Abstract
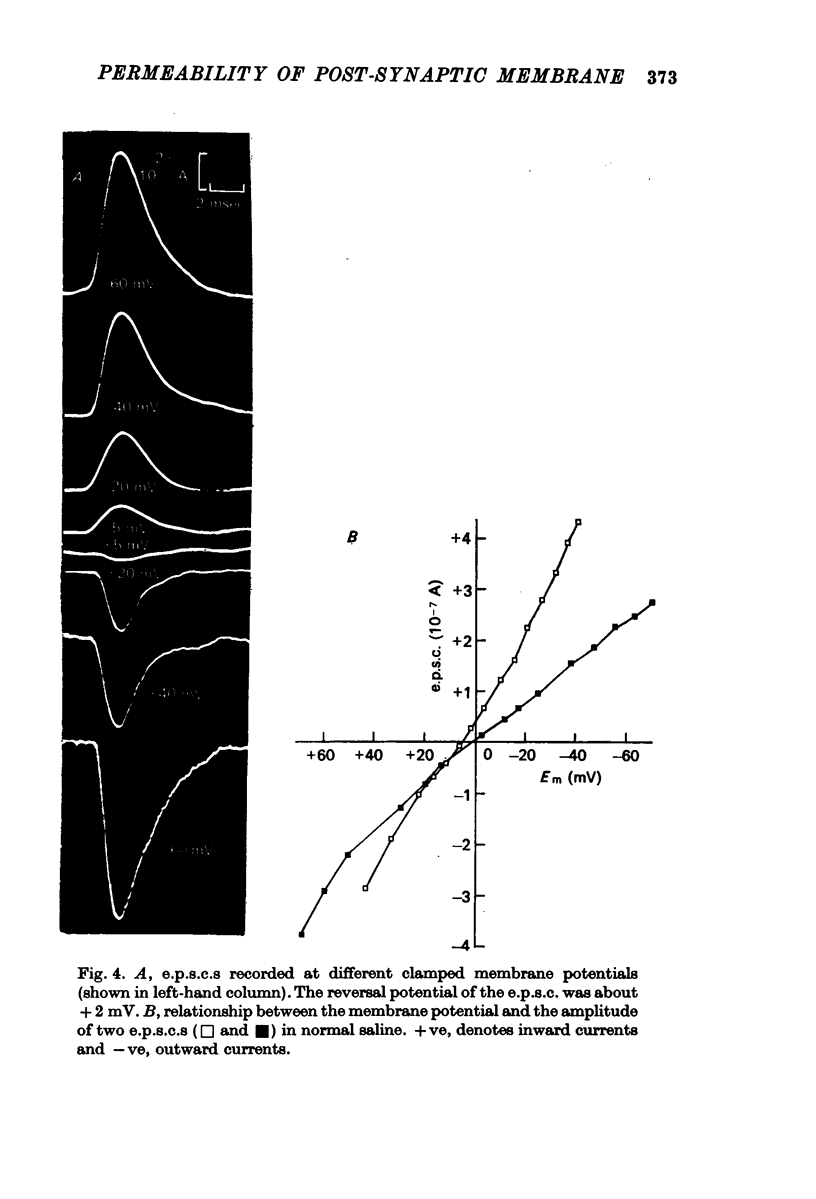
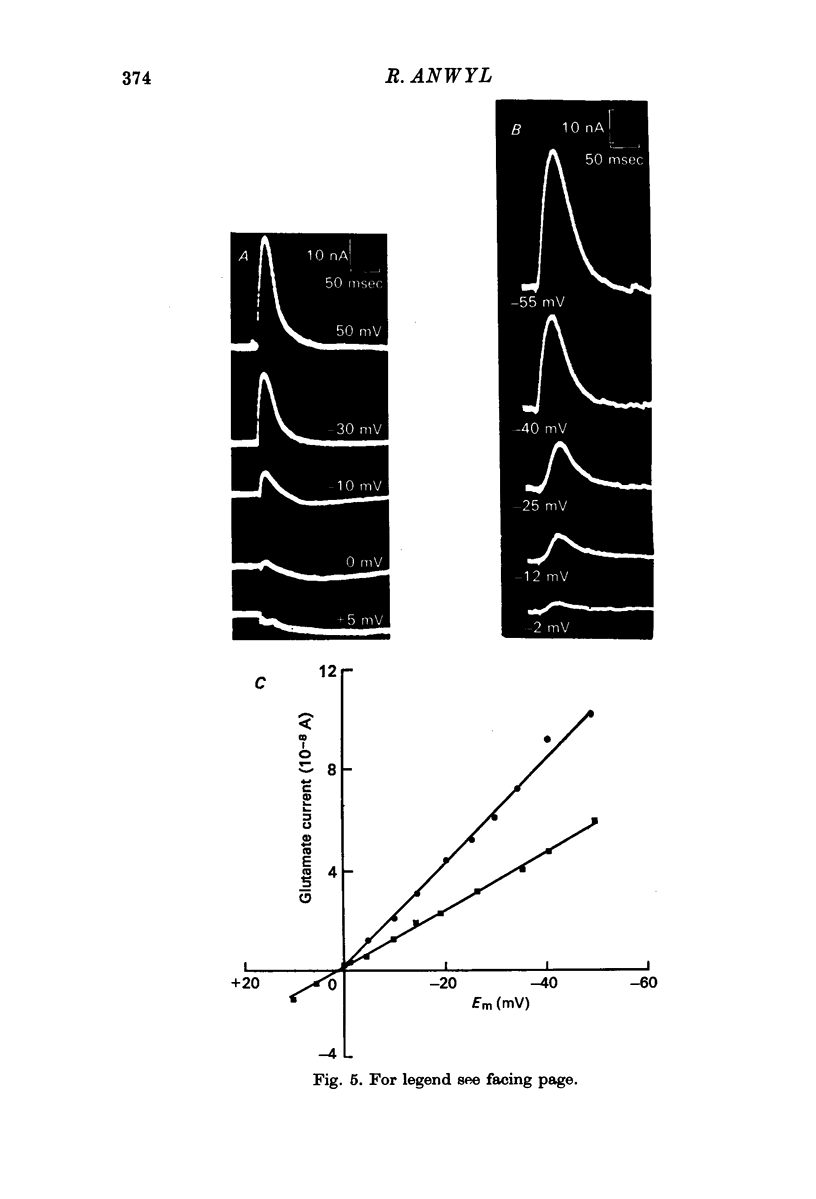
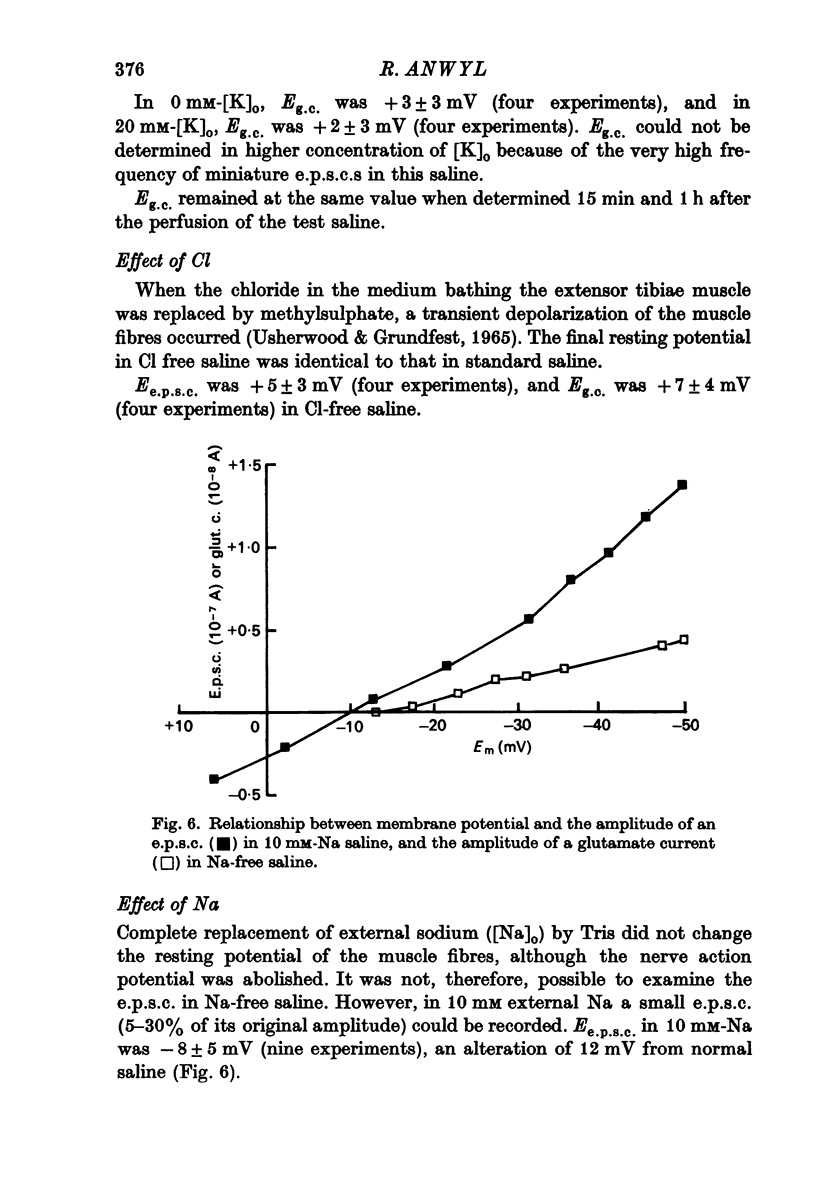
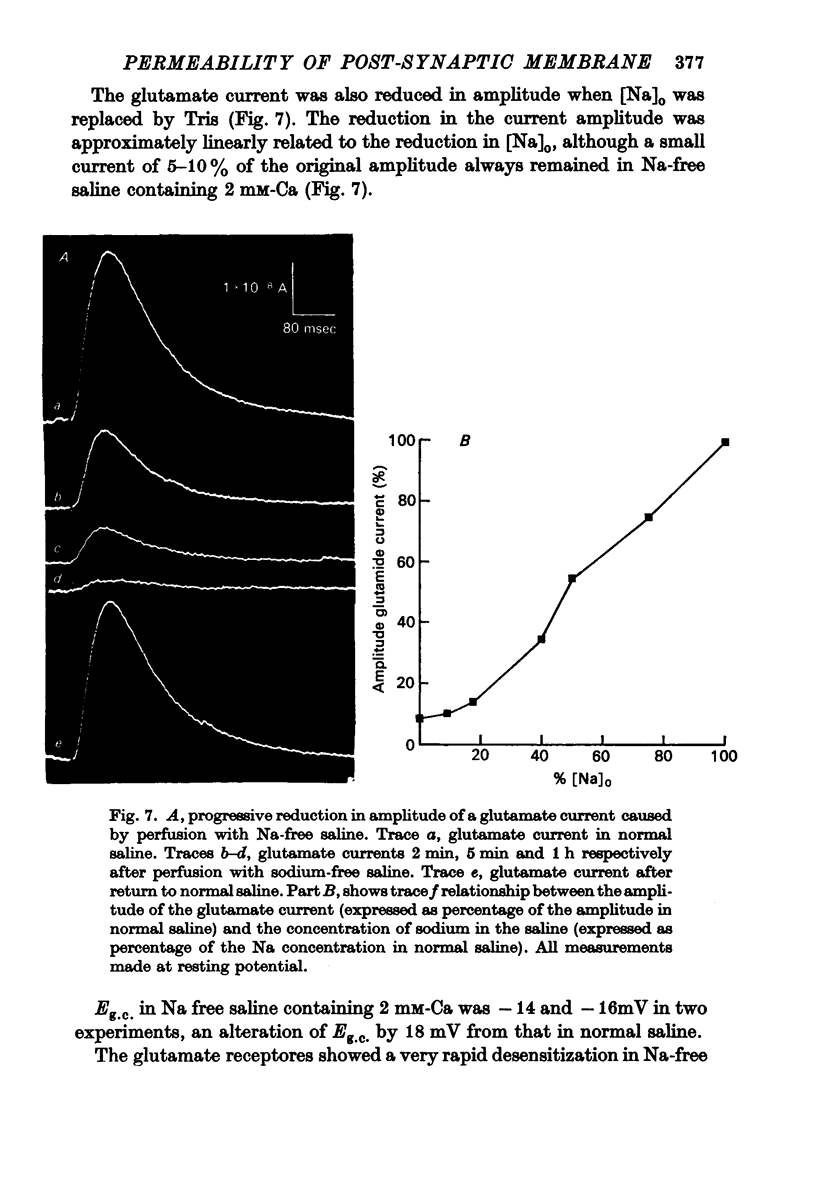
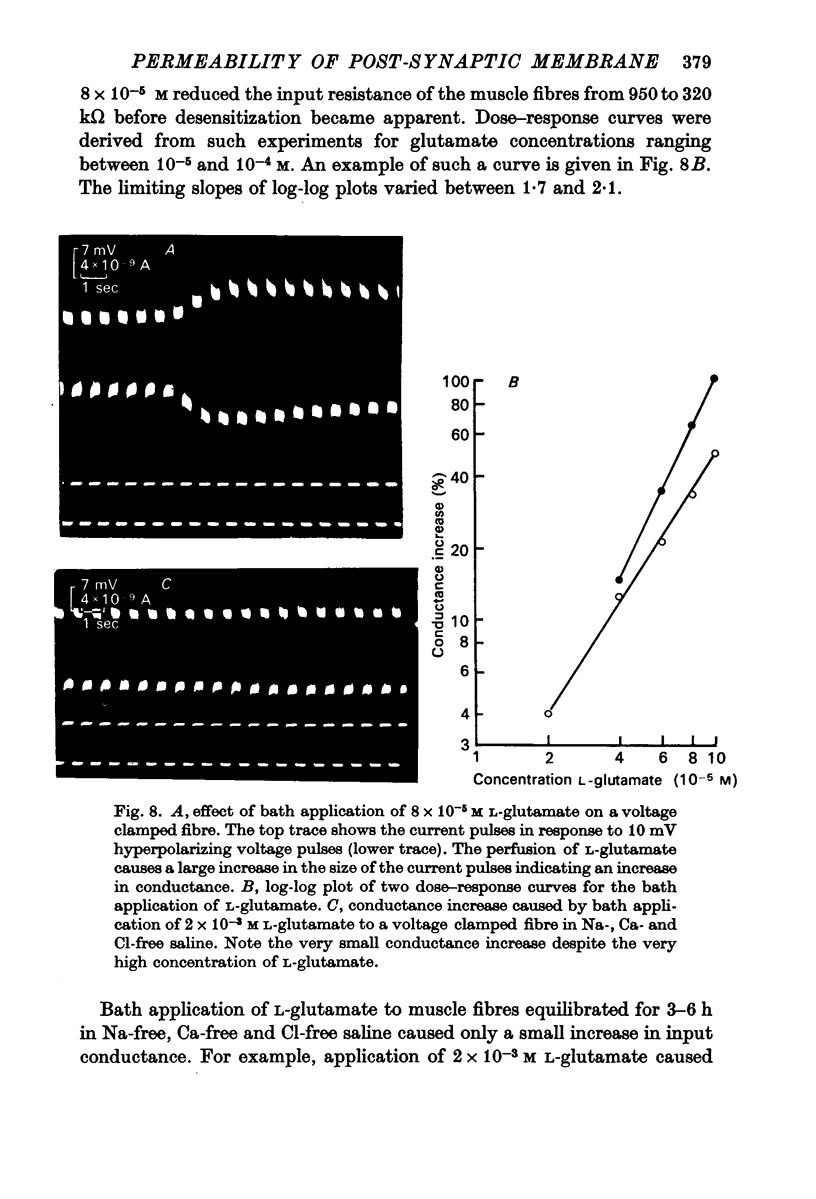
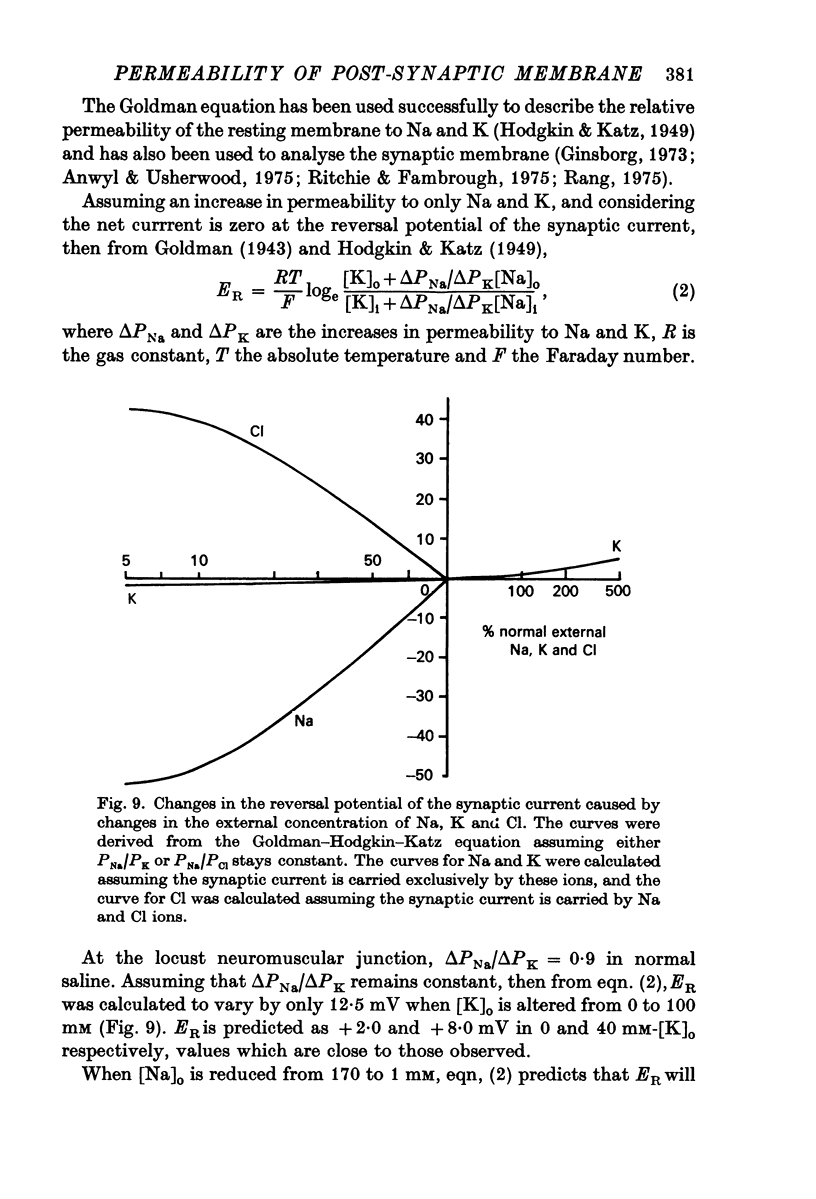
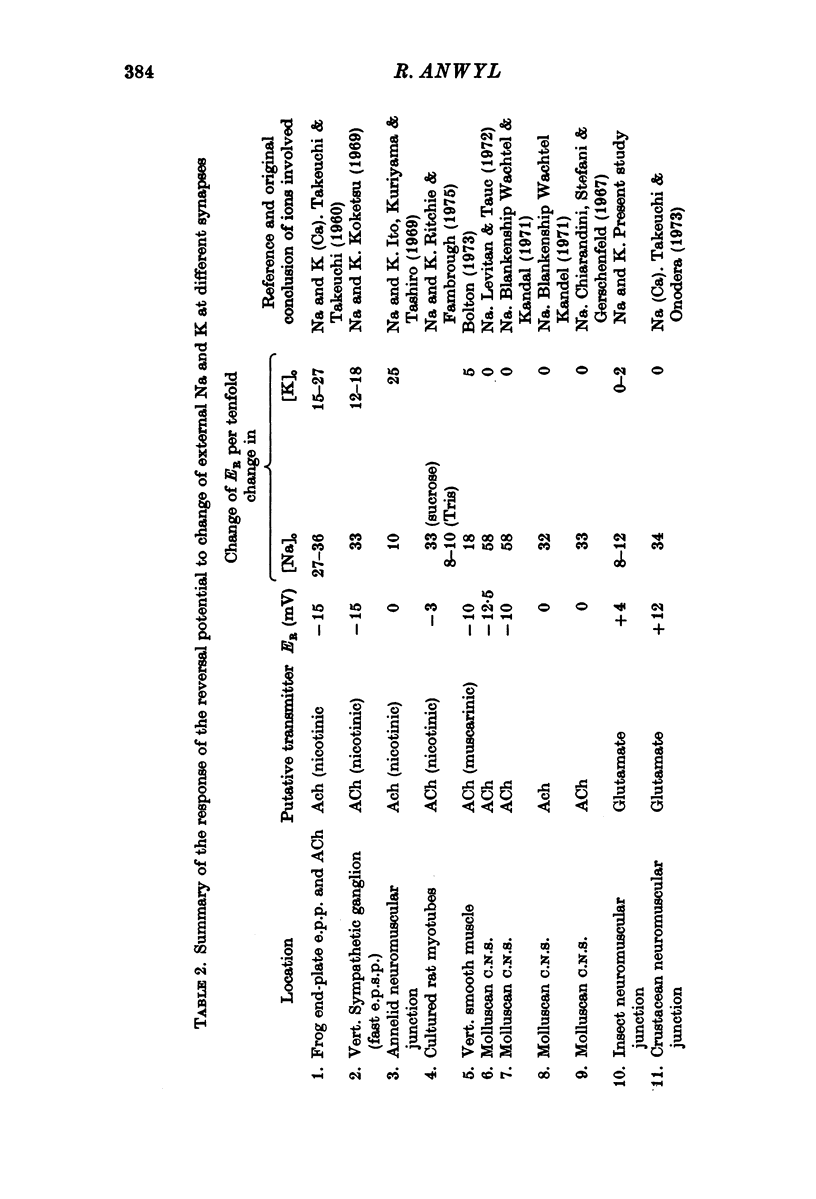
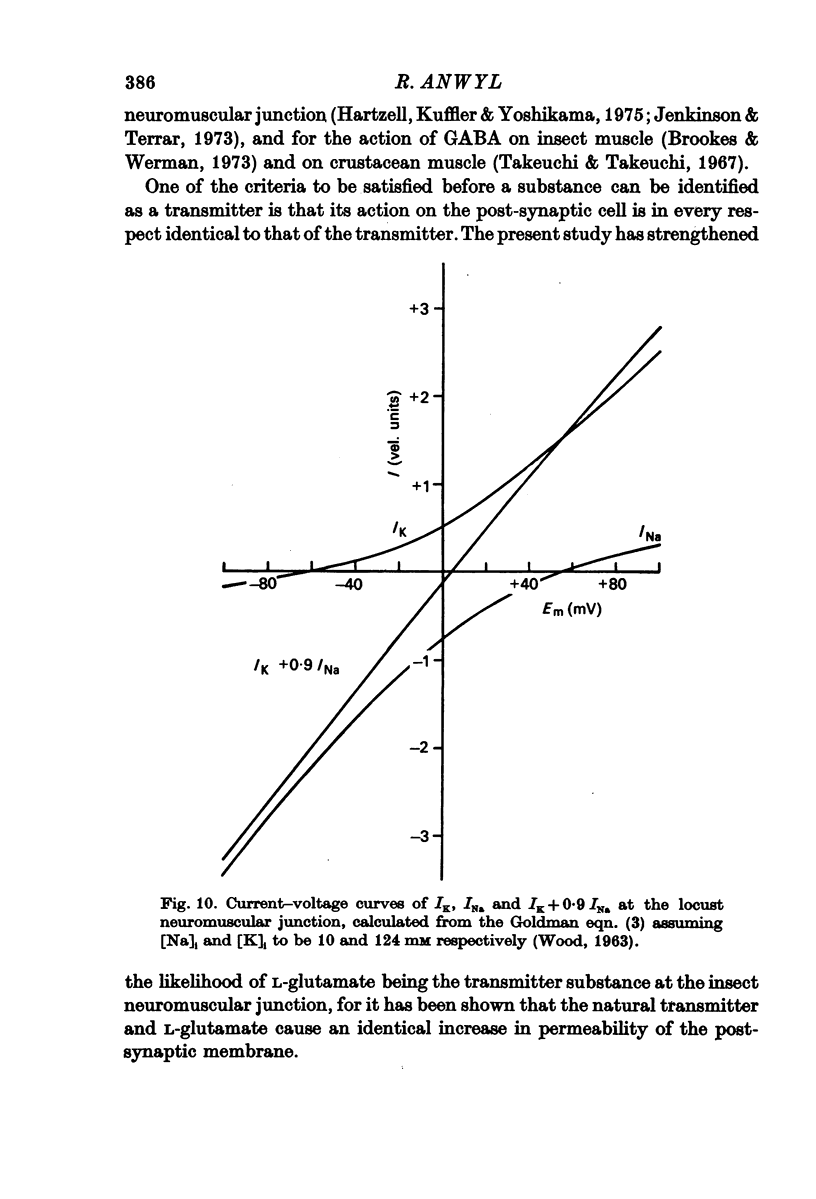
1. The changes in permeability of the post-synaptic membrane at the insect skeletal neuromuscular junction caused by the excitatory transmitter and L-glutamate have been studied using the voltage clamp technique. 2. The reversal potential (ER) of the excitatory post-synaptic current and the glutamate current was +3 and +4 mV respectively. 3. ER of the synaptic current did not change when external K was altered between 0 and 20 mM, but did show a small positive shift in 40 mM external K. Reducing external Na to 1-10 mM changes ER by 12-18 mV. Reducing external Cl to to zero caused no change in ER. 4. It is proposed that the transmitter and