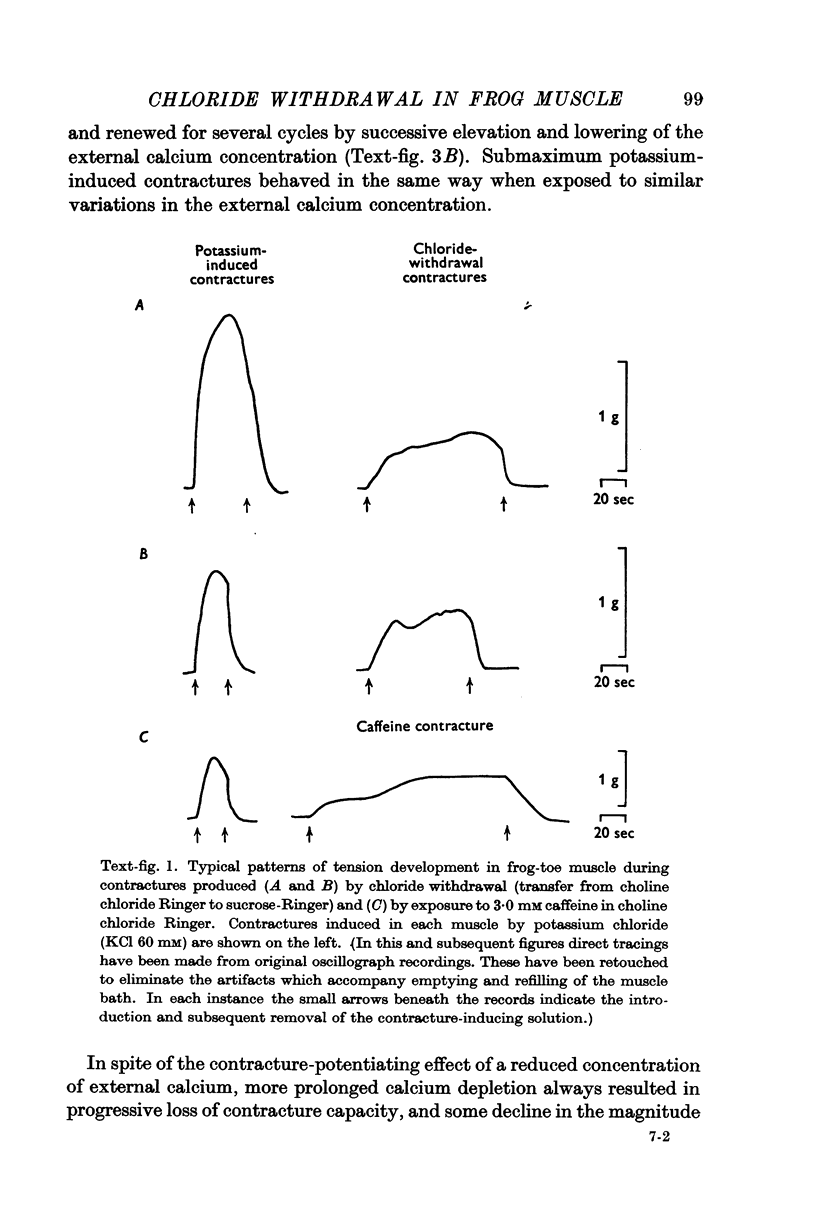
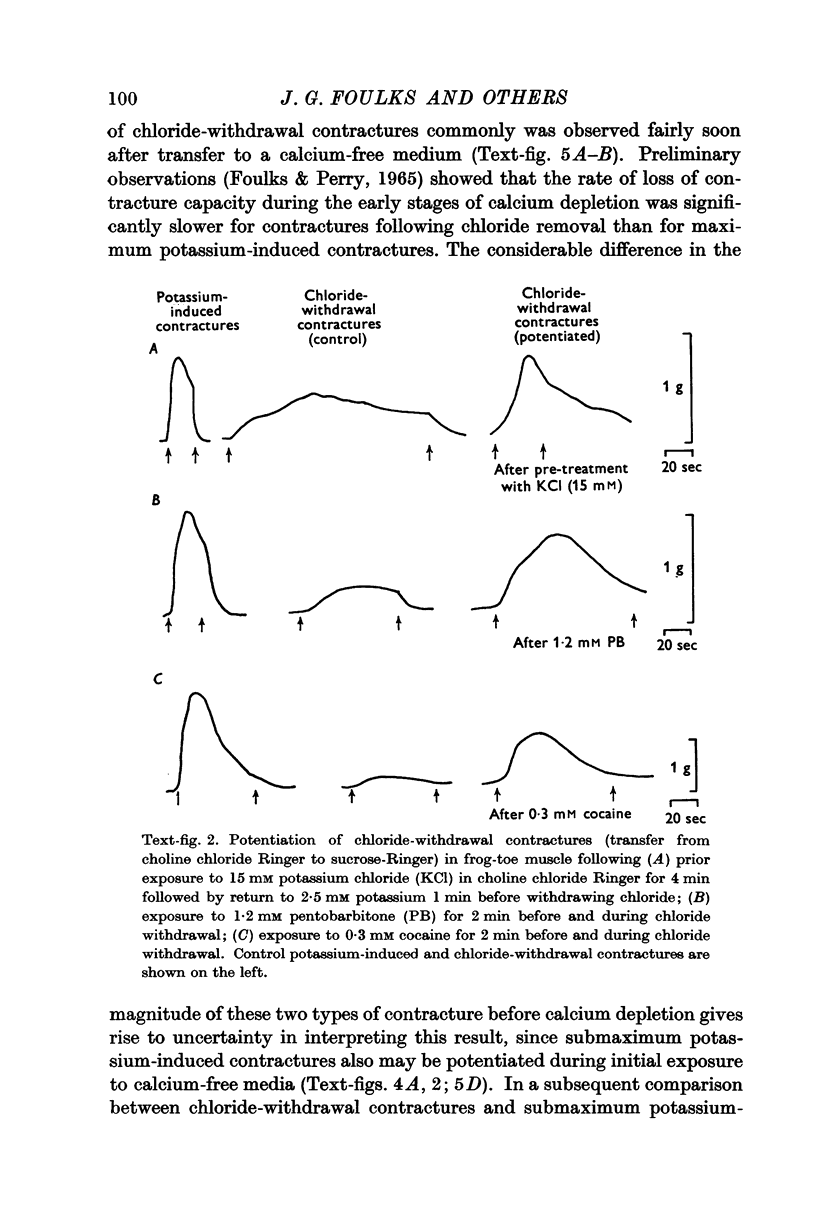
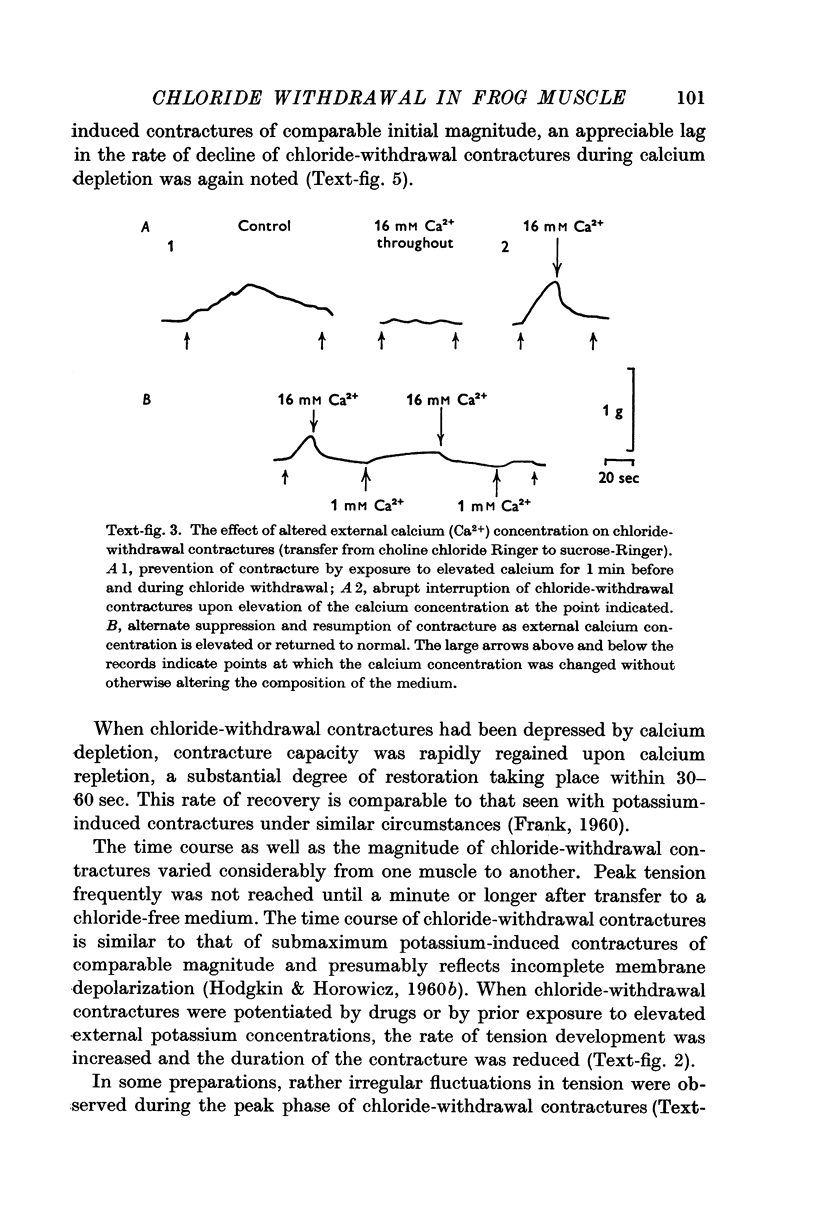
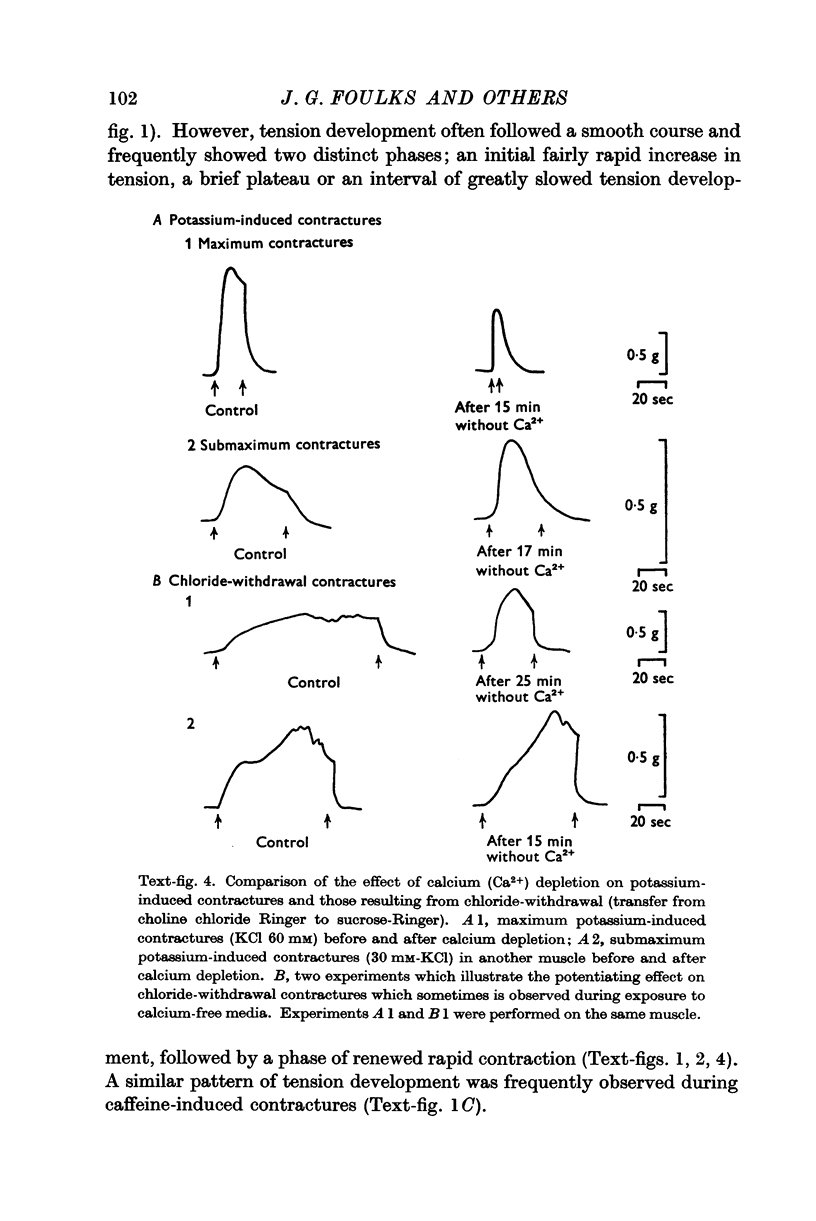
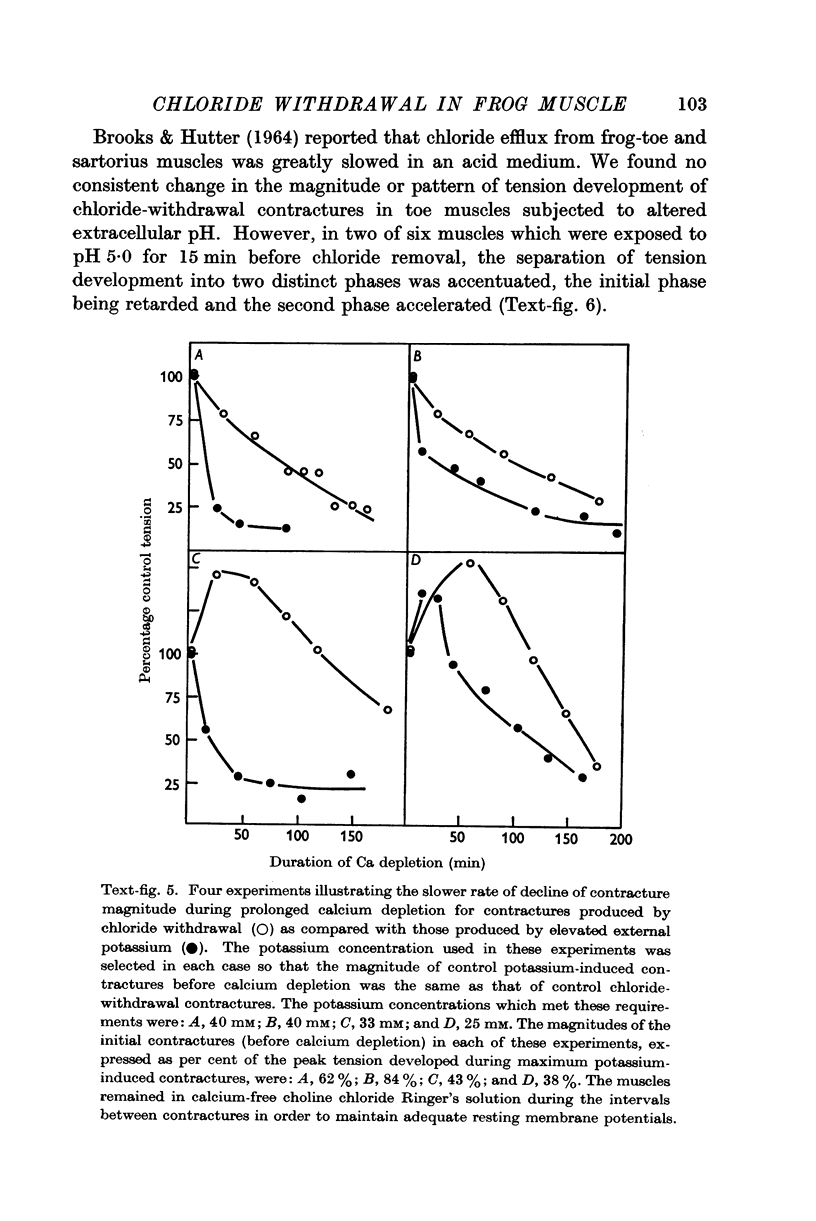
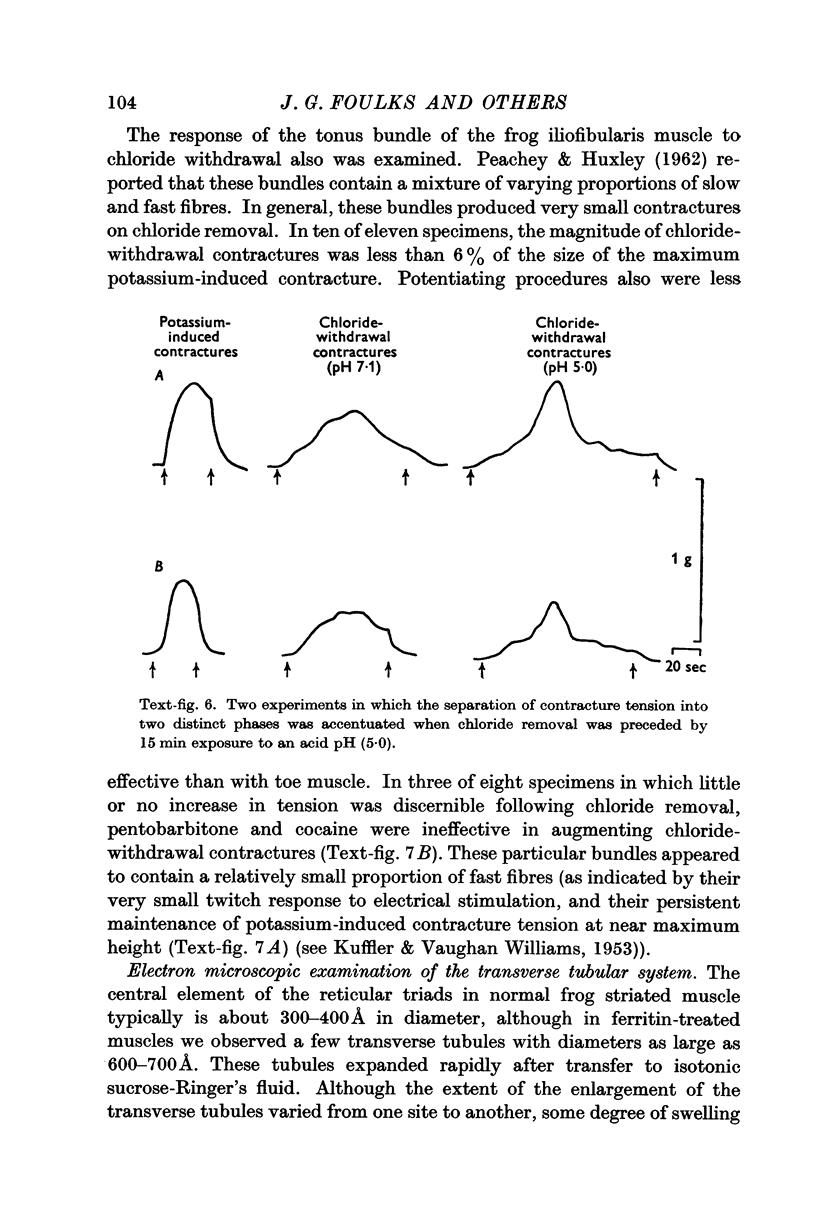
Full text
PDF


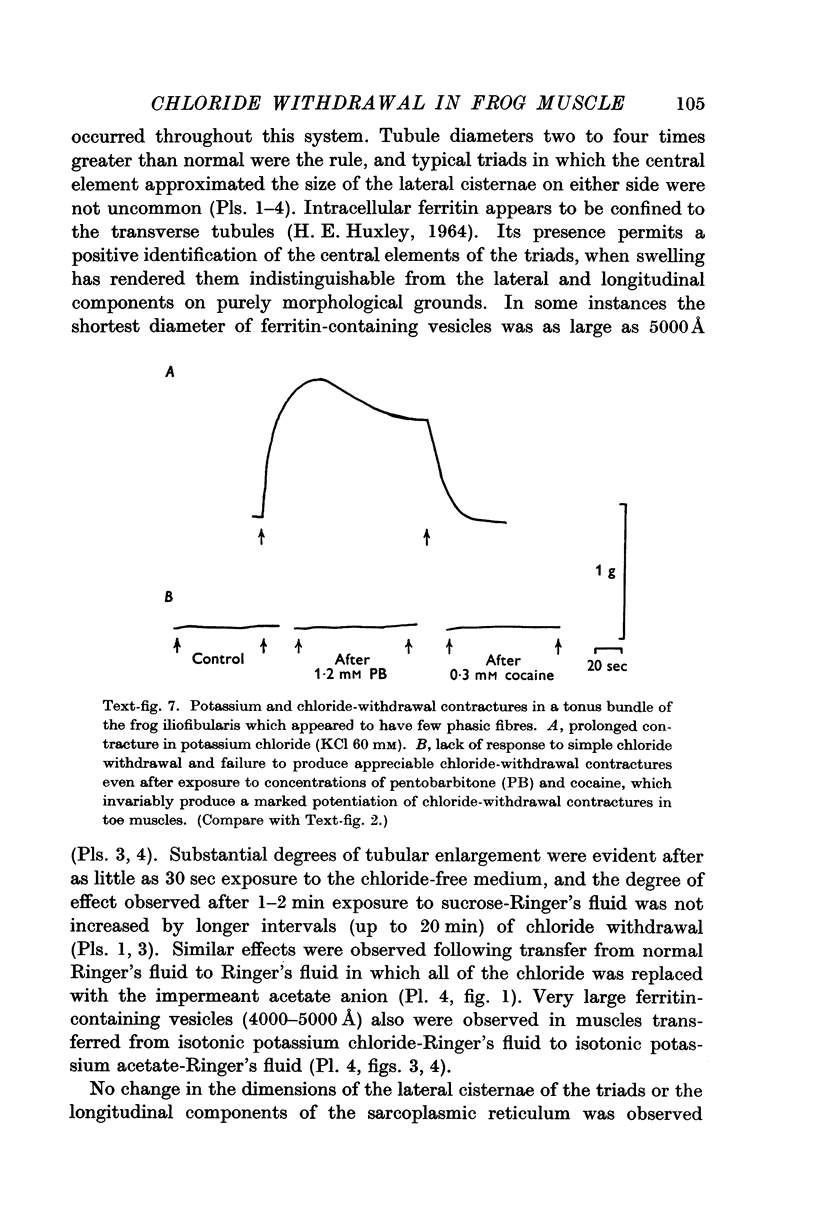














Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADRIAN R. H. Movement of inorganic ions across the membrane of striated muscle. Circulation. 1962 Nov;26:1214–1223. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.26.5.1214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ADRIAN R. H. Potassium chloride movement and the membrane potential of frog muscle. J Physiol. 1960 Apr;151:154–185. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Freygang W. H. The potassium and chloride conductance of frog muscle membrane. J Physiol. 1962 Aug;163(1):61–103. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENNETT H. S. Modern concepts of structure of striated muscle. Am J Phys Med. 1955 Feb;34(1):46–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle P. J., Conway E. J. Potassium accumulation in muscle and associated changes. J Physiol. 