Abstract
1. Drugs have been applied micro-electrophoretically to units in the hippocampal cortex of the anaesthetized cat, and their effects on cell firing were recorded simultaneously.
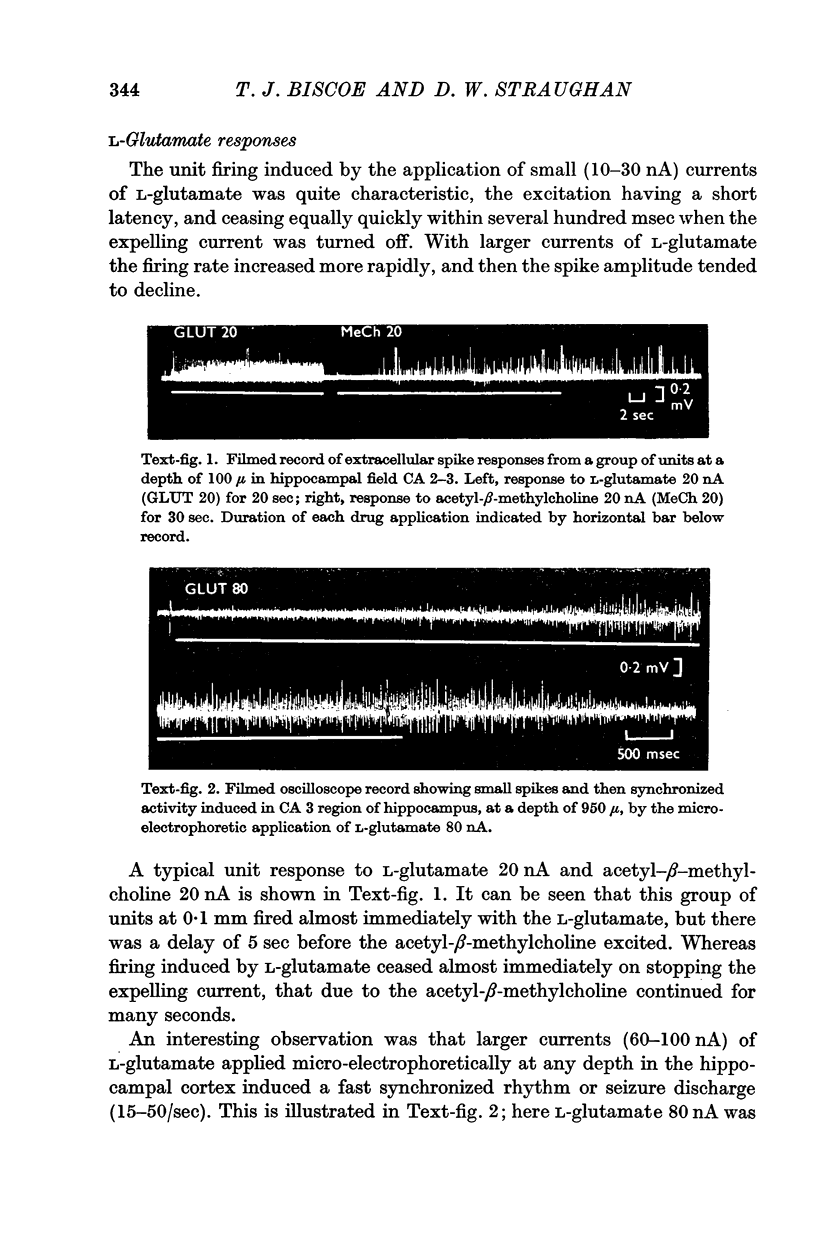
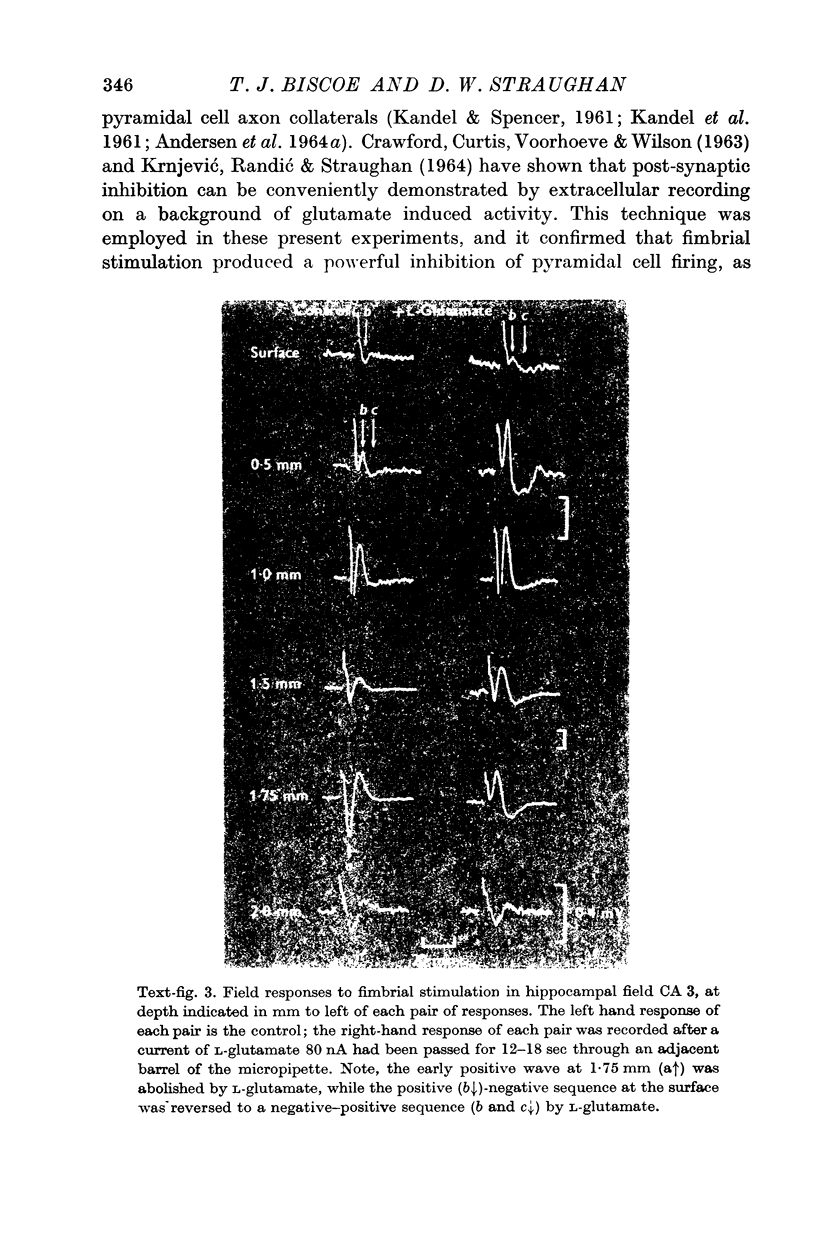
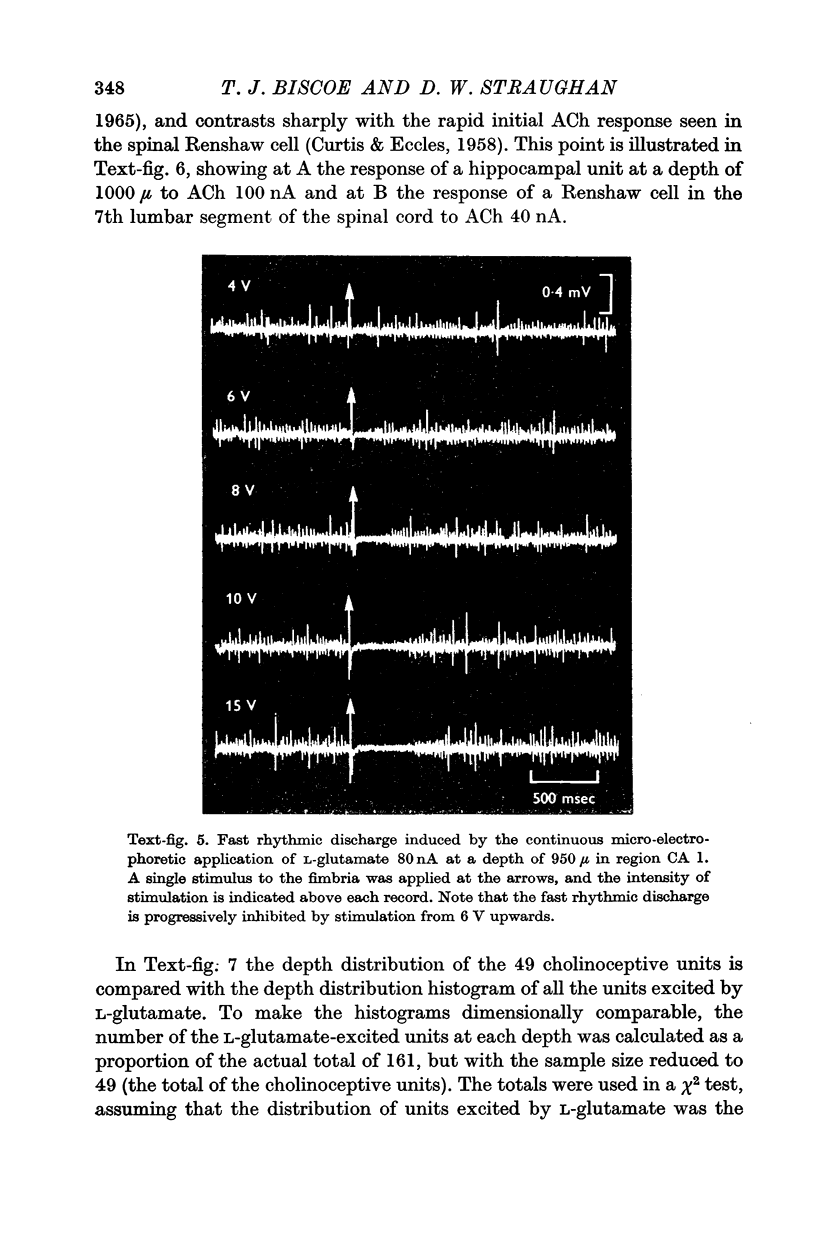
