Abstract
1. Unitary activities of muscular thin fibre afferents, which were not sensitive to muscle stretching, were recorded from the nerve of the medial gastrocnemius muscle of the dog. Responses to mechanical stimulation, intra-arterial injection and local application of chemical solutions, and thermal stimulation of the surface of the muscle were studied. It was observed that polymodal receptors which responded to all types of stimulation existed in the thin fibre afferents of the muscle.
2. The receptive area of these units tested by mechanical stimulation was spot-like and appeared to be located not only on the surface but in the midst of the muscle.
3. The mechanical response varied among these units with respect to the threshold and the pattern of discharges.
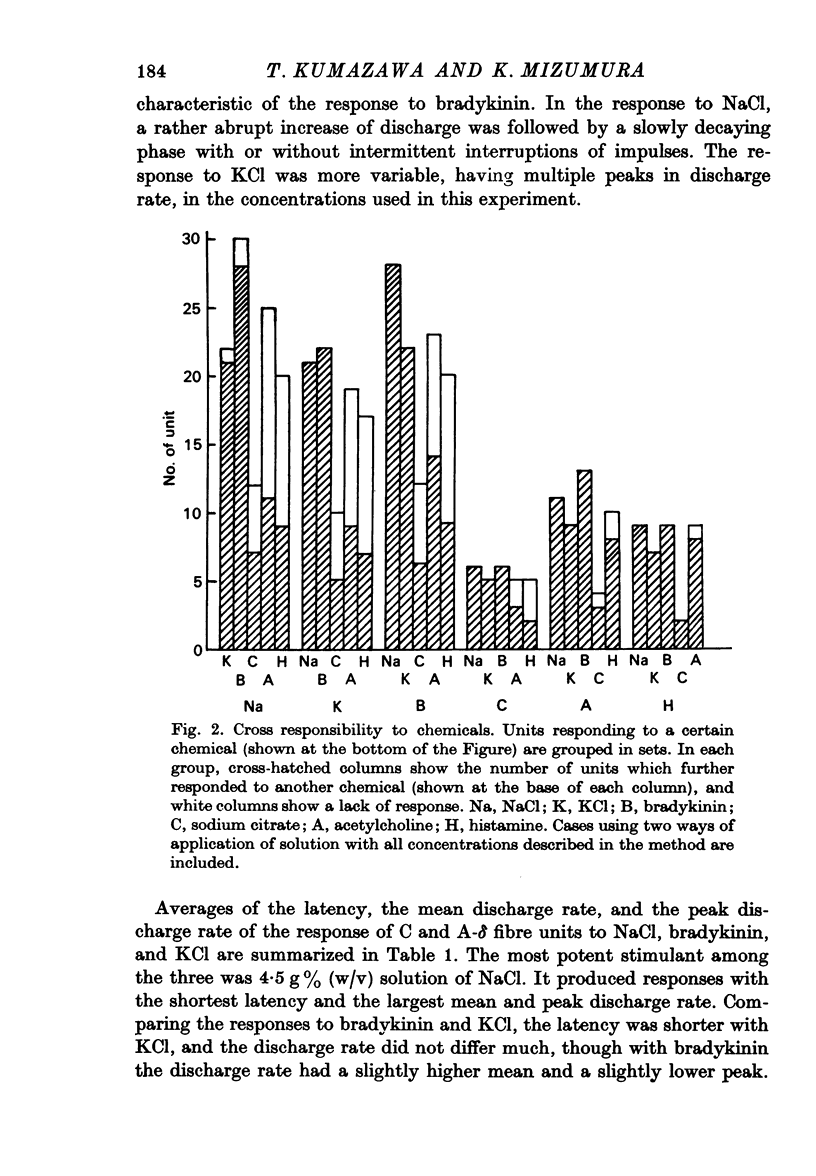
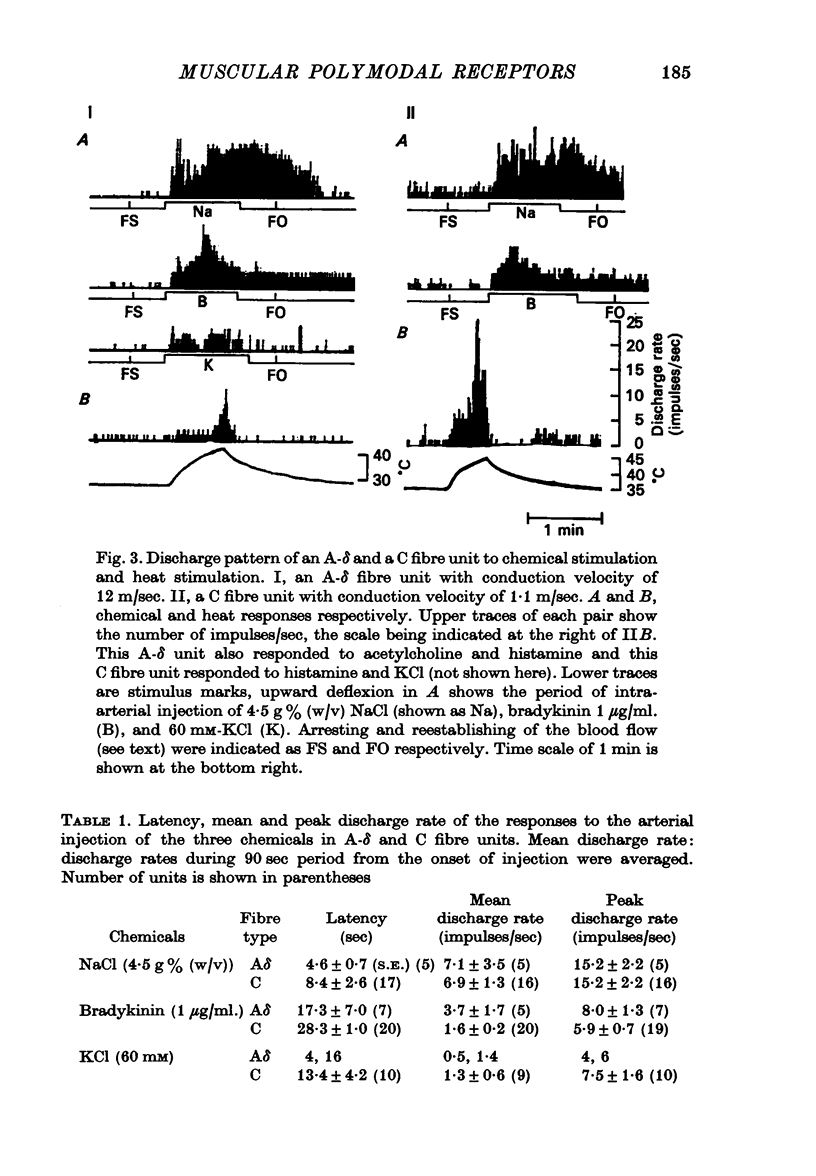
