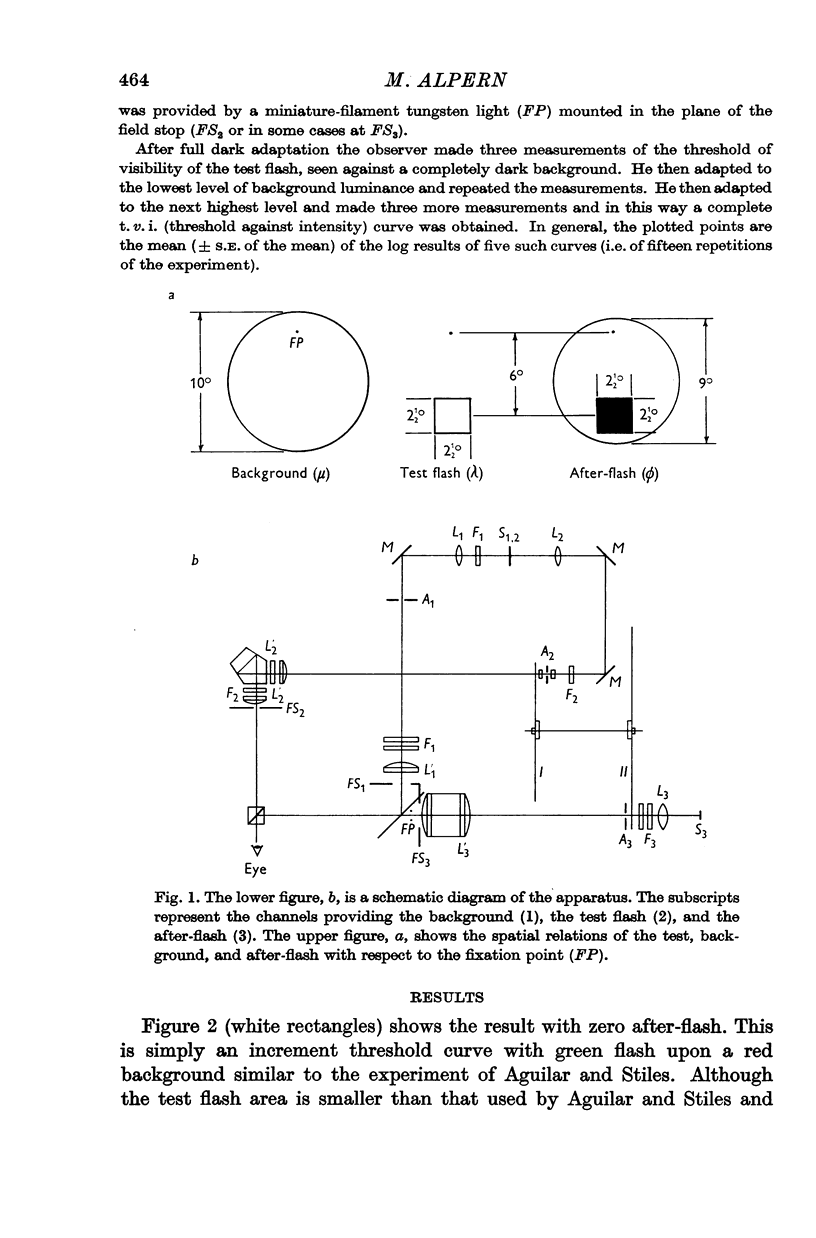
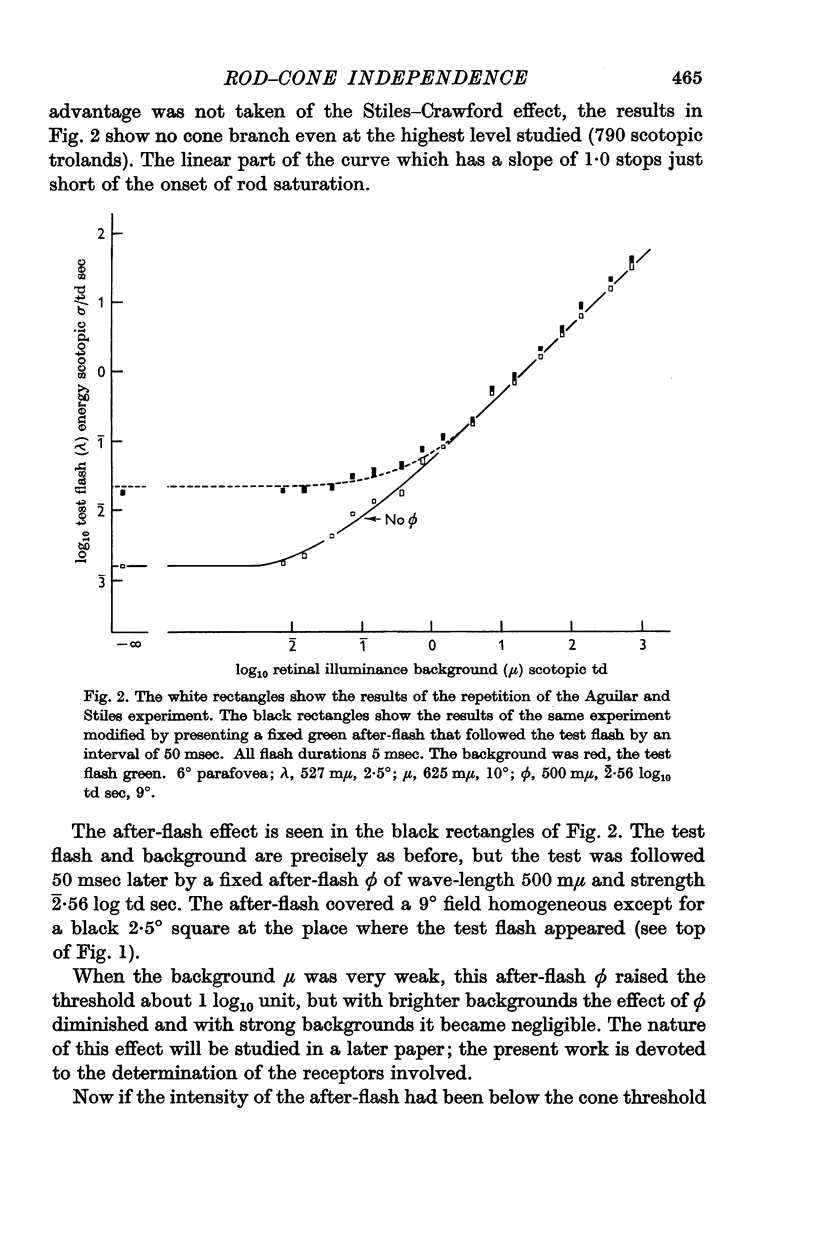
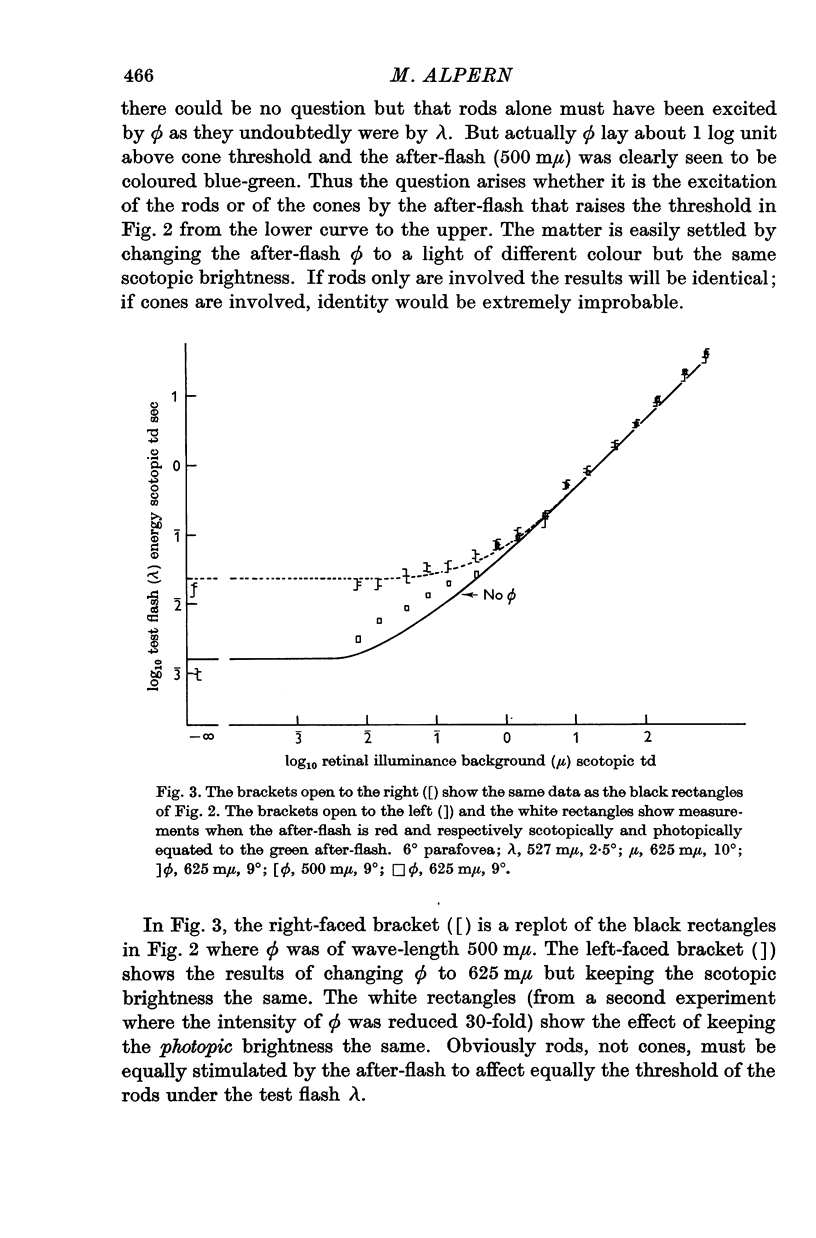
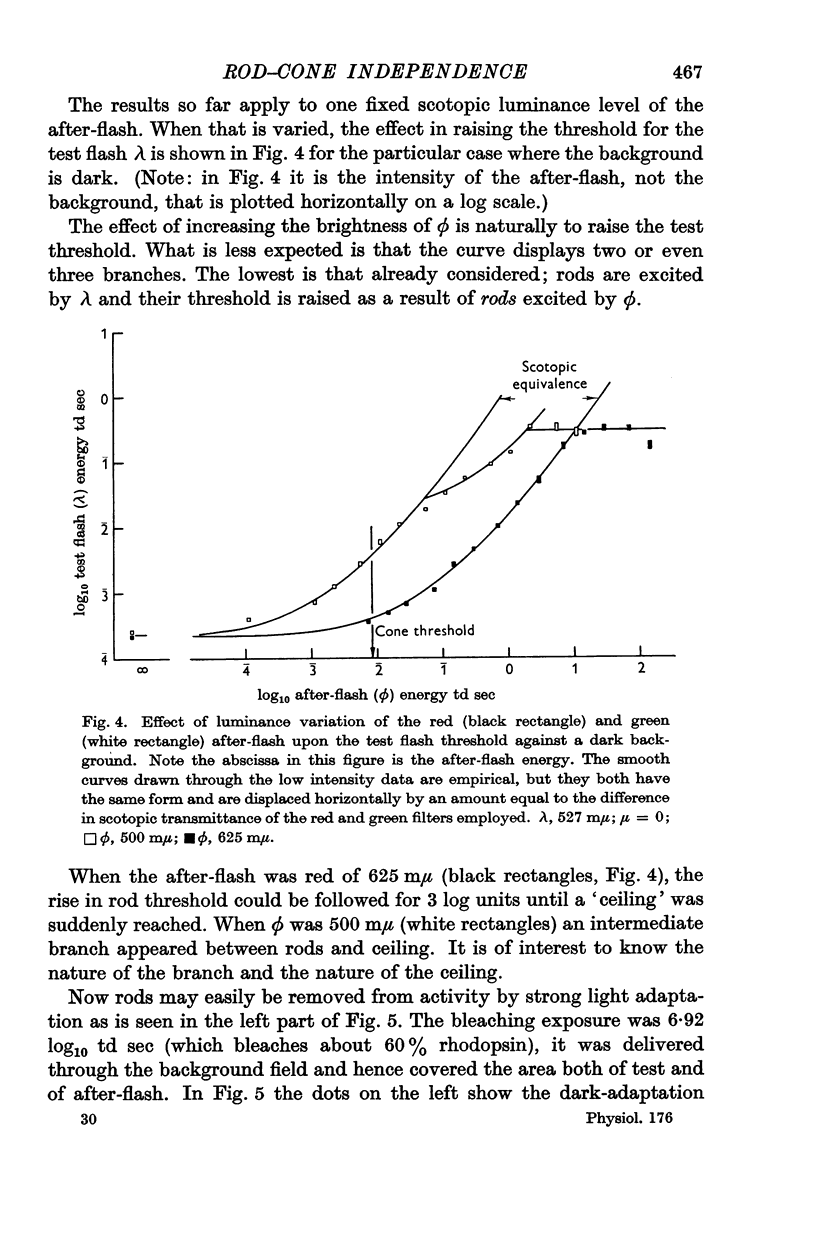
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALPERN M. Metacontrast. J Opt Soc Am. 1953 Aug;43(8):648–657. doi: 10.1364/josa.43.000648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN P. K., WALD G. VISUAL PIGMENTS IN SINGLE RODS AND CONES OF THE HUMAN RETINA. DIRECT MEASUREMENTS REVEAL MECHANISMS OF HUMAN NIGHT AND COLOR VISION. Science. 1964 Apr 3;144(3614):45–52. doi: 10.1126/science.144.3614.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONNER K. O., RUSHTON W. A. Rod-cone interaction in the frog's retina analysed by the Stiles-Crawford effect and by dark adaptation. J Physiol. 1959 Dec;149:303–317. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flamant F., Stiles W. S. The directional and spectral sensitivities of the retinal rods to adapting fields of different wave-lengths. J Physiol. 1948 Mar 15;107(2):187–202. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1948.sp004262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARKS W. B., DOBELLE W. H., MACNICHOL E. F., Jr VISUAL PIGMENTS OF SINGLE PRIMATE CONES. Science. 1964 Mar 13;143(3611):1181–1183. doi: 10.1126/science.143.3611.1181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