L-glutamate cause an increase in permeability to Na and K, but not to Cl. 5. In normal saline, the ratio of the permeability increase to Na and K (delta PNa/delta PK) is 0.9. 6. The changes in ER caused by altering external K were similar to those predicted by the Goldman-Hodgkin-Katz equation, assuming delta PNa/delta PK stays constant. 7. The changes in ER caused by alterations of external Na are much less than those predicted by the Goldman equation. 8. No glutamate current could be recorded in Na- and Ca-free saline either at the resting potential or at depolarized or hyperpolarized membrane potentials. 9. It is proposed that the outward K current is dependent upon the inward Na current, and that the increase in K permeability is abolished in zero external Na.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anwyl R., Usherwood P. N. Voltage clamp studies of glutamate synapse. Nature. 1974 Dec 13;252(5484):591–593. doi: 10.1038/252591a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOISTEL J., FATT P. Membrane permeability change during inhibitory transmitter action in crustacean muscle. J Physiol. 1958 Nov 10;144(1):176–191. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blankenship J. E., Wachtel H., Kandel E. R. Ionic mechanisms of excitatory, inhibitory, and dual synaptic actions mediated by an identified interneuron in abdominal ganglion of Aplysia. J Neurophysiol. 1971 Jan;34(1):76–92. doi: 10.1152/jn.1971.34.1.76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brookes N. Werman R:The cooperativity of -aminobutyric action on the membrane of locust muscle fibers. Mol Pharmacol. 1973 Jul;9(4):571–579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clusin W. T., Bennett M. V. Calcium-activated conductance in skate electroreceptors: voltage clamp experiments. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Feb;69(2):145–182. doi: 10.1085/jgp.69.2.