Abstract
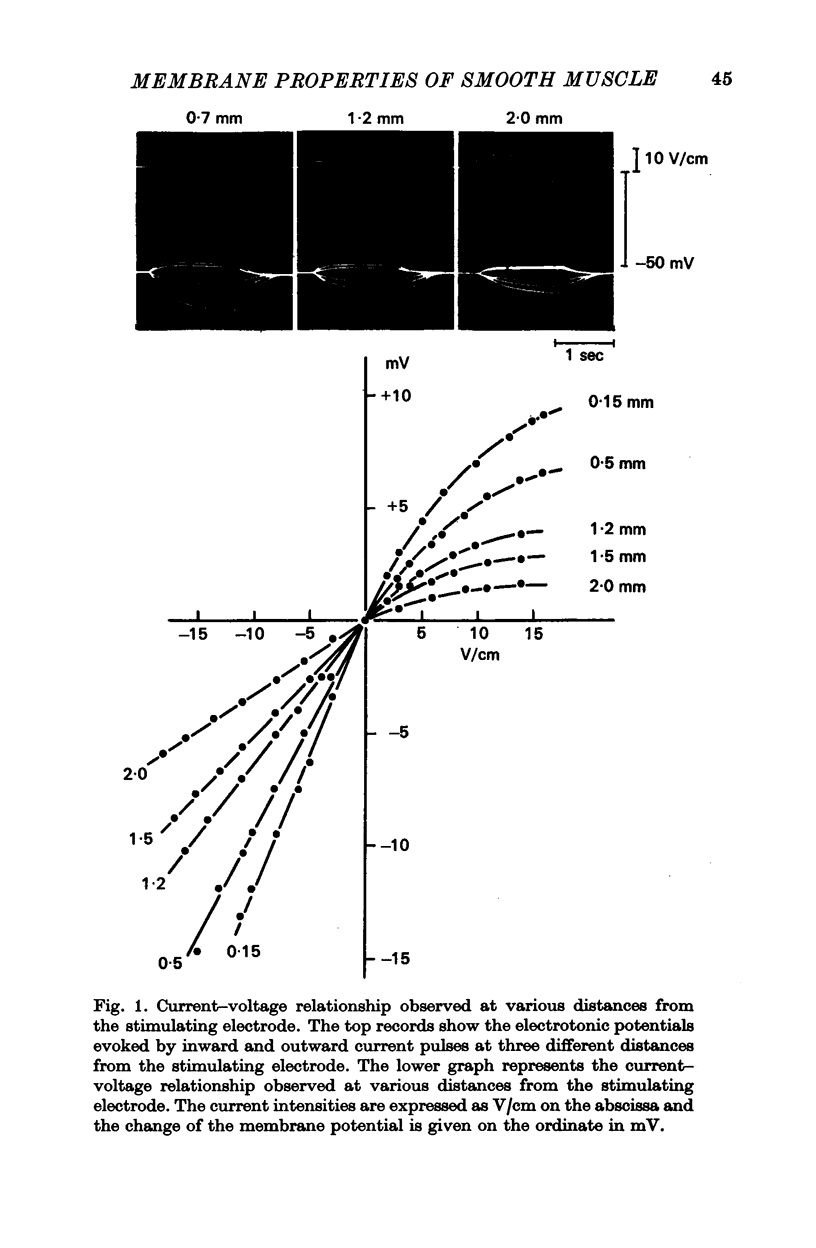
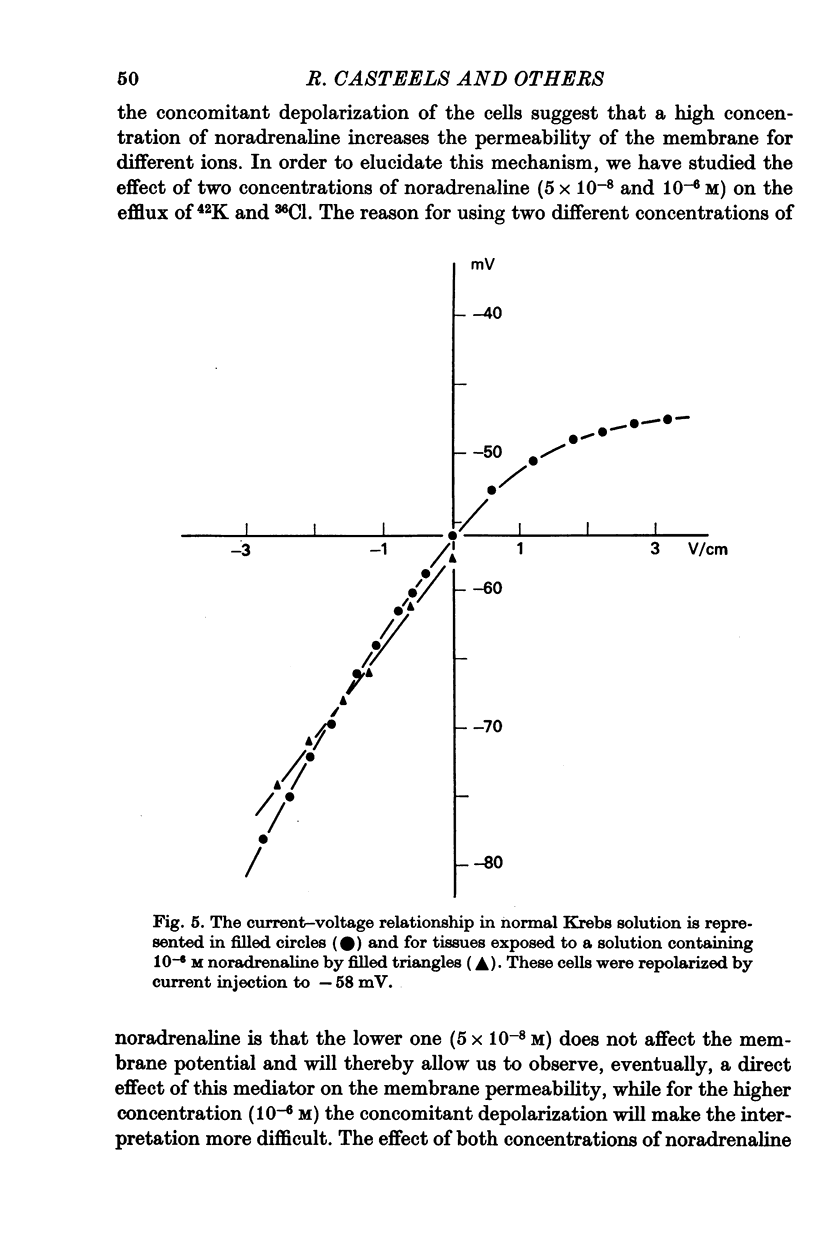
1. The membrane potential of the smooth muscle cells of the rabbit main pulmonary artery amounts to -57 mV, the length constant of the tissue is 1·48 mm and the time constant of the membrane 182 msec. On the basis of the electrical properties of its membrane, this smooth muscle tissue is classified as a single-unit type. During outward current pulses, the membrane shows marked rectification and action potentials can never be generated.
