Abstract
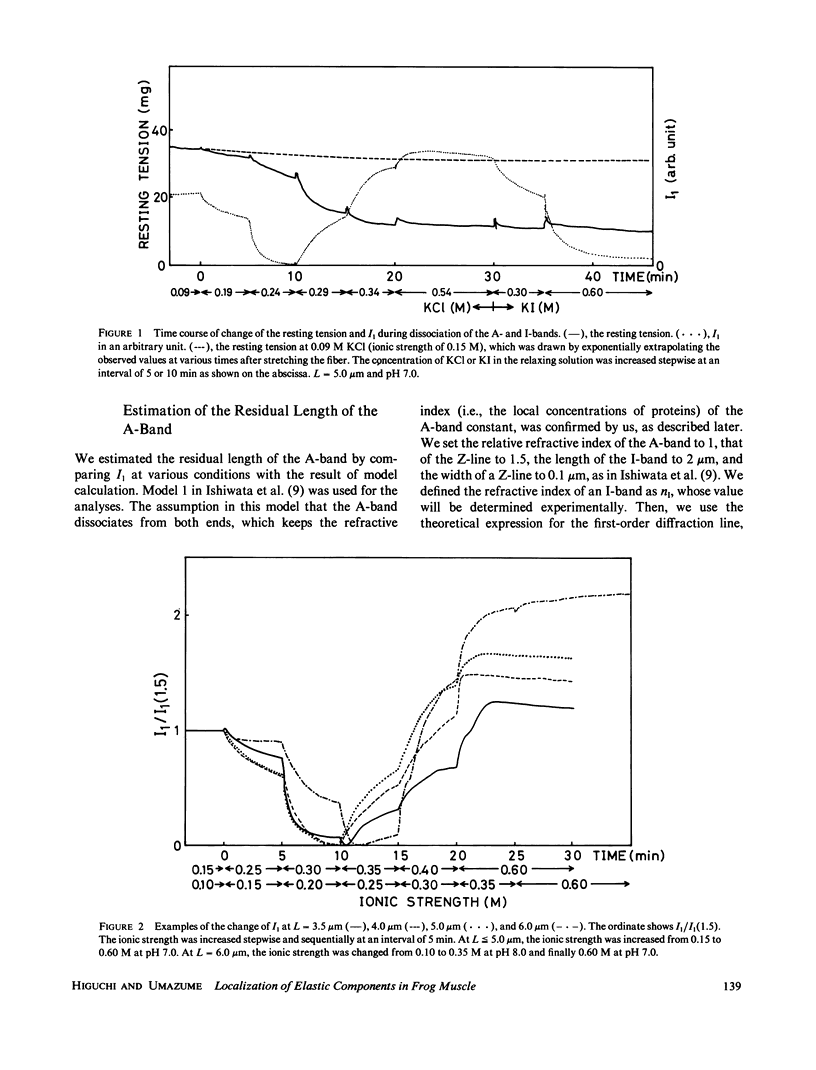
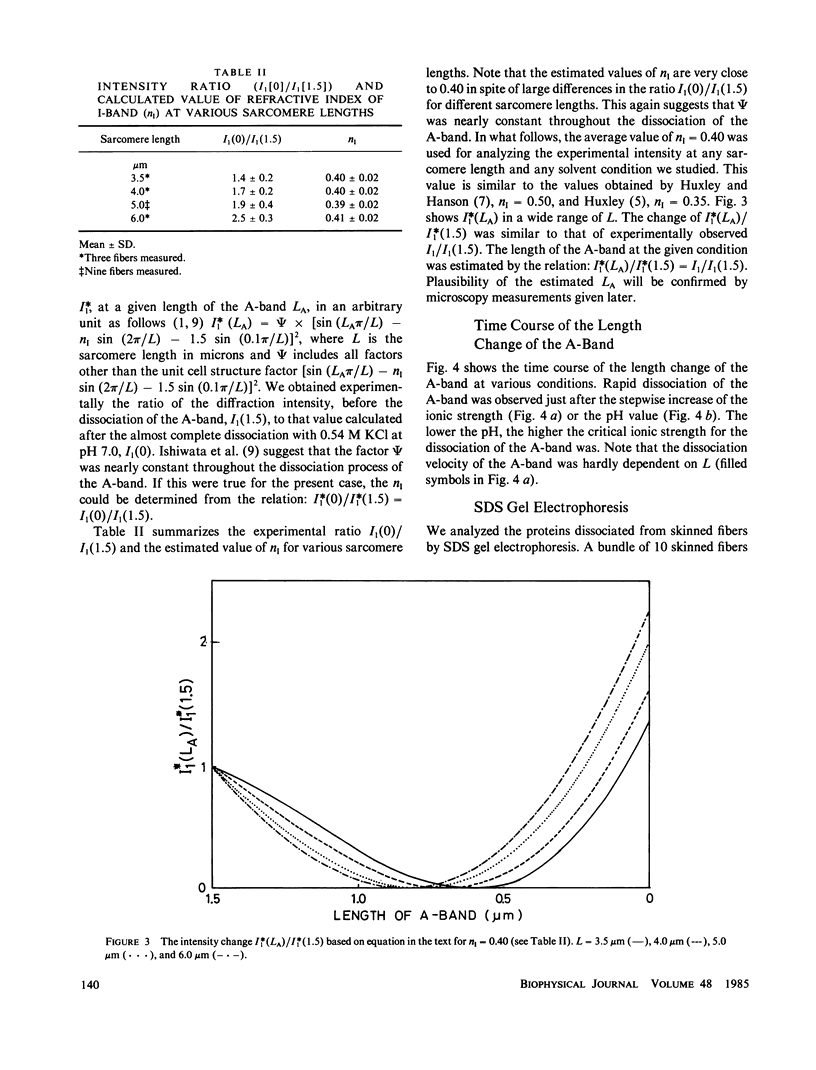
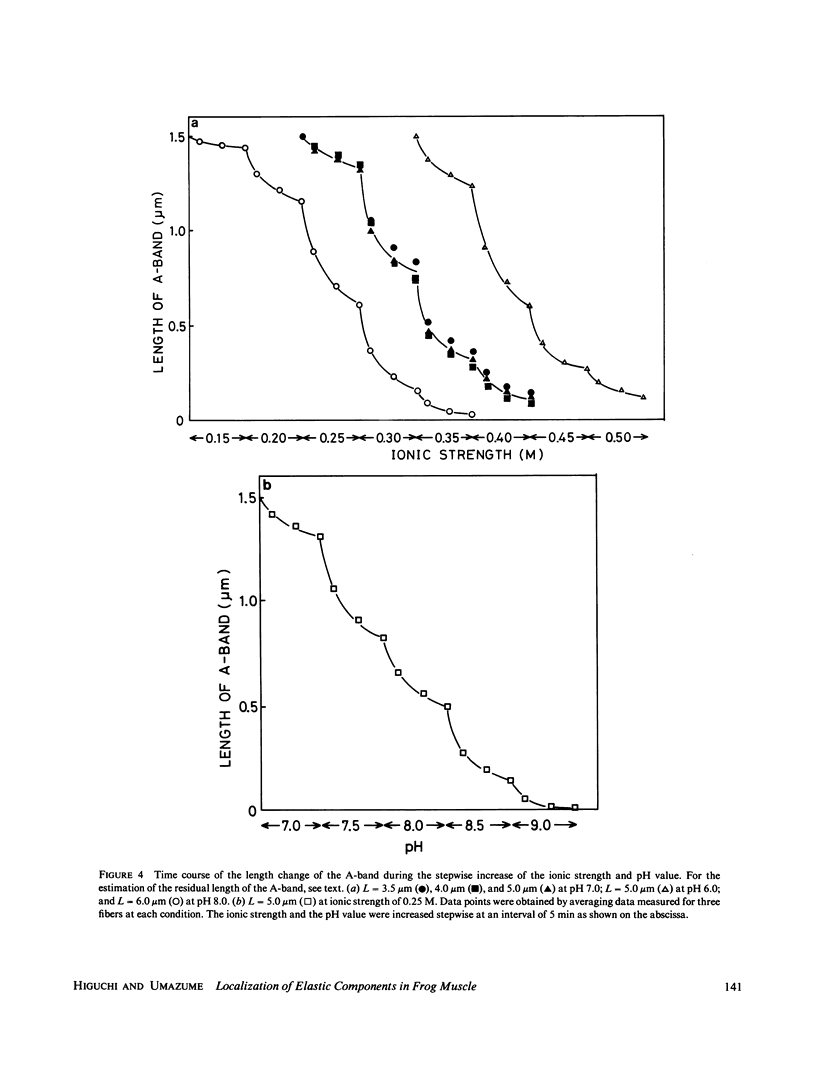
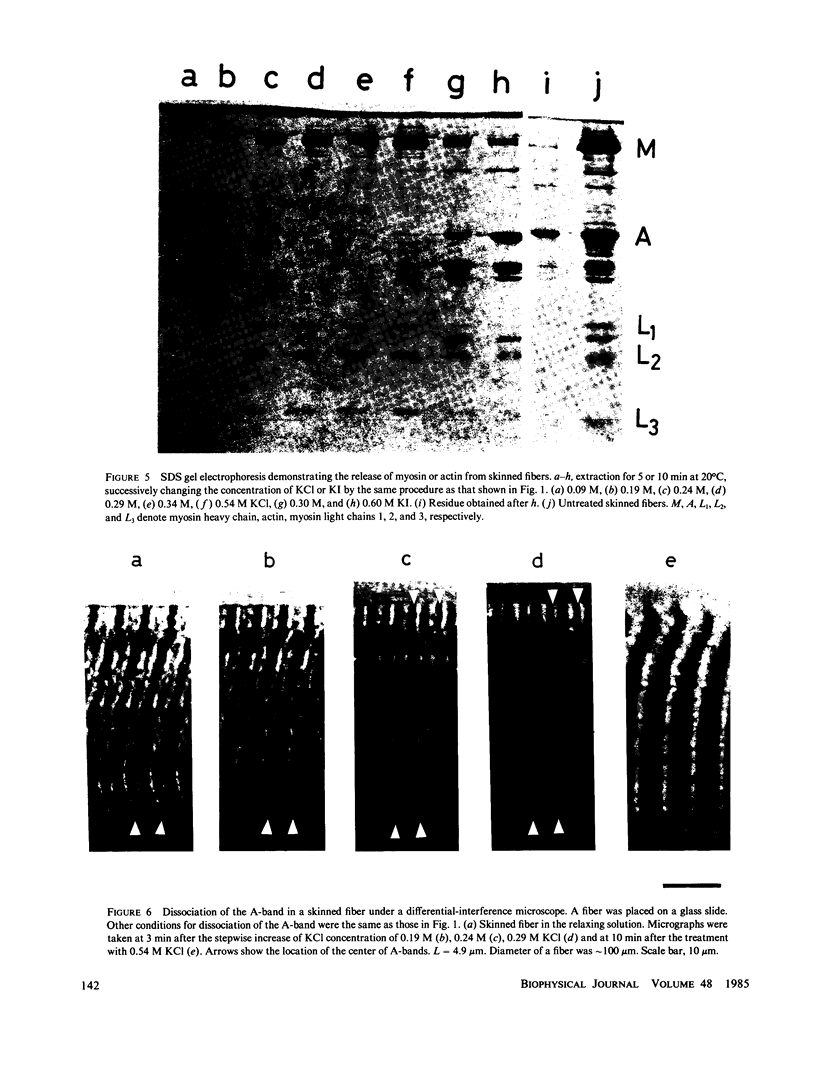
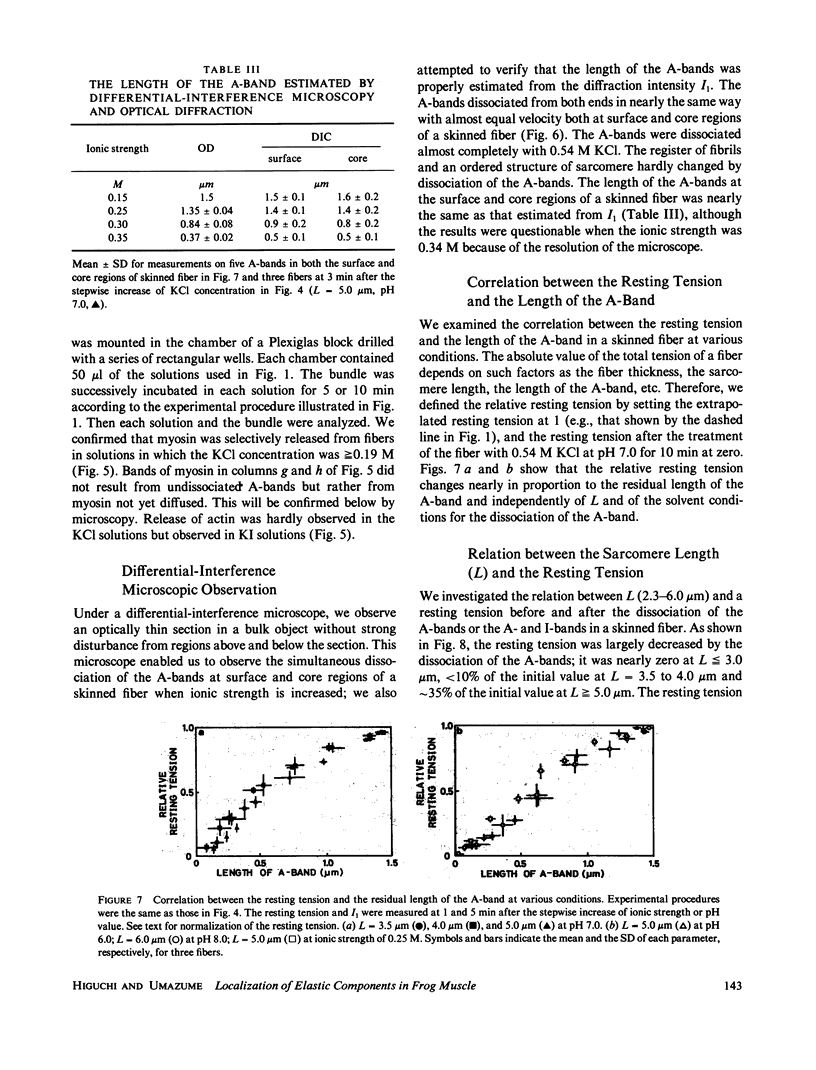
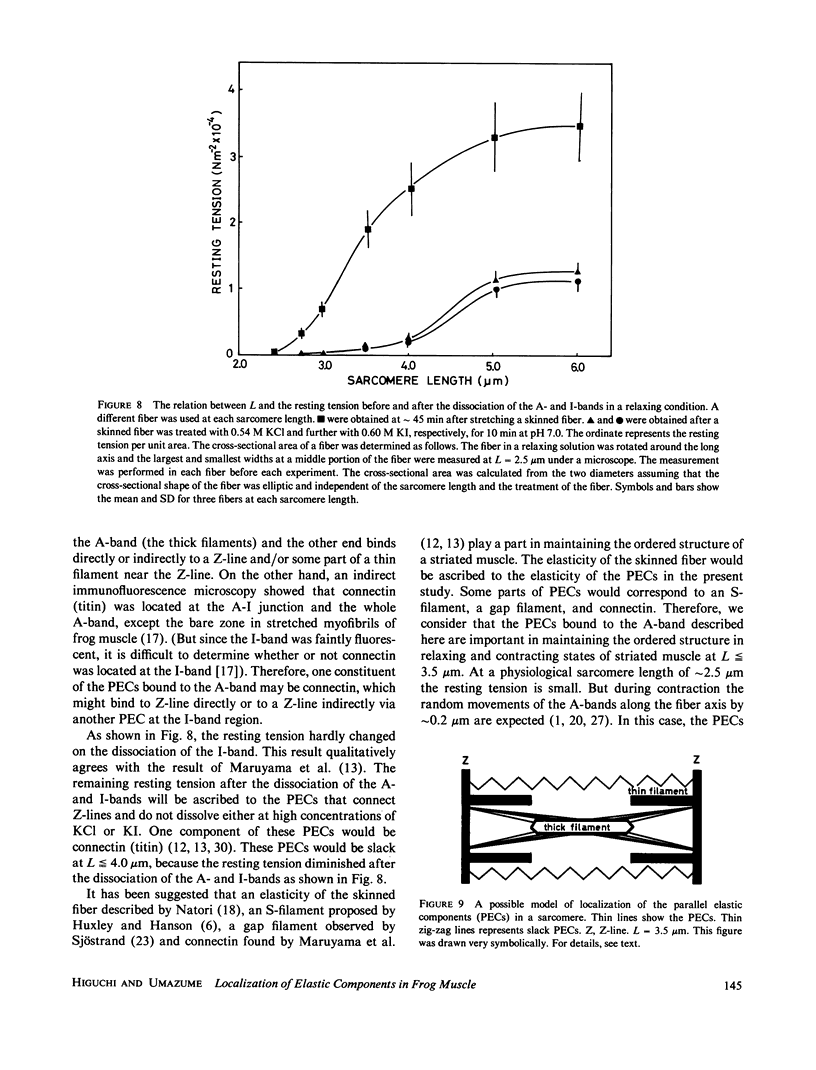
Localization of the parallel elastic components (PECs) in skinned muscle fibers was investigated by analyzing the change of the resting tension, which accompanies the dissociation of the A- and I-bands. The A-band was dissociated from both ends by increasing the concentration of KCl under relaxing conditions (0.09-0.54 M KCl, 4.0 mM MgATP, 1.0 mM Mg2+, 4.0 mM EGTA, pH 6.0-9.0, 20 degrees C). At sarcomere lengths greater than or equal to 3.5 microns, the length of the A-band was estimated by comparing the intensity of the first-order optical diffraction line with the results of model calculations. These results were supported by differential-interference microscopy and sodium dodecyl sulfate gel electrophoresis. It was shown that the resting tension decreased nearly in proportion to the residual length of the A-band. At sarcomere lengths less than or equal to 4.0 microns, the resting tension after the dissociation of the A-band was lowered to less than 10% of the initial value. On the other hand, at sarcomere lengths greater than or equal to 5.0 microns the resting tension after the dissociation of the A-band still showed approximately 35% of the initial value and did not change even after the I-band was dissociated by a solution containing KI. From these results, we propose that most of the PECs contributing to resting tension bind almost uniformly to the A-band and there are also PECs connecting Z-lines.
