Abstract
1. Synaptic transmission was studied in visually identified parasympathetic ganglion cells that modulate the heart beat of the mudpuppy Necturus maculosus).
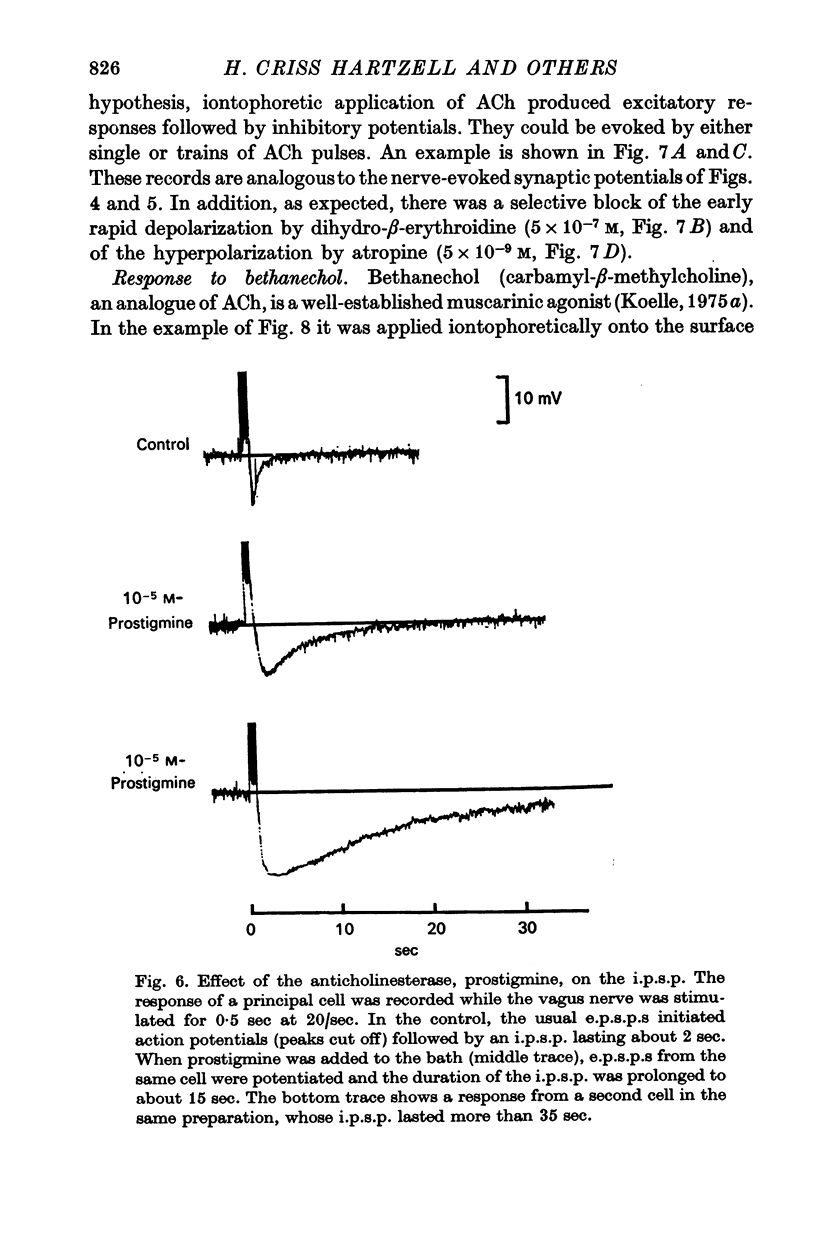
2. The brief pulse of acetylcholine (ACh) released from terminals of the vagus nerve after each impulse can produce two distinct post-synaptic responses in individual principal cells of the ganglion: (i) within a milli-second of release, ACh generates a rapid and strong excitatory post-synaptic potential (e.p.s.p.) that normally initiates a post-synaptic impulse; (ii) this excitation is usually followed by a slow hyperpolarizing inhibitory post-synaptic potential (i.p.s.p.) that lasts for several seconds. The magnitude and time course of the i.p.s.p. depends on the frequency and number of vagal stimuli. When the hydrolysis of ACh is inhibited by prostigmine, a train of nerve stimuli may be followed by an i.p.s.p. lasting half a minute or longer.