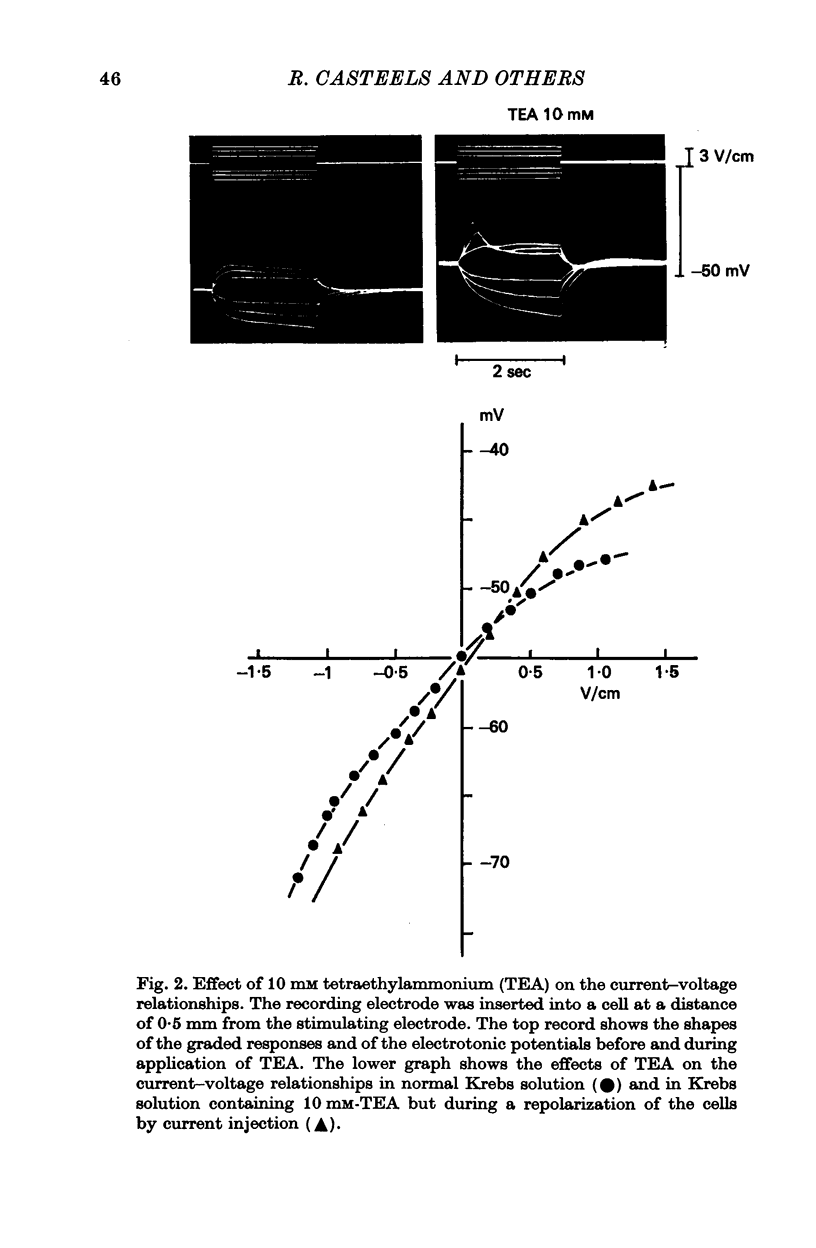
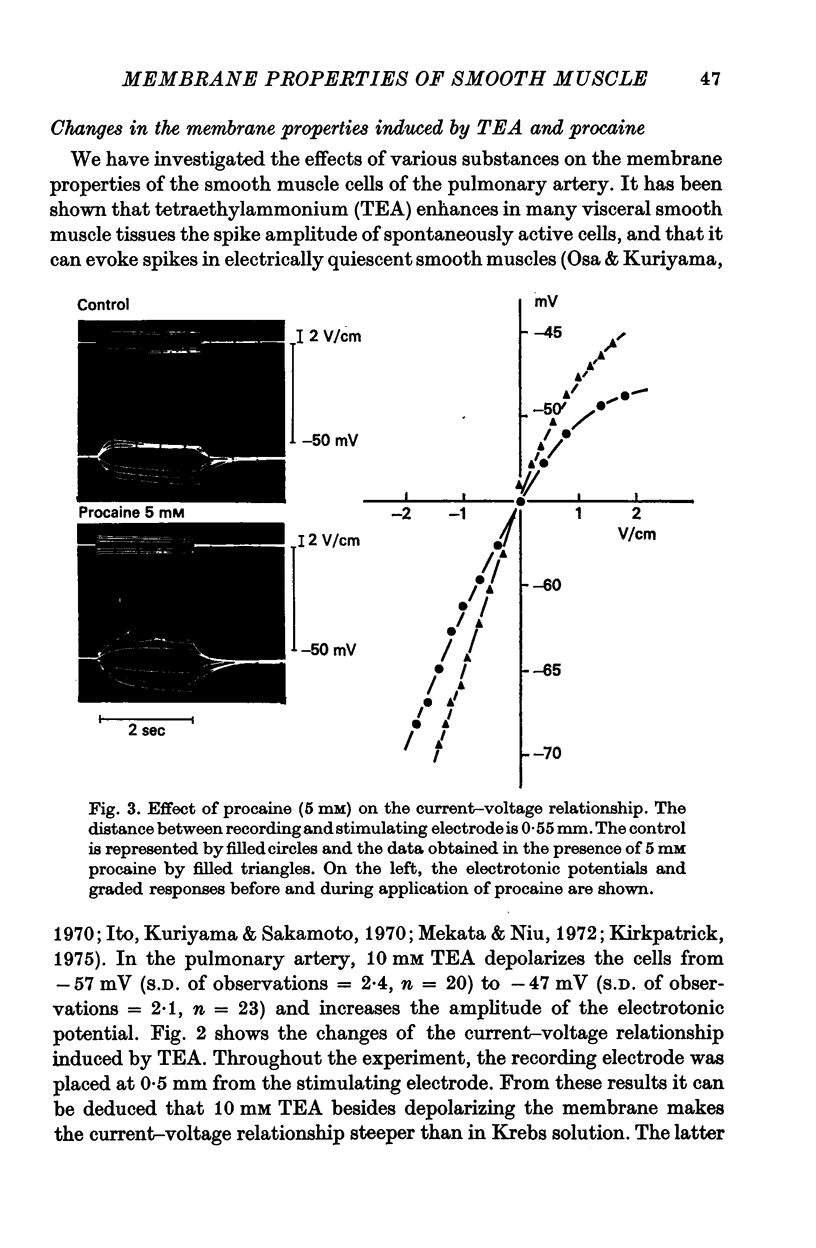
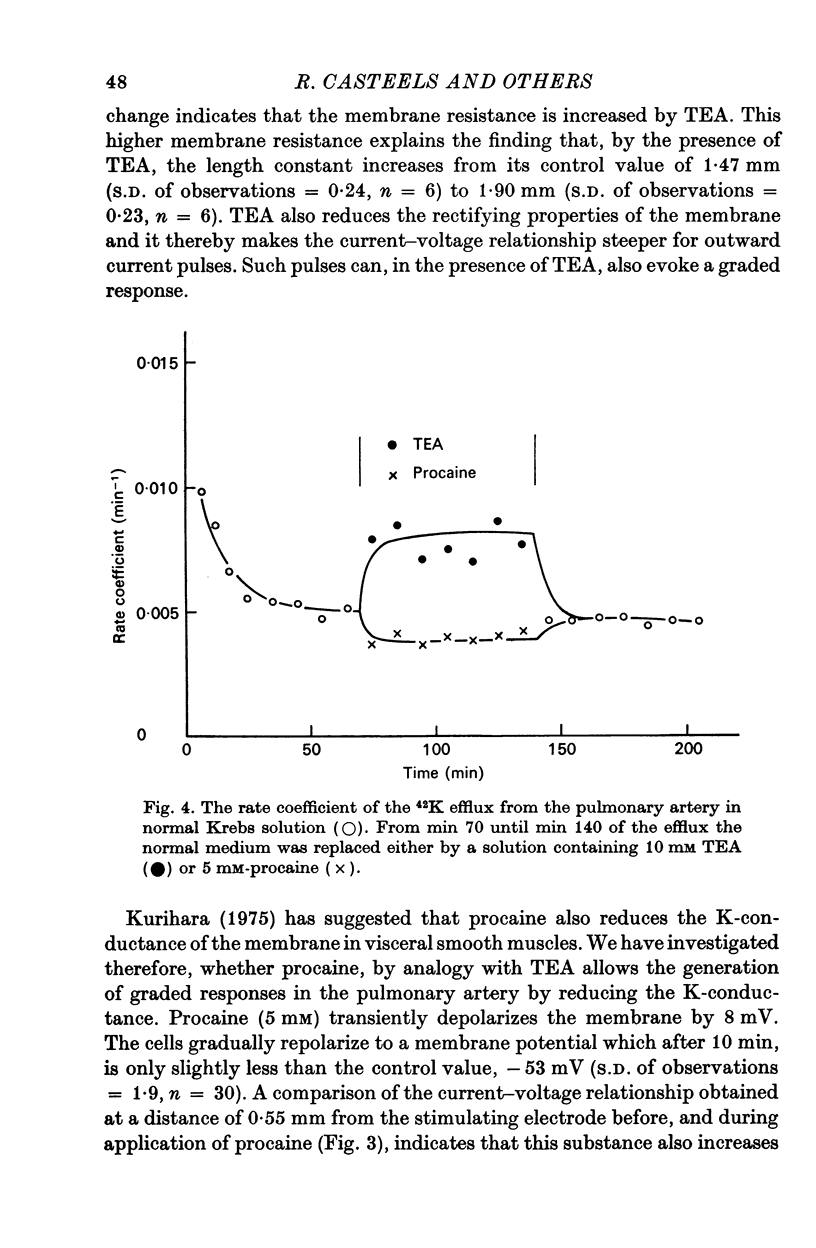
2. Tetraethylammonium (10 mM) and procaine (5 mM) depolarize the membrane and increase the membrane resistance. By studying the effect of both substances on the 42K efflux, it could be concluded that they reduce the K-permeability of the membrane. They also suppress the rectification of the membrane and increase the length constant of the membrane. In the presence of TEA and procaine, a graded response of the membrane can be induced by outward current pulses, but overshoot potentials never occur.
