Abstract
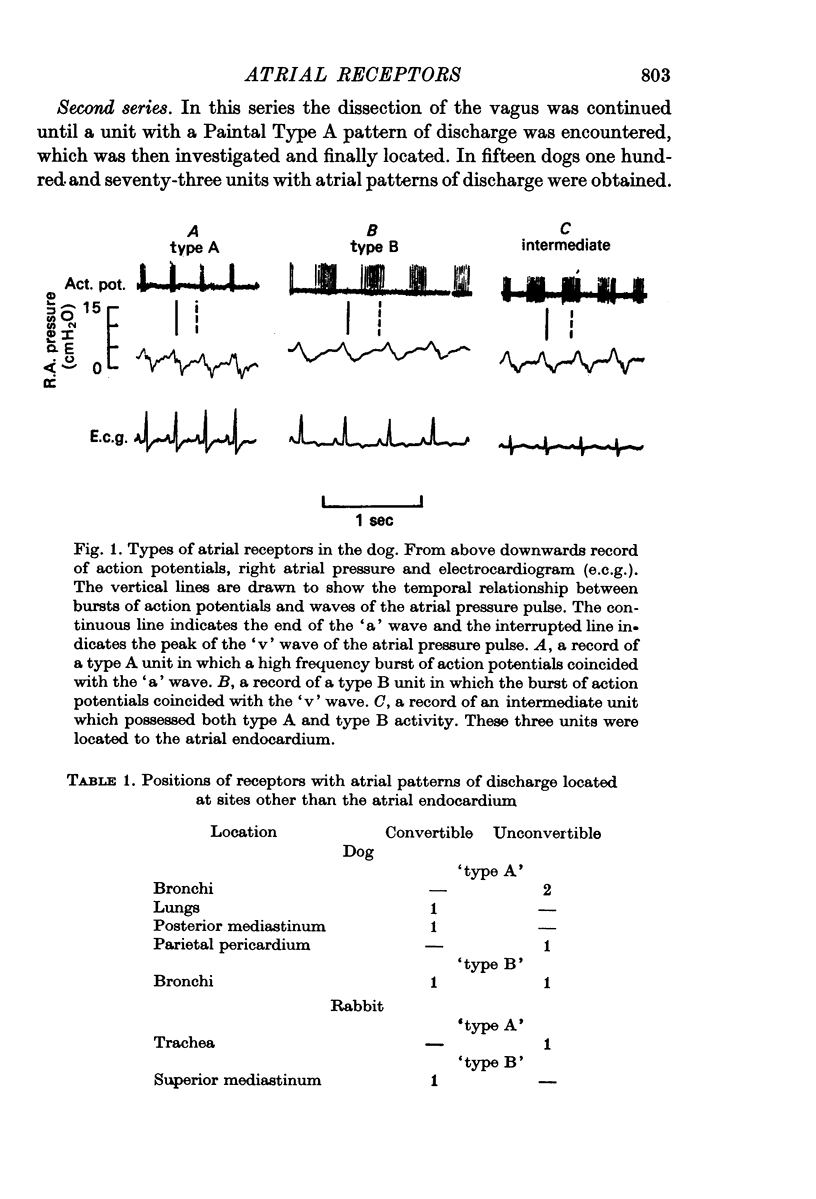
1. Action potentials were recorded from slips of the cervical vagi in anaesthetized dogs and rabbits. Single functional units with atrial patterns of discharge (Paintal Type A, B and intermediate) were obtained and then attempts were made to alter (i.e. convert) their patterns of discharge. Finally the points of origin of these action potentials were located.