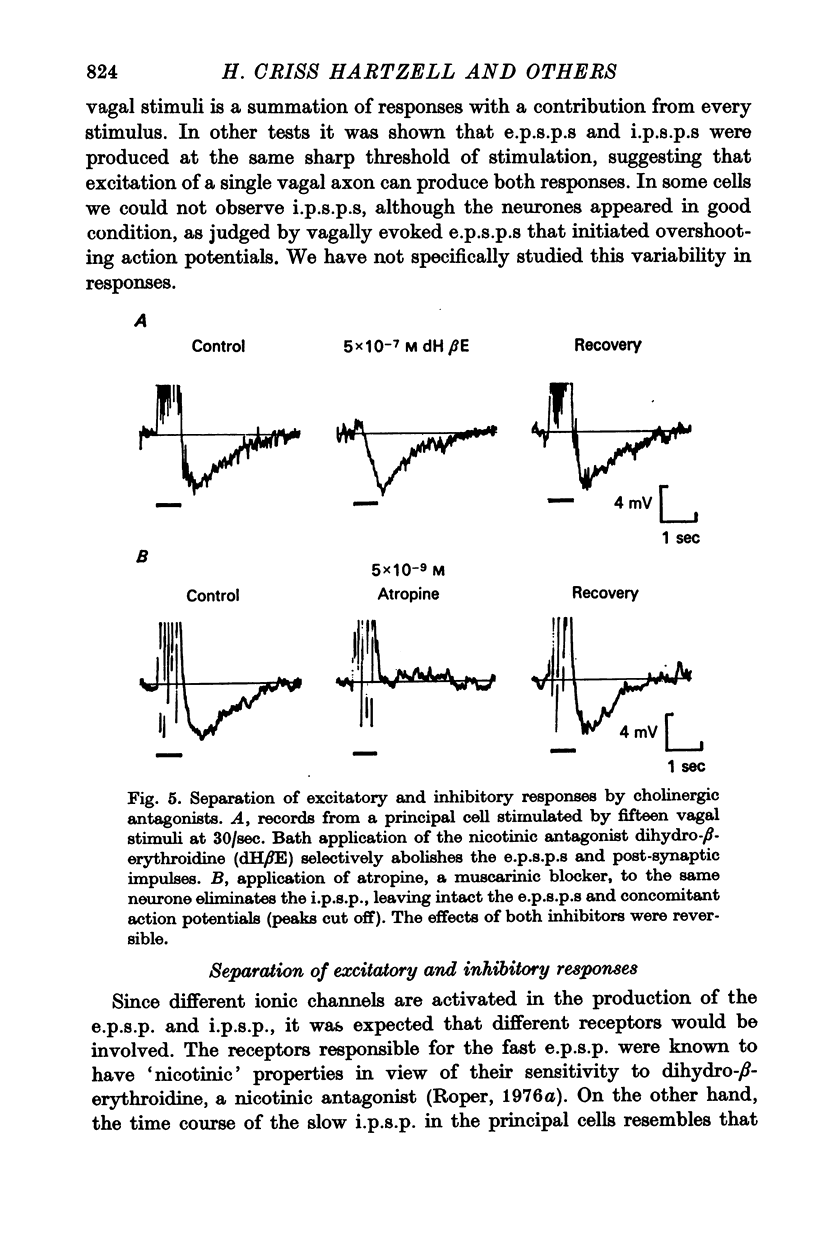
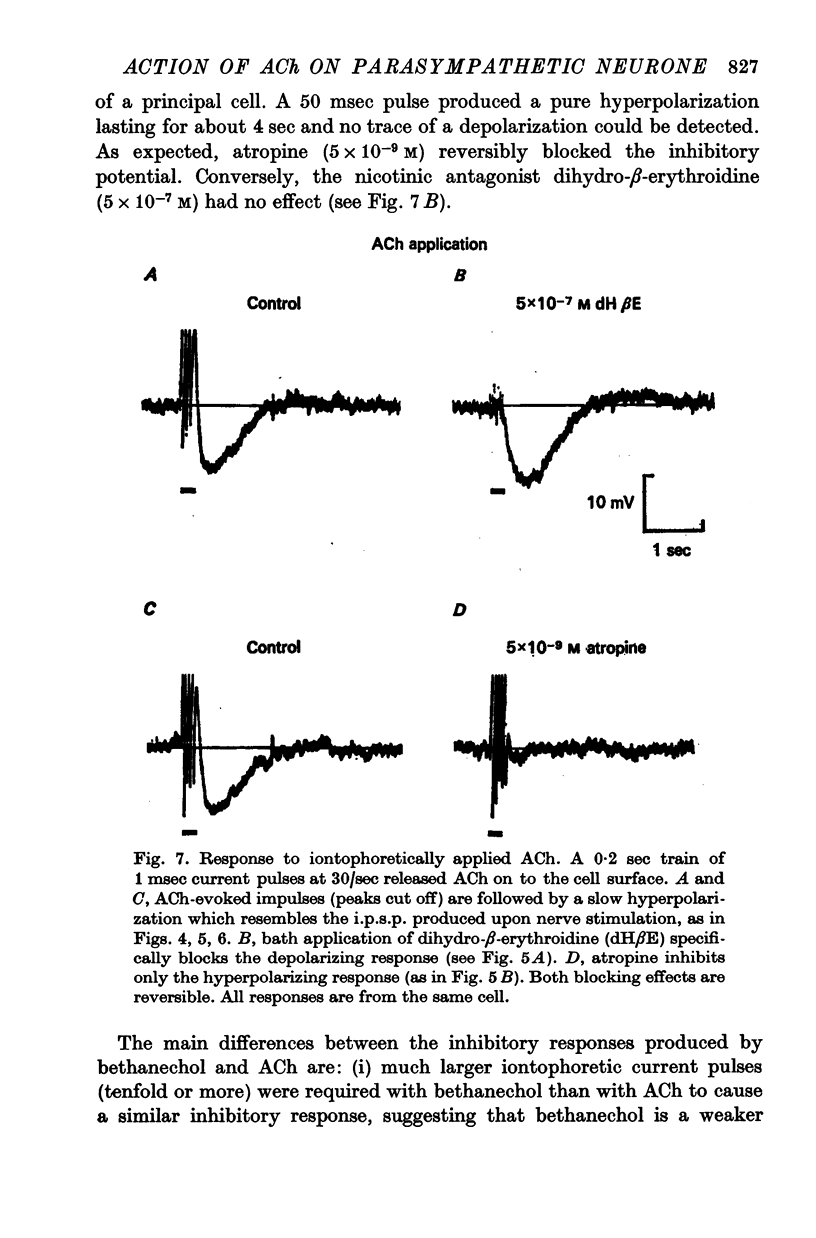
3. The rapid e.p.s.p. and slow i.p.s.p. result from the direct action of ACh on two different types of chemoreceptors in the post-synaptic membrane of the principal cell. The e.p.s.p. can be preferentially blocked by the nicotinic antagonist dihydro-β-erythroidine (5 × 10-7 M), while the i.p.s.p. is selectively blocked by the muscarinic antagonist atropine (5 × 10-9 M).
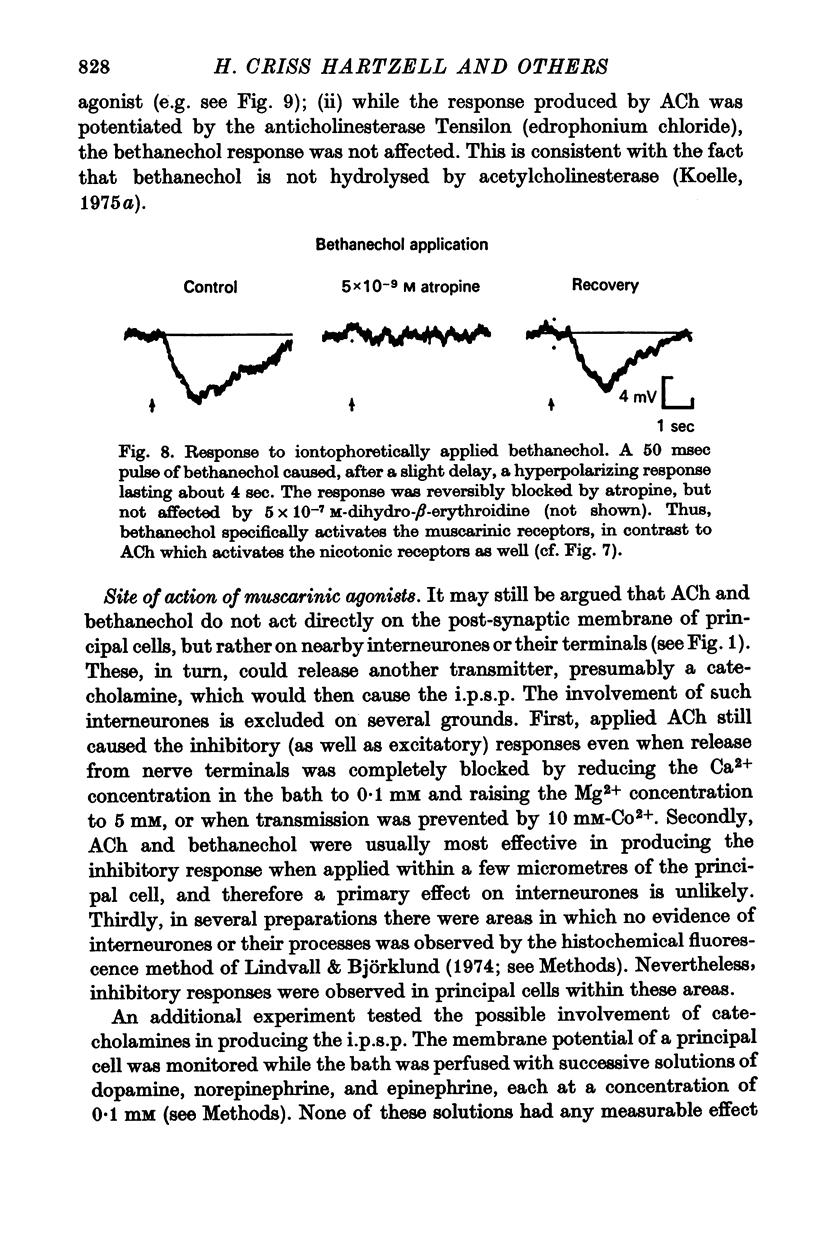
4. Potentials resembling nerve-evoked e.p.s.p.s and i.p.s.p.s can be produced by iontophoretic release of ACh from micropipettes onto the post-synaptic membrane. Application of the muscarinic agonist bethanechol generates exclusively inhibitory responses.