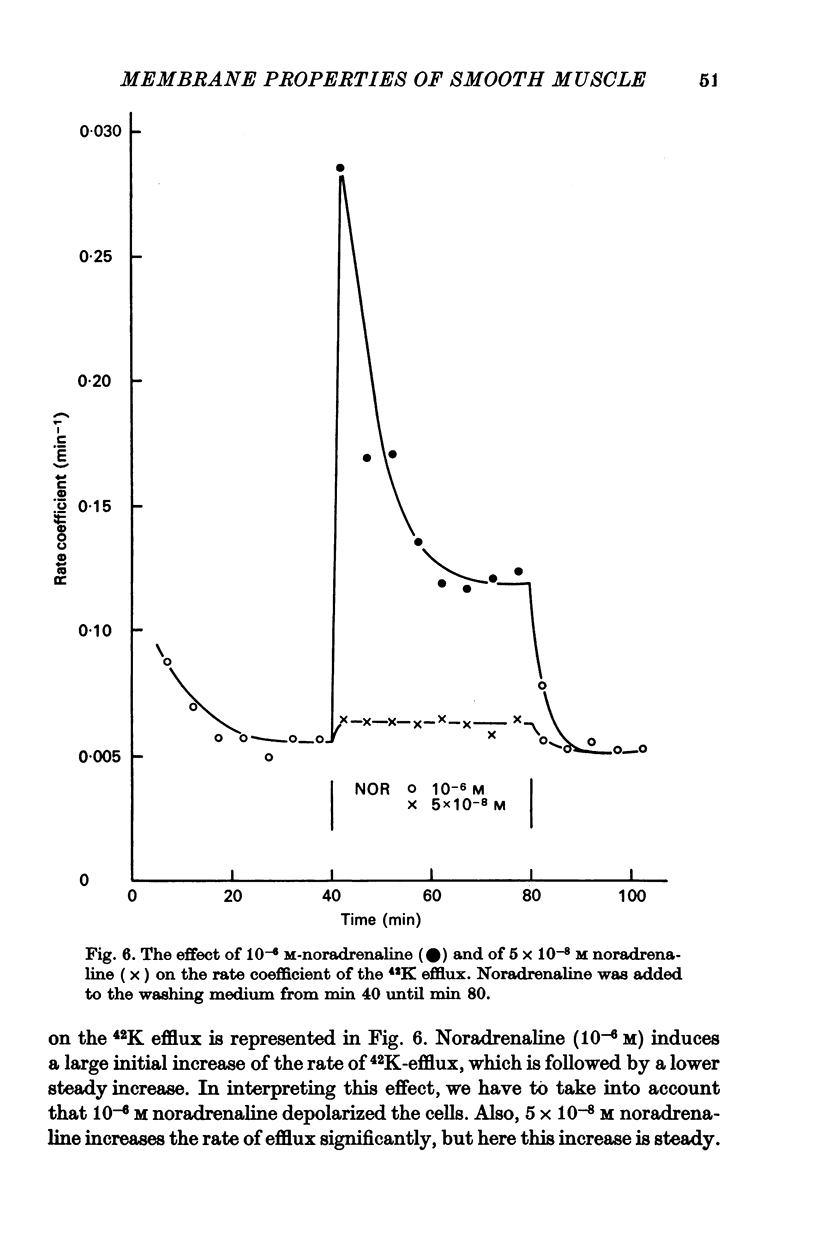
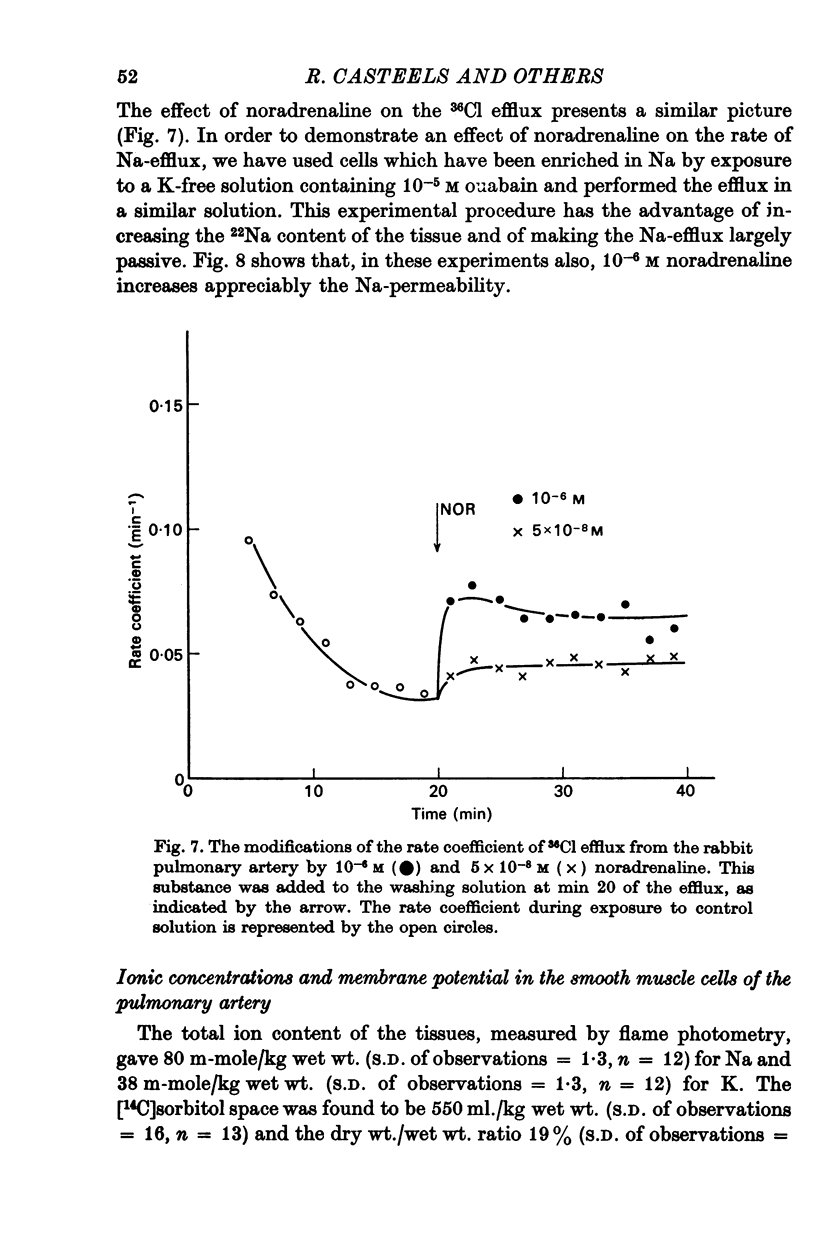
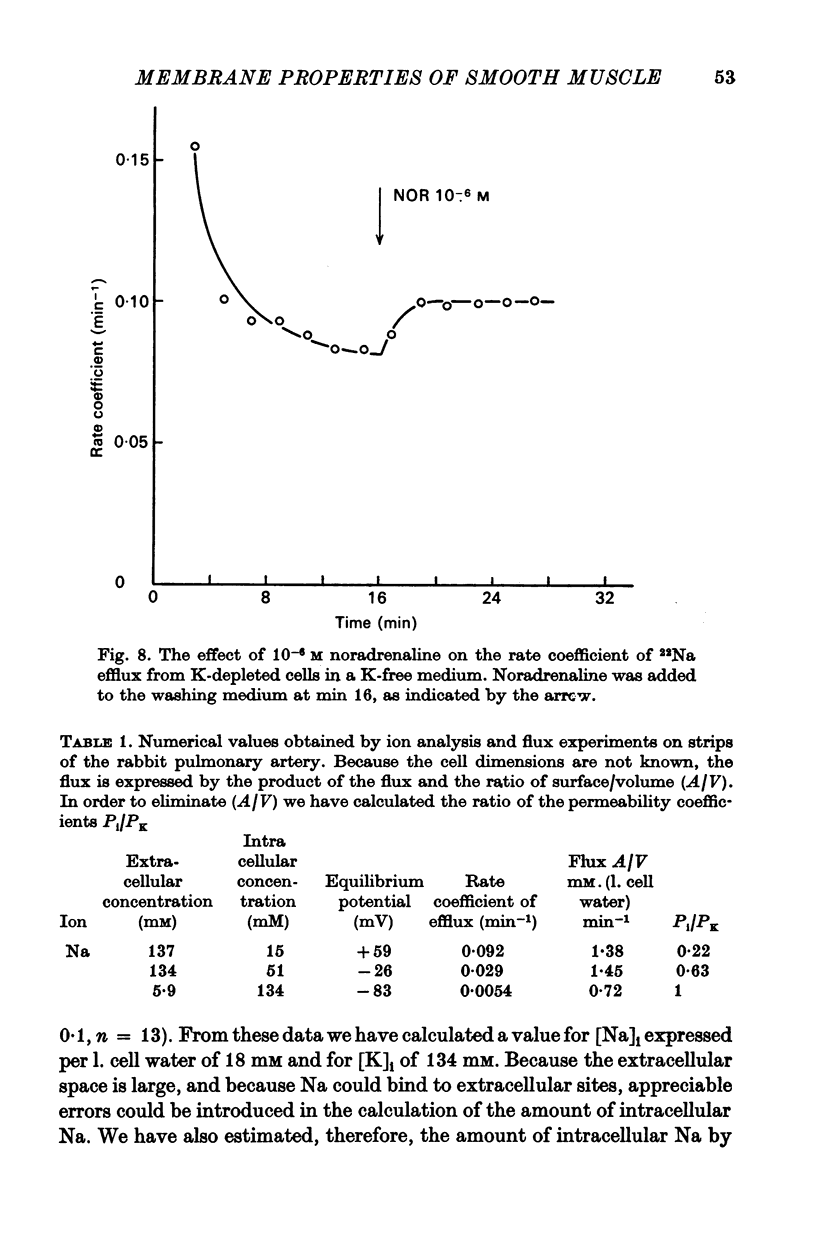
3. Noradrenaline, in concentrations between 2 × 10-8 and 10-7 M, evokes contraction without depolarizing the membrane. When the concentration is increased above 2 × 10-7 M, noradrenaline depolarizes the membrane and reduces the membrane resistance. A study of the effect of noradrenaline on the K, Cl and Na fluxes has revealed that it increases the permeability of the membrane for these three ions.
4. The tissue concentrations of Na and K are 80 and 38 m-mole/kg wet wt., respectively. The amount of Cl in the cellular compartment was measured by an extrapolation procedure and found to be 13 m-mole/kg wet wt. The extracellular space measured with [14C]sorbitol is 550 ml./kg wet wt. and the dry wt./wet wt. ratio 19%. The calculated equilibrium potentials for K, Na and Cl (EK, ENa and ECl) are -83, +59 and -26 mV, respectively. In efflux experiments under steady-state conditions, the following rate constants have been calculated: 0·092 min-1 for Na, 0·029 min-1 for Cl and 0·0054 min-1 for K. The calculated value for the ratio PNa/PK was 0·22 and for PCl/PK 0·63.
