Abstract
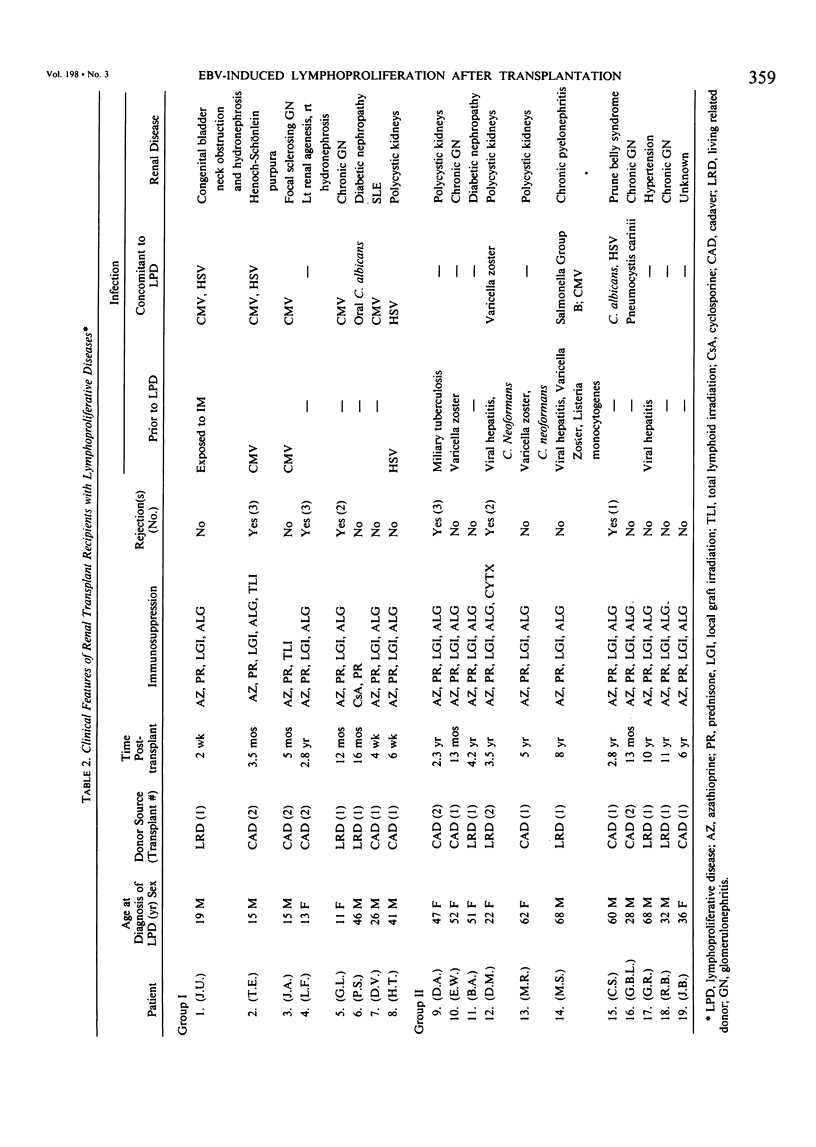
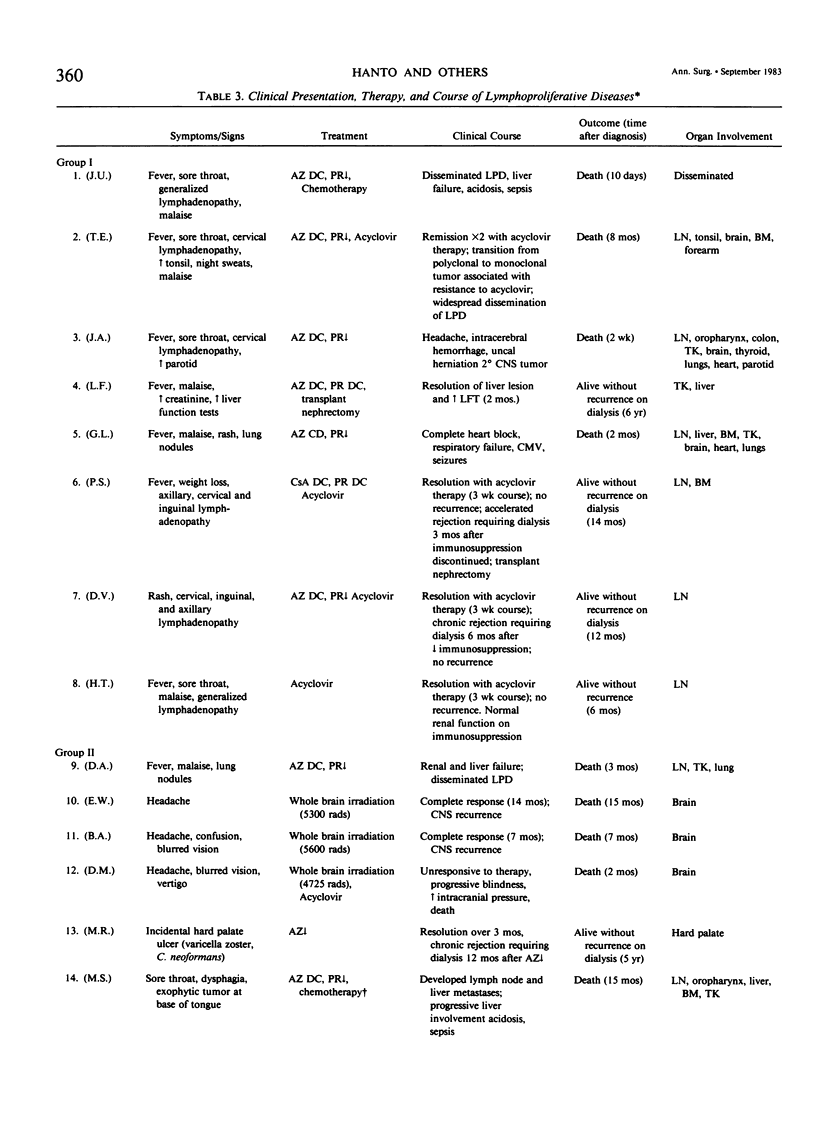
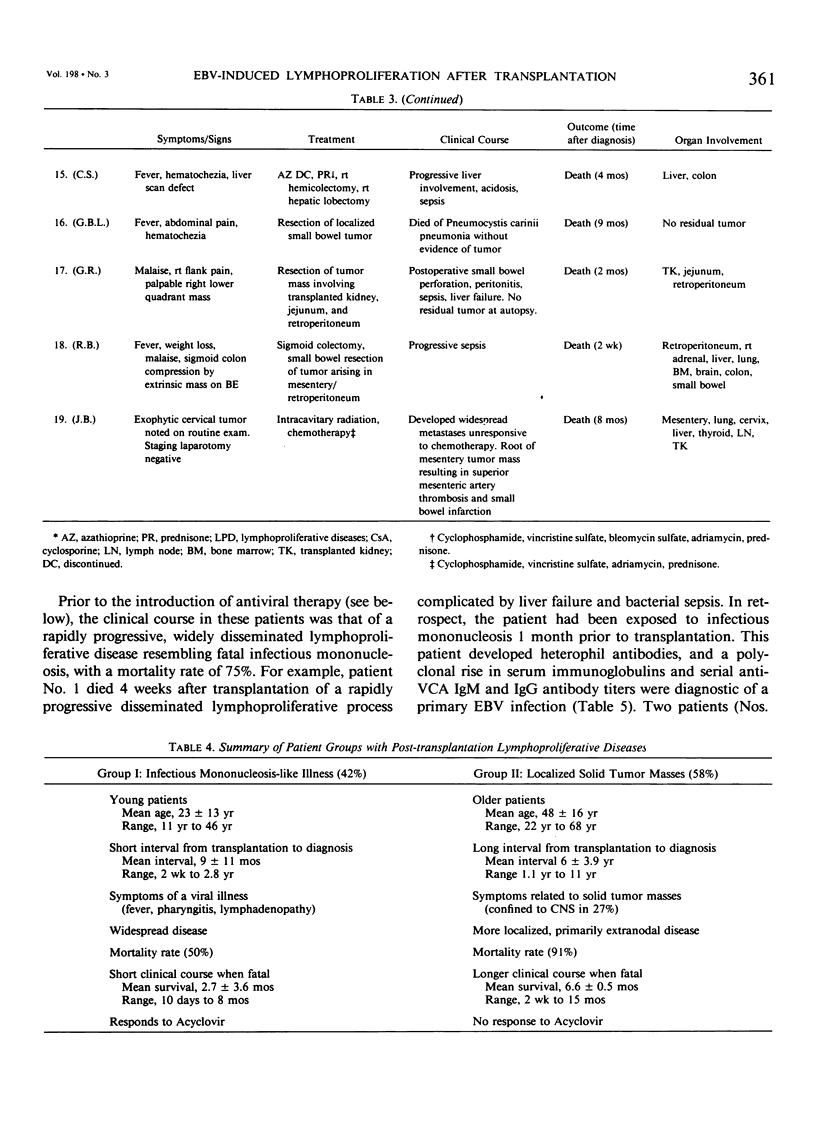
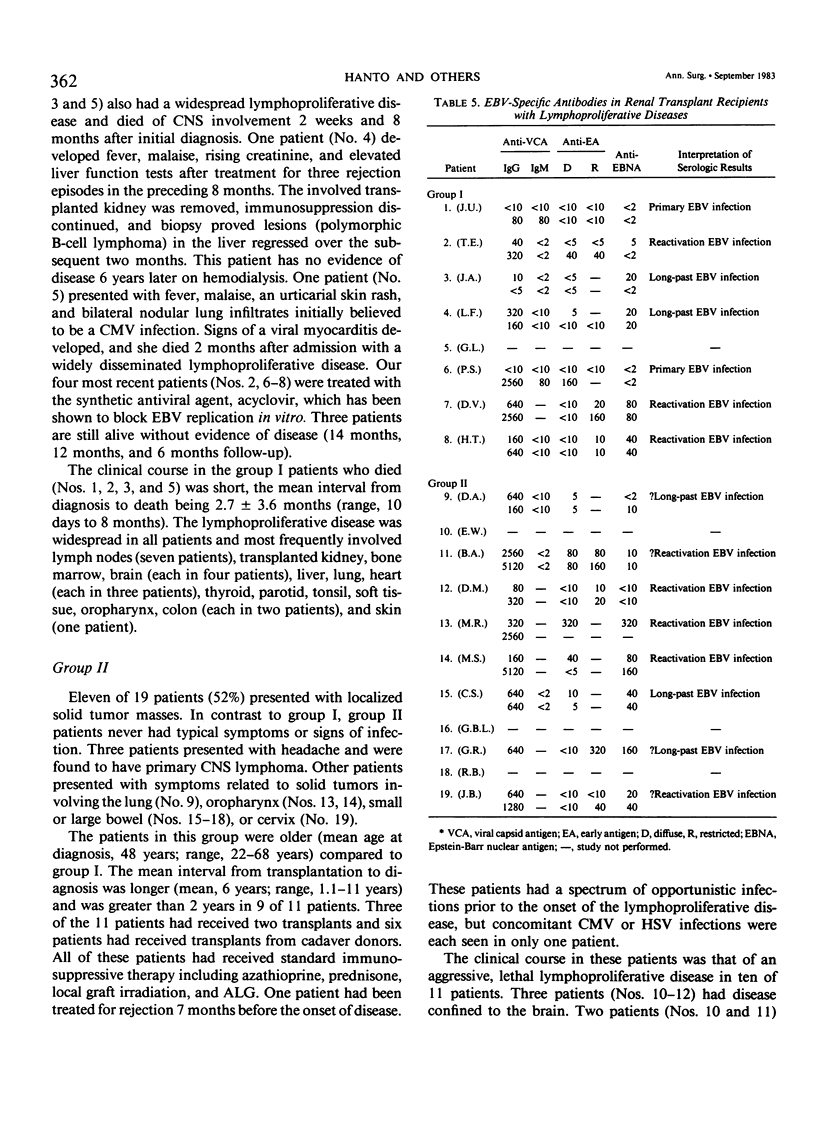
Nineteen renal allograft recipients developed B-cell lymphoproliferative diseases. Clinically there were two groups: a) young patients (mean age, 23 years) who presented soon (mean, 9 months) after transplantation or antirejection therapy with fever, pharyngitis, and lymphadenopathy resembling infectious mononucleosis, and b) older patients (mean age, 48 years) who presented later (mean, 6 years) after transplantation with localized tumor masses. Histologically, the diseases were classified as polymorphic diffuse B-cell hyperplasia (PDBH) or polymorphic B-cell lymphoma (PBL). Immunologic cell typing revealed either polyclonal or monoclonal B-cell proliferations. Malignant transformation of polyclonal proliferations in two patients was suggested by the finding of clonal cytogenetic abnormalities. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) specific serology, staining of biopsy specimens for the Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen, and EBV DNA molecular hybridization studies implicated EBV as the cause of both PDBH and PBL. Acyclovir, an antiviral agent that blocks EBV replication in vitro, inhibited oropharyngeal shedding of EBV and caused complete remission in four patients with polyclonal B-cell proliferations. The monoclonal tumors were acyclovir resistant. We suggest that surgical treatment, radiotherapy, or chemotherapy may be more appropriate therapy in selected patients with acyclovir resistant tumors. Therapeutic decisions require not only documentation of the viral etiology of these tumors, but also immunologic and cytogenetic analysis to determine the stage of tumor evolution in individual patients.