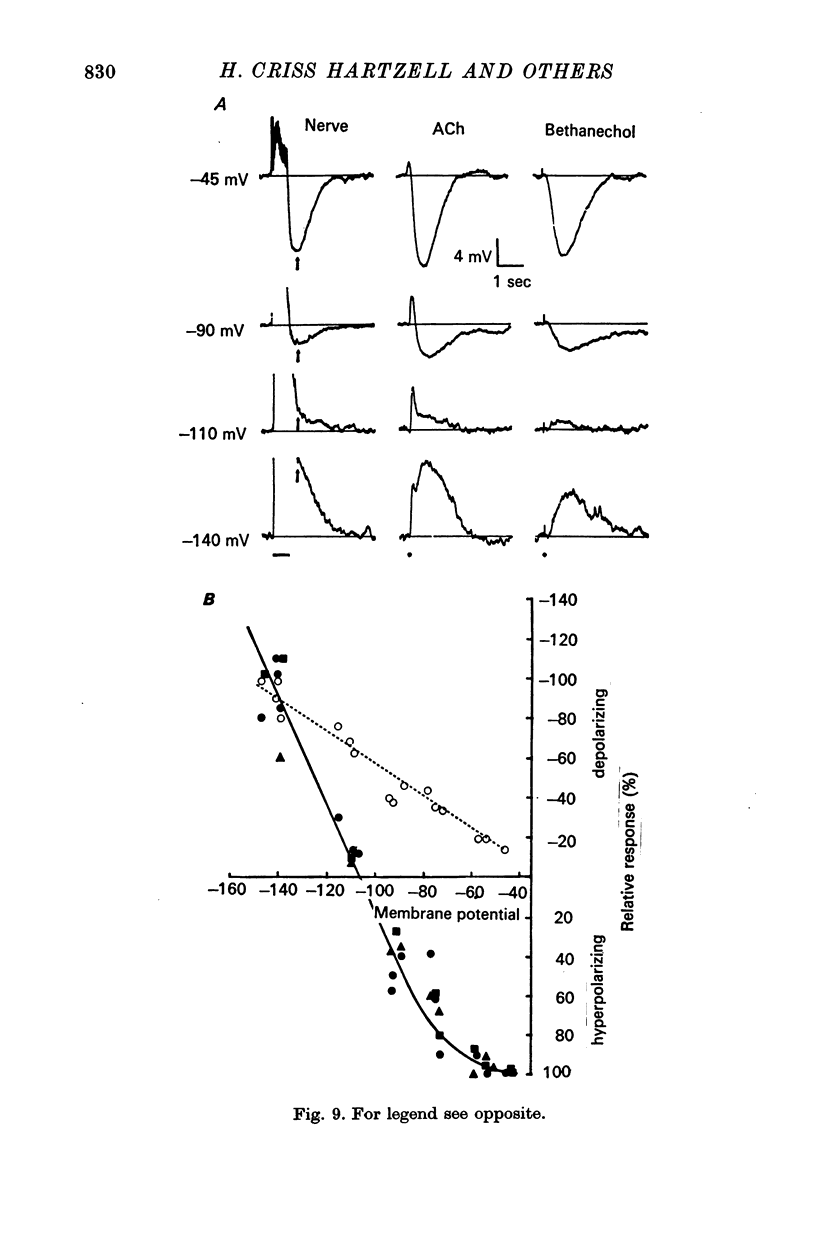
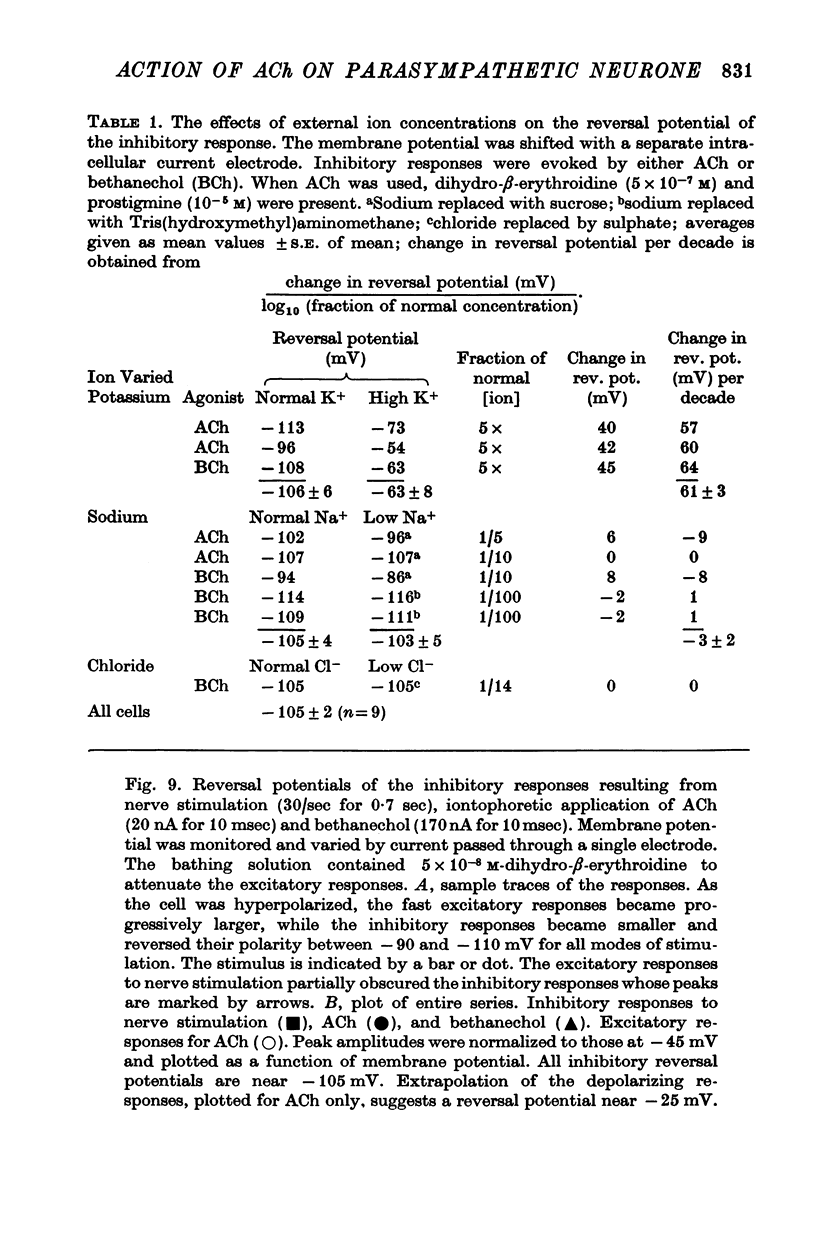
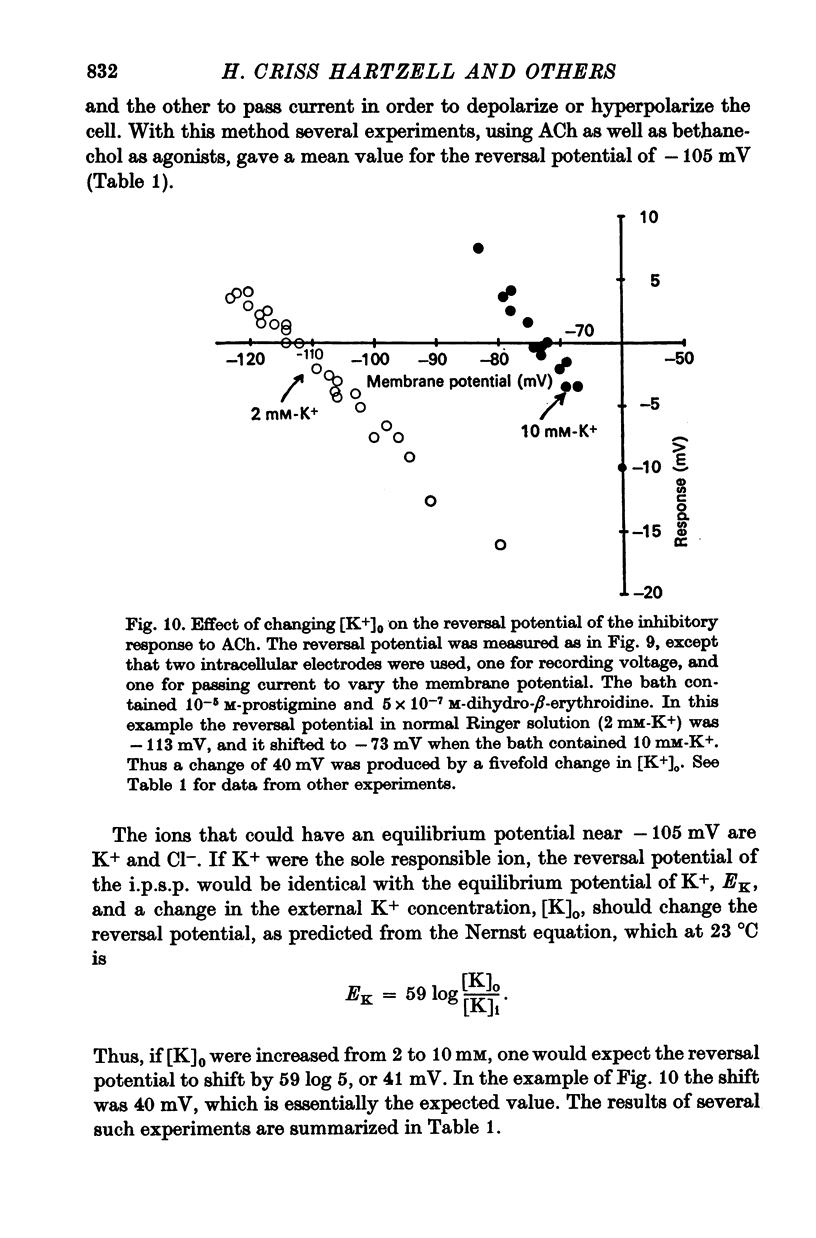
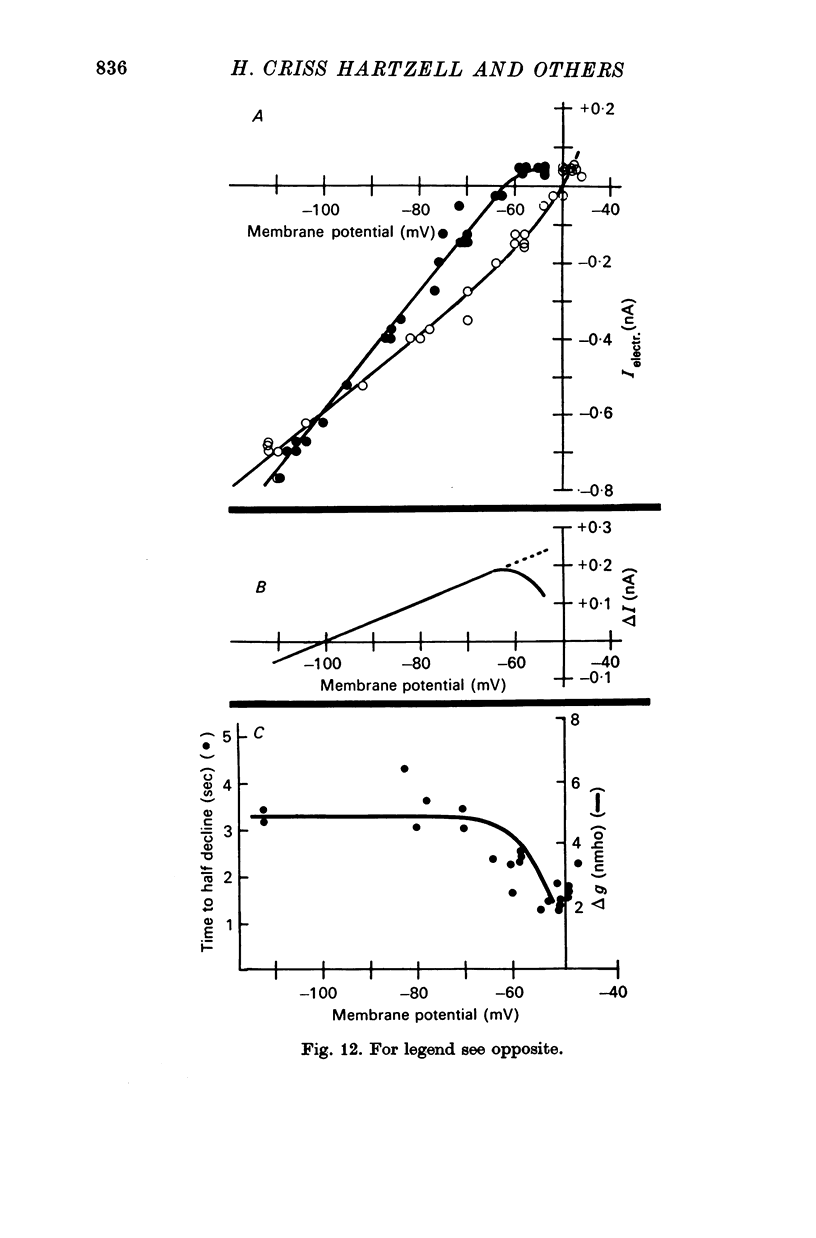
5. The reversal potential for the i.p.s.p. is about -105 mV, which is approximately the equilibrium potential for potassium (EK). When the external K+ concentration is altered, the reversal potential for inhibition is shifted to the new value of EK as expected from the Nernst equation. Changes in the external Na+ and Cl- concentrations have no appreciable effect on the reversal potential. Thus, the i.p.s.p. is the result of a conductance increase for K+.