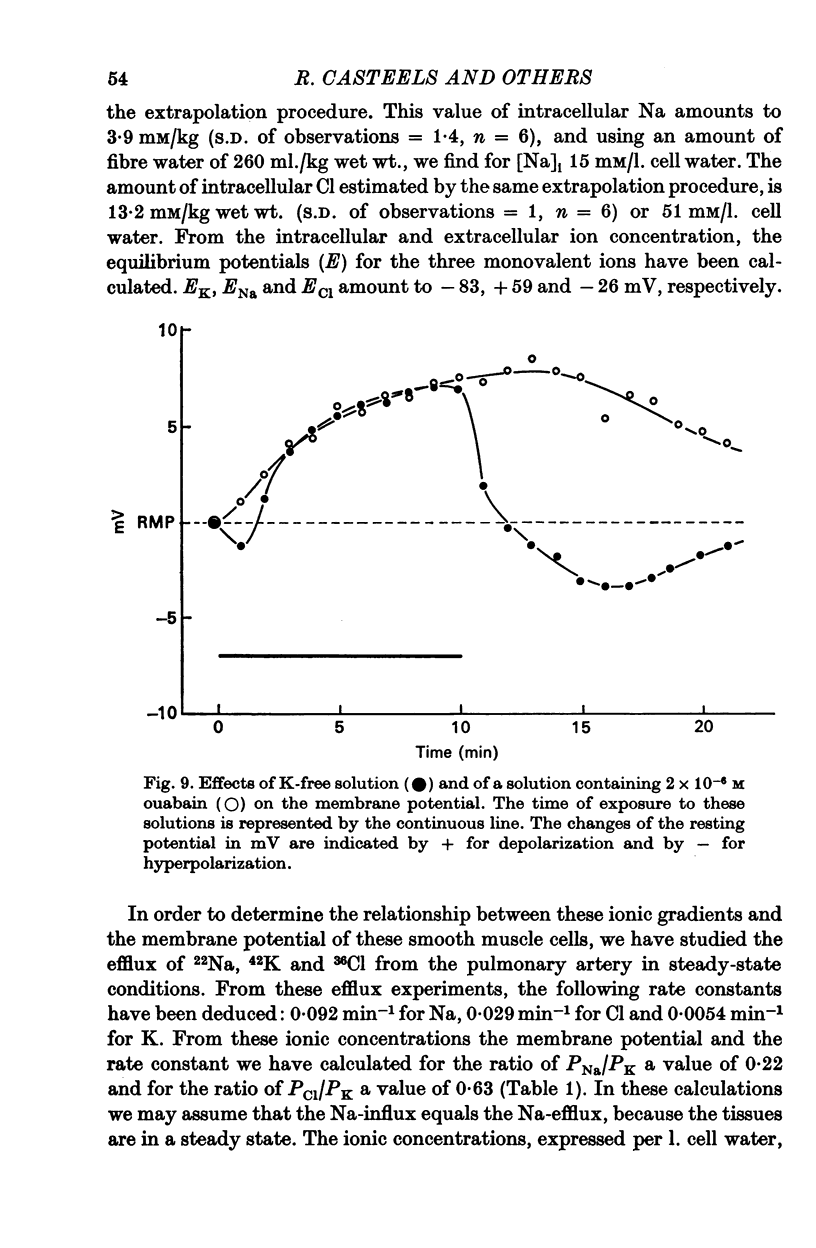
5. K-free solution and 2 × 10-6 M ouabain depolarize the cells by about 8 mV. After exposure of the cells to K-free solution, they hyperpolarize on readmission of K, suggesting that part of the membrane potential could be due to electrogenic transport of ions.
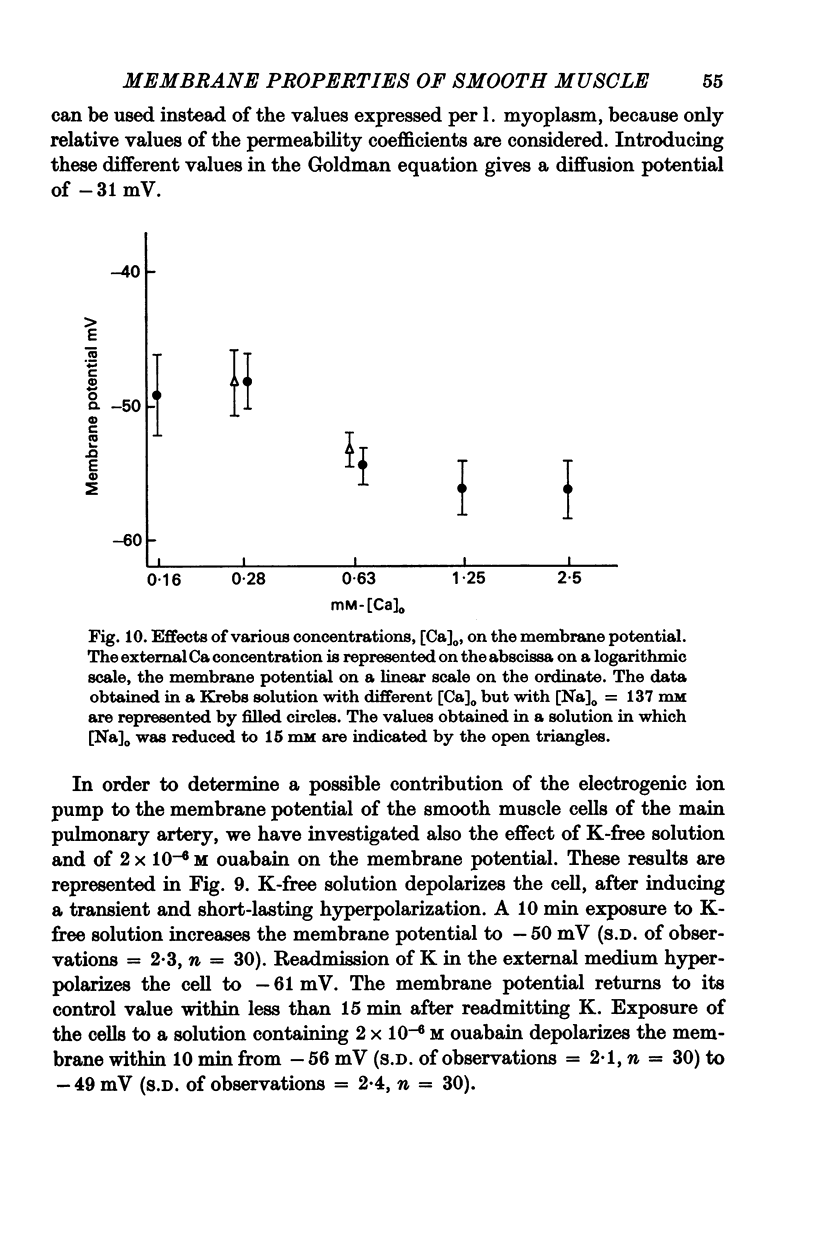
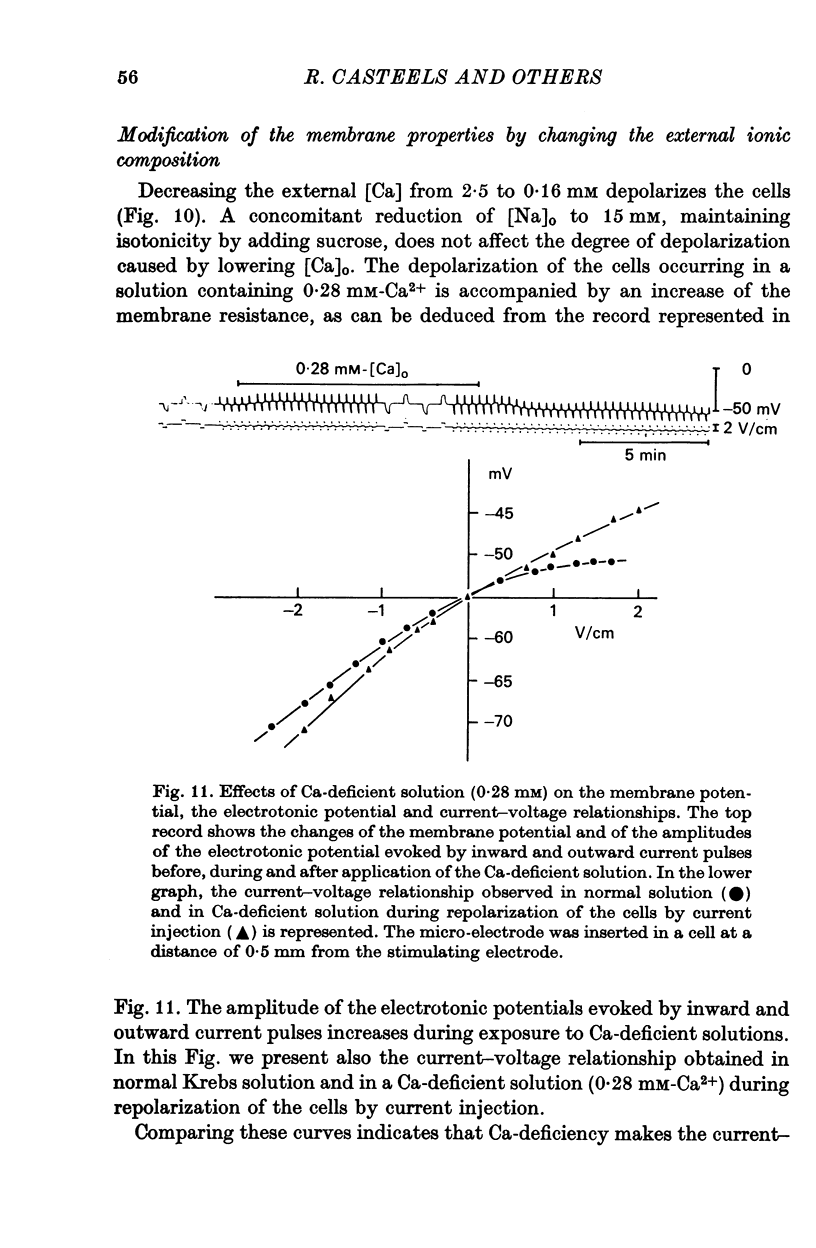
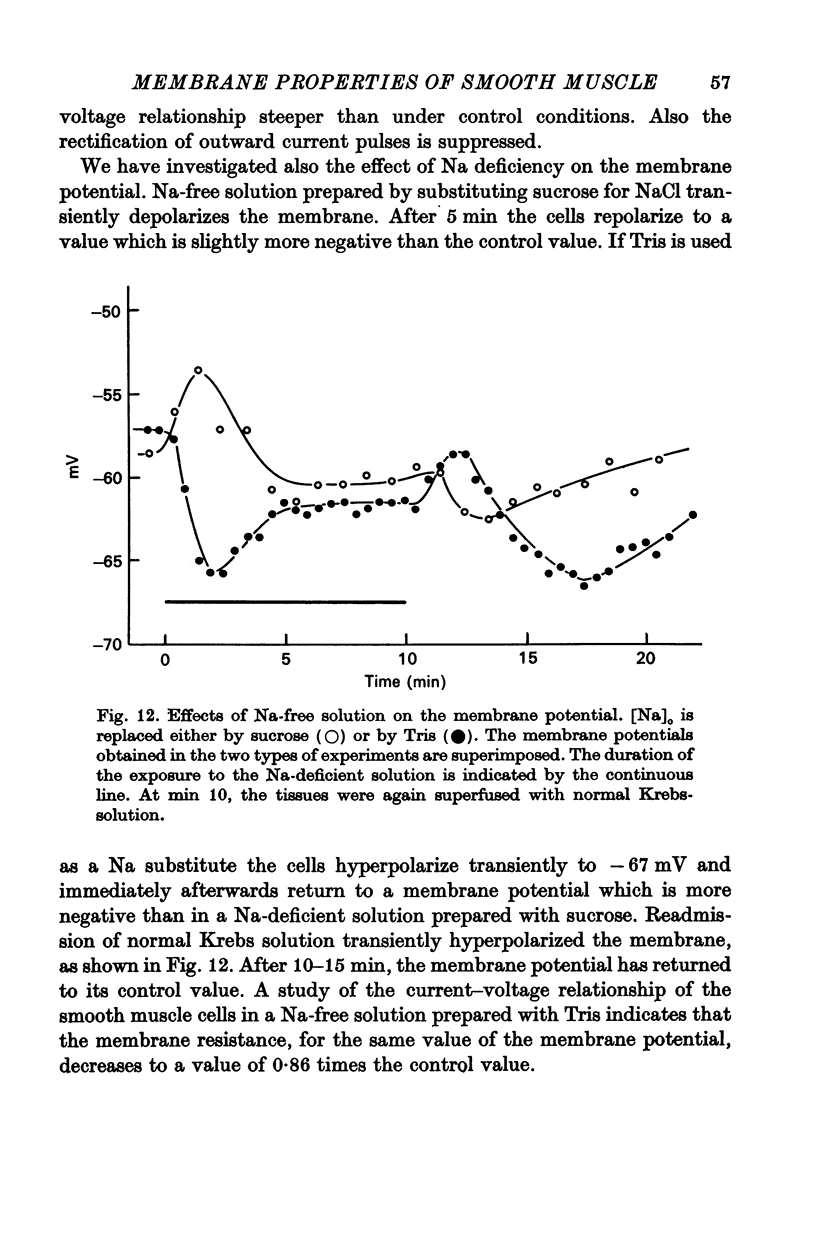
6. A decrease of external Ca depolarizes the cells and increases the membrane resistance. Na-deficiency hyperpolarizes these smooth muscle cells but this procedure does not prevent the depolarization induced by Ca deficiency.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe Y., Tomita T. Cable properties of smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1968 May;196(1):87–100. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BULBRING E., KURIYAMA H. Effects of changes in ionic environment on the action of acetylcholine and adrenaline on the smooth muscle cells of guinea-pig taenia coli. J Physiol. 1963 Apr;166:59–74. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan J. A., Su C. Sympathetic mechanisms in blood vessels: nerve and muscle relationships. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1973;13:269–285. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.13.040173.001413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bülbring E., Tomita T. Effect of calcium, barium and manganese on the action of adrenaline in the smooth muscle of the guinea-pig taenia coli. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1969 Mar 11;172(1027):121–136. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1969.0015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casteels R. Calculation of the membrane potential in smooth muscle cells of the guinea-pig's taenia coli by the Goldman equation. J Physiol. 1969 Nov;205(1):193–208. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casteels R., Kitamura K., Kuriyama H., Suzuki H. Excitation-contraction coupling in the smooth muscle cells of the rabbit main pulmonary artery. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;271(1):63–79. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casteels R. The distribution of chloride ions in the smooth muscle cells of the guinea-pig's taenia coli. J Physiol. 1971 Apr;214(2):225–243. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haeusler G. Differential effect of verapamil on excitation-contraction coupling in smooth muscle and on excitation-secretion coupling in adrenergic nerve terminals. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1972 Mar;180(3):672–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickx H., Casteels R. Electrogenic sodium pump in arterial smooth muscle cells. Pflugers Arch. 1974;346(4):299–306. doi: 10.1007/BF00596185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Kuriyama H., Sakamoto Y. Effects of tetraethylammonium chloride on the membrane activity of guinea-pig stomach smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1970 Dec;211(2):445–460. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkpatrick C. T. Excitation and contraction in bovine tracheal smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1975 Jan;244(2):263–281. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurihara S. The effect of procaine on the mechanical and electrical activities of the smooth muscle cells of the guineal pig urinary bladder. Jpn J Physiol. 