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bloomfield C. D., Gajl-Peczalska K. J. The clinical relevance of lymphocyte surface markers in leukemia and lymphoma. Curr Top Hematol. 1980;3:175–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calne R. Y., Rolles K., White D. J., Thiru S., Evans D. B., McMaster P., Dunn D. C., Craddock G. N., Henderson R. G., Aziz S. Cyclosporin A initially as the only immunosuppressant in 34 recipients of cadaveric organs: 32 kidneys, 2 pancreases, and 2 livers. Lancet. 1979 Nov 17;2(8151):1033–1036. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92440-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colby B. M., Shaw J. E., Elion G. B., Pagano J. S. Effect of acyclovir [9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl)guanine] on Epstein-Barr virus DNA replication. J Virol. 1980 May;34(2):560–568. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.2.560-568.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Kieras R. M., Faras A. J. Studies on the replication of reticuloendotheliosis virus: detection of viral-specific DNA sequences in infected chick cells. Virology. 1975 Jun;65(2):436–445. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90049-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta A. K., Colby B. M., Shaw J. E., Pagano J. S. Acyclovir inhibition of Epstein-Barr virus replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5163–5166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson R. M., Rynasiewicz J. J., Sutherland D. E., Simmons R. L., Najarian J. S. Cyclosporin A in renal transplantation: a prospective randomized trial. Surgery. 