2. L-Glutamate rapidly and powerfully excited hippocampal units, an effect which was quickly reversed on stopping the expelling current. The local application of L-glutamate also excited a fast seizure discharge at 15-50/sec. Both these effects of L-glutamate were strongly depressed by fimbrial stimulation.
3. γ-Aminobutyric acid had a strong depressant action on all the units on which it was tested; the time course of this effect was rapid.
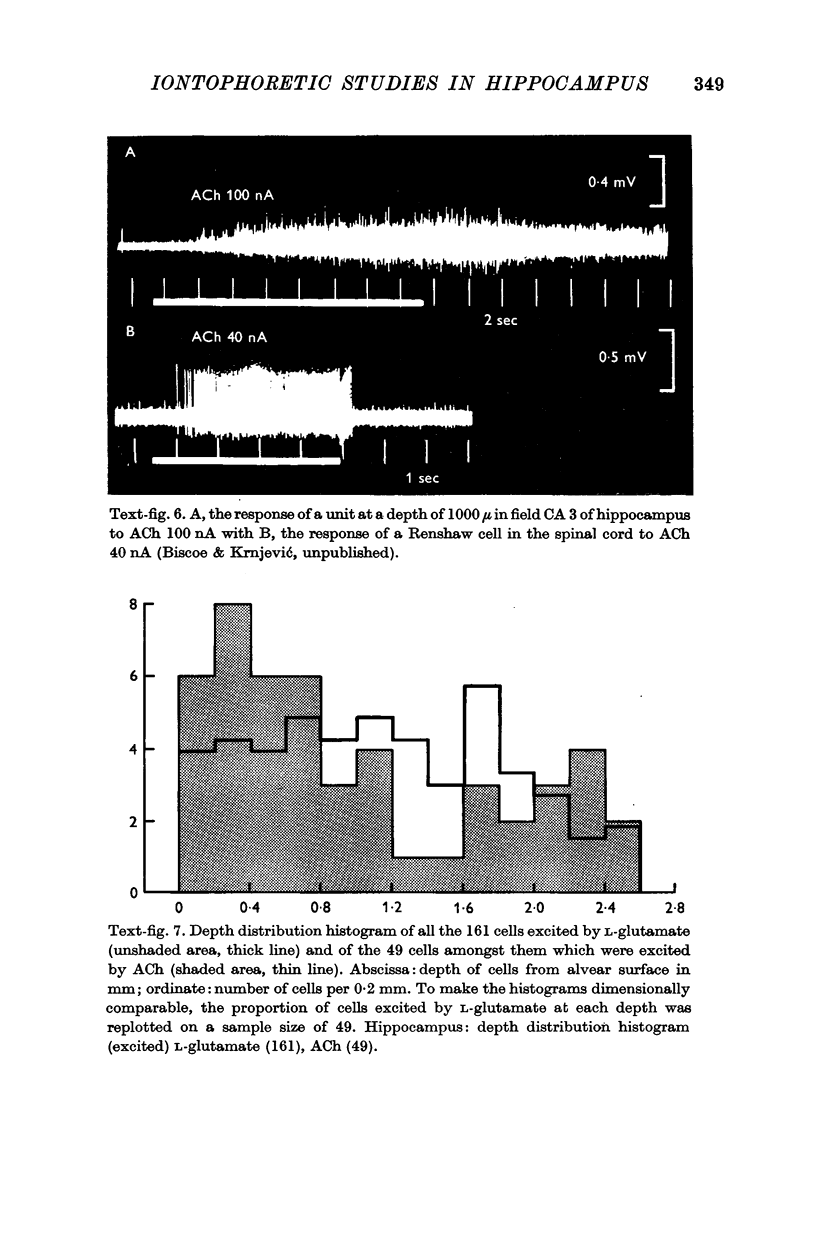
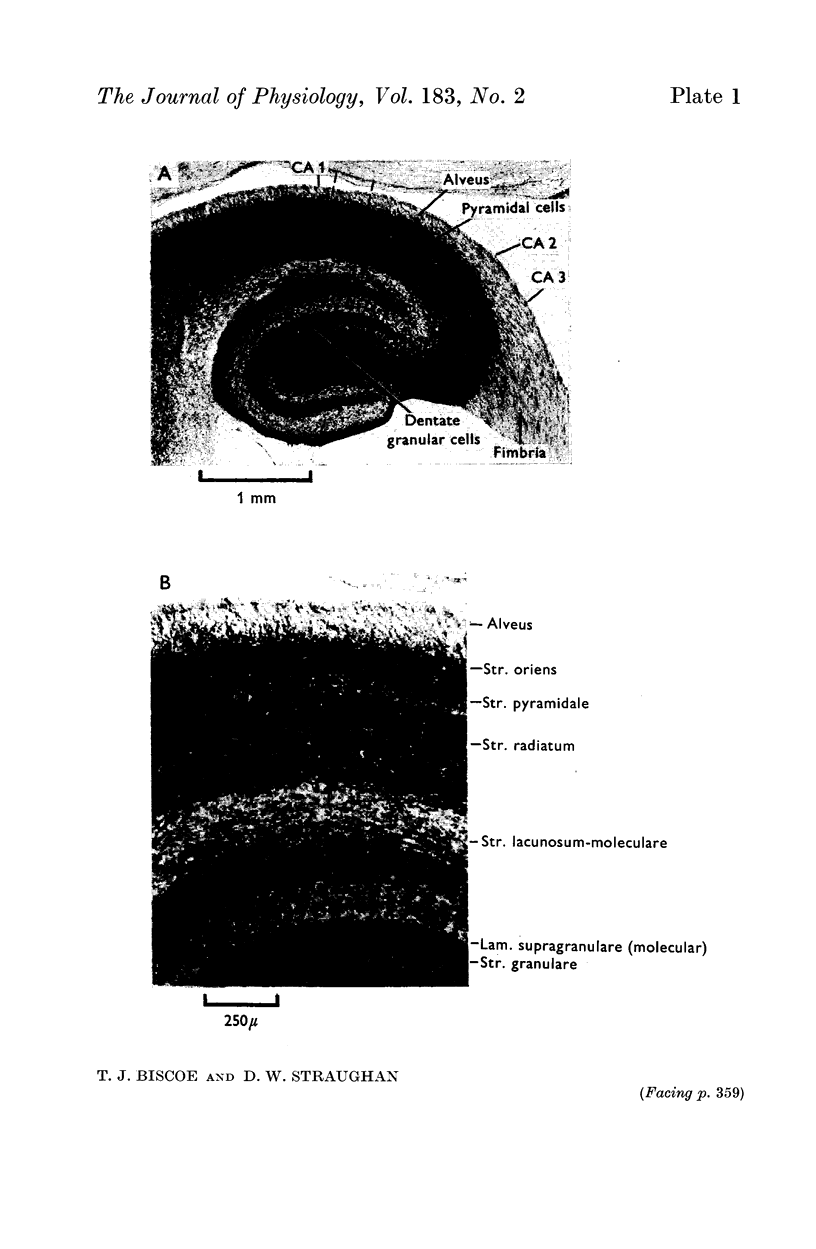
4. ACh excited half the units to which it was applied. Characteristically this excitation developed slowly over many seconds and persisted after stopping the expelling current. Most cholinoceptive units were found to be concentrated in the superficial layer of the cortex corresponding to the hippocampal pyramidal cells and their main dendritic processes.