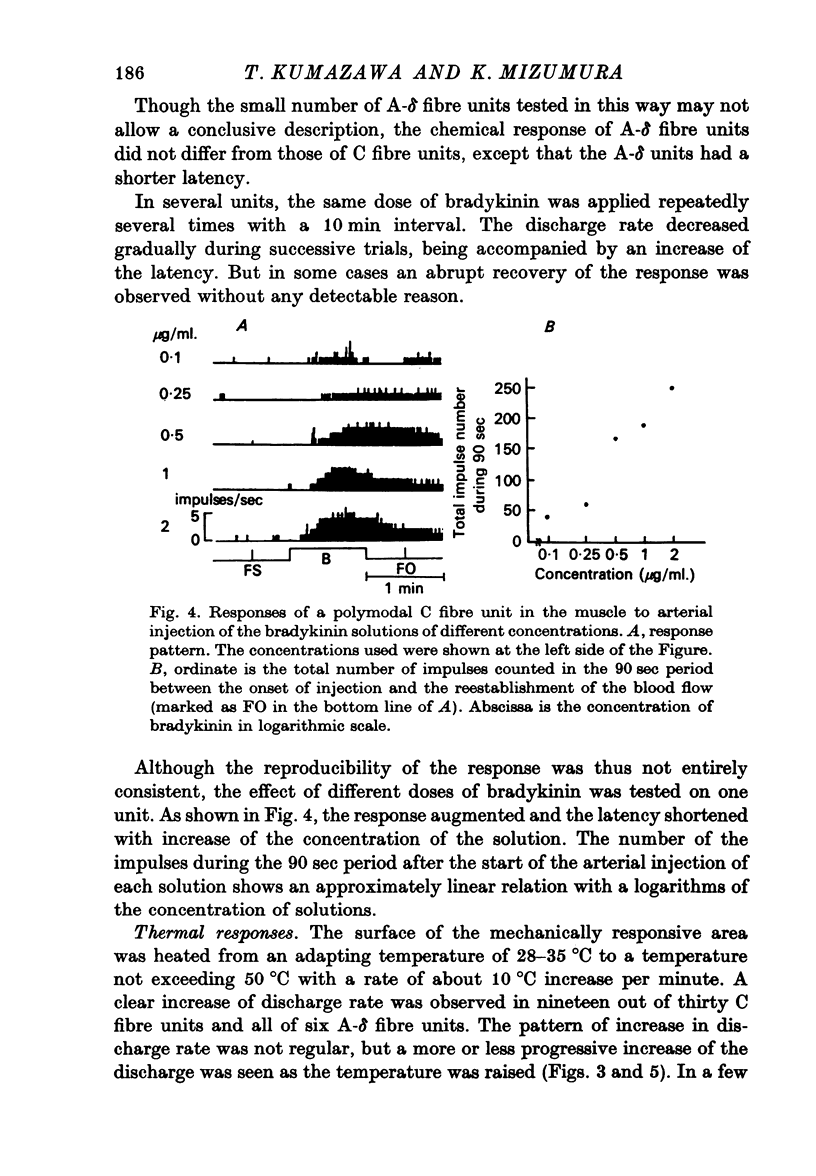
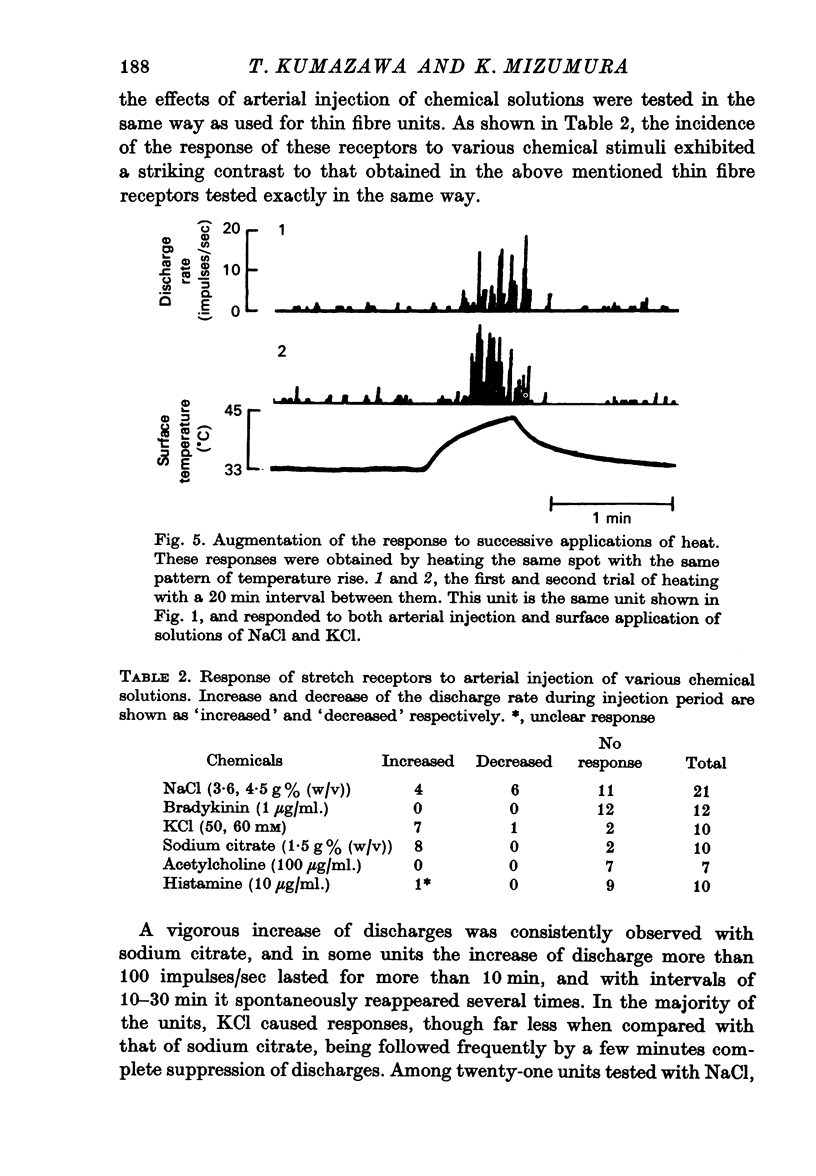
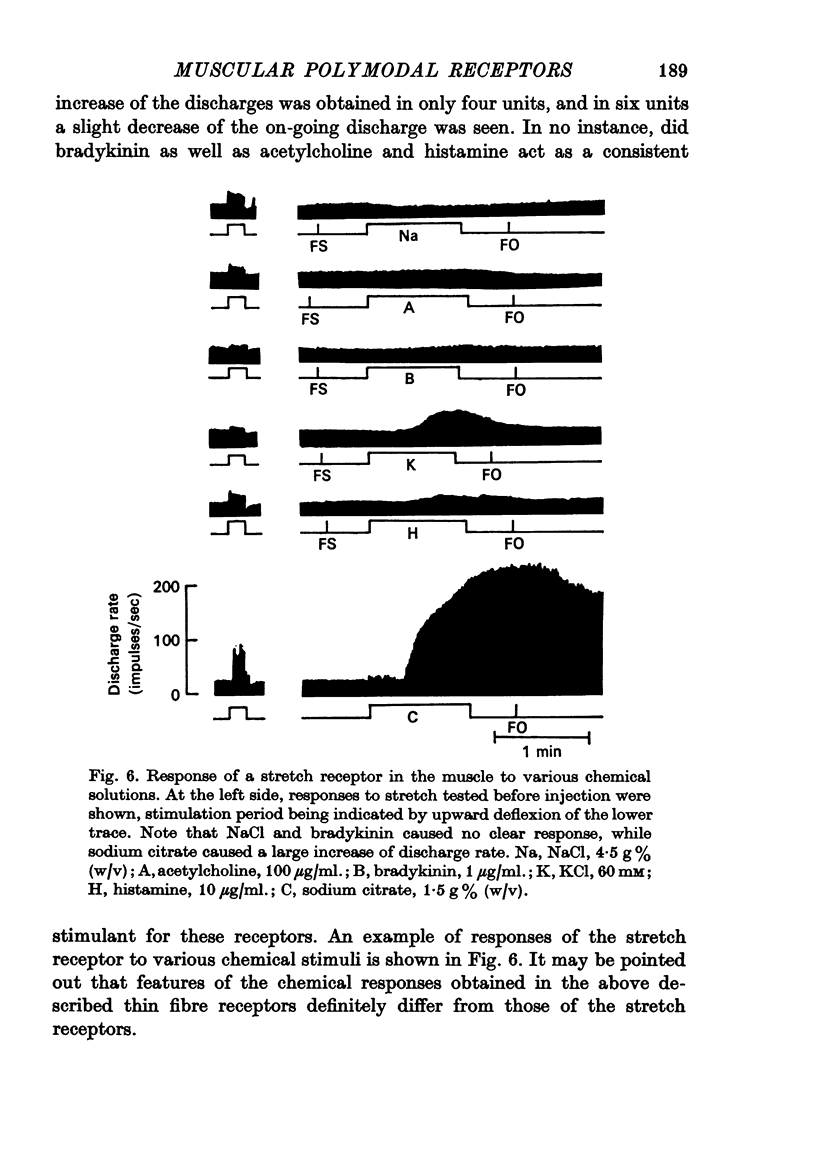
4. In these units, NaCl, KCl, and bradykinin consistently evoked responses, with differences in the latencies and discharge patterns, while solutions of histamine, acetylcholine and sodium citrate caused responses less consistently and less effectively. In the stretch receptors, chemical stimulation applied in the same way as tested in the thin fibre afferents produced quite different features in their responses.
5. Heating the receptive area of the muscle surface caused responses in twenty-five out of thirty-six units, which were sensitive both to mechanical and to chemical stimulations. The threshold varied from 38·0 to 48·3 °C, with a mean of 43·1 °C for C fibre units and 41 °C for A-δ fibre units.