1982 Aug;92(2):175–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanto D. W., Frizzera G., Gajl-Peczalska J., Purtilo D. T., Klein G., Simmons R. L., Najarian J. S. The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in the pathogenesis of posttransplant lymphoma. Transplant Proc. 1981 Mar;13(1 Pt 2):756–760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanto D. W., Frizzera G., Gajl-Peczalska K. J., Sakamoto K., Purtilo D. T., Balfour H. H., Jr, Simmons R. L., Najarian J. S. Epstein-Barr virus-induced B-cell lymphoma after renal transplantation: acyclovir therapy and transition from polyclonal to monoclonal B-cell proliferation. N Engl J Med. 1982 Apr 15;306(15):913–918. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198204153061506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanto D. W., Frizzera G., Purtilo D. T., Sakamoto K., Sullivan J. L., Saemundsen A. K., Klein G., Simmons R. L., Najarian J. S. Clinical spectrum of lymphoproliferative disorders in renal transplant recipients and evidence for the role of Epstein-Barr virus. Cancer Res. 1981 Nov;41(11 Pt 1):4253–4261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanto D. W., Frizzera G., Purtilo D. T., Sakamoto K., Sullivan J. L., Saemundsen A. K., Klein G., Simmons R. L., Najarian J. S. Clinical spectrum of lymphoproliferative disorders in renal transplant recipients and evidence for the role of Epstein-Barr virus. Cancer Res. 1981 Nov;41(11 Pt 1):4253–4261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanto D. W., Sakamoto K., Purtilo D. T., Simmons R. L., Najarian J. S. The Epstein-Barr virus in the pathogenesis of posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders. Clinical, pathologic, and virologic correlation. Surgery. 1981 Aug;90(2):204–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardie I. R., Strong R. W., Hartley L. C., Woodruff P. W., Clunie G. J. Skin cancer in Caucasian renal allograft recipients living in a subtropical climate. Surgery. 