1941 Aug 11;100(1):1–63. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1941.sp003922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE SOUZA SANTOS P., EDWARDS G. A., RUSKA H., VALLEJO-FREIRE A. Comparative cytophysiology of striated muscle with special reference to the role of the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1956 Jul 25;2(4 Suppl):143–156. doi: 10.1083/jcb.2.4.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENDO M. ENTRY OF A DYE INTO THE SARCOTUBULAR SYSTEM OF MUSCLE. Nature. 1964 Jun 13;202:1115–1116. doi: 10.1038/2021115b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FALK G., FATT P. LINEAR ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES OF STRIATED MUSCLE FIBRES OBSERVED WITH INTRACELLULAR ELECTRODES. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1964 Apr 14;160:69–123. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1964.0030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FALK G., LANDA J. F. Prolonged response of skeletal muscle in the absence of penetrating anions. Am J Physiol. 1960 Feb;198:289–299. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.198.2.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAWCETT D. W., REVEL J. P. The sarcoplasmic reticulum of a fast-acting fish muscle. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Aug;10(4):89–109. doi: 10.1083/jcb.10.4.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANK G. B. Effects of changes in extracellular calcium concentration on the potassium-induced contracture of frog's skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1960 Jun;151:518–538. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANZINI-ARMSTRONG C. PORES IN THE SARCOPLASMIC RETICULUM. J Cell Biol. 1963 Dec;19:637–641. doi: 10.1083/jcb.19.3.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANZINI-ARMSTRONG C., PORTER K. R. SARCOLEMMAL INVAGINATIONS CONSTITUTING THE T SYSTEM IN FISH MUSCLE FIBERS. J Cell Biol. 1964 Sep;22:675–696. doi: 10.1083/jcb.22.3.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREYGANG W. H., Jr, GOLDSTEIN D. A., HELLAM D. C. THE AFTER-POTENTIAL THAT FOLLOWS TRAINS OF IMPULSES IN FROG MUSCLE FIBERS. J Gen Physiol. 