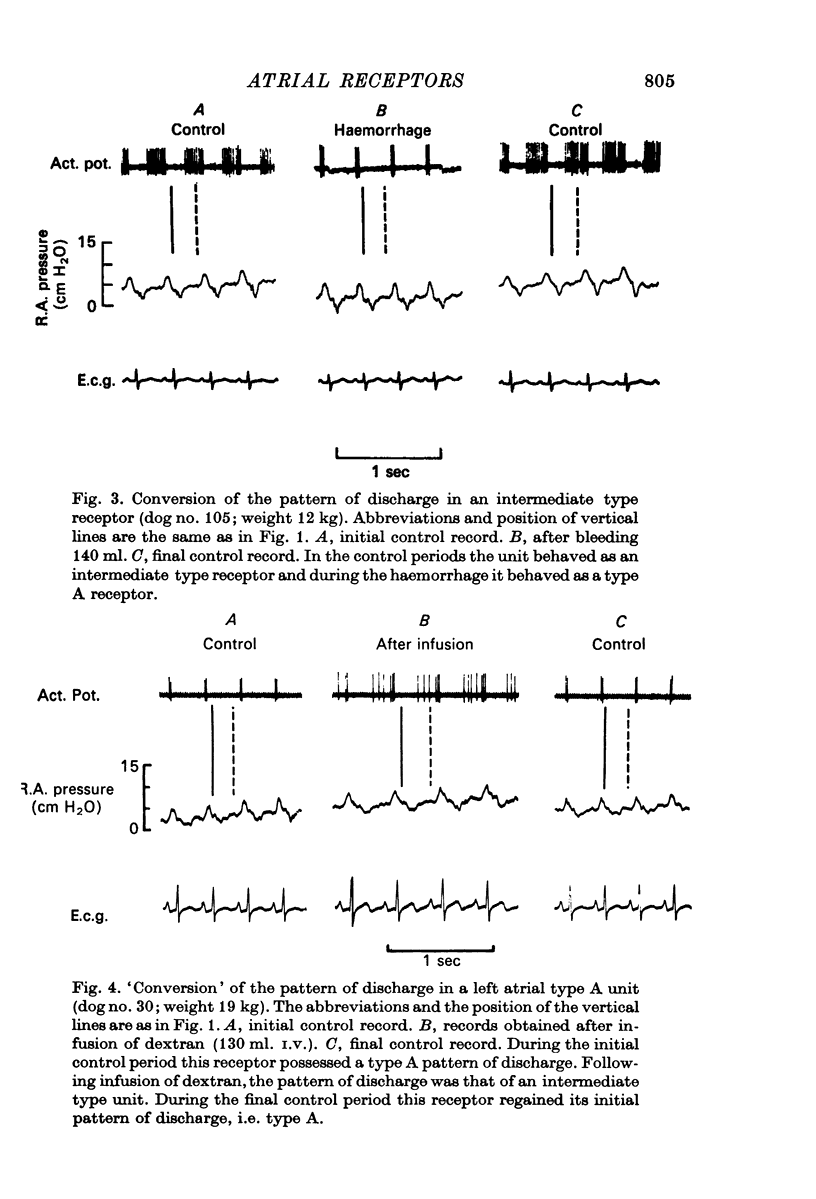
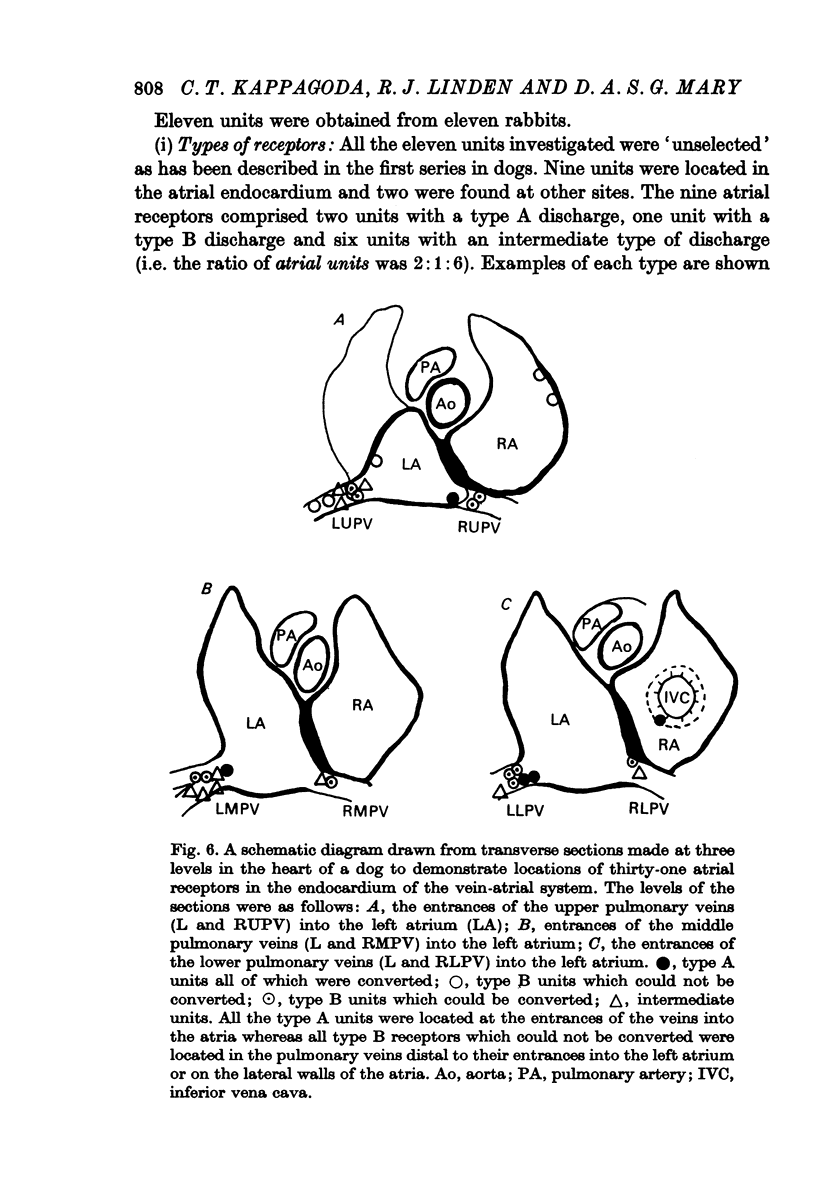
2. Thirty unselected units were investigated in thirty dogs. Twenty-seven of these were located in the endocardium of the vein-atrial system and the ratio of the type A, type B and intermediate type receptors was 1:16:10; three units were located elsewhere in the chest. Conversion of the pattern of discharge was achieved in twenty of the twenty-seven units; conversion was achieved in the single type A unit.
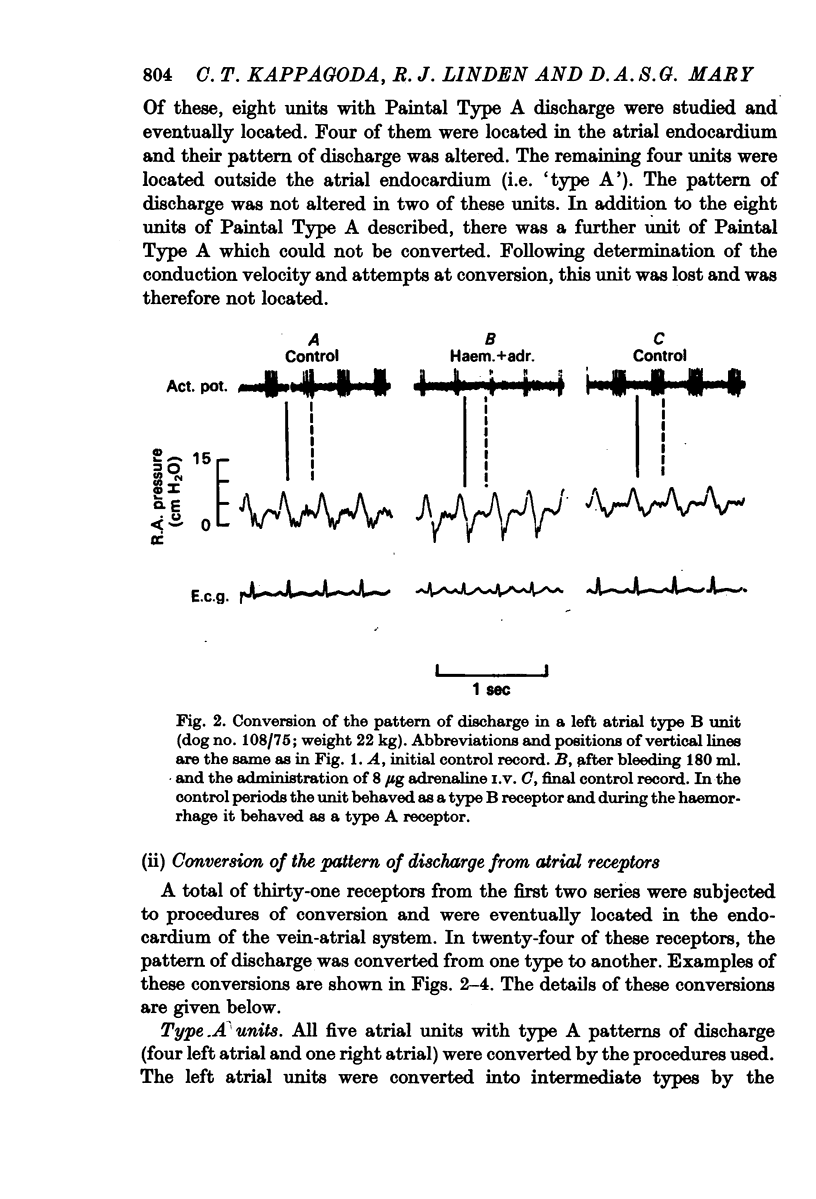
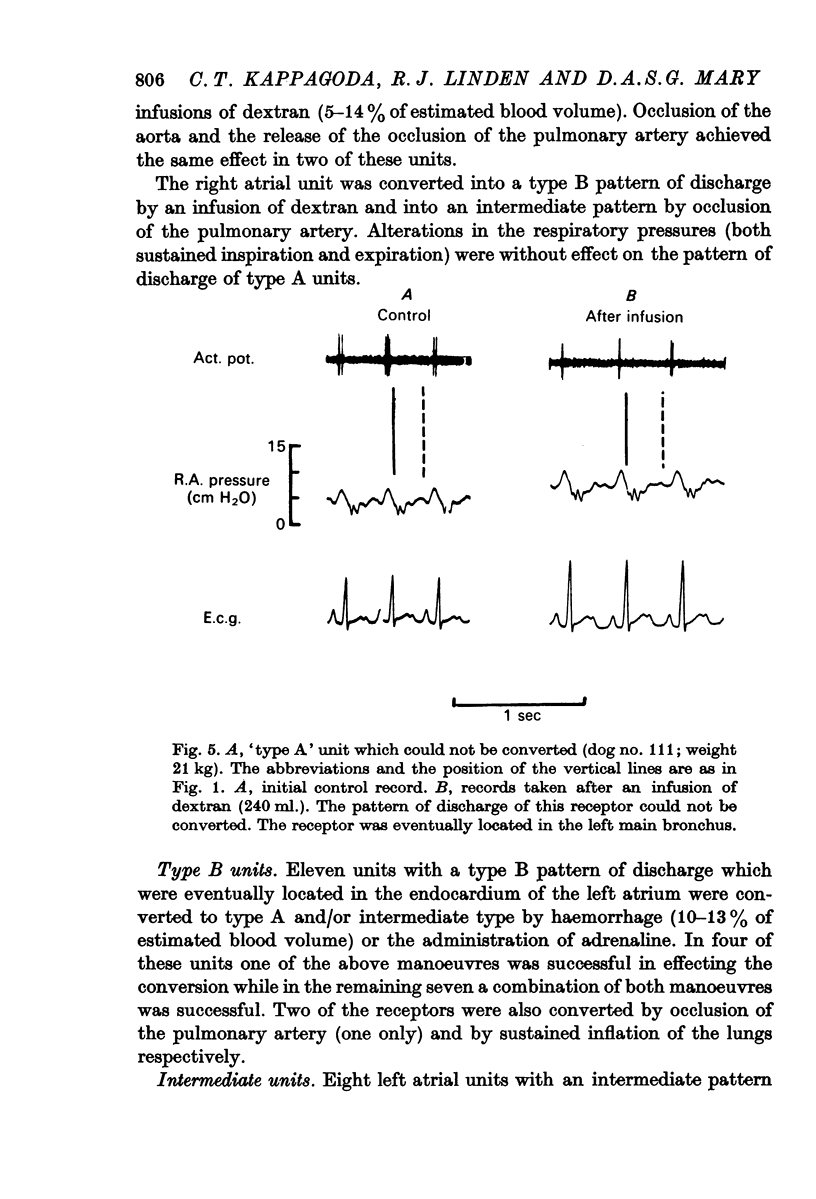
3. In a second series of experiments in dogs, eight Paintal Type A units were selectively studied in fifteen animals. Four of these were located in the endocardium and all were converted. The remaining four were located outside the endocardium and conversion could not be achieved in two of these. Thus in the entire investigation, the `type A' units which could not be converted were all located at sites other than the atrial endocardium.