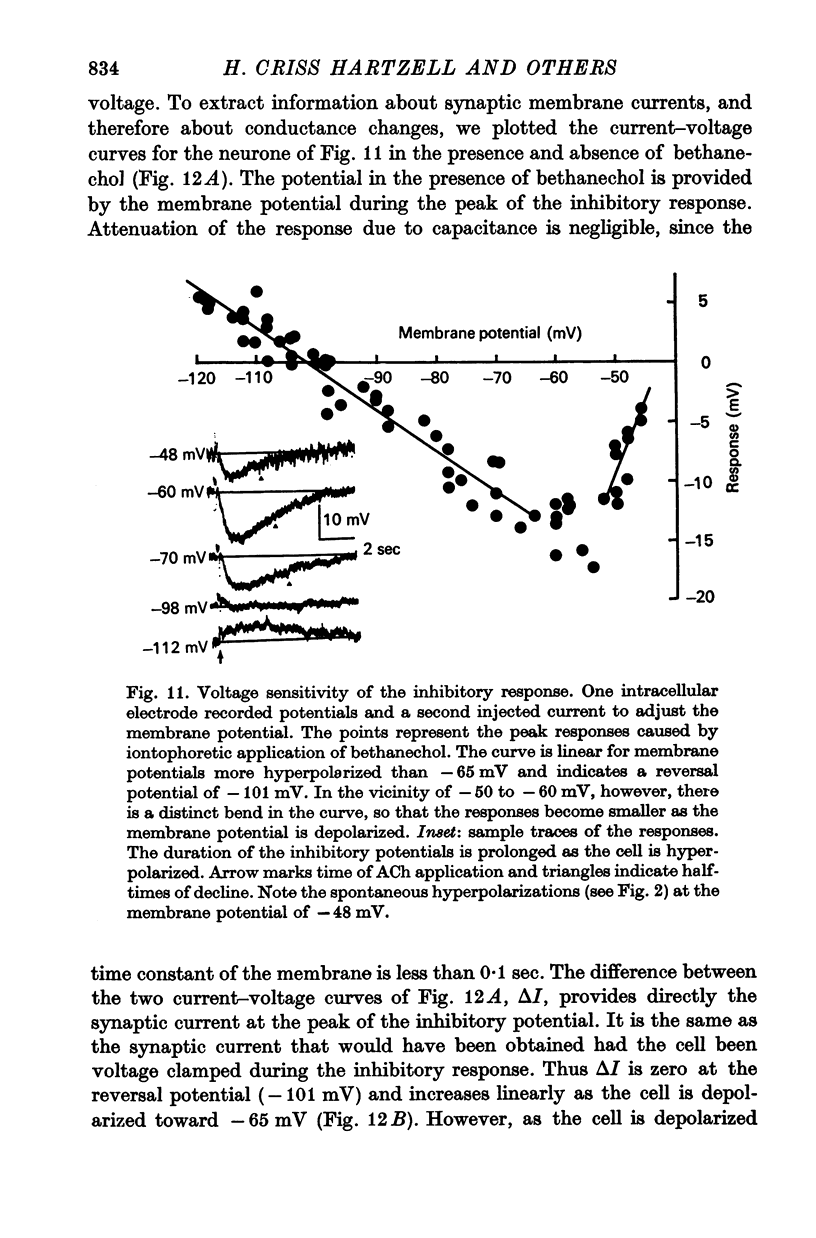
6. The conductance change producing the i.p.s.p. is voltage sensitive. When the membrane potential is shifted from -40 to -60 mV, the i.p.s.p becomes larger and longer. Beyond -60 mV the inhibitory response decreases in proportion to the driving force on K+ without any further change in time course.
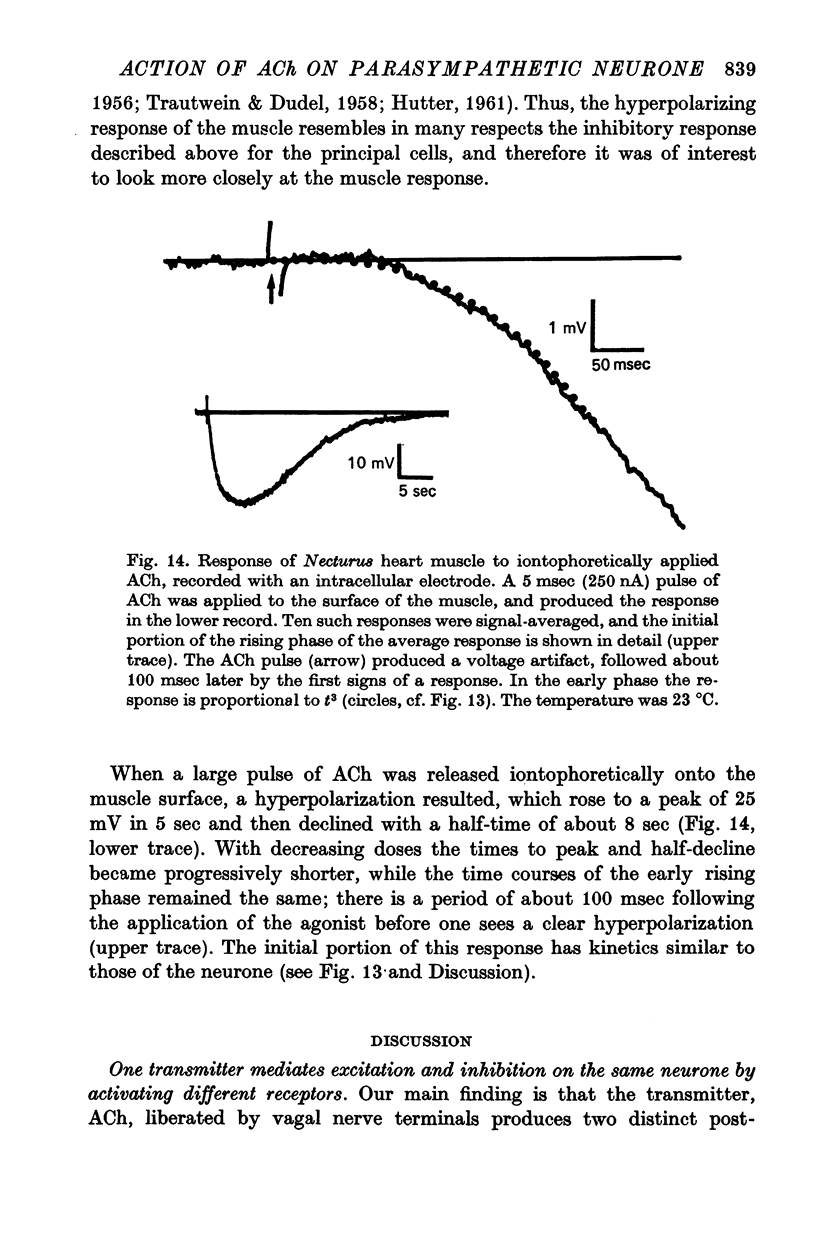
7. The inhibitory response produced by an iontophoretically applied pulse of bethanechol has a delayed onset of about 150 msec at 24 °C. The early portion of this response, including the delay, is proportional to t3, where t is time. The proportionality factor (the apparent rate constant) decreases elevenfold when the temperature is lowered by 10 °C. This suggests that a multi-step process is involved in the activation of the conductance increase that leads to the inhibitory response. Inhibitory responses with similar kinetics were produced in heart muscles of the mudpuppy upon application of ACh.