1964 May;47:929–952. doi: 10.1085/jgp.47.5.929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIRARDIER L., REUBEN J. P., BRANDT P. W., GRUNDFEST H. EVIDENCE FOR ANION-PERMSELECTIVE MEMBRANE IN CRAYFISH MUSCLE FIBERS AND ITS POSSIBLE ROLE IN EXCITATION-CONTRACTION COUPLING. J Gen Physiol. 1963 Sep;47:189–214. doi: 10.1085/jgp.47.1.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY E. G. The structures of fast and slow muscle fibres in the frog. J Anat. 1958 Oct;92(4):559–562. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS E. J. The site of swelling in muscle. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:502–504. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HOROWICZ P. Potassium contractures in single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1960 Sep;153:386–403. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HOROWICZ P. The effect of sudden changes in ionic concentrations on the membrane potential of single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1960 Sep;153:370–385. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HOROWICZ P. The influence of potassium and chloride ions on the membrane potential of single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:127–160. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUTTER O. F., NOBLE D. The chloride conductance of frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1960 Apr;151:89–102. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY A. F. MUSCLE. Annu Rev Physiol. 1964;26:131–152. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.26.030164.001023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY A. F., TAYLOR R. E. Function of Krause's membrane. Nature. 1955 Dec 3;176(4492):1068–1068. doi: 10.1038/1761068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY A. F., TAYLOR R. E. Local activation of striated muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1958 Dec 30;144(3):426–441. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY H. E. EVIDENCE FOR CONTINUITY BETWEEN THE CENTRAL ELEMENTS OF THE TRIADS AND EXTRACELLULAR SPACE IN FROG SARTORIUS MUSCLE. Nature. 1964 Jun 13;202:1067–1071. doi: 10.1038/2021067b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARNOVSKY M. J. Simple methods for "staining with lead" at high pH in electron microscopy. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Dec;11:729–732. doi: 10.1083/jcb.11.3.729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUFFLER S. W., VAUGHAN WILLIAMS E. M. Properties of the 'slow' skeletal muscles fibres of the frog. J Physiol. 1953 Aug;121(2):318–340. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUETTGAU H. C. THE ACTION OF CALCIUM IONS ON POTASSIUM CONTRACTURES OF SINGLE MUSCLE FIBRES. J Physiol. 1963 Oct;168:679–697. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEACHEY L. D., HUXLEY A. F. Structural identification of twitch and slow striated muscle fibers of the frog. J Cell Biol. 1962 Apr;13:177–180. doi: 10.1083/jcb.13.1.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTER K. R. Electron microscopy of basophilic components of cytoplasm. J Histochem Cytochem. 1954 Sep;2(5):346–375. doi: 10.1177/2.5.346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTER K. R., PALADE G. E. Studies on the endoplasmic reticulum. III. Its form and distribution in striated muscle cells. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1957 Mar 25;3(2):269–300. doi: 10.1083/jcb.3.2.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTER K. R. The sarcoplasmic reticulum in muscle cells of Amblystoma larvae. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1956 Jul 25;2(4 Suppl):163–170. doi: 10.1083/jcb.2.4.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REVEL J. P., NAPOLITANO L., FAWCETT D. W. Identification of glycogen in electron micrographs of thin tissue sections. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1960 Dec;8:575–589. doi: 10.1083/jcb.8.3.575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REVEL J. P. The sarcoplasmic reticulum of the bat cricothroid muscle. J Cell Biol. 1962 Mar;12:571–588. doi: 10.1083/jcb.12.3.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHANES A. M. Drug and ion effects in frog muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1950 Jul 20;33(6):729–744. doi: 10.1085/jgp.33.6.729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHANES A. M. Electrochemical aspects of physiological and pharmacological action in excitable cells. II. The action potential and excitation. Pharmacol Rev. 1958 Jun;10(2):165–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]