1980 Feb;87(2):177–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hozier J. C., Lindquist L. L. Banded karyotypes from bone marrow: a clinical useful approach. Hum Genet. 1980 Feb;53(2):205–209. doi: 10.1007/BF00273497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M., Klein G. Surface markers on human B and T lymphocytes. II. Presence of Epstein-Barr virus receptors on B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1973 Dec 1;138(6):1365–1378. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.6.1365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G. Lymphoma development in mice and humans: diversity of initiation is followed by convergent cytogenetic evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2442–2446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKhann C. F. Primary malignancy in patients undergoing immunosuppression for renal transplantation. Transplantation. 1969 Aug;8(2):209–212. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196908000-00033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson K., Giovanella B. C., Stehlin J. S., Klein G. Tumorigenicity of human hematopoietic cell lines in athymic nude mice. Int J Cancer. 1977 Mar 15;19(3):337–344. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910190309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn I., Hammond W., Brettschneider L., Starzl T. E. Malignant lymphomas in transplantation patients. Transplant Proc. 1969 Mar;1(1):106–112. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn I. The price of immunotherapy. Curr Probl Surg. 1981 Nov;18(11):681–751. doi: 10.1016/s0011-3840(81)80011-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedman B. M., Klein G. Cellular localization of an Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated complement-fixing antigen in producer and non-producer lymphoblastoid cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1973 May;11(3):499–520. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910110302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. E., Brown N., Andiman W., Halliday K., Francke U., Robert M. F., Andersson-Anvret M., Horstmann D., Miller G. Diffuse polyclonal B-cell lymphoma during primary infection with Epstein-Barr virus. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jun 5;302(23):1293–1297. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198006053022306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosén A., Gergely P., Jondal M., Klein G., Britton S. Polyclonal Ig production after Epstein-Barr virus infection of human lymphocytes in vitro. Nature. 1977 May 5;267(5606):52–54. doi: 10.1038/267052a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saemundsen A. K., Purtilo D. T., Sakamoto K., Sullivan J. L., Synnerholm A. C., Hanto D., Simmons R., Anvret M., Collins R., Klein G. Documentation of Epstein-Barr virus infection in immunodeficient patients with life-threatening lymphoproliferative diseases by Epstein-Barr virus complementary RNA/DNA and viral DNA/DNA hybridization. Cancer Res. 1981 Nov;41(11 Pt 1):4237–4242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto K., Freed H. J., Purtilo D. T. Antibody responses to Epstein-Barr virus in families with the X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome. J Immunol. 1980 Aug;125(2):921–925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez O., Escobar J. I., Yunis J. J. A simple G-banding technique. Lancet. 1973 Aug 4;2(7823):269–269. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)93180-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