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G., Usherwood P. N. Two populations of L-glutamate receptors on locust muscle fibres. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):62–64. doi: 10.1038/newbio246062a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FURSHPAN E. J., POTTER D. D. Transmission at the giant motor synapses of the crayfish. J Physiol. 1959 Mar 3;145(2):289–325. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerschenfeld H. M. Chemical transmission in invertebrate central nervous systems and neuromuscular junctions. Physiol Rev. 1973 Jan;53(1):1–119. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1973.53.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsborg B. L. Electrical changes in the membrane in junctional transmission. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Nov 28;300(3):289–317. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(73)90007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsborg B. L., Kado R. T. Voltage-current relationship of a carbachol-induced potassium-ion pathway in Aplysia neurones. J Physiol. 1975 Mar;245(3):713–725. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KATZ B. The effect of sodium ions on the electrical activity of giant axon of the squid. J Physiol. 1949 Mar 1;108(1):37–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell H. C., Kuffler S. W., Yoshikami D. Post-synaptic potentiation: interaction between quanta of acetylcholine at the skeletal neuromuscular synapse. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;251(2):427–463. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyer C. B., Lux H. D. Control of the delayed outward potassium currents in bursting pace-maker neurones of the snail, Helix pomatia. J Physiol. 1976 Nov;262(2):349–382. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Kuriyama H., Tashiro N. Miniature excitatory junction potentials in the somatic muscle of the earthworm, Pheretima communissima, in sodium free solution. J Exp Biol. 1969 Aug;51(1):107–118. doi: 10.1242/jeb.51.1.