Full text
PDF


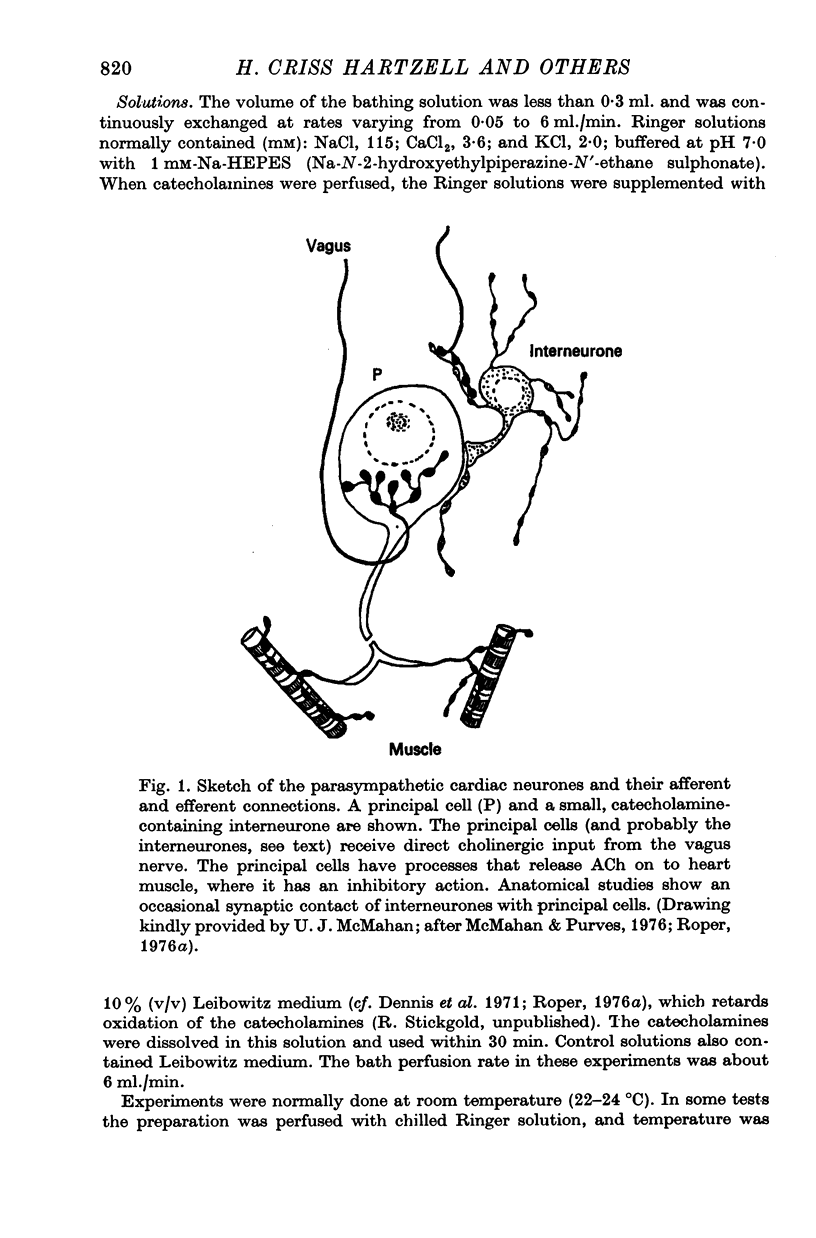
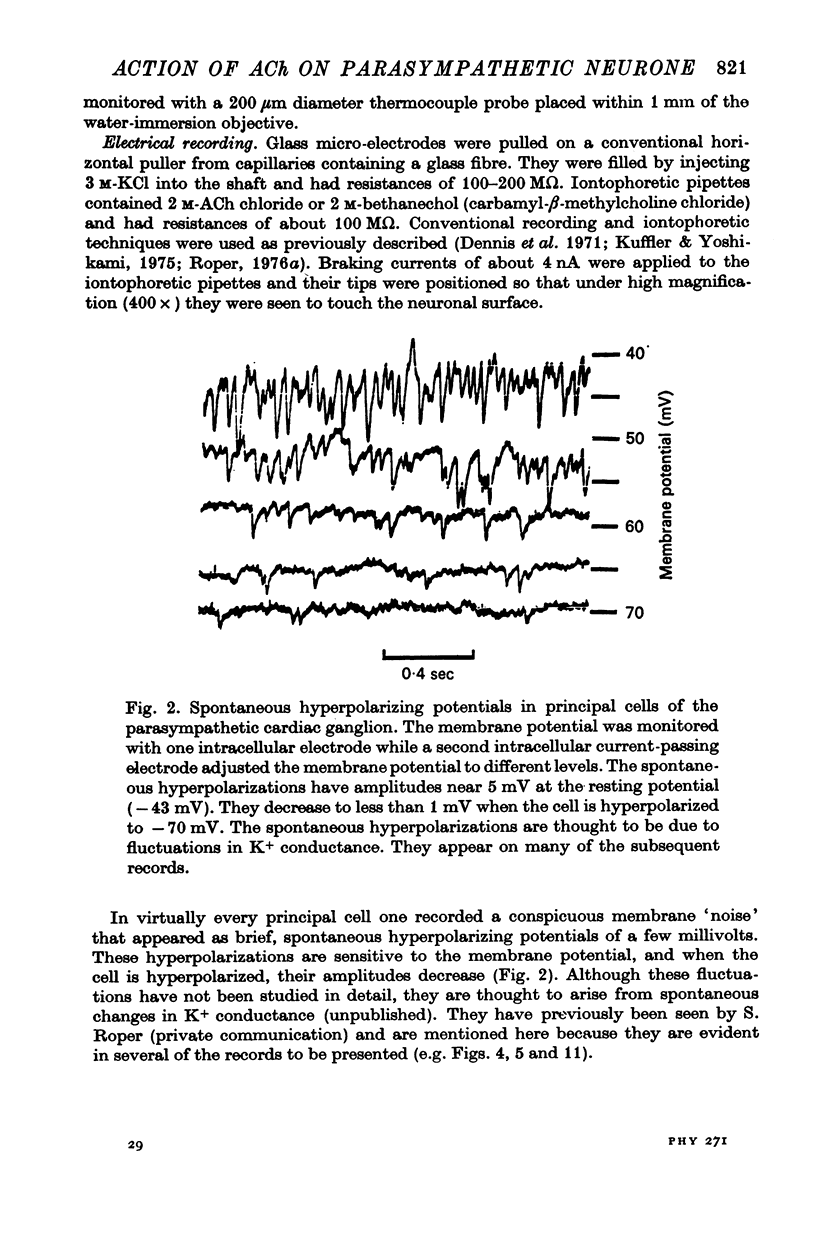
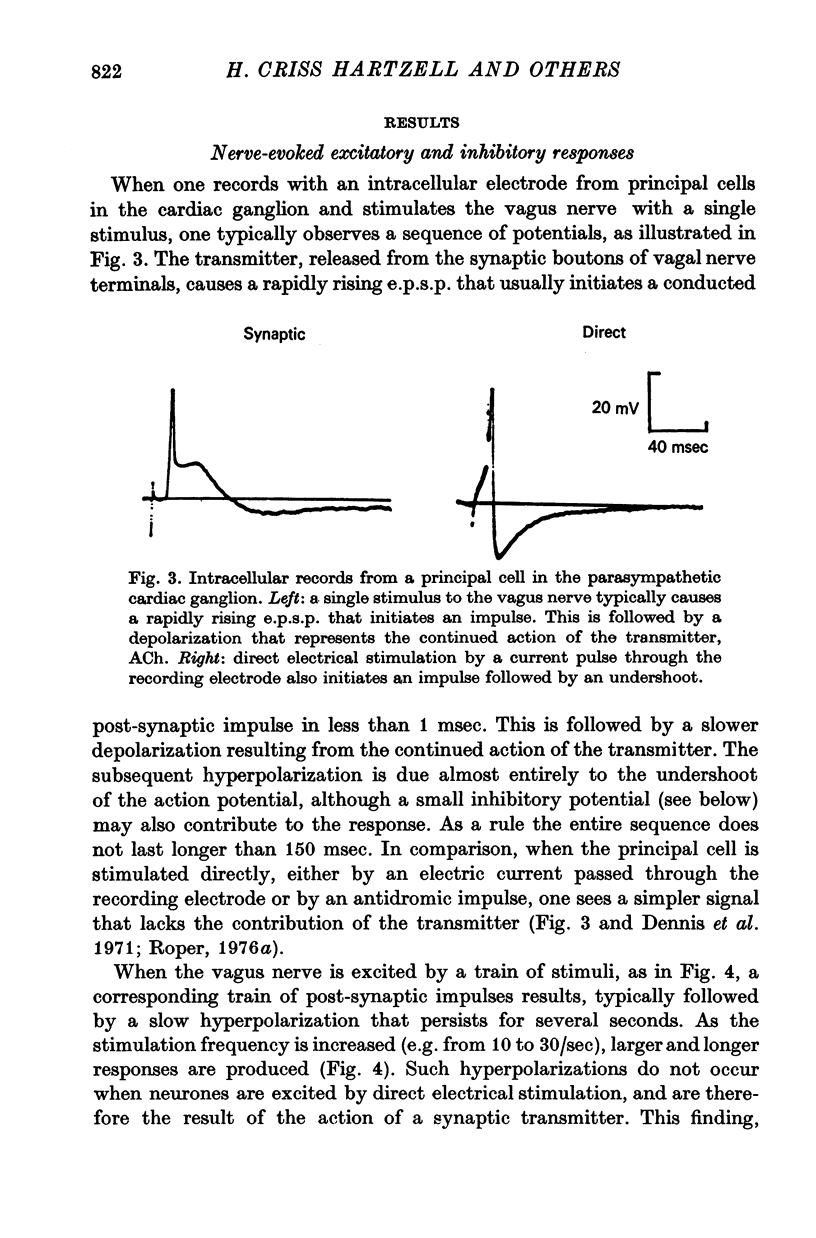
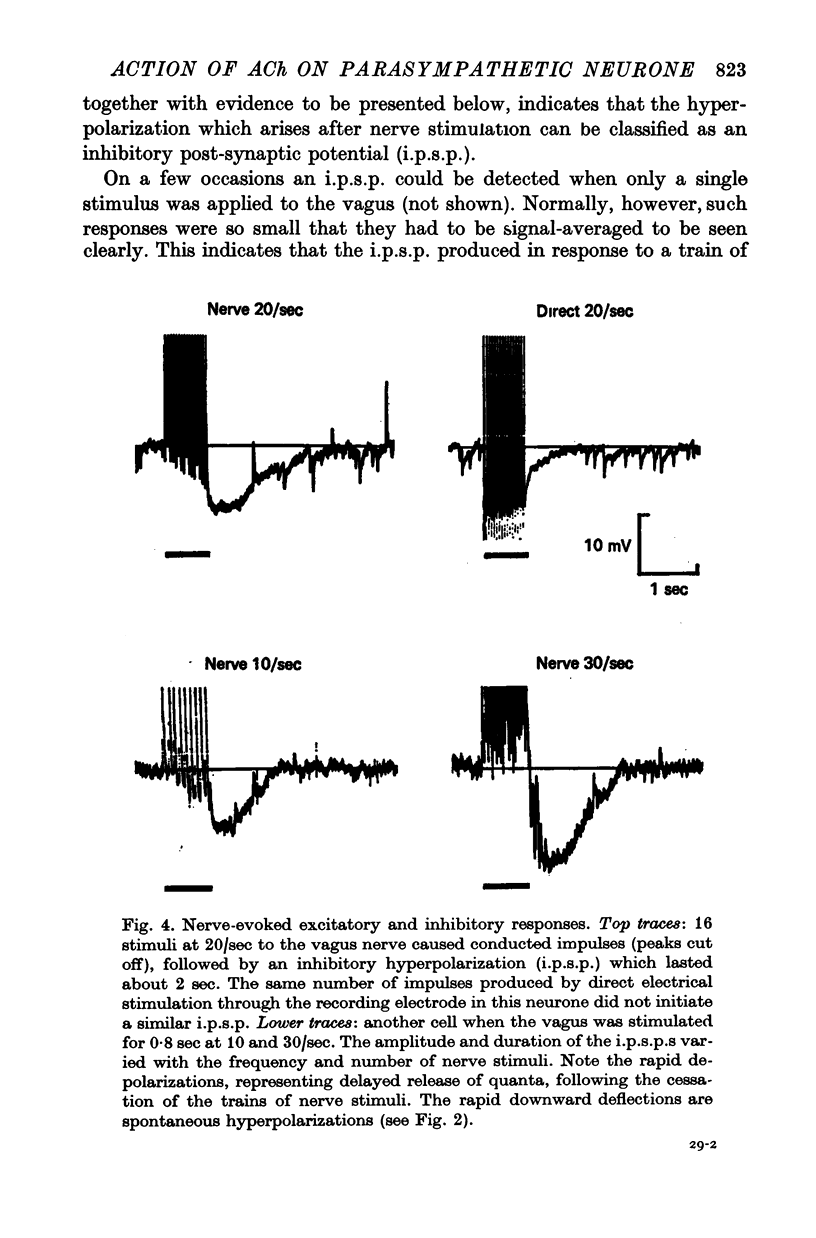













Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. R., Cull-Candy S. G., Miledi R. Glutamate and quisqualate noise in voltage-clamped locust muscle fibres. Nature. 1976 May 13;261(5556):151–153. doi: 10.1038/261151a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C. R., Stevens C. F. Voltage clamp analysis of acetylcholine produced end-plate current fluctuations at frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1973 Dec;235(3):655–691. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton T. B. On the latency and form of the membrane responses of smooth muscle to the iontophoretic application of acetylcholine or carbachol. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1976 Aug 27;194(1114):99–119. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1976.0068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Ryall R. W. The acetylcholine receptors of Renshaw cells. Exp Brain Res. 1966;2(1):66–80. doi: 10.1007/BF00234361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. On the localization of acetylcholine receptors. J Physiol. 1955 Apr 28;128(1):157–181. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. The membrane change produced by the neuromuscular transmitter. J Physiol. 1954 Sep 28;125(3):546–565. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis M. J., Harris A. J., Kuffler S. W. Synaptic transmission and its duplication by focally applied acetylcholine in parasympathetic neurons in the heart of the frog. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1971 Apr 27;177(1049):509–539. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1971.0045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudel J. Nonlinear voltage dependence of excitatory synaptic current in crayfish muscle. Pflugers Arch. 1974;352(3):227–241. doi: 10.1007/BF00590488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES R. M., LIBET B. Origin and blockade of the synaptic responses of curarized sympathetic ganglia. J Physiol. 1961 Aug;157:484–503. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., KATZ B. Spontaneous subthreshold activity at motor nerve endings. J Physiol. 1952 May;117(1):109–128. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerschenfeld H. M. Chemical transmission in invertebrate central nervous systems and neuromuscular junctions. Physiol Rev. 1973 Jan;53(1):1–119. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1973.53.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giles W., Noble S. J. Changes in membrane currents in bullfrog atrium produced by acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1976 Sep;261(1):103–123. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greengard P. Possible role for cyclic nucleotides and phosphorylated membrane proteins in postsynaptic actions of neurotransmitters. Nature. 1976 Mar 11;260(5547):101–108. doi: 10.1038/260101a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard J. I. Microphysiology of vertebrate neuromuscular transmission. Physiol Rev. 1973 Jul;53(3):674–723. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1973.53.3.674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., MILEDI R. THE MEASUREMENT OF SYNAPTIC DELAY, AND THE TIME COURSE OF ACETYLCHOLINE RELEASE AT THE NEUROMUSCULAR JUNCTION. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1965 Feb 16;161:483–495. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1965.0016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuffler S. W., Yoshikami D. The distribution of acetylcholine sensitivity at the post-synaptic membrane of vertebrate skeletal twitch muscles: iontophoretic mapping in the micron range. J Physiol. 1975 Jan;244(3):703–730. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libet B. Generation of slow inhibitory and excitatory postsynaptic potentials. Fed Proc. 1970 Nov-Dec;29(6):1945–1956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libet B., Tosaka T. Dopamine as a synaptic transmitter and modulator in sympathetic ganglia: a different mode of synaptic action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):667–673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindvall O., Björklund A. The glyoxylic acid fluorescence histochemical method: a detailed account of the methodology for the visualization of central catecholamine neurons. Histochemistry. 1974 Apr 22;39(2):97–127. doi: 10.1007/BF00492041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahan U. J., Purves D. Visual identification of two kinds of nerve cells and their synaptic contacts in a living autonomic ganglion of the mudpuppy (Necturus maculosus). J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(2):405–425. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purves R. D. Function of muscarinic and nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Nature. 1976 May 13;261(5556):149–151. doi: 10.1038/261149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purves R. D. Muscarinic excitation: a microelectrophoretic study on cultured smooth muscle cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Sep;52(1):77–86. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1974.tb09689.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roper S. An electrophysiological study of chemical and electrical synapses on neurones in the parasympathetic cardiac ganglion of the mudpuppy, Necturus maculosus: evidence for intrinsic ganglionic innervation. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(2):427–454. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roper S. The acetylcholine sensitivity of the surface membrane of multiply-innervated parasympathetic ganglion cells in the mudpuppy before and after partial denervation. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(2):455–473. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRAUTWEIN W., DUDEL J. Zum Mechanismus der Membranwirkung des Acetylcholin an der Herzmuskelfaser. Pflugers Arch. 1958;266(3):324–334. doi: 10.1007/BF00416781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosaka T., Chichibu S., Libet B. Intracellular analysis of slow inhibitors and excitatory postsynaptic potentials in sympathetic ganglia of the frog. J Neurophysiol. 1968 May;31(3):396–409. doi: 10.1152/jn.1968.31.3.396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachtel H., Kandel E. R. Conversion of synaptic excitation to inhibition at a dual chemical synapse. J Neurophysiol. 1971 Jan;34(1):56–68. doi: 10.1152/jn.1971.34.1.56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weight F. F., Padjen A. Acetylcholine and slow synaptic inhibition in frog sympathetic ganglion cells. Brain Res. 1973 May 30;55(1):225–228. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90506-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weight F. F., Padjen A. Slow synaptic inhibition: evidence for synaptic inactivation of sodium conductance in sympathetic ganglion cells. Brain Res. 1973 May 30;55(1):219–224. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90505-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


