Abstract
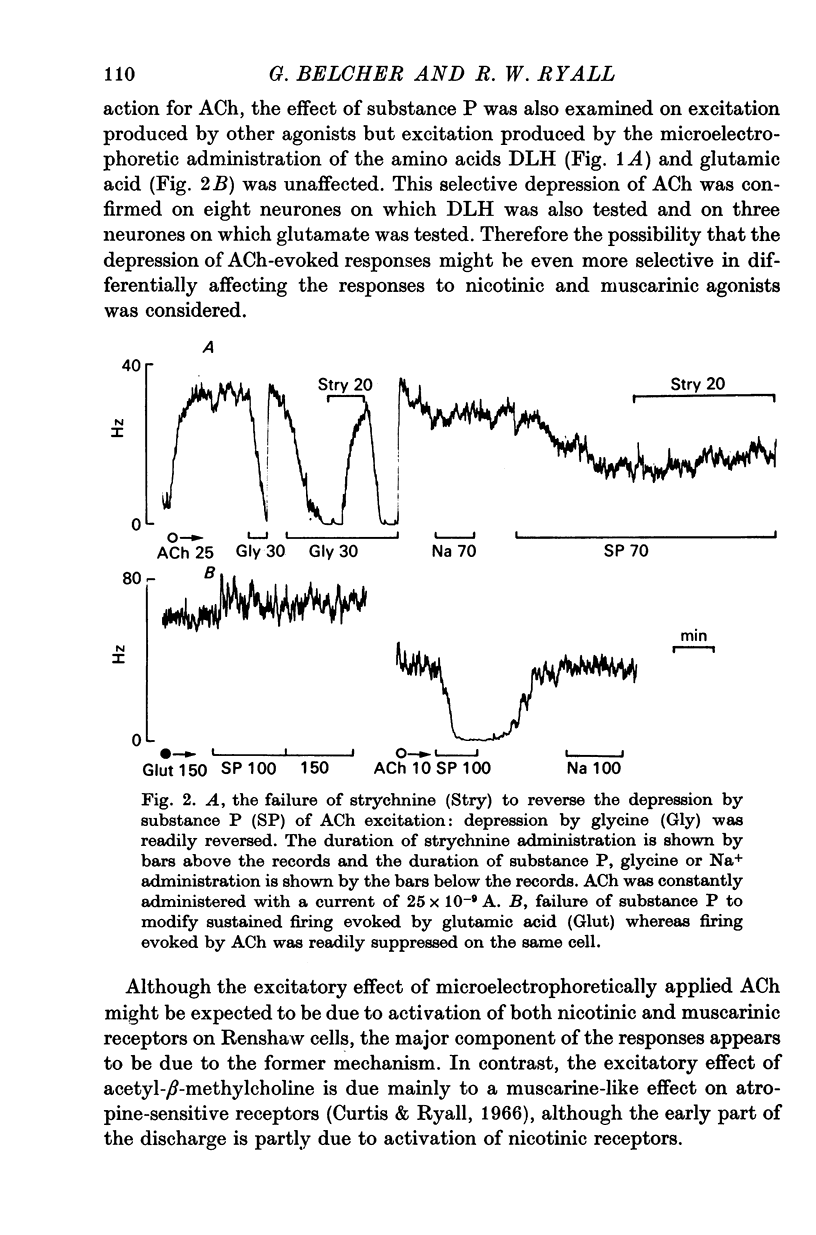
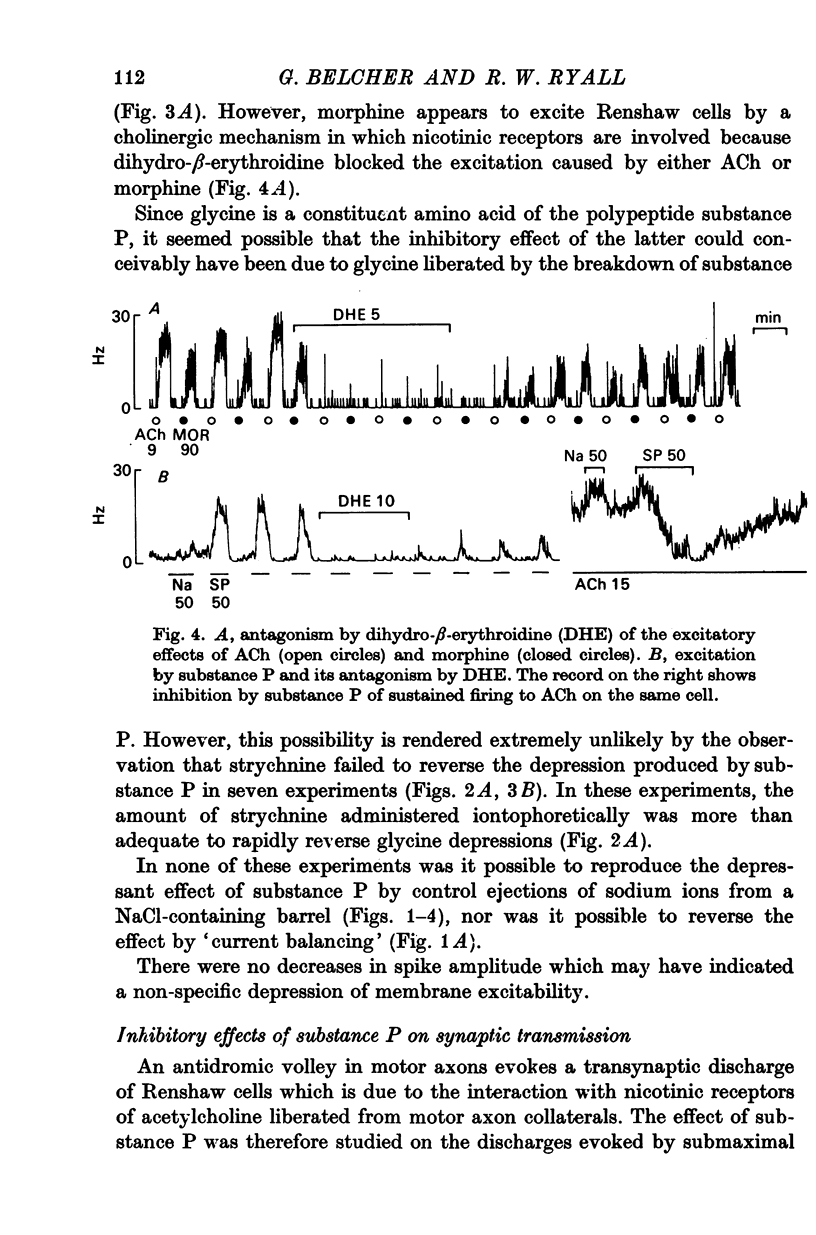
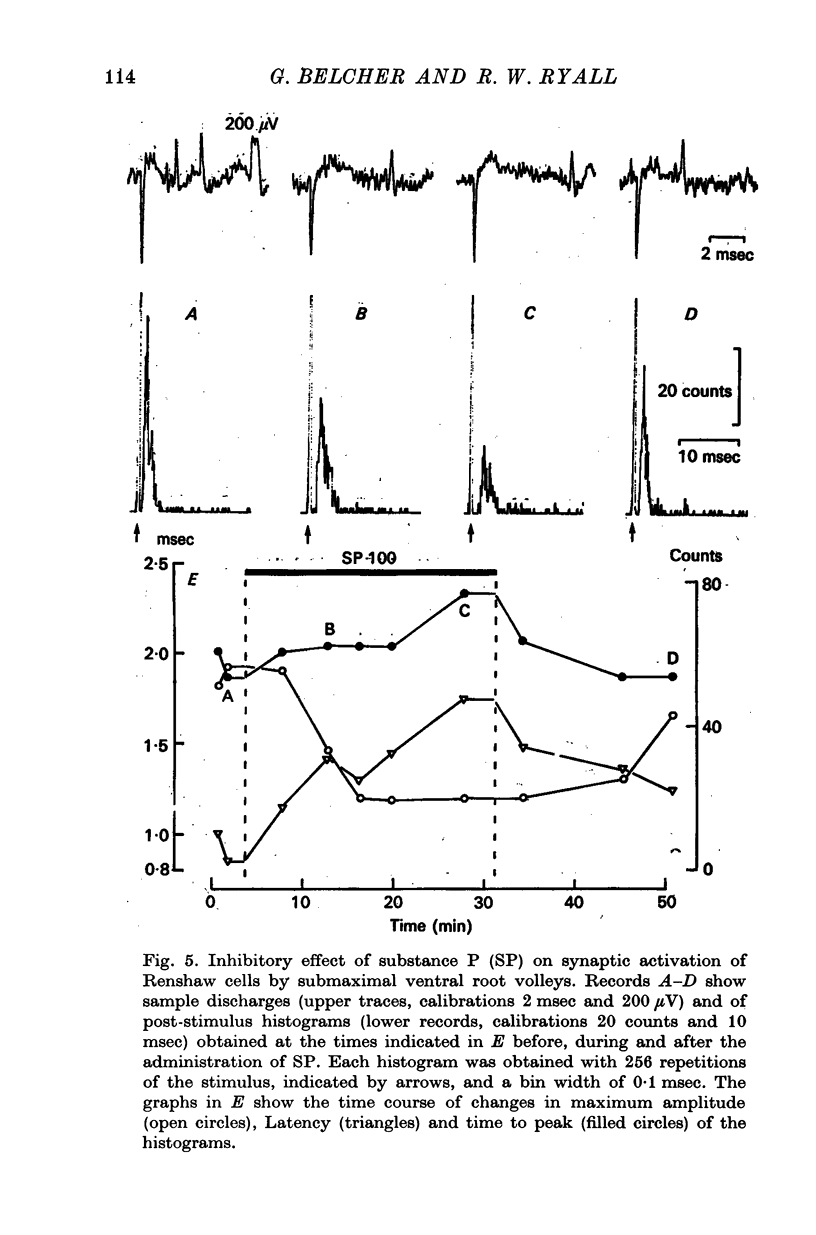
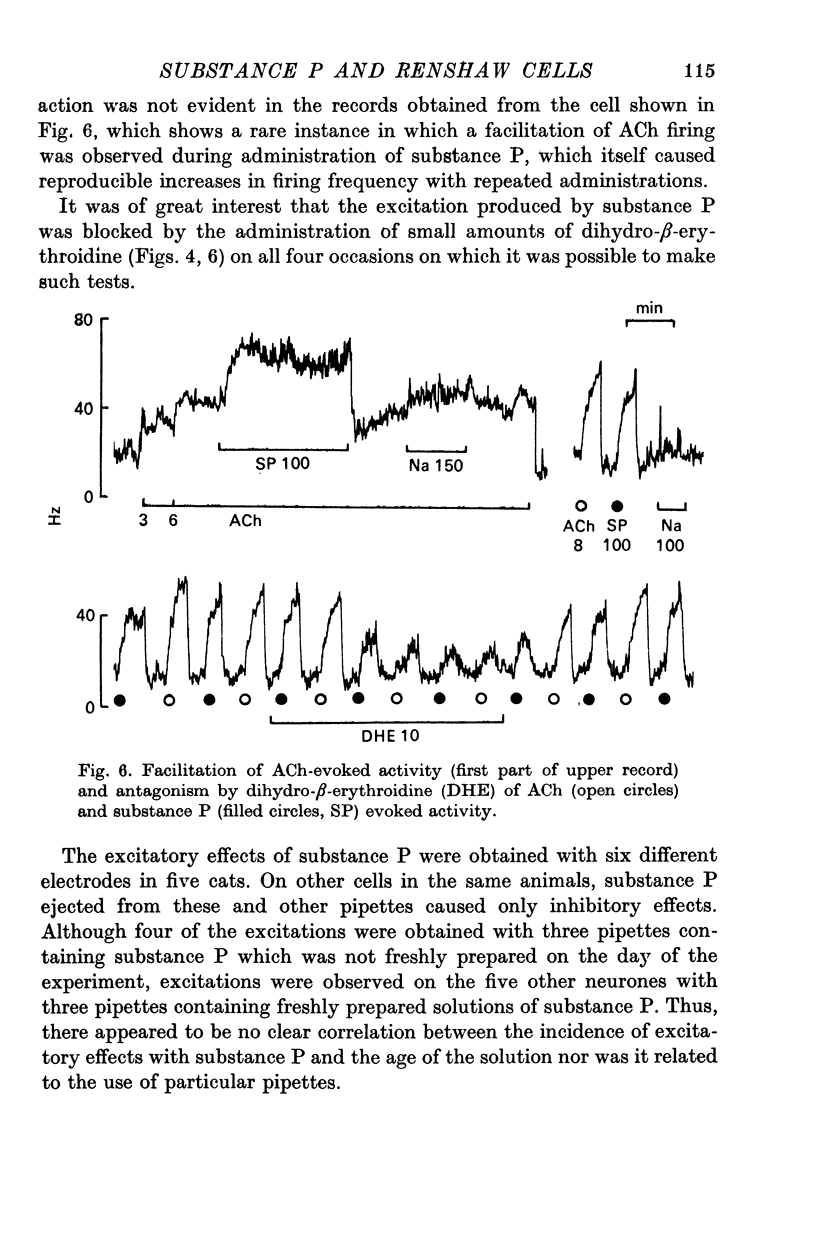
1. The actions of microelectrophoretically administered substance P on Renshaw cells in pentobarbitone anaesthetized cats were investigated. 2. The effects on spontaneous and synaptic firing and interactions with a number of other agents including acetylcholine, acetyl-beta-methylcholine, acidic amino acids, morphine, dihydro-beta-erythroidine and strychnine were studied in attempts to elucidate the mechanism of action of substance P. 3. Substance P usually selectively depressed the excitation by ACh, and also reduced submaximal synaptically evoked discharges which activate nicotinic receptors, but failed to modify excitation caused either by acetyl-beta-methylcholine, which activates muscarinic receptors, or excitation caused by glutamate or homocysteate. Substance P also depressed excitation by morphine which acted via the nicotinic receptors. 4. The inhibitory effect was not blocked by strychinine and was considered to be unlikely to be due to interaction between the polypeptide and either glycine or GABA receptors. 5. On some cells substance P caused excitation which was blocked by dihydro-beta-erythroidine. Mixed excitatory-inhibitory effects were observed on some of these neurones. 6. The results are discussed in relation to the possibility that substance P could function as a synaptic inhibitory mediator with an unusual selectivity of action.