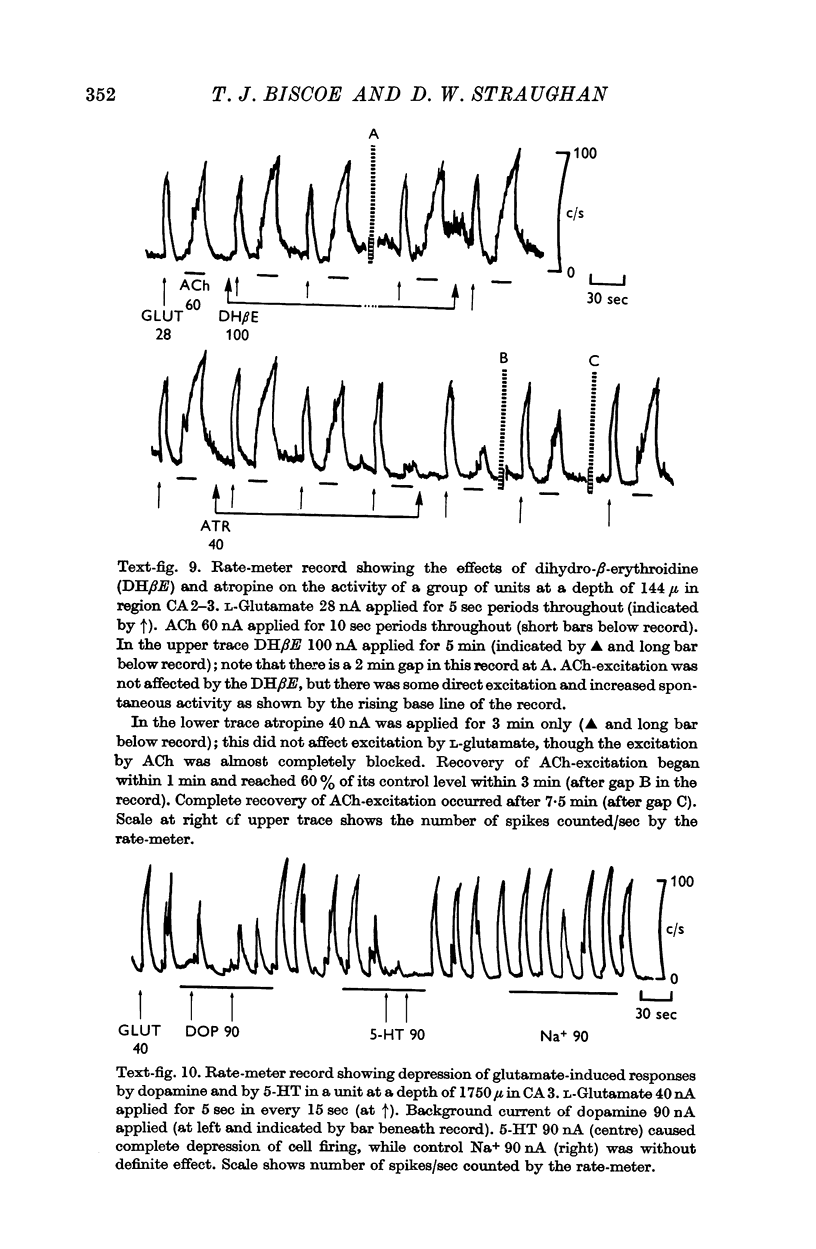
5. Atropine selectively blocked the excitation of cholinoceptive units by ACh, but not the excitation by L-glutamate. No cholinoceptive units were blocked by dihydro-β-erythroidine, though several were selectively blocked by dimethyl (+)-tubocurarine.