Full text
PDF




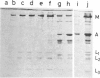
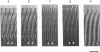
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fujime S. Optical diffraction study of muscle fibers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jan 30;379(1):227–238. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90026-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon A. M., Godt R. E., Donaldson S. K., Harris C. E. Tension in skinned frog muscle fibers in solutions of varying ionic strength and neutral salt composition. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Nov;62(5):550–574. doi: 10.1085/jgp.62.5.550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY A. F. Muscle structure and theories of contraction. Prog Biophys Biophys Chem. 1957;7:255–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY H. E., HANSON J. Quantitative studies on the structure of cross-striated myofibrils. I. Investigations by interference microscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Feb;23(2):229–249. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90325-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY H., HANSON J. Changes in the cross-striations of muscle during contraction and stretch and their structural interpretation. Nature. 1954 May 22;173(4412):973–976. doi: 10.1038/173973a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi H., Ishiwata S. Disassembly kinetics of thick filaments in rabbit skeletal muscle fibers. Effects of ionic strength, Ca2+ concentration, pH, temperature, and cross-bridges on the stability of thick filament structure. Biophys J. 1985 Mar;47(3):267–275. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83916-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiwata S. Melting from both ends of an A-band in a myofibril. Observation with a phase-contrast microscope. J Biochem. 1981 May;89(5):1647–1650. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiwata S., Muramatsu K., Higuchi H. Disassembly from both ends of thick filaments in rabbit skeletal muscle fibers. An optical diffraction study. Biophys J. 1985 Mar;47(3):257–266. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83915-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magid A., Ting-Beall H. P., Carvell M., Kontis T., Lucaveche C. Connecting filaments, core filaments, and side-struts: a proposal to add three new load-bearing structures to the sliding filament model. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1984;170:307–328. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-4703-3_26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama K., Kimura S., Ohashi K., Kuwano Y. Connectin, an elastic protein of muscle. Identification of "titin" with connectin. J Biochem. 1981 Mar;89(3):701–709. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama K., Natori R., Nonomura Y. New elastic protein from muscle. Nature. 1976 Jul 1;262(5563):58–60. doi: 10.1038/262058a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama K., Sawada H., Kimura S., Ohashi K., Higuchi H., Umazume Y. Connectin filaments in stretched skinned fibers of frog skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;99(4 Pt 1):1391–1397. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.4.1391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PODOLSKY R. J. THE MAXIMUM SARCOMERE LENGTH FOR CONTRACTION OF ISOLATED MYOFIBRILS. J Physiol. 1964 Jan;170:110–123. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paolini P. J., Sabbadini R., Roos K. P., Baskin R. J. Sarcomere length dispersion in single skeletal muscle fibers and fiber bundles. Biophys J. 1976 Aug;16(8):919–930. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85742-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson S. P., Kerrick W. G. The effects of pH on Ca2+-activated force in frog skeletal muscle fibers. Pflugers Arch. 1979 May 15;380(1):41–45. doi: 10.1007/BF00582610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thames M. D., Teichholz L. E., Podolsky R. J. Ionic strength and the contraction kinetics of skinned muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Apr;63(4):509–530. doi: 10.1085/jgp.63.4.509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umazume Y., Fujime S. Electro-optical property of extremely stretched skinned muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1975 Feb;15(2 Pt 1):163–180. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(75)85799-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umazume Y., Kasuga N. Radial stiffness of frog skinned muscle fibers in relaxed and rigor conditions. Biophys J. 1984 Apr;45(4):783–788. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84222-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang K., McClure J., Tu A. Titin: major myofibrillar components of striated muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3698–3702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang K., Ramirez-Mitchell R. A network of transverse and longitudinal intermediate filaments is associated with sarcomeres of adult vertebrate skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;96(2):562–570. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.2.562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshino S., Umazume Y., Natori R., Fujime S., Chiba S. Optical diffraction study of muscle fibers. II. Electro-optical properties of muscle fibers. Biophys Chem. 1978 Sep;8(4):317–326. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(78)80014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]