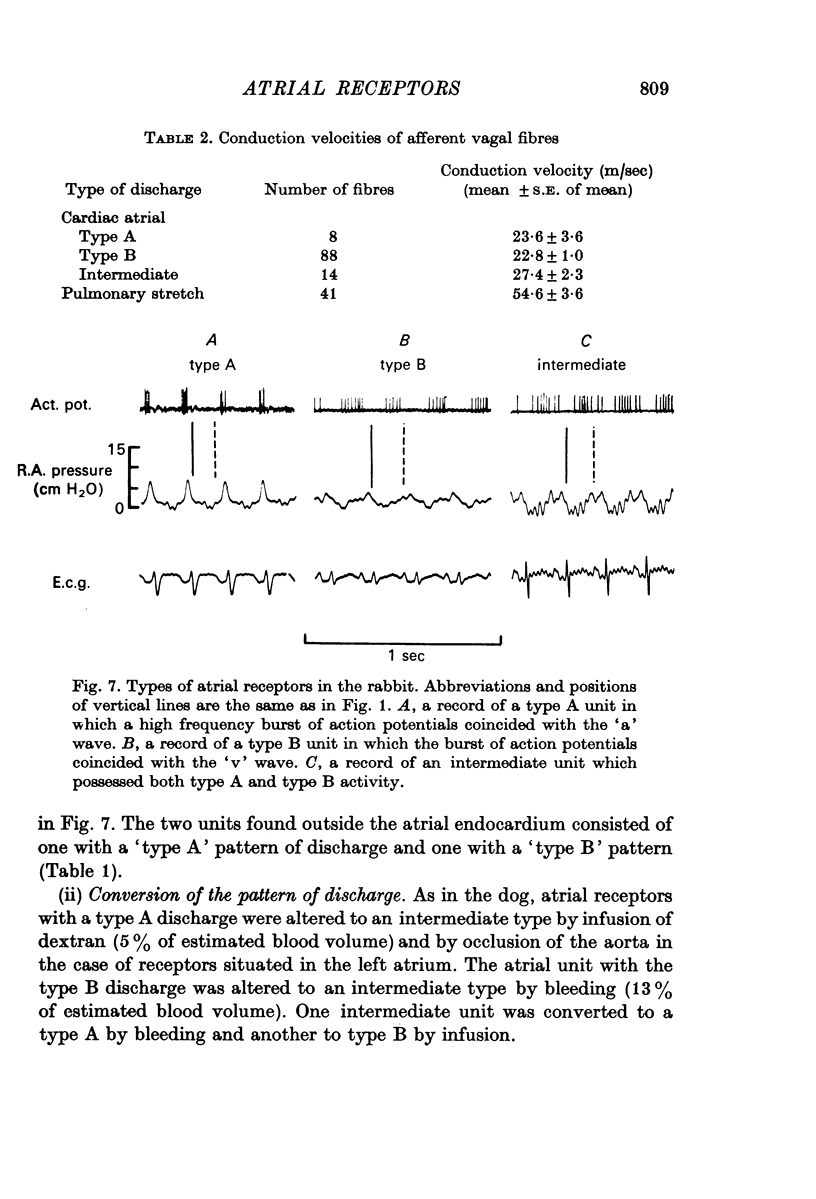
4. In the corresponding unselected study in the rabbit, eleven units were studied in eleven animals. Nine of these units were located in the atrial endocardium and the ratio of the type A, type B and intermediate type receptors was 2:1:6. Conversion was achieved in both type A units, the sole type B unit and two of the intermediate units. One of the two units found outside the atrial endocardium was a `type A' unit and could not be converted.
5. The present investigation has shown that the atrial receptors with a Paintal Type A pattern of discharge are relatively rare in both dogs and rabbits. Conversion of the pattern of discharge is a relatively common phenomenon. Evidence for the proposition that there is one basic type of atrial receptor whose pattern of discharge is determined by its precise location in the vein-atrial system is discussed.