6. The most usual effect seen with 5-HT was depression, though several units were found to be excited. Some of the units tested with 3-hydroxytyramine (dopamine) or noradrenaline were found to be depressed.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSEN P., CURTIS D. R. THE EXCITATION OF THALAMIC NEURONES BY ACETYLCHOLINE. Acta Physiol Scand. 1964 May-Jun;61:85–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1964.tb02945.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANDERSEN P., CURTIS D. R. THE PHARMACOLOGY OF THE SYNAPTIC AND ACETYLCHOLINE-INDUCED EXCITATION OF VENTROBASAL THALAMIC NEURONES. Acta Physiol Scand. 1964 May-Jun;61:100–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1964.tb02946.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANDERSEN P., ECCLES J. C., LOYNING Y. LOCATION OF POSTSYNAPTIC INHIBITORY SYNAPSES ON HIPPOCAMPAL PYRAMIDS. J Neurophysiol. 1964 Jul;27:592–607. doi: 10.1152/jn.1964.27.4.592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANDERSEN P., ECCLES J. C., LOYNING Y. PATHWAY OF POSTSYNAPTIC INHIBITION IN THE HIPPOCAMPUS. J Neurophysiol. 1964 Jul;27:608–619. doi: 10.1152/jn.1964.27.4.608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANDERSEN P. Interhippocampal impulses. I. Origin, course and distribution in cat, rabbit and rat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1959 Sep 30;47:63–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1960.tb01821.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANDERSEN P. Interhippocampal impulses. II. Apical dendritic activation of CAI neurons. Acta Physiol Scand. 1960 Mar 18;48:178–208. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1960.tb01858.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BISCOE T. J., STRAUGHAN D. W. THE PHARMACOLOGY OF HIPPOCAMPAL NEURONES. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1965 Jan;17:60–61. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1965.tb07571.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADLEY P. B., NICHOLSON A. N. The effect of some drugs on hippocampal arousal. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1962 Dec;14:824–834. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(62)90132-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADLEY P. B., WOLSTENCROFT J. H. ACTIONS OF DRUGS ON SINGLE NEURONES IN THE BRAIN-STEM. Br Med Bull. 1965 Jan;21:15–18. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROOKS D. C. Rhinencephalic spikes and beta waves in the cat under pentobarbital. Am J Physiol. 1962 Jun;202:1221–1229. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1962.202.6.1221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRUECKE F., GOGOLAK G., STUMPF C. [Microelectrode examination of the stimulus response and cell activity in the hippocampus during septum stimulation]. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1963;276:456–470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANG H. T. Similarity in action between curare and strychnine on cortical neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1953 May;16(3):221–233. doi: 10.1152/jn.1953.16.3.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COSTA E., PSCHEIDT G. R., VAN METER W. G., HIMWICH H. E. Brain concentrations of biogenic amines and EEG paterns of rabbits. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1960 Sep;130:81–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COSTA E., RINALDI F. Biochemical and electroencephalographic changes in the brain of rabbits injected with 5-hydroxytryptophan (influence of chlorpromazine premedication). Am J Physiol. 1958 Jul;194(1):214–220. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1958.194.1.214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAWFORD J. M., CURTIS D. R. THE EXCITATION AND DEPRESSION OF MAMMALIAN CORTICAL NEURONES BY AMINO ACIDS. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1964 Oct;23:313–329. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1964.tb01589.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAWFORD J. M., CURTIS D. R., VOORHOEVE P. E., WILSON V. J. STRYCHNINE AND CORTICAL INHIBITION. Nature. 1963 Nov 30;200:845–846. doi: 10.1038/200845a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R., ECCLES R. M. The excitation of Renshaw cells by pharmacological agents applied electrophoretically. J Physiol. 1958 May 28;141(3):435–445. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp005987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R., RYALL R. W. NICOTINIC AND MUSCARINIC RECEPTORS OF RENSHAW CELLS. Nature. 1964 Aug 8;203:652–653. doi: 10.1038/203652a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELDBERG W., MALCOLM J. Experiments on the site of action of tubocurarine when applied via the cerebral ventricles. J Physiol. 