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Curtis D. R., Ryall R. W. The acetylcholine receptors of Renshaw cells. Exp Brain Res. 1966;2(1):66–80. doi: 10.1007/BF00234361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Dray A. Substance P in the substantia nigra. Brain Res. 1976 May 14;107(3):623–627. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90150-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. Effects of morphine and naloxone on Renshaw cells and spinal interneurones in morphine dependent and non-dependent rats. Brain Res. 1976 Aug 27;113(2):311–326. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90943-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duggan A. W., Davies J., Hall J. G. Effects of opiate agonists and antagonists on central neurons of the cat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Jan;196(1):107–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry J. L. Effects of substance P on functionally identified units in cat spinal cord. Brain Res. 1976 Sep 24;114(3):439–451. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90965-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry J. L., Krnjevíc K., Morris M. E. Substance P and spinal neurones. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1975 Jun;53(3):423–432. doi: 10.1139/y75-061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Kellerth J. O., Nilsson G., Pernow B. Substance p: localization in the central nervous system and in some primary sensory neurons. Science. 1975 Nov 28;190(4217):889–890. doi: 10.1126/science.242075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATAOKA K. The subcellular distribution of substance P in the nervous tissues. Jpn J Physiol. 1962 Feb 15;12:81–96. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.12.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi S., Otsuka M. Excitatory action of hypothalamic substance P on spinal motoneurones of newborn rats. Nature. 1974 Dec 20;252(5485):734–735. doi: 10.1038/252734a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Morris M. E. An excitatory action of substance P on cuneate neurones. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1974 Jun;52(3):736–744. doi: 10.1139/y74-094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leeman S. E., Mroz E. A. Substance P. Life Sci. 1974 Dec 15;15(12):2033–2044. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(74)90020-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodge D., Headley P. M., Duggan A. W., Biscoe T. J. The effects of morphine, etorphine and sinomenine on the chemical sensitivity and synaptic responses of Renshaw cells and other spinal neurones in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1974 May;26(2):277–284. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(74)90238-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nistri A. Proceedings: Effects of morphine on acetylcholine release from the frog spinal cord. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 Mar;56(3):352P–352P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka M., Konishi S. Substance P and excitatory transmitter of primary sensory neurons. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:135–143. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepeu G. The release of acetylcholine from the brain: an approach to the study of the central cholinergic mechanisms. Prog Neurobiol. 1973;2(3):259–288. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(73)90009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillis J. W., Limacher J. J. Substance P excitation of cerebral cortical Betz cells. Brain Res. 1974 Mar 29;69(1):158–163. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90383-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell D., Leeman S., Tregear G. W., Niall H. D., Potts J. T., Jr Radioimmunoassay for substance P. Nat New Biol. 1973 Feb 21;241(112):252–254. doi: 10.1038/newbio241252a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYALL R. W. THE SUBCELLULAR DISTRIBUTIONS OF ACETYLCHOLINE, SUBSTANCE P, 5-HYDROXYTRYPTAMINE, GAMMA-AMINOBUTYRIC ACID AND GLUTAMIC ACID IN BRAIN HOMOGENATES. J Neurochem. 1964 Mar;11:131–145. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1964.tb06124.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Otsuka M. Regional distribution of substance P in the spinal cord and nerve roots of the cat and the effect of dorsal root section. Brain Res. 1975 Apr 4;87(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90774-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terenius L. Effect of peptides and amino acids on dihydromorphine binding to the opiate receptor. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1975 Jun;27(6):450–452. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1975.tb09480.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tregear G. W., Niall H. D., Potts J. T., Jr, Leeman S. E., Chang M. M. Synthesis of substance P. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jul 21;232(29):87–89. doi: 10.1038/newbio232087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


