Abstract
1. A study was made of the functional and structural changes that occur during the decrease in multiaxonal innervation of neonate rat muscle fibres 2-14 days after birth. 2. In day 8 to day 14 animals there was a constant daily loss in the average number of functionally transmitting axons/muscle fibre measured electrophysiologically. An investigation of synaptic transmission during this period revealed that the loss of functional contact from the supernumerary axons was not preceded by any sign of failing terminal conduction or a gradual decrease in transmission efficacy but rather appeared to occur abruptly. 3. Neonate end-plates showing signs of abnormal ultrastructure were observed during the period of synapse elimination. Some axon terminals had a high cytoplasmic density and condensation of synaptic vesicles. Signs of Schwann cell encroachment into the synaptic cleft were readily found and large areas of post-junctional membrane apposed only by Schwann cell were evident. 4. It is suggested that the mechanics of the process of synapse elimination in neonates is similar to that occurring during degeneration in the denervated adult. Transmission failure occurs abruptly at the supernumerary endings and they are disposed of by the Schwann cell.
Full text
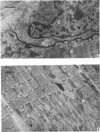
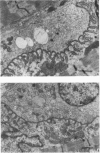
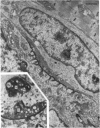
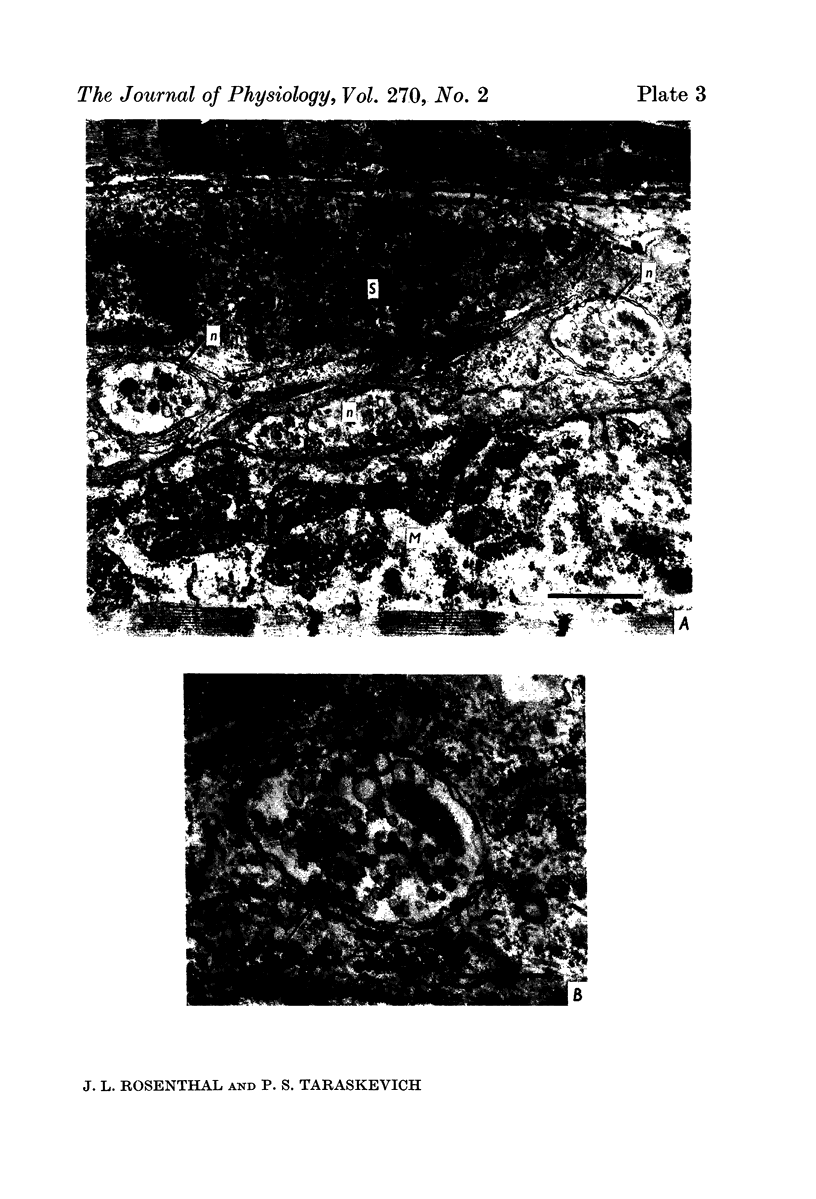
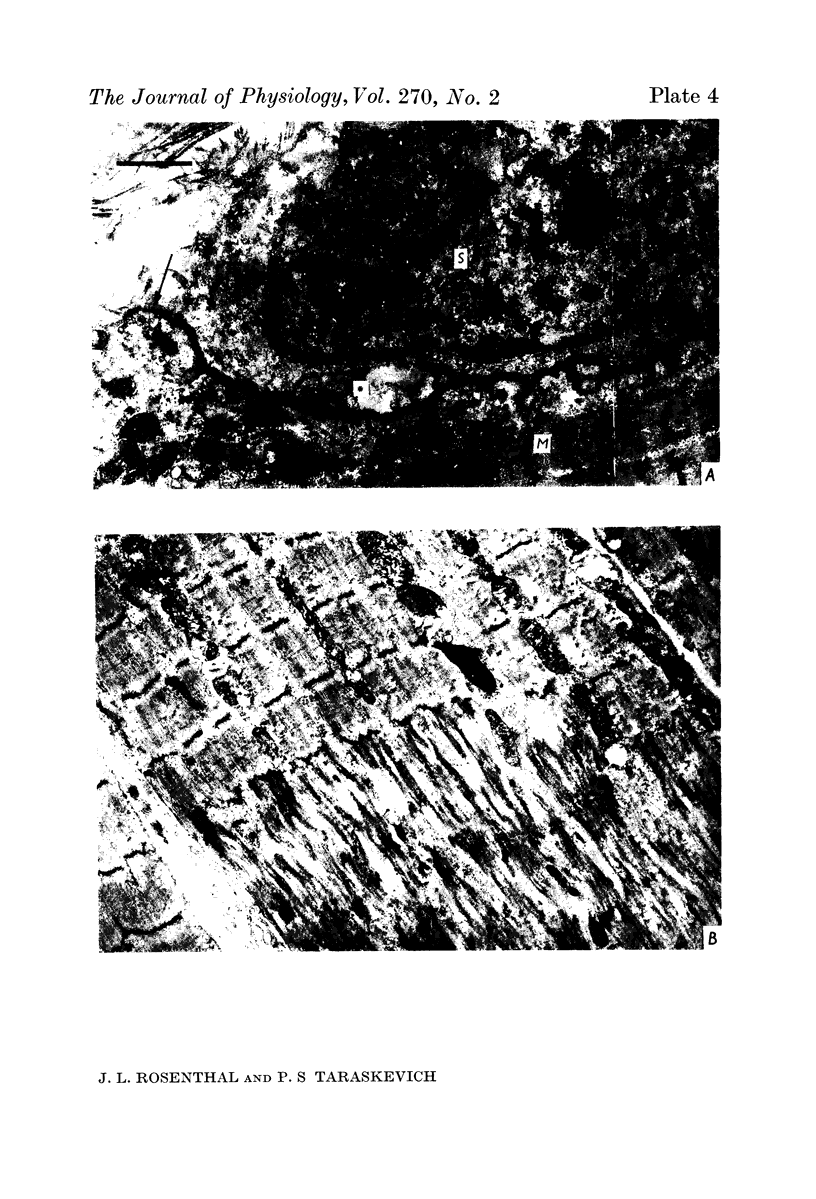
PDF

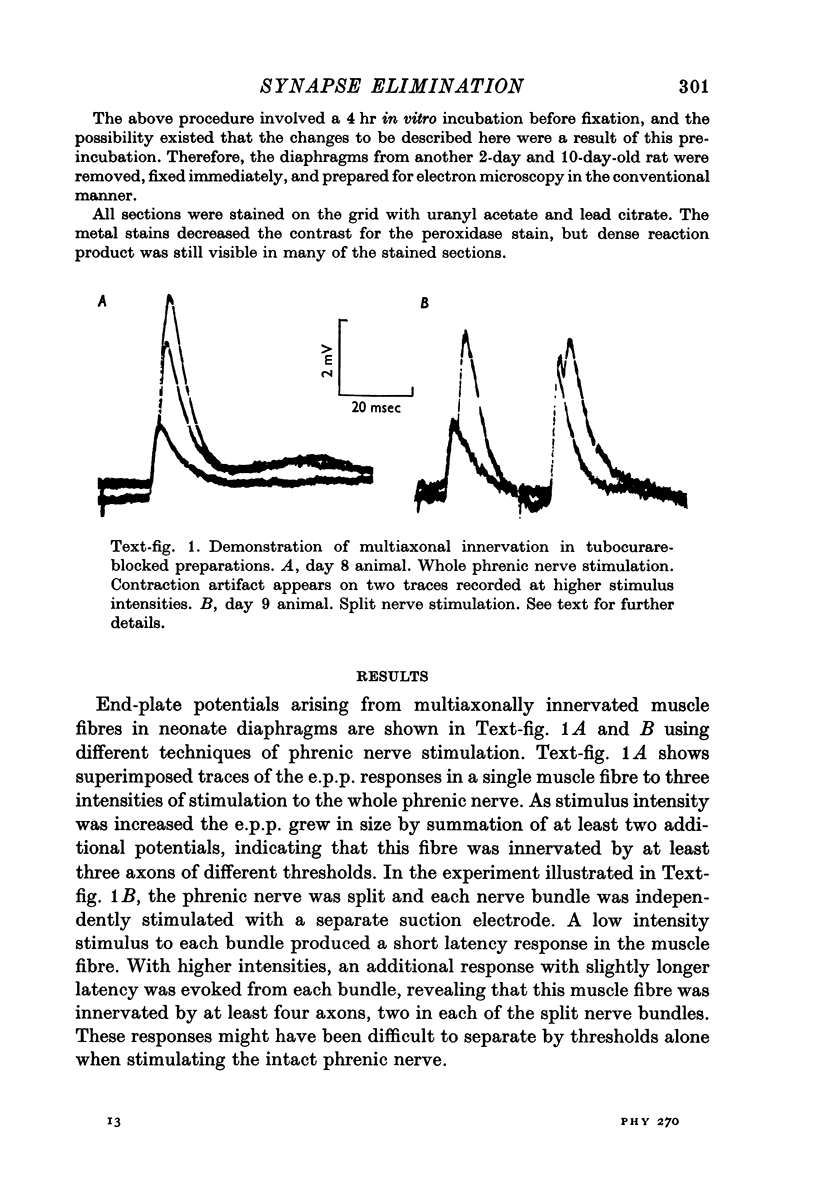
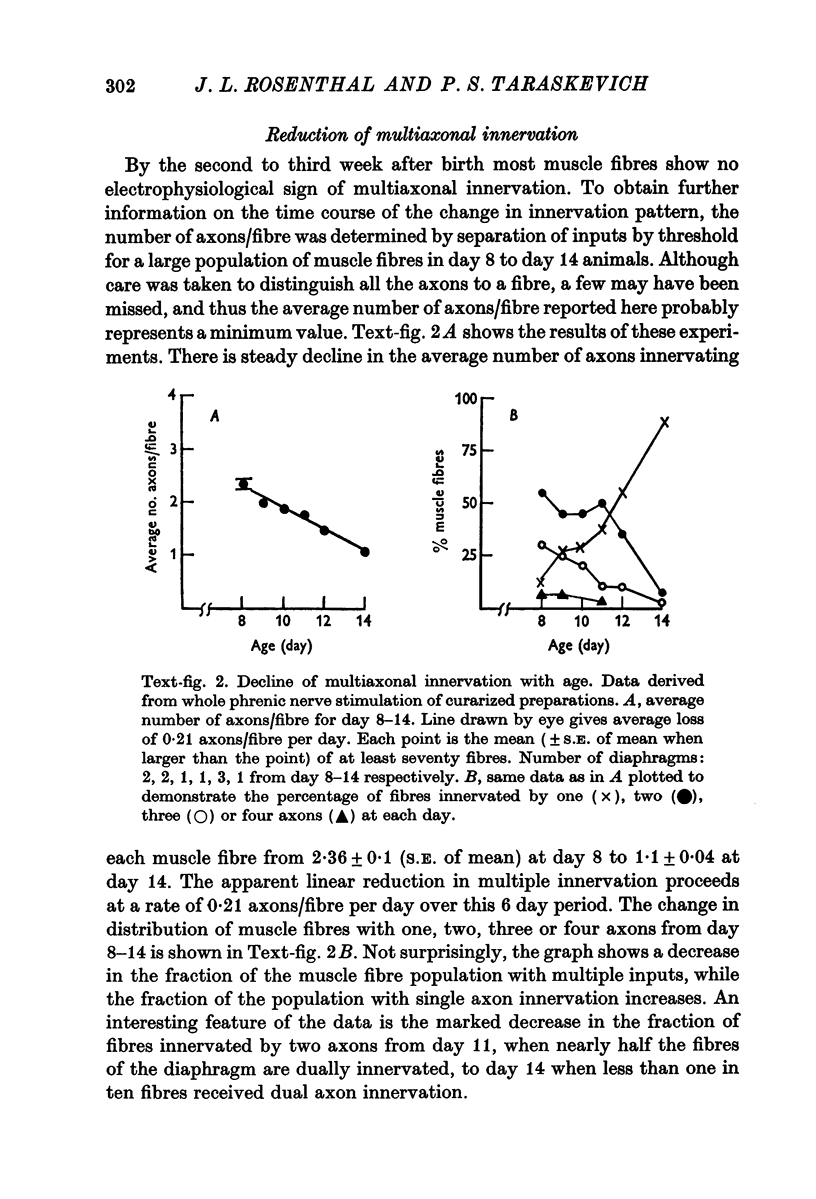








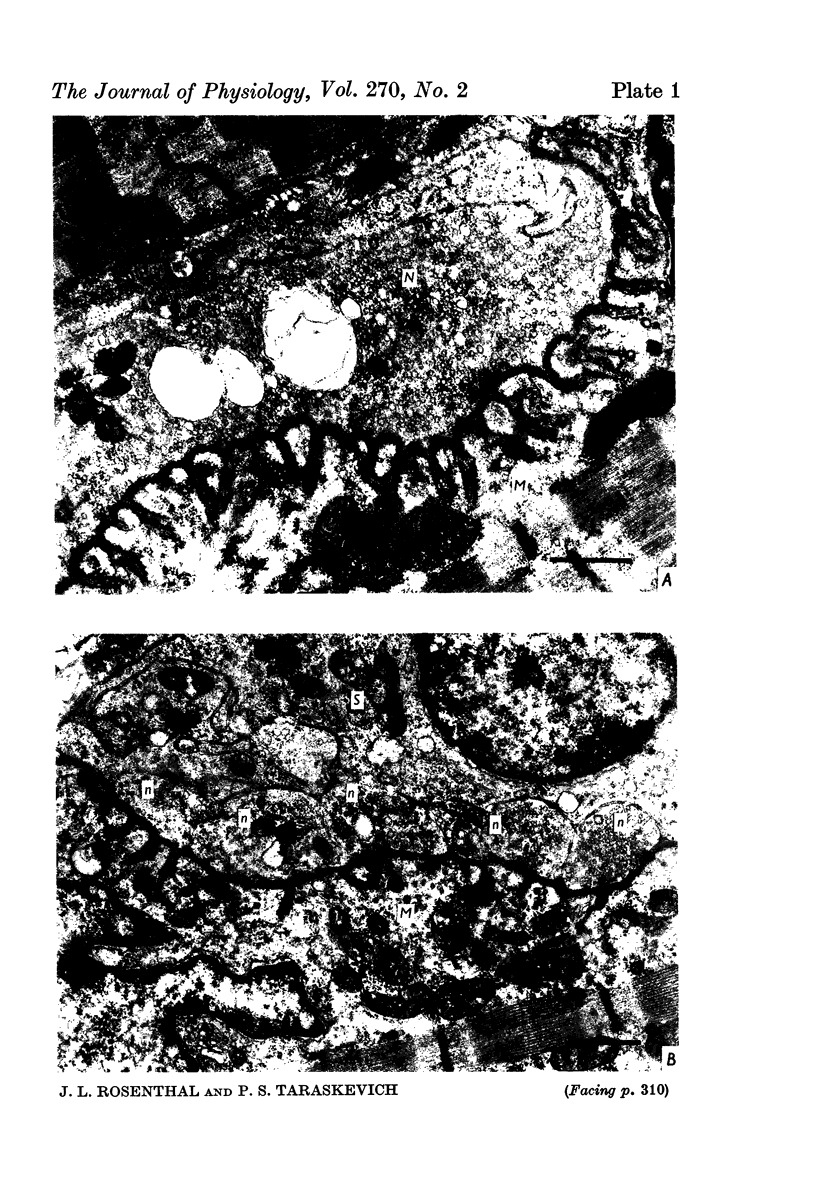
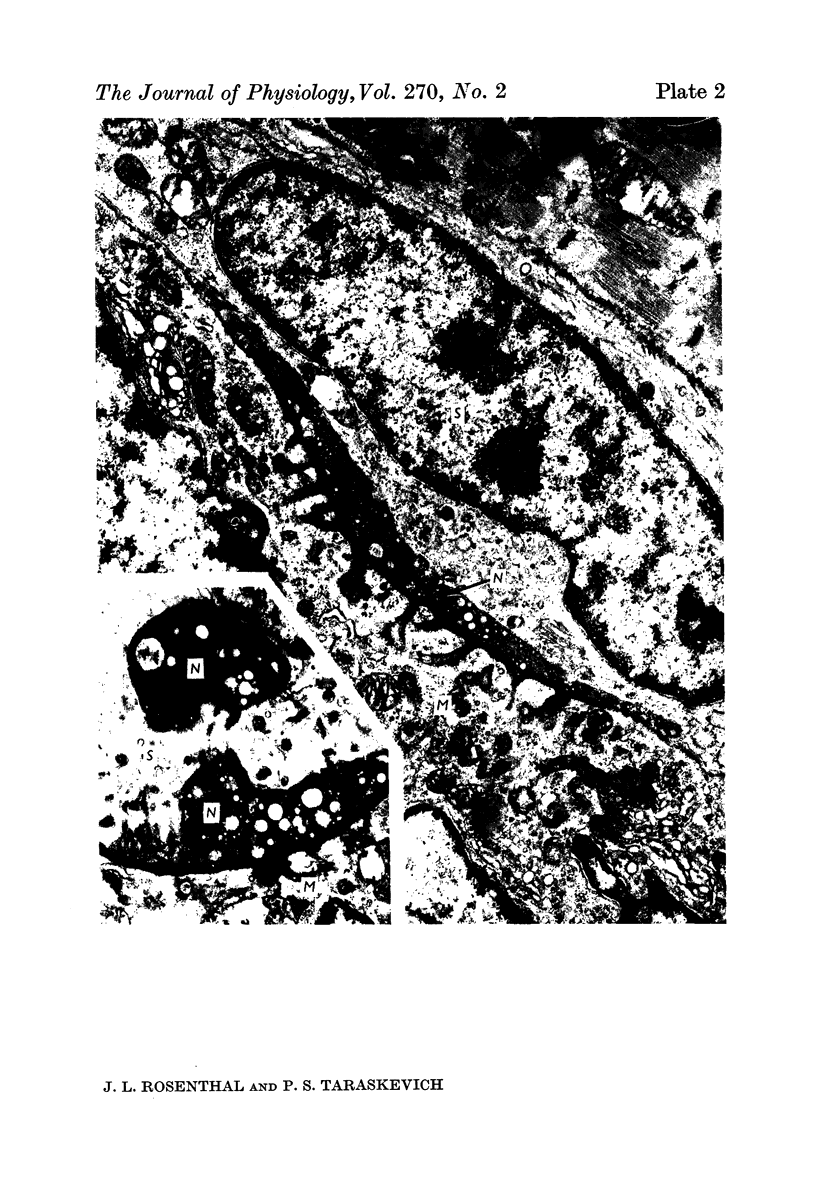
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagust J., Lewis D. M., Westerman R. A. Polyneuronal innervation of kitten skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1973 Feb;229(1):241–255. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., Pettigrew A. G. The formation of synapses in striated muscle during development. J Physiol. 1974 Sep;241(2):515–545. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoit P., Changeux J. P. Consequences of tenotomy on the evolution of multiinnervation in developing rat soleus muscle. Brain Res. 1975 Dec 5;99(2):354–358. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90036-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. C., Jansen J. K., Van Essen D. Polyneuronal innervation of skeletal muscle in new-born rats and its elimination during maturation. J Physiol. 1976 Oct;261(2):387–422. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couteaux R., Fessard M. A. Facteurs de la différenciation des "zones actives" des membranes présynaptiques. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1975 Jan 20;280(3):299–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couteaux R., Pécot-Dechavassine M. Vésicules synaptiques et poches au niveau des "zones actives" de la jonction neuromusculaire. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1970 Dec 21;271(25):2346–2349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Quantal components of the end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):560–573. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIAMOND J., MILEDI R. A study of foetal and new-born rat muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1962 Aug;162:393–408. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen J. K., Van Essen D. C., Brown M. C. Formation and elimination of synapses in skeletal muscles of rat. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:425–434. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korneliussen H., Jansen J. K. Morphological aspects of the elimination of polyneuronal innervation of skeletal muscle fibres in newborn rats. J Neurocytol. 1976 Oct;5(8):591–604. doi: 10.1007/BF01175572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuno M., Turkanis S. A., Weakly J. N. Correlation between nerve terminal size and transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction of the frog. J Physiol. 1971 Mar;213(3):545–556. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manolov S. Initial changes in the neuromuscular synapses of denervated rat diaphragm. Brain Res. 1974 Jan 11;65(2):303–316. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Slater C. R. On the degeneration of rat neuromuscular junctions after nerve section. J Physiol. 1970 Apr;207(2):507–528. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickel E., Waser P. G. Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen am Diaphragma der Maus nach einseitiger Phrenikotomie. I. Die degenerierende motorische Endplatte. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1968;88(2):278–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redfern P. A. Neuromuscular transmission in new-born rats. J Physiol. 1970 Aug;209(3):701–709. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teräväinen H. Development of the myoneural junction in the rat. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1968;87(2):249–265. doi: 10.1007/BF00319723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]