1959 Dec;149:58–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN J. D., ARDUINI A. A. Hippocampal electrical activity in arousal. J Neurophysiol. 1954 Nov;17(6):533–557. doi: 10.1152/jn.1954.17.6.533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN J. D. THE HIPPOCAMPUS. Physiol Rev. 1964 Oct;44:561–608. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1964.44.4.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEBB C. O., SILVER A. Choline acetylase in the central nervous system of man and some other mammals. J Physiol. 1956 Dec 28;134(3):718–728. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANDEL E. R., SPENCER W. A., BRINLEY F. J., Jr Electrophysiology of hippocampal neurons. I. Sequential invasion and synaptic organization. J Neurophysiol. 1961 May;24:225–242. doi: 10.1152/jn.1961.24.3.225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANDEL E. R., SPENCER W. A. Electrophysiology of hippocampal neurons. II. After-potentials and repetitive firing. J Neurophysiol. 1961 May;24:243–259. doi: 10.1152/jn.1961.24.3.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRNJEVIC K., PHILLIS J. W. Acetylcholine-sensitive cells in the cerebral cortex. J Physiol. 1963 Apr;166:296–327. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRNJEVIC K., PHILLIS J. W. Iontophoretic studies of neurones in the mammalian cerebral cortex. J Physiol. 1963 Feb;165:274–304. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRNJEVIC K., RANDIC M., STRAUGHAN D. W. CORTICAL INHIBITION. Nature. 1964 Mar 28;201:1294–1296. doi: 10.1038/2011294a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Phillis J. W. Pharmacological properties of acetylcholine-sensitive cells in the cerebral cortex. J Physiol. 1963 May;166(2):328–350. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Silver A. A histochemical study of cholinergic fibres in the cerebral cortex. J Anat. 1965 Oct;99(Pt 4):711–759. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACLEAN P. D. Chemical and electrical stimulation of hippocampus in unrestrained animals. I. Methods and electroencephalographic findings. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1957 Aug;78(2):113–127. doi: 10.1001/archneurpsyc.1957.02330380003001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATHISEN J. S., BLACKSTAD T. W. CHOLINESTERASE IN THE HIPPOCAMPAL REGION. DISTRIBUTION AND RELATION TO ARCHITECTONICS AND AFFERENT SYSTEMS. Acta Anat (Basel) 1964;56:216–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORLOCK N., WARD A. A., Jr The effects of curare on cortical activity. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1961 Feb;13:60–67. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(61)90075-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCance I., Phillis J. W. The action of acetylcholine on cells in cat cerebellar cortex. Experientia. 1964 Apr 15;20(4):217–218. doi: 10.1007/BF02135411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAASONEN M. K., MACLEAN P. D., GIARMAN N. J. 5-Hydroxytryptamine (serotonin, enteramine) content of structures of the limbic system. J Neurochem. 1957;1(4):326–333. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1957.tb12089.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RECH R. H., DOMINO E. F. Effects of various drugs on activity of the neuronally isolated cerebral cortex. Exp Neurol. 1960 Aug;2:364–378. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(60)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHUTE C. C., LEWIS P. R. CHOLINESTERASE-CONTAINING SYSTEMS OF THE BRAIN OF THE RAT. Nature. 1963 Sep 21;199:1160–1164. doi: 10.1038/1991160a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STUMPF C., PETSCHE H., GOGOLAK G. The significance of the rabbit's septum as a relay station between the midbrain and the hippocampus. II. The differential influence of drugs upon both the septal cell firing pattern and the hippocampus theta activity. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1962 Apr;14:212–219. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(62)90031-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stumpf C. Drug action on the electrical activity of the hippocampus. Int Rev Neurobiol. 1965;8:77–138. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7742(08)60756-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillie J. A Contribution to the Pharmacology of Curare and its Alkaloids: Part I. J Anat Physiol. 1890 Apr;24(Pt 3):379–406. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UDENFRIEND S., WEISSBACH H., BOGDANSKI D. F. Biochemical findings relating to the action of serotonin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1957 Mar 14;66(3):602–608. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1957.tb40750.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]