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COLERIDGE H. M., COLERIDGE J. C., KIDD C. CARDIAC RECEPTORS IN THE DOG, WITH PARTICULAR REFERENCE TO TWO TYPES OF AFFERENT ENDING IN THE VENTRICULAR WALL. J Physiol. 1964 Nov;174:323–339. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLERIDGE J. C., HEMINGWAY A., HOLMES R. L., LINDEN R. J. The location of atrial receptors in the dog: a physiological and histological study. J Physiol. 1957 Apr 3;136(1):174–197. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta B. N. The location and distribution of type A and type B atrial endings in cats. Pflugers Arch. 1977 Jan 17;367(3):271–275. doi: 10.1007/BF00581365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappagoda C. T., Linden R. J., Mary D. A. Atrial receptors in the cat. J Physiol. 1976 Nov;262(2):431–446. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappagoda C. T., Linden R. J., Snow H. M. The effect of stretching the superior vena caval-right atrial junction on right atrial receptors in the dog. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(3):875–887. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER M. R., KASAHARA M. STUDIES ON THE NERVE ENDINGS IN THE HEART. Am J Anat. 1964 Sep;115:217–233. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001150203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAINTAL A. S. The conduction velocities of respiratory and cardiovascular afferent fibres in the vagus nerve. J Physiol. 1953 Aug;121(2):341–359. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAINTAL A. S. VAGAL AFFERENT FIBRES. Ergeb Physiol. 1963;52:74–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paintal A. S. Vagal sensory receptors and their reflex effects. Physiol Rev. 1973 Jan;53(1):159–227. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1973.53.1.159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao P. S., Fahim M., Gupta B. N. Relative distribution of types A and B atrial receptors in dogs, cats, monkeys and rabbits. Experientia. 1975 Oct 15;31(10):1174–1175. doi: 10.1007/BF02326777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recordati G., Lombardi F., Bishop V. S., Malliani A. Mechanical stimuli exciting type A atrial vagal receptors in the cat. Circ Res. 1976 May;38(5):397–403. doi: 10.1161/01.res.38.5.397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recordati G., Lombardi F., Bishop V. S., Malliani A. Response of type B atrial vagal receptors to changes in wall tension during atrial filling. Circ Res. 1975 Jun;36(6):682–691. doi: 10.1161/01.res.36.6.682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


