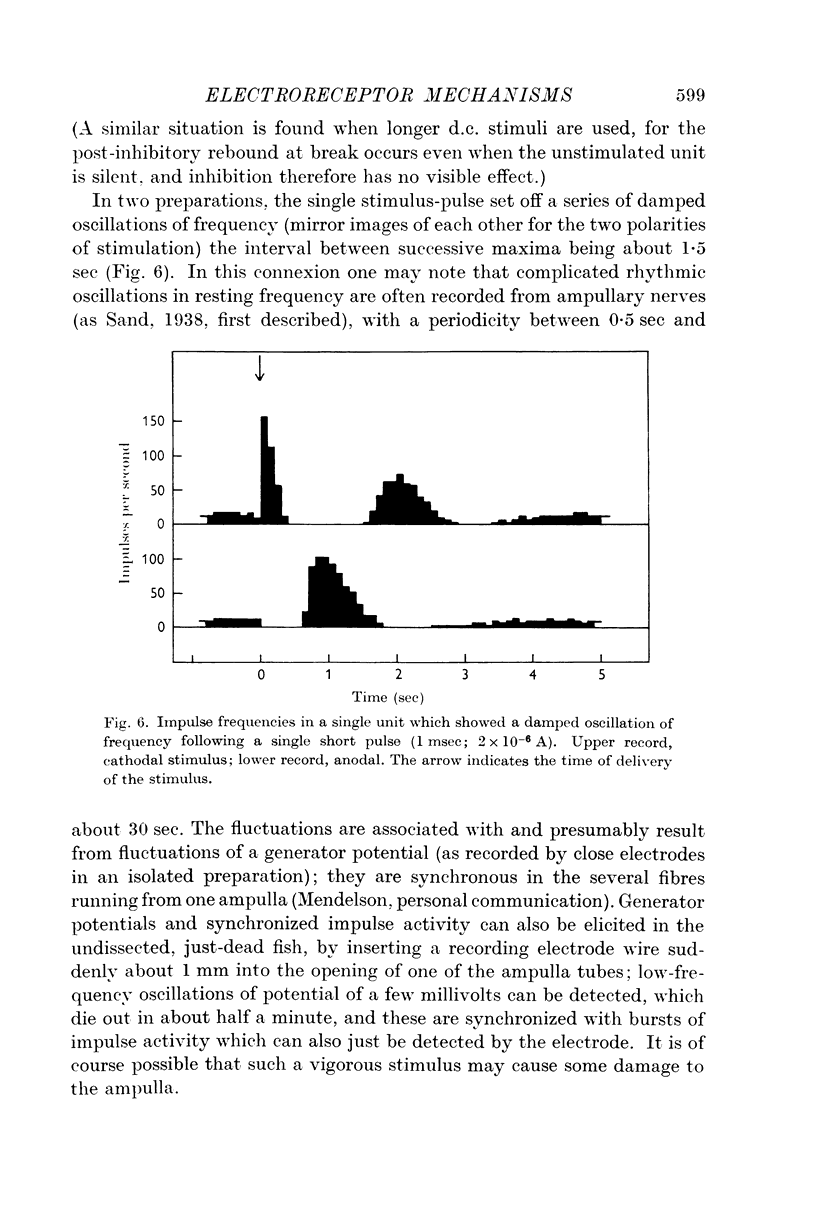
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DIJKGRAAF S. The functioning and significance of the lateral-line organs. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 1963 Feb;38:51–105. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1963.tb00654.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROEN J. J., LOWENSTEIN O., VENDRIK J. H. The mechanical analysis of the responses from the end-organs of the horizontal semicircular canal in the isolated elasmobranch labyrinth. J Physiol. 1952 Jul;117(3):329–346. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAGIWARA S., KUSANO K., NEGISHI K. Physiological properties of electroreceptors of some gymnotids. J Neurophysiol. 1962 May;25:430–449. doi: 10.1152/jn.1962.25.3.430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAGIWARA S., MORITA H. Coding mechanisms of electro-receptor fibers in some electric fish. J Neurophysiol. 1963 Jul;26:551–567. doi: 10.1152/jn.1963.26.4.551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATSUKI Y., YOSHINO S. Response of the single lateral-line nerve fiber to the linearly rising current stimulating the endorgan. Jpn J Physiol. 1952 Feb;2(3):219–231. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.2.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LISSMANN H. W., MACHIN K. E. ELECTRIC RECEPTORS IN A NON-ELECTRIC FISH (CLARIAS). Nature. 1963 Jul 6;199:88–89. doi: 10.1038/199088a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOEWENSTEIN W. R., ISHIKO N. Sodium chloride sensitivity and electrochemical effects in a Lorenzinian ampulla. Nature. 1962 Apr 21;194:292–294. doi: 10.1038/194292b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOEWENSTEIN W. R. Mechanisms of nerve impulse initiation in a pressure receptor (Lorenzinian ampulla). Nature. 1960 Dec 17;188:1034–1035. doi: 10.1038/1881034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MULLINGER A. M. THE FINE STRUCTURE OF AMPULLARY ELECTRIC RECEPTORS IN AMIURUS. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1964 Sep 29;160:345–359. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1964.0044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURRAY R. W. The response of the ampullae of Lorenzini of elasmobranchs to electrical stimulation. J Exp Biol. 1962 Mar;39:119–128. doi: 10.1242/jeb.39.1.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURRAY R. W. The response of the ampullae of Lorenzini to combined stimulation by temperature change and weak direct currents. J Physiol. 1959 Jan 28;145(1):1–13. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURRAY R. W. The response of the lateralis organs of Xenopus laevis to electrical stimulation by direct current. J Physiol. 1956 Nov 28;134(2):408–420. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


