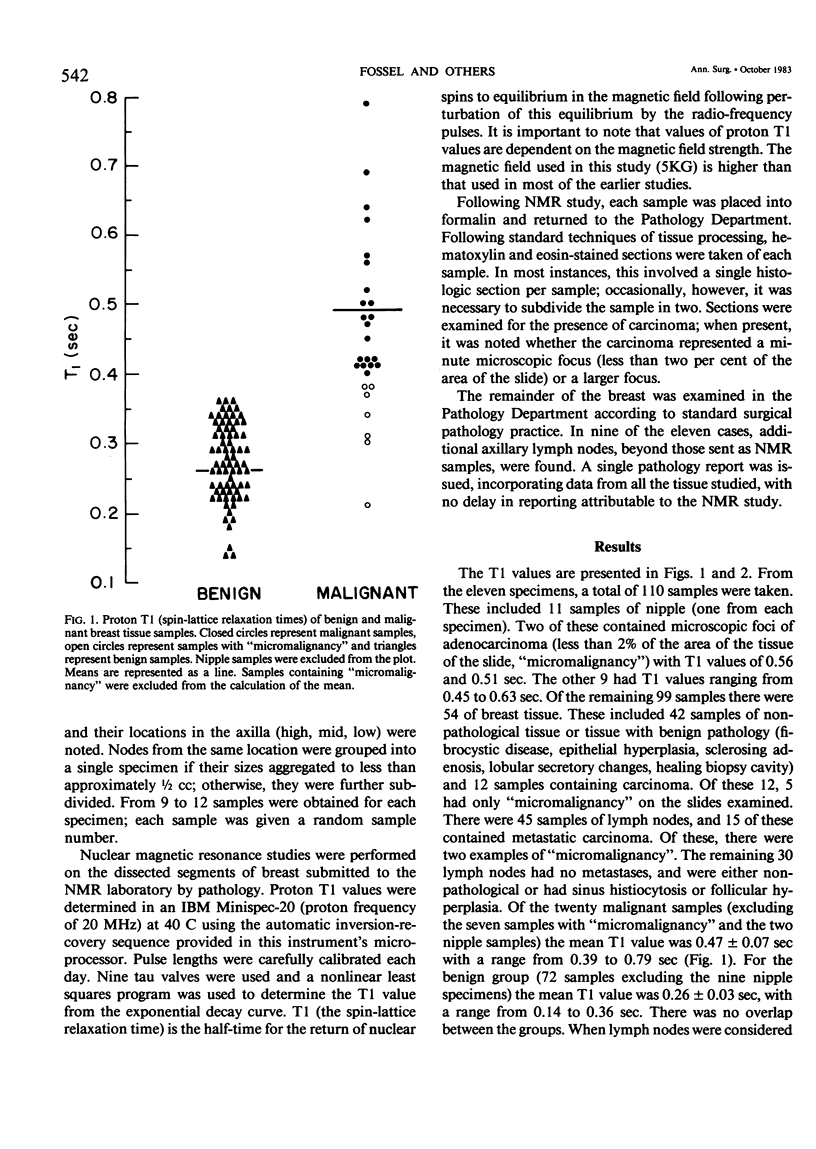
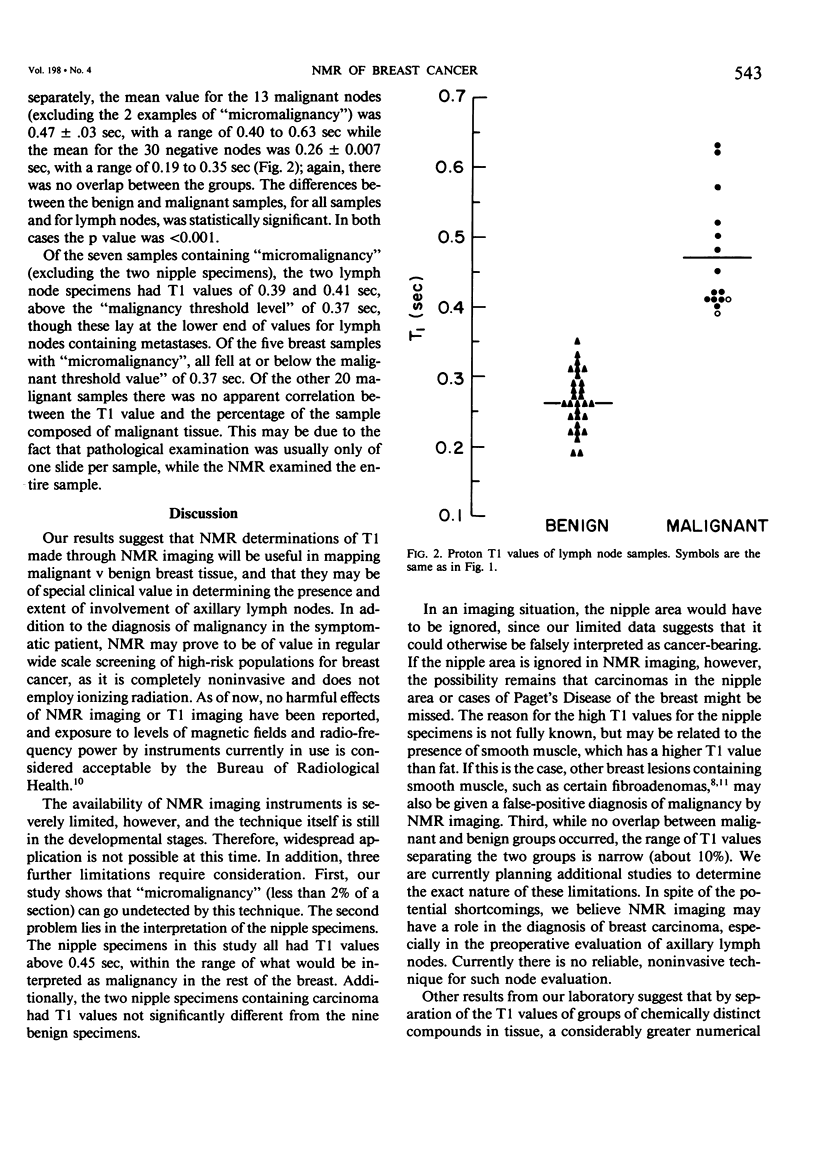
We have utilized proton T1 (spin-lattice relaxation time) values of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance to study 110 tissue samples obtained from 11 mastectomy specimens. Samples of 1 cm3 from primary tumor sites, nipples, and other breast quadrants, as well as intact lymph nodes were studied and then histologically scored for the presence or absence of carcinoma and, if present, whether it was an isolated microscopic focus (micro). Of 54 samples of breast tissue, 12 contained carcinoma, 5 micro: of 45 lymph nodes, 15 contained metastatic carcinoma, 2 micro; of the 11 nipples, 2 had carcinoma, both micro. For the malignant samples (excluding micro) mean T1 value was 0.47 +/- 0.07 sec, (range 0.39-0.79 sec). For the 72 benign samples (excluding nipple) mean T1 value was 0.26 +/- 0.03 sec (range 0.14-0.36 sec). The 13 tumor-bearing nodes had a mean T1 value of 0.47 +/- 0.03 sec (range 0.40-0.63 sec); mean for the benign nodes was 0.26 +/- 0.007 sec (range 0.19-0.35 sec). The differences were highly significant in each case (p less than 0.001). For micro examples, T1 values were at malignancy threshold levels or just below, except for nipple tissues, where discrimination was poor. For the 20 other malignant samples, there was no correlation between T1 value and the per cent of sample containing malignancy.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brownell G. L., Budinger T. F., Lauterbur P. C., McGeer P. L. Positron tomography and nuclear magnetic resonance imaging. Science. 1982 Feb 5;215(4533):619–626. doi: 10.1126/science.215.4533.619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damadian R. Tumor detection by nuclear magnetic resonance. Science. 1971 Mar 19;171(3976):1151–1153. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3976.1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein F. H. Nuclear magnetic resonance: a new tool in clinical medicine. N Engl J Med. 1981 May 28;304(22):1360–1361. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198105283042212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith M., Koutcher J. A., Damadian R. NMR in cancer, XIII: application of the NMR malignancy index to human mammary tumours. Br J Cancer. 1978 Oct;38(4):547–554. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1978.243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman Z. D., Taxy J. B. Fibroadenomas of the breast with prominent smooth muscle. Am J Surg Pathol. 1981 Jan;5(1):99–101. doi: 10.1097/00000478-198101000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazlewood C. F., Cleveland G., Medina D. Relationship between hydration and proton nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation times in tissues of tumor-bearing and non-tumor-bearing mice: implications for cancer detection. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Jun;52(6):1849–1853. doi: 10.1093/jnci/52.6.1849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansfield P., Maudsley A. A. Medical imaging by NMR. Br J Radiol. 1977 Mar;50(591):188–194. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-50-591-188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medina D., Hazlewood C. F., Cleveland G. G., Chang D. C., Spjut H. J., Moyers R. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies on human breast dysplasias and neoplasms. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Apr;54(4):813–818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