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKINSON D. H., NICHOLLS J. G. Contractures and permeability changes produced by acetylcholine in depolarized denervated muscle. J Physiol. 1961 Nov;159:111–127. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkinson D. H., Terrar D. A. Influence of chloride ions on changes in membrane potential during prolonged application of carbachol to frog skeletal muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Feb;47(2):363–376. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb08334.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehoe J. Ionic mechanisms of a two-component cholinergic inhibition in Aplysia neurones. J Physiol. 1972 Aug;225(1):85–114. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitan H., Tauc L. Acetylcholine receptors: topographic distribution and pharmacological properties of two receptor types on a single molluscan neurone. J Physiol. 1972 May;222(3):537–558. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onodera K., Takeuchi A. Ionic mechanism of the excitatory synaptic membrane of the crayfish neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;252(1):295–318. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rang H. P. Acetylcholine receptors. Q Rev Biophys. 1974 Jul;7(3):283–399. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500001463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie A. K., Fambrough D. M. Ionic properties of the acetylcholine receptor in cultured rat myotubes. J Gen Physiol. 1975 Jun;65(6):751–767. doi: 10.1085/jgp.65.6.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandblom J. P., Eisenman G. Membrane potentials at zero current. The significance of a constant ionic permeability ratio. Biophys J. 1967 May;7(3):217–242. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(67)86585-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEUCHI A., TAKEUCHI N. THE EFFECT ON CRAYFISH MUSCLE OF IONTOPHORETICALLY APPLIED GLUTAMATE. J Physiol. 1964 Mar;170:296–317. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEUCHI N. Effects of calcium on the conductance change of the end-plate membrane during the action of transmitter. J Physiol. 1963 Jun;167:141–155. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRAUTWEIN W., DUDEL J. Zum Mechanismus der Membranwirkung des Acetylcholin an der Herzmuskelfaser. Pflugers Arch. 1958;266(3):324–334. doi: 10.1007/BF00416781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi A., Onodera K. Reversal potentials of the excitatory transmitter and L-glutamate at the crayfish neuromuscular junction. Nat New Biol. 1973 Mar 28;242(117):124–126. doi: 10.1038/newbio242124a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- USHERWOOD P. N., GRUNDFEST H. PERIPHERAL INHIBITION IN SKELETAL MUSCLE OF INSECTS. J Neurophysiol. 1965 May;28:497–518. doi: 10.1152/jn.1965.28.3.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


