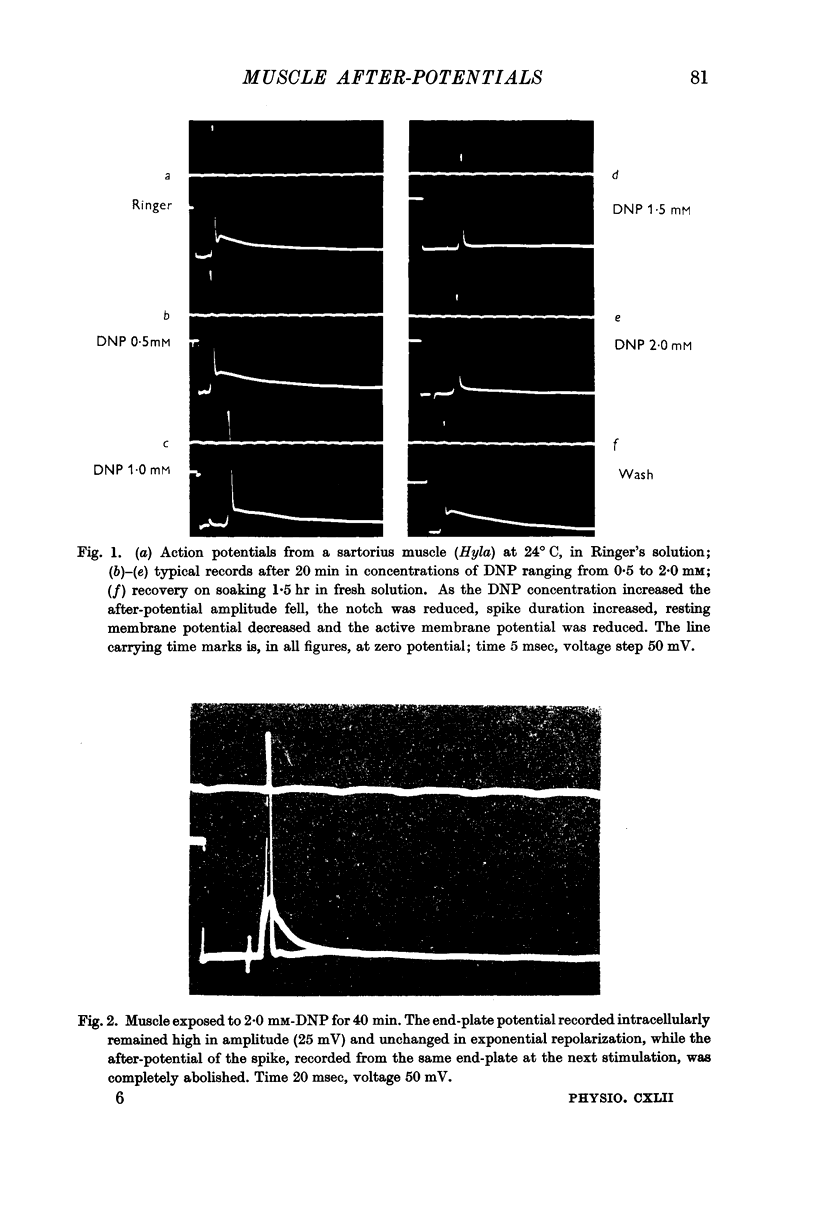
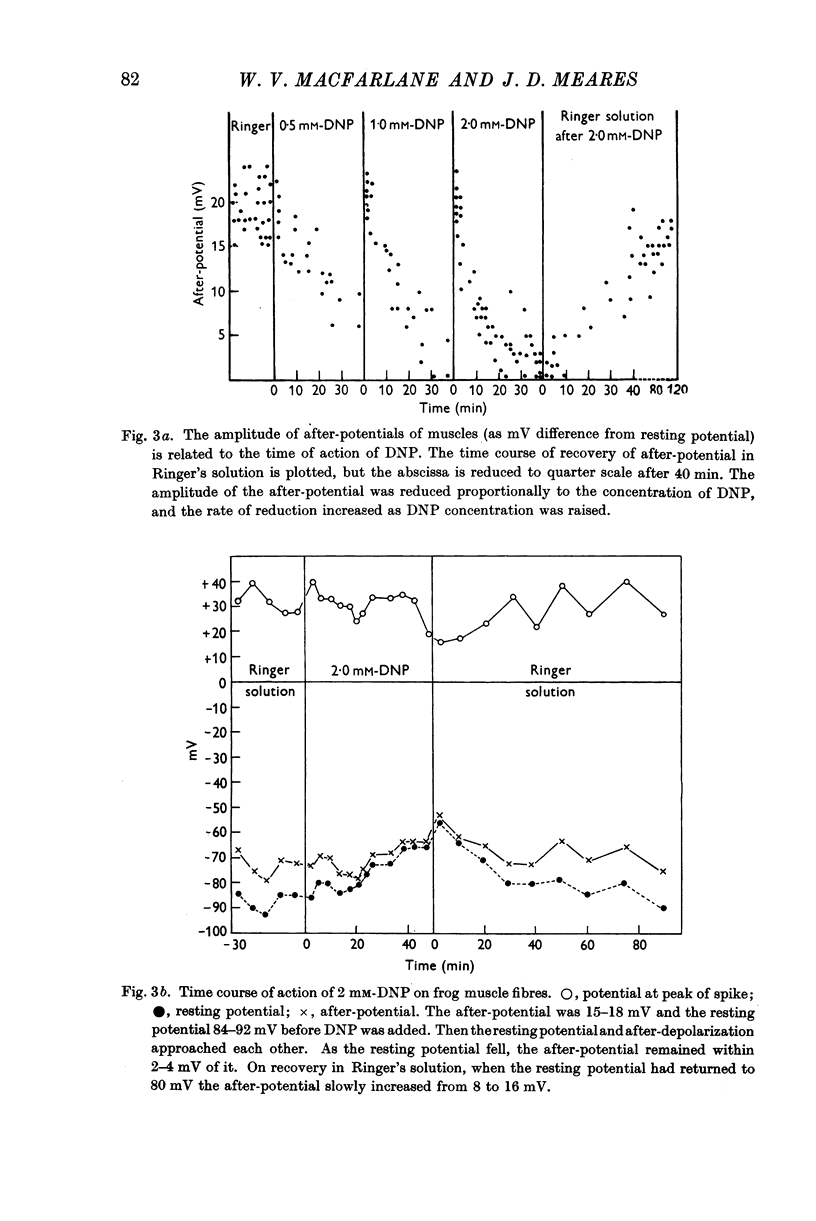
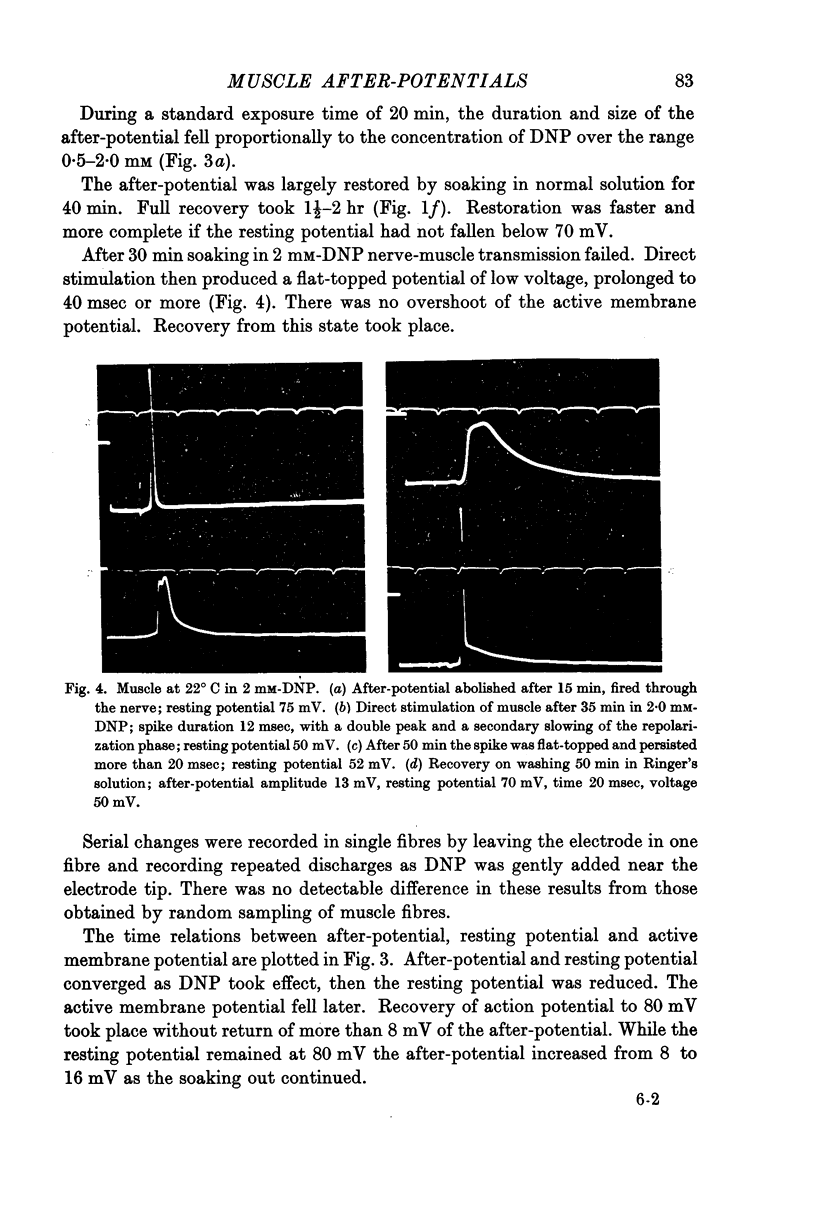
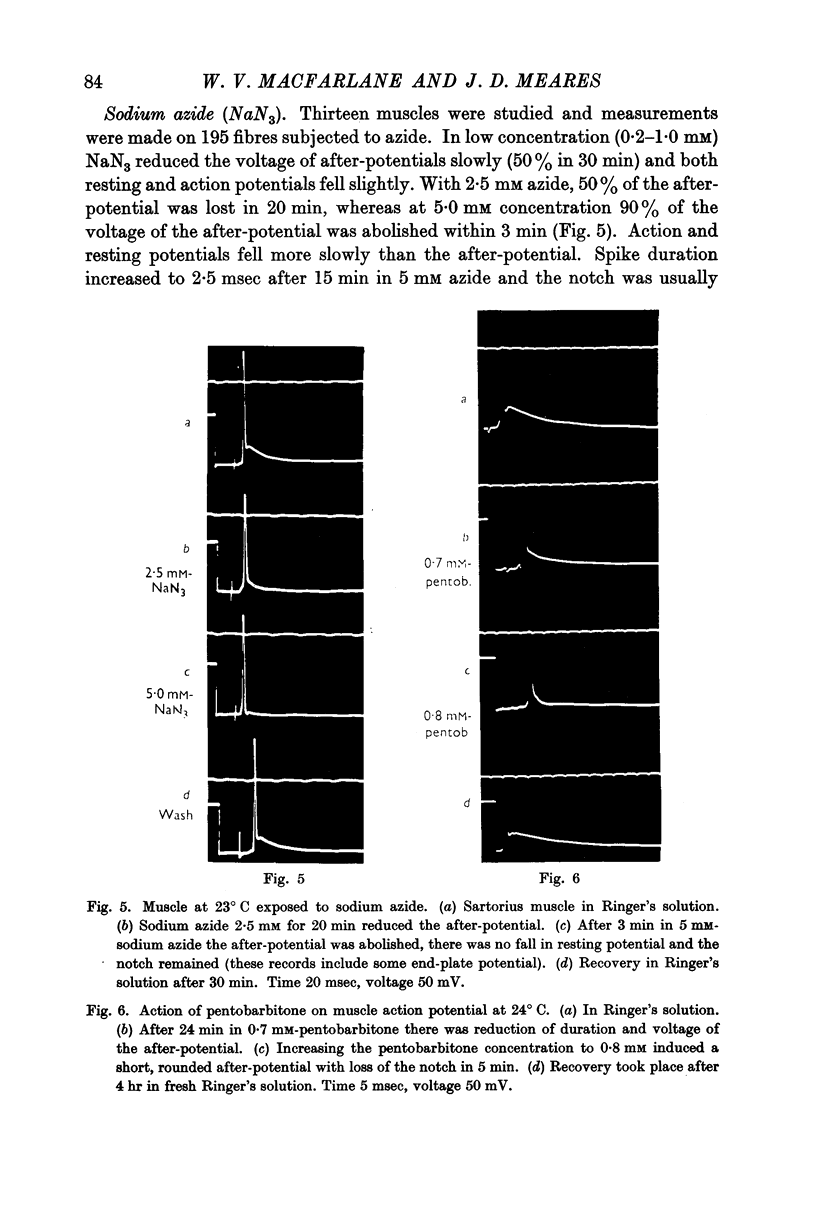
Full text
PDF



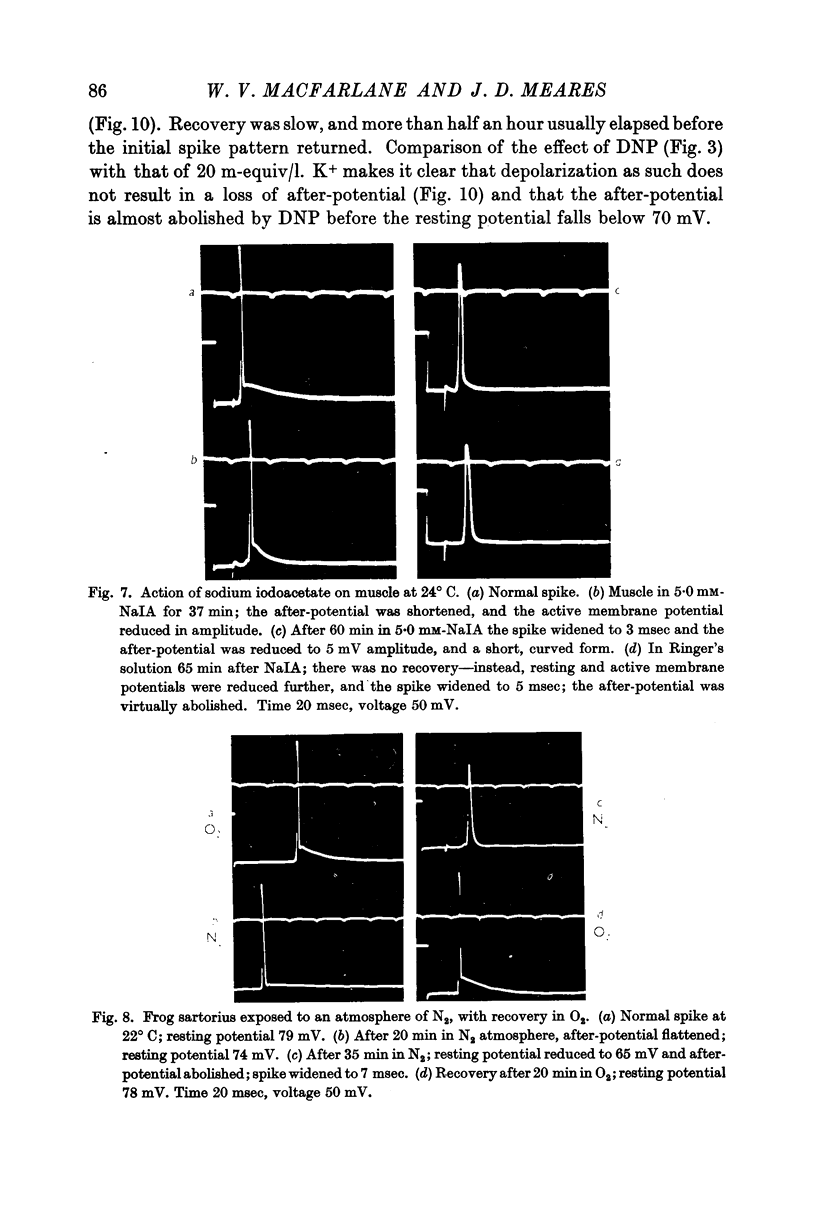
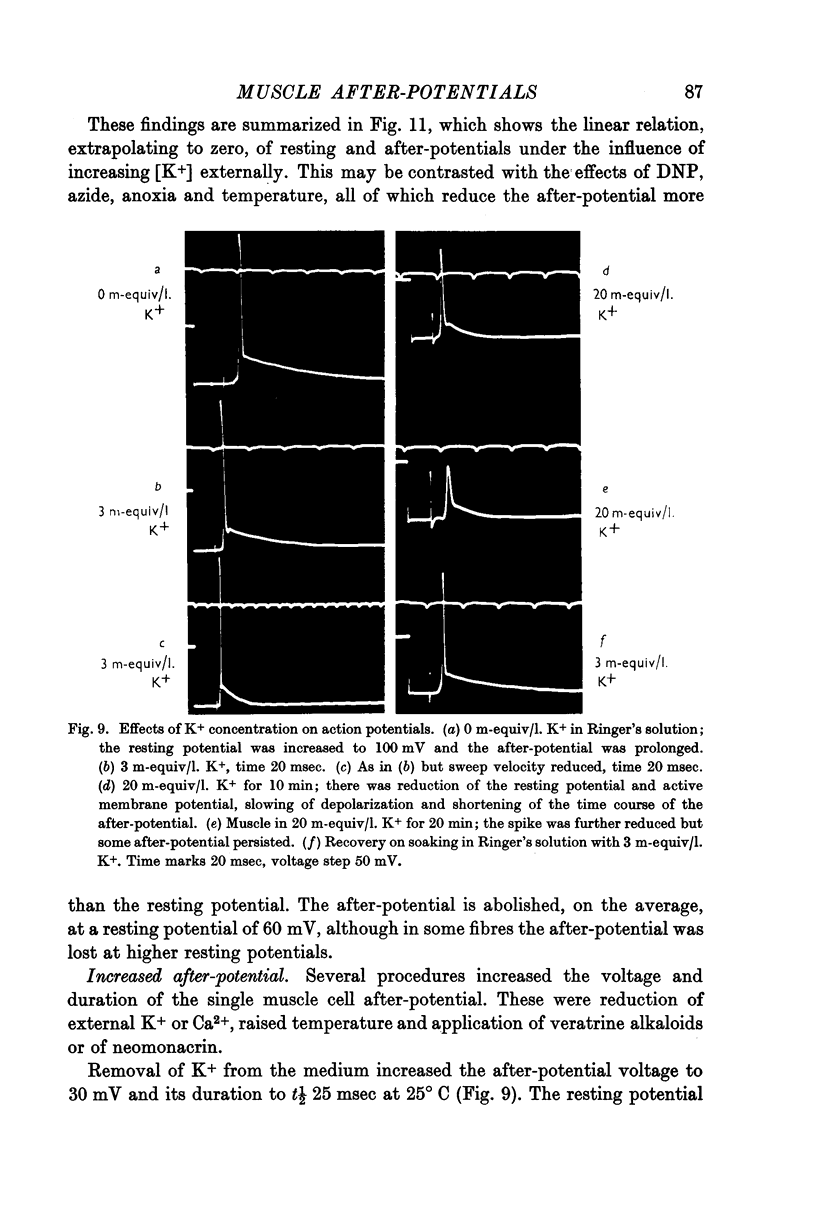
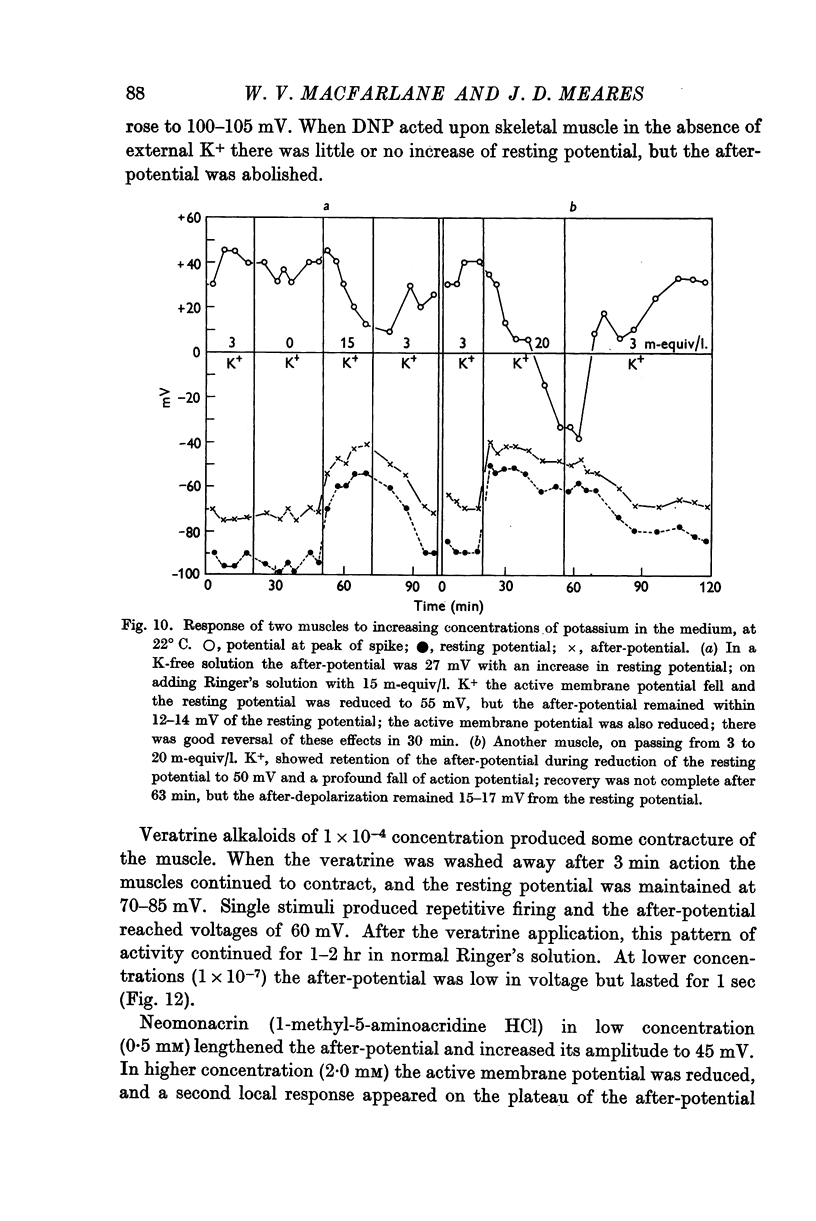
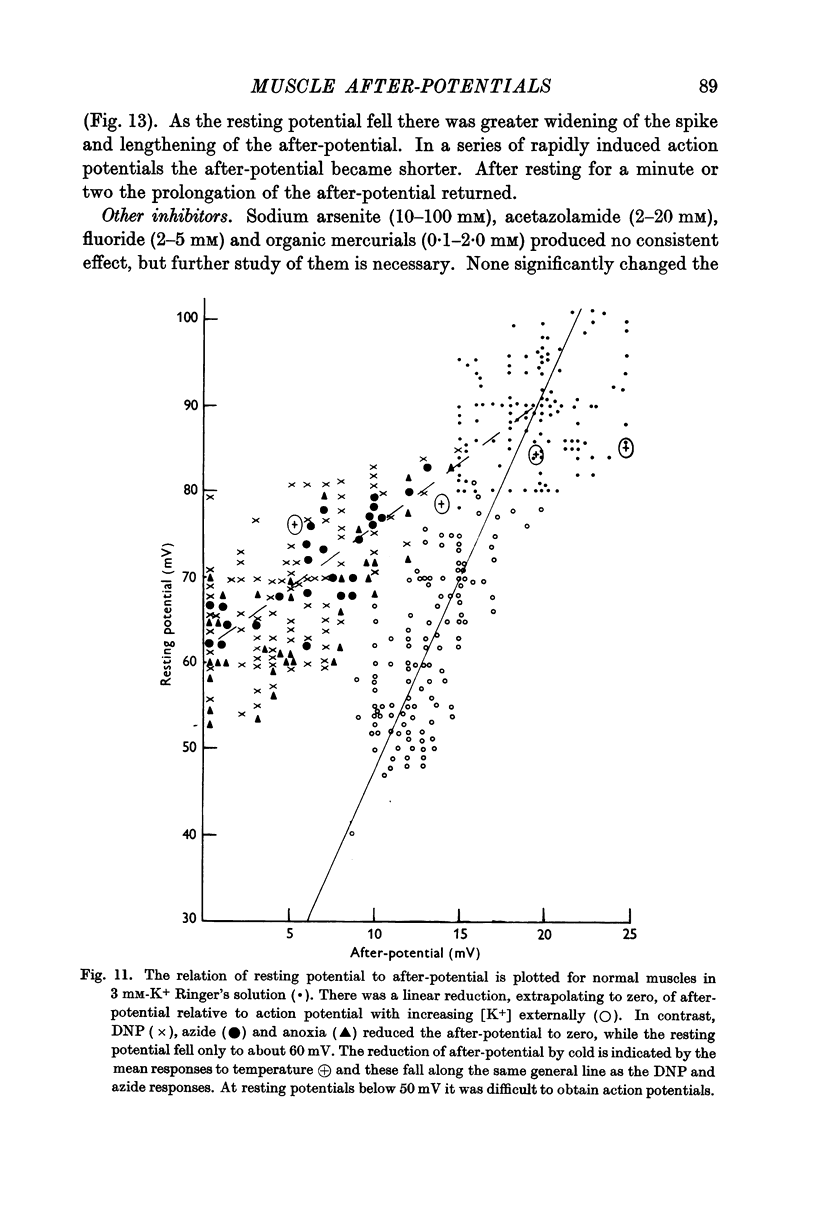






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian E. D. The recovery process of excitable tissues: Part I. J Physiol. 1920 Aug 19;54(1-2):1–31. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1920.sp001905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARNES J. M., DUFF J. I., THRELFALL C. J. The behaviour of mammalian striated muscle in the presence of 2:4-dinitrophenol. J Physiol. 1955 Dec 29;130(3):585–600. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BREMER F. Etude du potentiel négatif tardif du muscle squelettique et considérations sur le déterminisme de la contraction vératrinique. Arch Int Physiol Biochim. 1955 Feb;63(1):70–93. doi: 10.3109/13813455509150862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRODY T. M., BAIN J. A. Effect of barbiturates on oxidative phosphorylation. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1951 May;77(1):50–53. doi: 10.3181/00379727-77-18674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONWAY E. J., RYAN H., CARTON E. Active transport of sodium ions from the yeast cell. Biochem J. 1954 Sep;58(1):158–167. doi: 10.1042/bj0580158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOMBS J. S., ECCLES J. C., FATT P. The electrical properties of the motoneurone membrane. J Physiol. 1955 Nov 28;130(2):291–325. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FENN W. O., GERSCHMAN R. The loss of potassium from frog nerves in anoxia and other conditions. J Gen Physiol. 1950 Jan 20;33(3):195–203. doi: 10.1085/jgp.33.3.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FITZHUGH R. Effects of azide and electrical polarization on refractory period in frog nerve. J Cell Physiol. 1954 Aug;44(1):117–140. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030440111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOULKES E. C. Cation transport in yeast. J Gen Physiol. 1956 May 20;39(5):687–704. doi: 10.1085/jgp.39.5.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F., KATZ B. Measurement of current-voltage relations in the membrane of the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):424–448. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KEYNES R. D. Active transport of cations in giant axons from Sepia and Loligo. J Physiol. 1955 Apr 28;128(1):28–60. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYNES R. D., MAISEL G. W. The energy requirement for sodium extrusion from a frog muscle. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1954 May 27;142(908):383–392. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1954.0031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYNES R. D. The ionic fluxes in frog muscle. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1954 May 27;142(908):359–382. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1954.0030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LING G., GERARD R. W. The membrane potential and metabolism of muscle fibers. J Cell Physiol. 1949 Dec;34(3):413–438. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030340307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOEWENSTEIN W. R., SZENT-GYORGYI A. The effect of dinitronaphtol on the membrane potential of the skeletal muscle fibre. J Cell Physiol. 1955 Oct;46(2):345–347. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030460211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUBIN M. The effect of iodide and thiocyanate ions on the mechanical and electrical properties of frog muscle. J Cell Physiol. 1957 Apr;49(2):335–349. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030490214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACFARLANE W. V., MEARES J. D. Intracellular recording of action and after-potentials of frog muscle between 0 and 45dgreeC. J Physiol. 1958 Jun 18;142(1):97–109. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACFARLANE W. V., MEARES J. D. Modification of the after-potential of single muscle fibres by 2:4-dinitrophenol. Nature. 1955 Aug 27;176(4478):403–404. doi: 10.1038/176403a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCLENNAN H. Physical and chemical factors affecting potassium movements in mammalian muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 Oct;22(1):30–37. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90219-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MYERS D. K., SLATER E. C. Hydrolysis of adenosine triphosphate by mitochondrial preparations. Nature. 