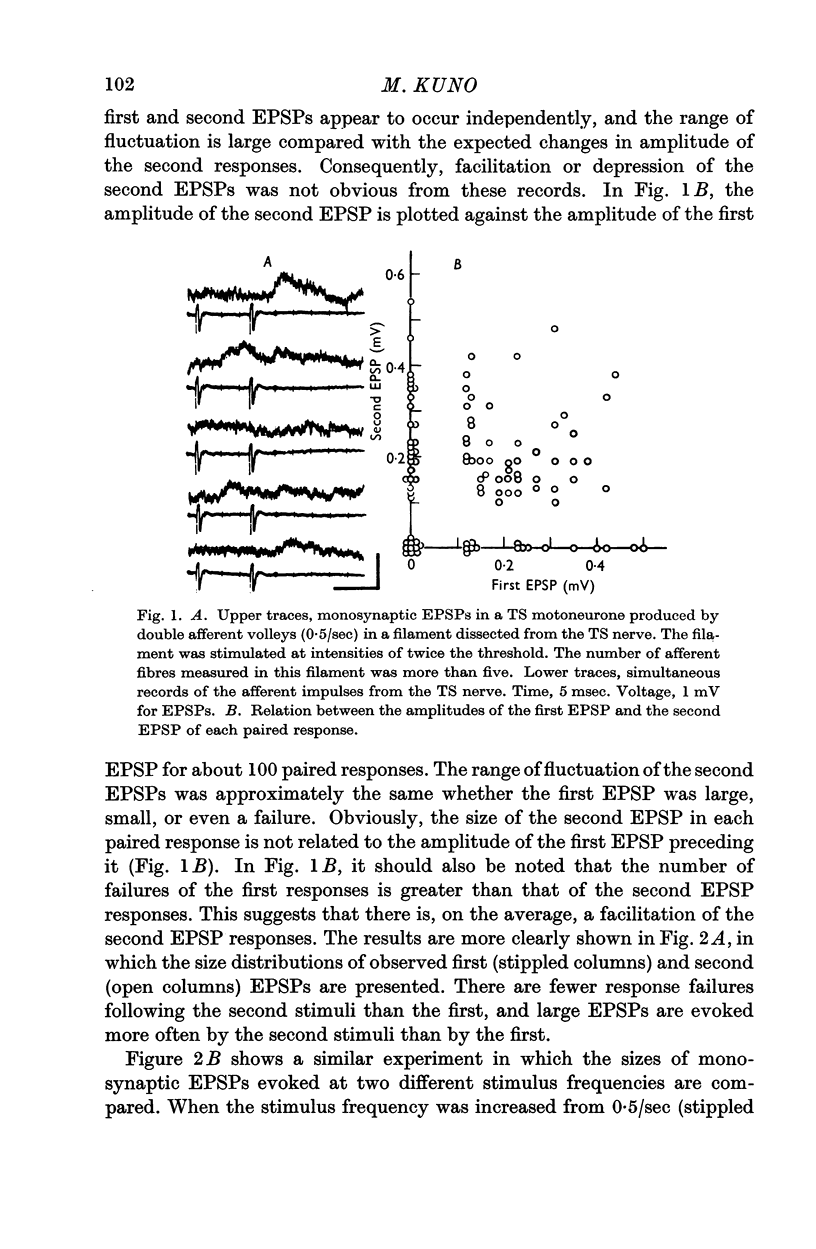
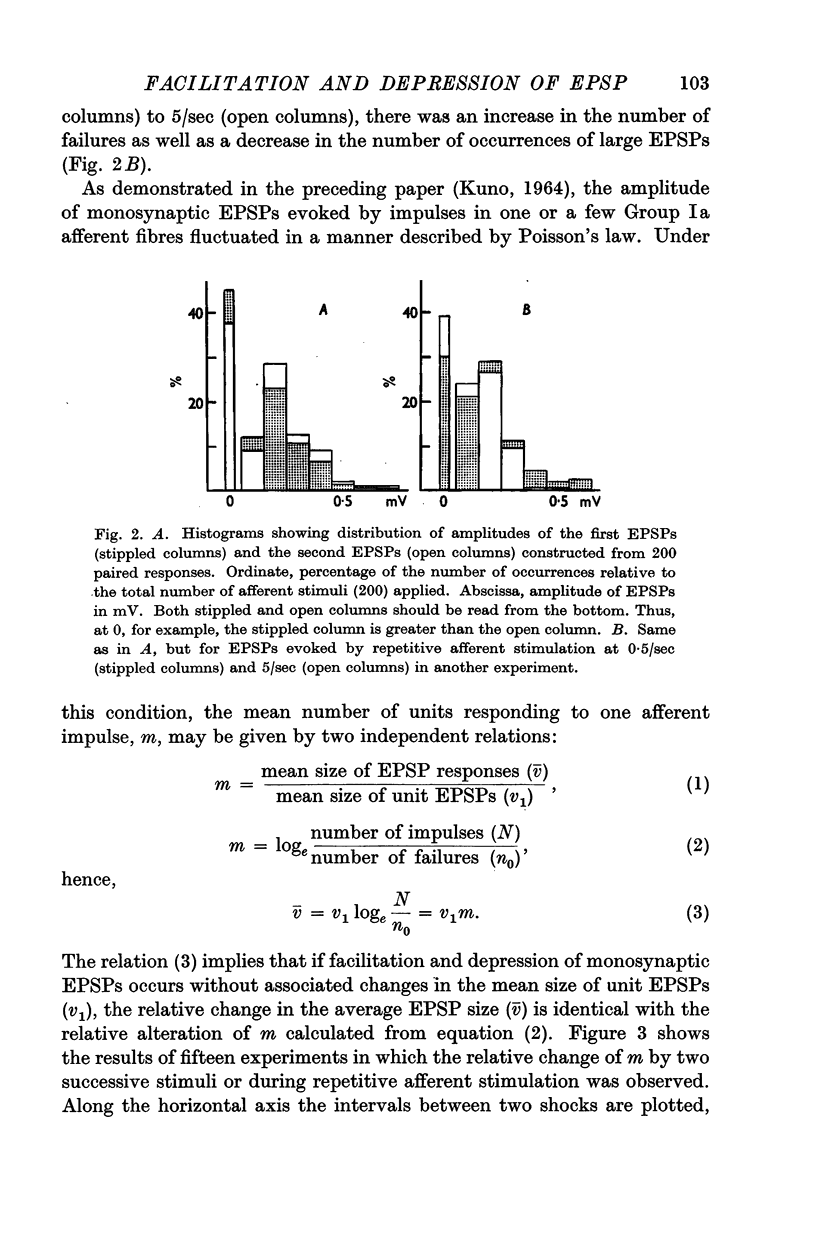
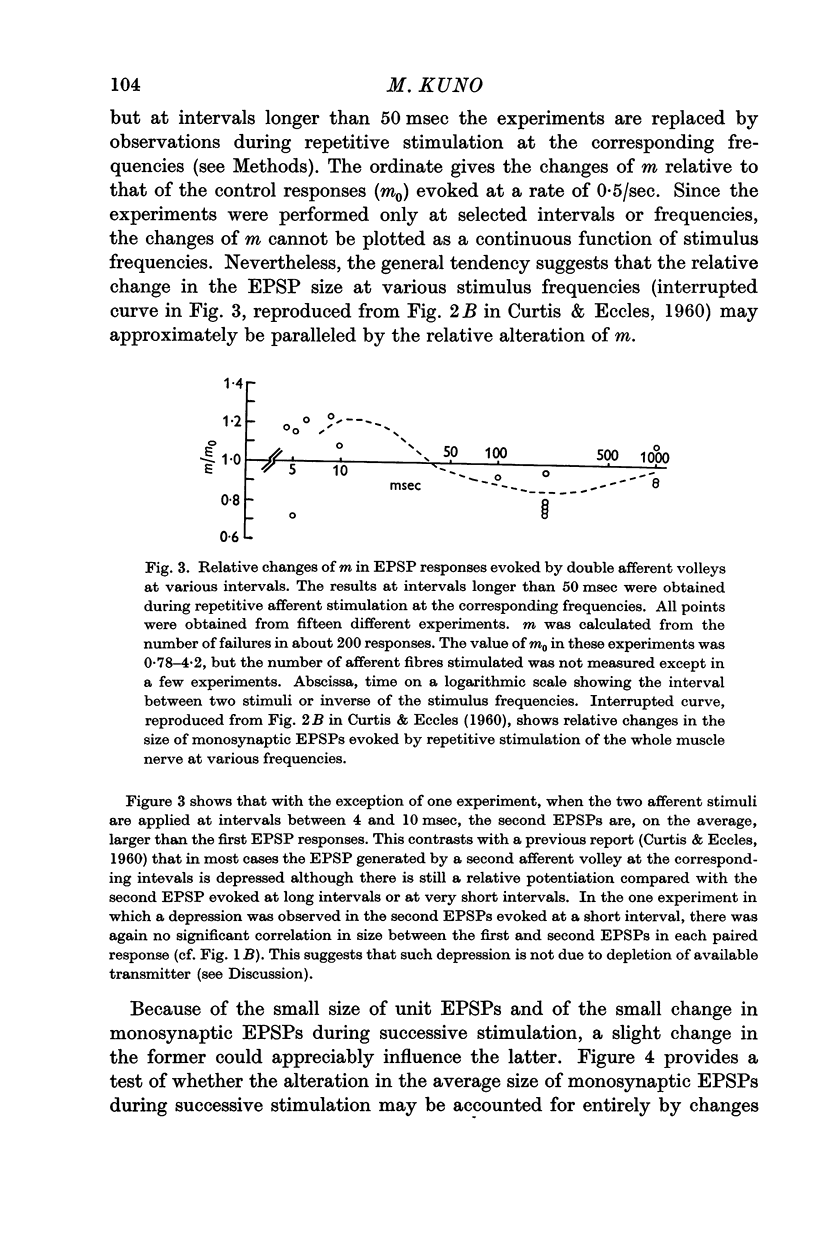
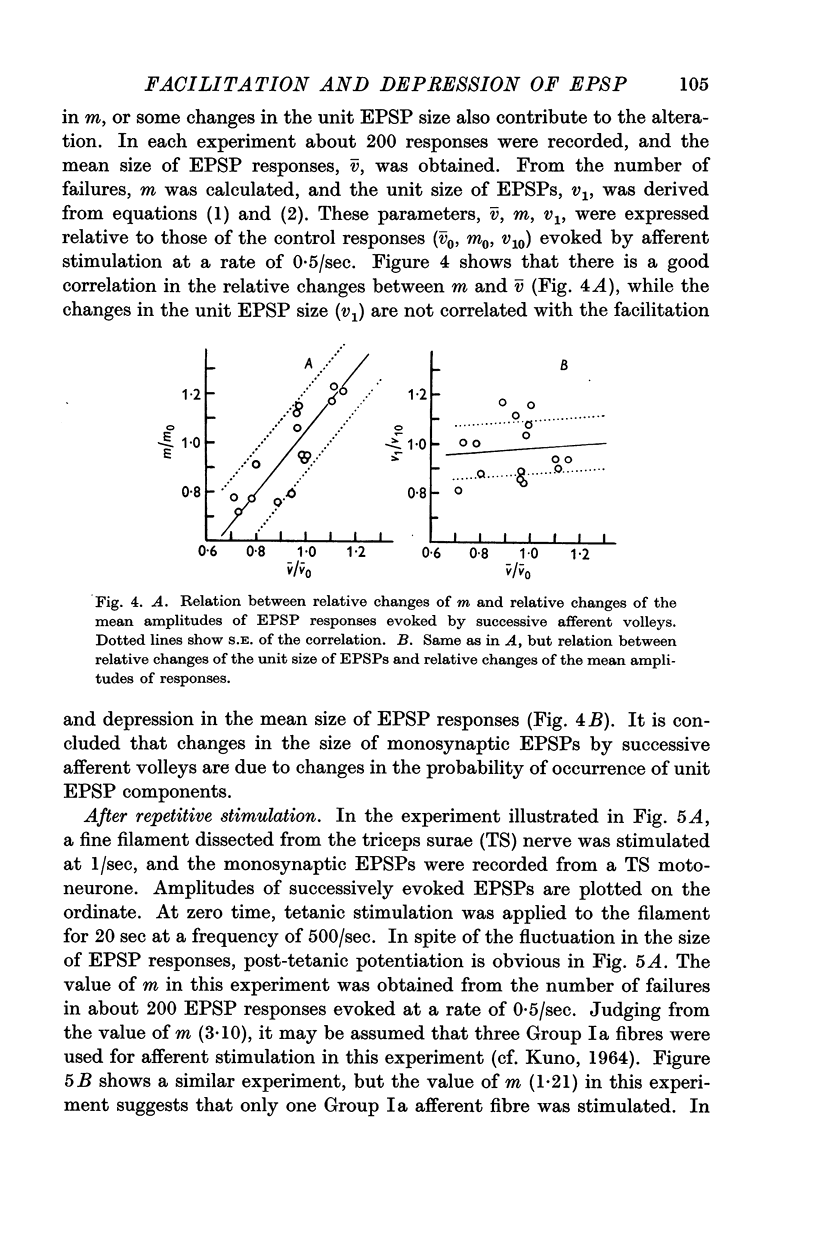
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BROOKS C. M., KOIZUMI K. Origin of the dorsal root reflex. J Neurophysiol. 1956 Jan;19(1):60–74. doi: 10.1152/jn.1956.19.1.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R., ECCLES J. C. Synaptic action during and after repetitive stimulation. J Physiol. 1960 Feb;150:374–398. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Statistical factors involved in neuromuscular facilitation and depression. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):574–585. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUDEL J., KUFFLER S. W. Mechanism of facilitation at the crayfish neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1961 Mar;155:530–542. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUDEL J., KUFFLER S. W. Presynaptic inhibition at the crayfish neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1961 Mar;155:543–562. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M., MAGNI F. Central inhibitory action attributable to presynaptic depolarization produced by muscle afferent volleys. J Physiol. 1961 Nov;159:147–166. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., KOZAK W., MAGNI F. Dorsal root reflexes of muscle group I afferent fibres. J Physiol. 1961 Nov;159:128–146. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., KRNJEVIC K., MILEDI R. Delayed effects of peripheral severance of afferent nerve fibres on the efficacy of their central synapses. J Physiol. 1959 Jan 28;145(1):204–220. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C. The mechanism of synaptic transmission. Ergeb Physiol. 1961;51:299–430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUBBARD J. I. REPETITIVE STIMULATION AT THE MAMMALIAN NEUROMUSCULAR JUNCTION, AND THE MOBILIZATION OF TRANSMITTER. J Physiol. 1963 Dec;169:641–662. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGHES J. R. Post-tetanic potentiation. Physiol Rev. 1958 Jan;38(1):91–113. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1958.38.1.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNO M. QUANTAL COMPONENTS OF EXCITATORY SYNAPTIC POTENTIALS IN SPINAL MOTONEURONES. J Physiol. 1964 Dec;175:81–99. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LLOYD D. P. C. Post-tetanic potentiation of response in monosynaptic reflex pathways of the spinal cord. J Gen Physiol. 1949 Nov;33(2):147–170. doi: 10.1085/jgp.33.2.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OTSUKA M., ENDO M., NONOMURA Y. Presynaptic nature of neuromuscular depression. Jpn J Physiol. 1962 Dec 15;12:573–584. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.12.573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THESLEFF S. Motor end-plate 'desensitization' by repetitive nerve stimuli. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:659–664. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