1975;25(6):775–788. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.25.775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekata F. Current spread in the smooth muscle of the rabbit aorta. J Physiol. 1974 Oct;242(1):143–155. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekata F., Niu H. Biophysical effects of adrenaline on the smooth muscle of the rabbit common carotid artery. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Jan;59(1):92–102. doi: 10.1085/jgp.59.1.92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osa T., Kuriyama H. The membrane properties and decremental conduction of excitation in the fundus of the guinea-pig stomach. Jpn J Physiol. 1970 Dec 15;20(6):626–639. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.20.626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATTERSON M. S., GREENE R. C. MEASUREMENT OF LOW ENERGY BETA-EMITTERS IN AQUEOUS SOLUTION BY LIQUID SCINTILLATION COUNTING OF EMULSIONS. Anal Chem. 1965 Jun;37:854–857. doi: 10.1021/ac60226a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SU C., BEVAN J. A., URSILLO R. C. ELECTRICAL QUIESCENCE OF PULMONARY ARTERY SMOOTH MUSCLE DURING SYMPATHOMIMETIC STIMULATION. Circ Res. 1964 Jul;15:26–27. doi: 10.1161/01.res.15.1.20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somlyo A. V., Somlyo A. P. Electromechanical and pharmacomechanical coupling in vascular smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1968 Jan;159(1):129–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Morita K., Kuriyama H. Innervation and properties of the smooth muscle of the dog trachea. Jpn J Physiol. 1976;26(3):303–320. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.26.303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


