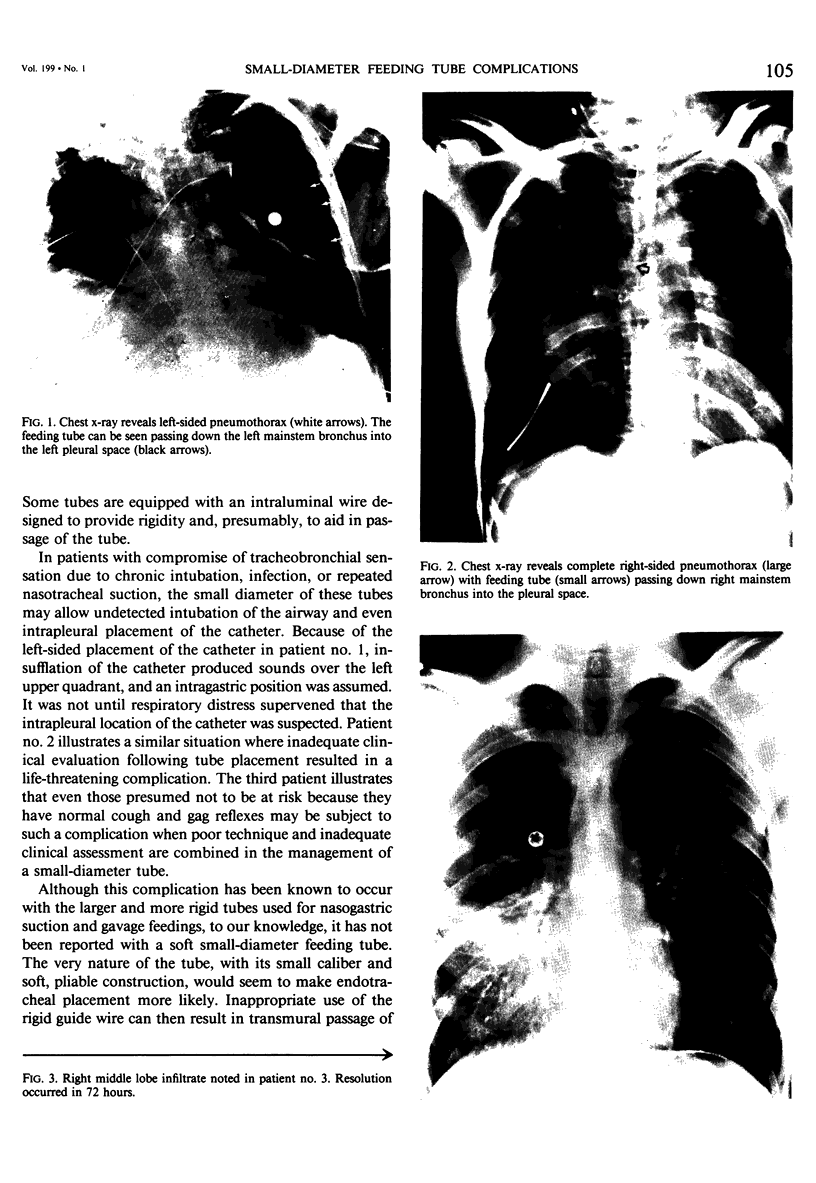
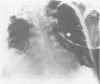
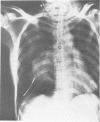
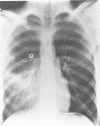
Abstract
The occurrence of nasotracheal intubation with feeding tubes of various types is well known but poorly documented. The small-diameter feeding tubes currently available for enteral hyperalimentation may be more prone to this complication because of their small size and the rigid guide wire which is required for placement. A high index of suspicion when placing these tubes in patients at risk, use of the wire guide to pass the nasopharynx only, and x-ray verification of tube location prior to usage should avert this potentially life-threatening mistake.
Full text
PDF