Abstract
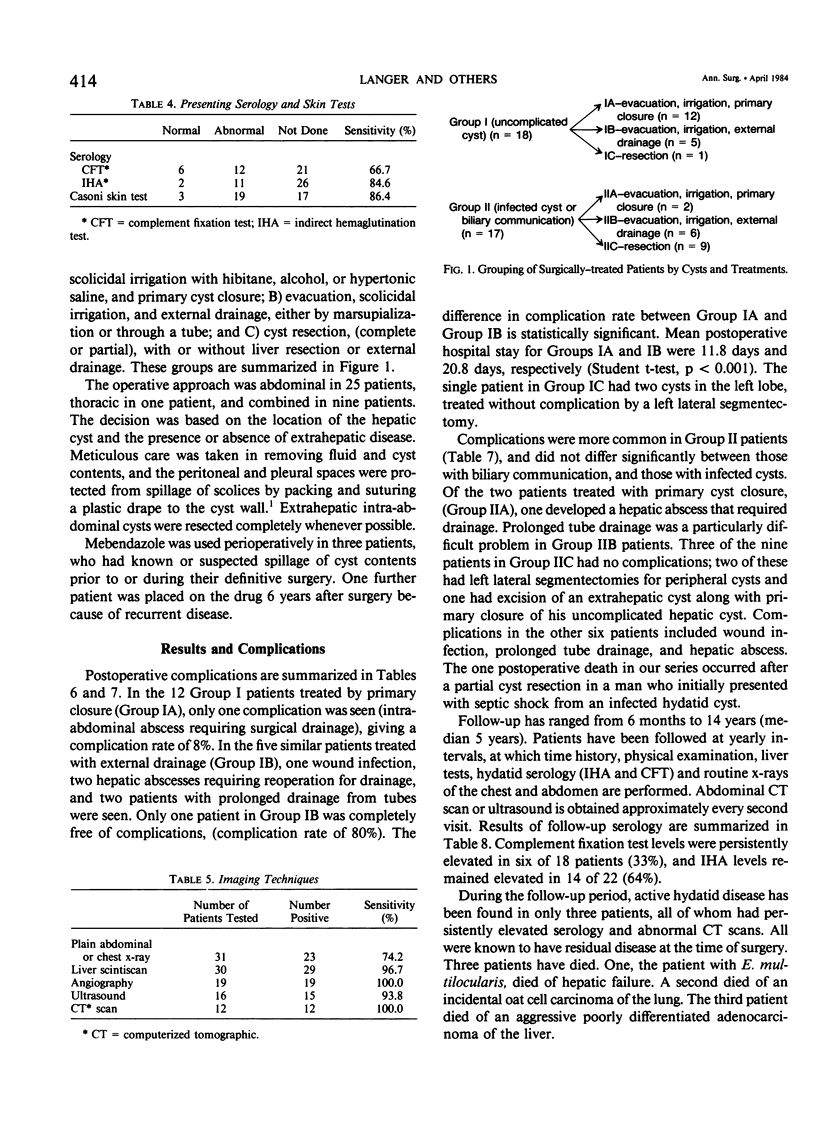
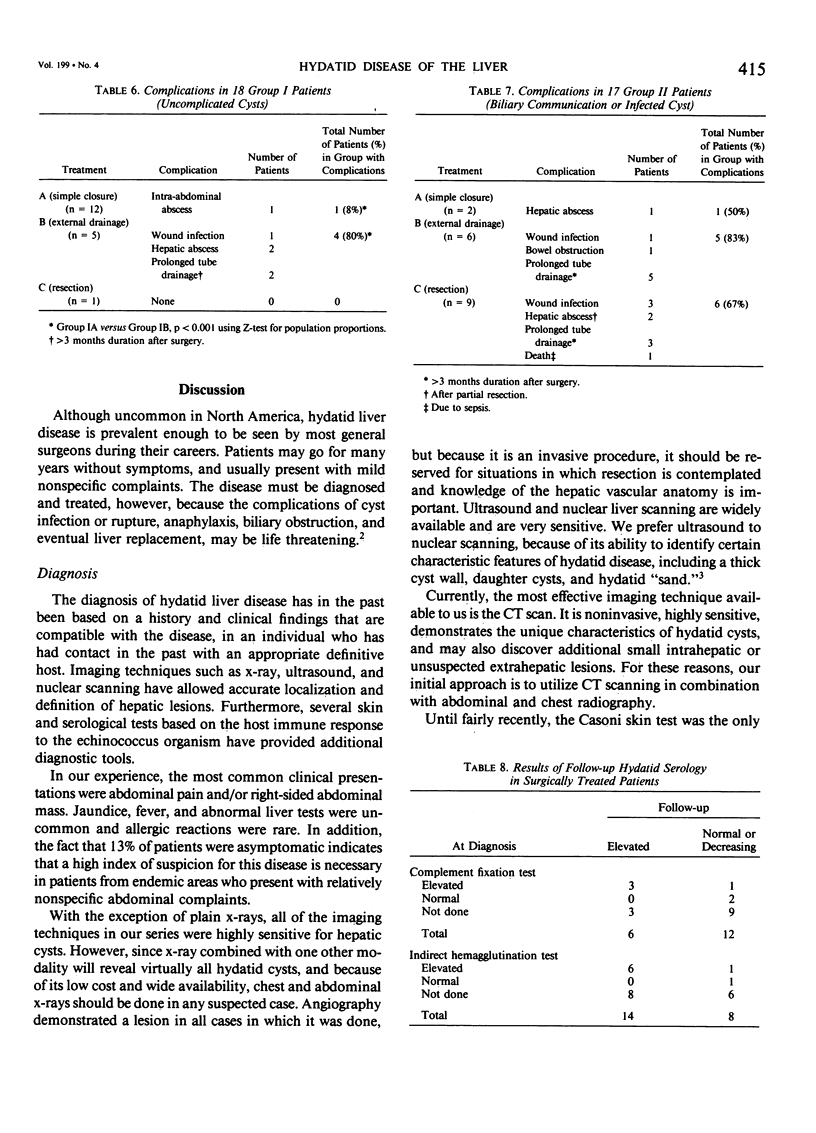
Since 1967, 40 patients with hydatid disease of the liver have been treated at our hospital. Diagnosis was made using clinical criteria, serology, skin tests, and imaging techniques. Thirty-five patients were operated upon. In 18 patients the cyst was uncomplicated (Group I), and in 17 the cyst was infected or communicated with the biliary tract (Group II). Three forms of surgical treatment were used: A) cyst evacuation, scolicidal irrigation, and primary cyst closure, B) evacuation, irrigation, and external drainage, and C) complete or partial cyst resection. Mebendazole was used in six patients, four of whom were also treated surgically. In Group I, one of 11 patients (8%) treated by primary closure had complications, versus four of five patients (80%) treated with external drainage (p less than 0.001). Mean postoperative hospital stay for these two groups was 11.8 versus 20.8 days, respectively (p less than 0.001). Complication rates in Group II were higher, and were evenly distributed among treatments. Patients have been followed yearly, with a median follow-up of 5 years. Active hydatid disease has been found in three patients, who all had known residual disease at initial operation. The best treatment for an uncomplicated hydatid liver cyst is evacuation, scolicidal irrigation, and primary closure. External drainage is used for infected cysts or those communicating with the biliary tract, and excision for extrahepatic and peripheral, easily resectable cysts. Mebendazole is used for intraperitoneal spillage of cyst contents and in patients with inoperable disease.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altemeier W. A., Schowengerdt C. G., Whiteley D. H. Abscesses of the liver: surgical considerations. Arch Surg. 1970 Aug;101(2):258–266. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1970.01340260162025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bekhti A., Schaaps J. P., Capron M., Dessaint J. P., Santoro F., Capron A. Treatment of hepatic hydatid disease with mebedazole: preliminary results in four cases. Br Med J. 1977 Oct 22;2(6094):1047–1051. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6094.1047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belli L., del Favero E., Marni A., Romani F. Resection versus pericystectomy in the treatment of hydatidosis of the liver. Am J Surg. 1983 Feb;145(2):239–242. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(83)90070-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger L. A., Osborne D. R. Treatment of pyogenic liver abscesses by percutaneous needle aspiration. Lancet. 1982 Jan 16;1(8264):132–134. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chemtai A. K., Bowry T. R., Ahmad Z. Evaluation of five immunodiagnostic techniques in echinococcosis patients. Bull World Health Organ. 1981;59(5):767–772. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen Z., Stone R. M., Langer B. Surgical treatment of hydatid disease of the liver. Can J Surg. 1976 Sep;19(5):416–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekrami Y. Surgical treatment of hydatid disease of the liver. Arch Surg. 1976 Dec;111(12):1350–1352. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1976.01360300040005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANKINS J. R. MANAGEMENT OF COMPLICATED HEPATIC HYDATID CYSTS. Ann Surg. 1963 Dec;158:1020–1034. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196312000-00014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagan I. G. A review of serological tests for the diagnosis of hydatid disease. Bull World Health Organ. 1968;39(1):25–37. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. W., Jr, Koss N., Kerstein M. D. A review of echinococcal disease. Ann Surg. 1975 Apr;181(4):390–396. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197504000-00004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J. P. Historical and current perspectives on surgical drainage. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1981 Apr;152(4):517–527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papadimitriou J., Mandrekas A. The surgical treatment of hydatid disease of the liver. Br J Surg. 1970 Jun;57(6):431–433. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800570607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pissiotis C. A., Wander J. V., Condon R. E. Surgical treatment of hydatid disease: prevention of complications and recurrences. Arch Surg. 1972 Apr;104(4):454–459. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1972.04180040068012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero-Torres R., Campbell J. R. An interpretive review of the surgical treatment of hydatid disease. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1965 Oct;121(4):851–864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saidi F., Nazarian I. Surgical treatment of hydatid cysts by freezing of cyst wall and instillation of 0.5 per cent silver nitrate solution. N Engl J Med. 1971 Jun 17;284(24):1346–1350. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197106172842403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayek I., Yalin R., Sanaç Y. Surgical treatment of hydatid disease of the liver. Arch Surg. 1980 Jul;115(7):847–850. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1980.01380070035007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schantz P. M., Van den Bossche H., Eckert J. Chemotherapy for larval echinococcosis in animals and humans: report of a workshop. Z Parasitenkd. 1982;67(1):5–26. doi: 10.1007/BF00929509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weirich W. L. Hydatid disease of the liver. Am J Surg. 1979 Dec;138(6):805–808. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(79)90300-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarzábal L. A., Schantz P. M., López-Lemes M. H. Comparative sensitivity and specificity of the Casoni intradermal and the immunoelectrophoresis tests for the diagnosis of hydatid disease. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1975 Sep;24(5):843–848. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1975.24.843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