6. The responses to heating were consistently obtained in the units responding to the surface application of chemical solutions. However, the above response was never obtained in the units which did not respond to surface chemical stimulation but responded to intra-arterial injection. These results suggest a large population of polymodal receptors in the muscular thin fibre afferents.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beck P. W., Handwerker H. O. Bradykinin and serotonin effects on various types of cutaneous nerve fibers. Pflugers Arch. 1974 Mar 11;347(3):209–222. doi: 10.1007/BF00592598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck P. W., Handwerker H. O., Zimmermann M. Nervous outflow from the cat's foot during noxious radiant heat stimulation. Brain Res. 1974 Mar 8;67(3):373–386. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90488-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beitel R. E., Dubner R. Response of unmyelinated (C) polymodal nociceptors to thermal stimuli applied to monkey's face. J Neurophysiol. 1976 Nov;39(6):1160–1175. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.6.1160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessou P., Perl E. R. Response of cutaneous sensory units with unmyelinated fibers to noxious stimuli. J Neurophysiol. 1969 Nov;32(6):1025–1043. doi: 10.1152/jn.1969.32.6.1025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croze S., Duclaux R., Kenshalo D. R. The thermal sensitivity of the polymodal nociceptors in the monkey. J Physiol. 1976 Dec;263(3):539–562. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fock S., Mense S. Excitatory effects of 5-hydroxytryptamine, histamine and potassium ions on muscular group IV afferent units: a comparison with bradykinin. Brain Res. 1976 Apr 9;105(3):459–469. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90593-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franz M., Mense S. Muscle receptors with group IV afferent fibres responding to application of bradykinin. Brain Res. 1975 Jul 18;92(3):369–383. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90323-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertel H. C., Howaldt B., Mense S. Responses of group IV and group III muscle afferents to thermal stimuli. Brain Res. 1976 Aug 20;113(1):201–205. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90020-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiss E., Mense S. Evidence for the existence of different receptor sites for algesic agents at the endings of muscular group IV afferent units. Pflugers Arch. 1976 Mar 30;362(2):141–146. doi: 10.1007/BF00583640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson H. J., Matthews P. B. The ineffectiveness of excitation of the primary endings of the muscle spindle by vibration as a respiratory stimulant in the decerebrate cat. J Physiol. 1968 Feb;194(2):555–563. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumazawa T., Mizumura K. The polymodal C-fiber receptor in the muscle of the dog. Brain Res. 1976 Jan 23;101(3):589–593. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90483-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynn B. Somatosensory receptors and their CNS connections. Annu Rev Physiol. 1975;37:105–127. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.37.030175.000541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCloskey D. I., Mitchell J. H. Reflex cardiovascular and respiratory responses originating in exercising muscle. J Physiol. 1972 Jul;224(1):173–186. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mense S., Schmidt R. F. Activation of group IV afferent units from muscle by algesic agents. Brain Res. 1974 Jun 7;72(2):305–310. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90870-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizumura K., Kumazawa T. Reflex respiratory response induced py chemical stimulation of muscle afferents. Brain Res. 1976 Jun 11;109(2):402–406. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90543-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAINTAL A. S. Functional analysis of group III afferent fibres of mammalian muscles. J Physiol. 1960 Jul;152:250–270. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perl E. R., Kumazawa T., Lynn B., Kenins P. Sensitization of high threshold receptors with unmyelinated (C) afferent fibers. Prog Brain Res. 1976;43:263–277. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)64359-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senapati J. M. Effect of stimulation of muscle afferents on ventilation of dogs. J Appl Physiol. 1966 Jan;21(1):242–246. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1966.21.1.242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacey M. J. Free nerve endings in skeletal muscle of the cat. J Anat. 1969 Sep;105(Pt 2):231–254. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taira N., Nakayama K., Hashimoto K. Vocalization response of puppies to intra-arterial administration of bradykinin and other algesic agents, and mode of actions of blocking agents. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1968 Dec;96(4):365–377. doi: 10.1620/tjem.96.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torebjörk H. E., Hallin R. G. Identification of afferent C units in intact human skin nerves. Brain Res. 1974 Mar 8;67(3):387–403. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90489-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Hees J., Gybels J. M. Pain related to single afferent C fibers from human skin. Brain Res. 1972 Dec 24;48:397–400. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90198-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WITT I., GRIFFIN J. P. Afferent cutaneous C-fibre reactivity to repeated thermal stimuli. Nature. 1962 May 26;194:776–777. doi: 10.1038/194776a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



