Abstract
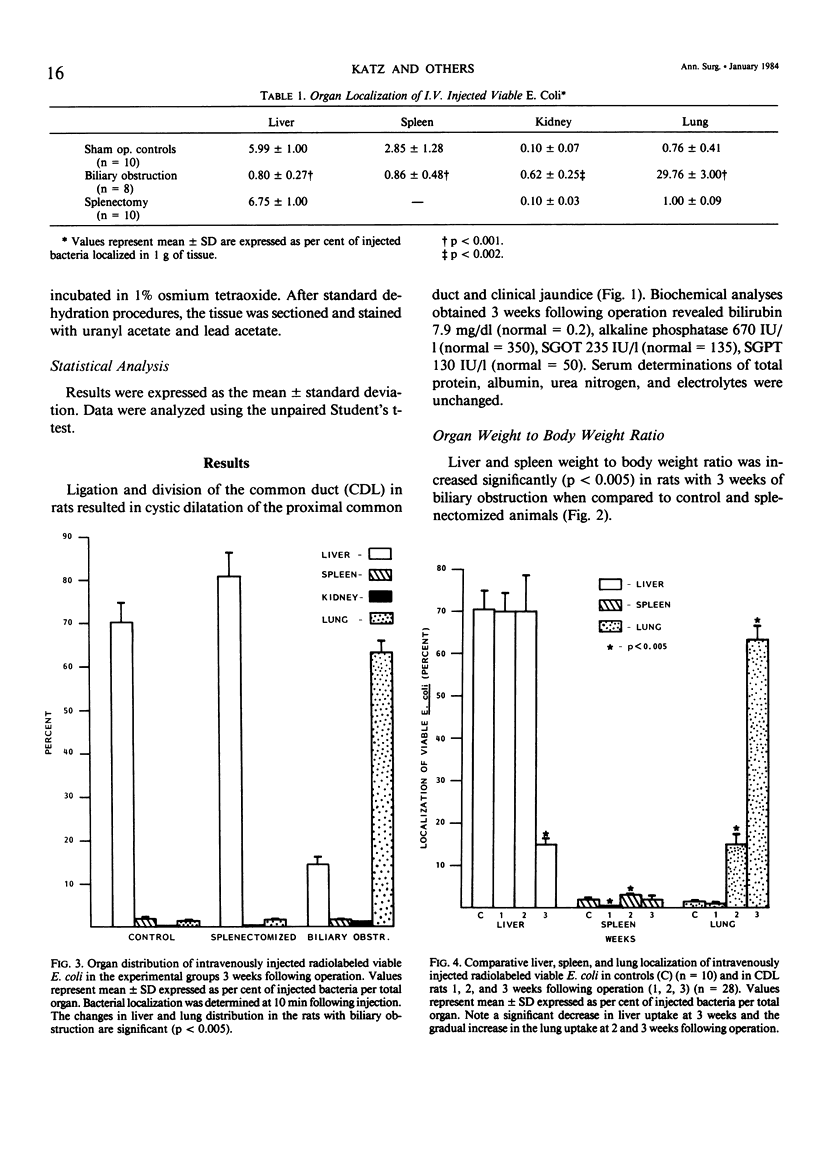
Sepsis is a major cause of mortality in patients with common bile duct obstruction. To define possible contributing factors to this phenomenon, this study evaluates the effect of biliary obstruction on the intravascular clearance and organ trapping of viable Escherichia coli using a rat model. Adult male Sprague-Dawley rats were placed in three groups: Group I controls had sham operation, Group II had division and ligation of common bile duct (CDL), and Group III underwent splenectomy. At 21 days following operation 10(9) radiolabeled E. coli were injected intravenously. At varying intervals after infusion, blood samples were obtained for clearance study. At 10 minutes, bacterial distribution in the liver, spleen, kidneys, and lungs was determined (expressed as the mean percentage of injected viable E. coli). Intravascular clearance was similar in all groups. There was a significant decrease in the trapping of bacteria by the liver of CDL rats 14.5% +/- 4.95 (vs. control = 70.0% +/- 13.3) (p less than 0.005). A significant increase of bacterial trapping by the lung was observed in the CDL animals: 63.1% +/- 7.06 (vs. controls 1.4% +/- 0.82) (p less than 0.005). There was no significant change in bacterial localization in splenectomized rats. These data suggest that biliary obstruction decreases hepatic phagocytosis and increases pulmonary localization of viable E. coli. As the Kupffer cells of the liver are usually effective in removal of blood borne bacteria, this phagocytic dysfunction may contribute to the increased susceptibility to infection noted in instances of biliary obstruction.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Drivas G., James O., Wardle N. Study of reticuloendothelial phagocytic capacity in patients with cholestasis. Br Med J. 1976 Jun 26;1(6025):1568–1569. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6025.1568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREEDMAN L. R., GOLDENBERG I. S. The relationship between bacterial infection of the hepato-biliary system and common bile duct obstruction in man. Yale J Biol Med. 1963 Feb;35:318–328. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holman J. M., Jr, Rikkers L. F. Biliary obstruction and host defense failure. J Surg Res. 1982 Mar;32(3):208–213. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(82)90092-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackaman F. R., Hilson G. R., Smith L. Bile bacteria in patients with benign bile duct stricture. Br J Surg. 1980 May;67(5):329–332. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800670509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanser M. E., Saba T. M. Neutrophil-mediated lung localization of bacteria: a mechanism for pulmonary injury. Surgery. 1981 Sep;90(3):473–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddocks A. C., Hilson G. R., Taylor R. The bacteriology of the obstructed biliary tree. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1973 May;52(5):316–319. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan J. P. Bacteria and the liver. N Engl J Med. 1978 Nov 9;299(19):1069–1071. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197811092991912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normann S. J. Kinetics of phagocytosis. II. Analysis of in vivo clearance with demonstration of competitive inhibition between similar and dissimilar foreign particles. Lab Invest. 1974 Aug;31(2):161–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira G. R., Sherman M. S., DiGiacomo J., Ziegler M., Roth K., Jacobowski D. Hyperalimentation-induced cholestasis. Increased incidence and severity in premature infants. Am J Dis Child. 1981 Sep;135(9):842–845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROGERS D. E. Host mechanisms which act to remove bacteria from the blood stream. Bacteriol Rev. 1960 Mar;24(1):50–66. doi: 10.1128/br.24.1.50-66.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROGERS D. E. Studies on bacteriemia. I. Mechanisms relating to the persistence of bacteriemia in rabbits following the intravenous injection of staphylococci. J Exp Med. 1956 Jun 1;103(6):713–742. doi: 10.1084/jem.103.6.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saba T. M., Di Luzio N. R. Reticuloendothelial blockade and recovery as a function of opsonic activity. Am J Physiol. 1969 Jan;216(1):197–205. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.1.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saba T. M. Physiology and physiopathology of the reticuloendothelial system. Arch Intern Med. 1970 Dec;126(6):1031–1052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saba T. M. Prevention of liver reticuloendothelial systemic host defense failure after surgery by intravenous opsonic glycoprotein therapy. Ann Surg. 1978 Aug;188(2):142–152. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197808000-00003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHIPPLE R. L., Jr, HARRIS J. F. B. coli septicemia in Laennec's cirrhosis of the liver. Ann Intern Med. 1950 Aug;33(2):462–466. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-33-2-462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