1957 Feb 16;179(4555):363–364. doi: 10.1038/179363a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RITCHIE J. M., STRAUB R. W. The hyperpolarization which follows activity in mammalian non-medullated fibres. J Physiol. 1957 Apr 3;136(1):80–97. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHATZMANN H. J., WITT P. N. Action of k-strophanthin on potassium leakage from frog sartorius muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1954 Dec;112(4):501–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHANES A. M., GRUNDFEST H., FREYGANG W. Low level impedance changes following the spike in the squid giant axon before and after treatment with "veratrine" alkaloids. J Gen Physiol. 1953 Sep;37(1):39–51. doi: 10.1085/jgp.37.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHANES A. M. Ionic transfer in nerve in relation to bio-electrical phenomena. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1952 Jun 30;55(1):1–36. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1952.tb26518.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAW F. H., SIMON S. E. Sodium extrusion in muscle. Nature. 1955 Nov 26;176(4491):1031–1032. doi: 10.1038/1761031b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TASAKI I., HAGIWAR A. S. Demonstration of two stable potential states in the squid giant axon under tetraethylammonium chloride. J Gen Physiol. 1957 Jul 20;40(6):859–885. doi: 10.1085/jgp.40.6.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THESLEFF S. The effect of anesthetic agents on skeletal muscle membrane. Acta Physiol Scand. 1956 Nov 5;37(4):335–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1956.tb01369.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


