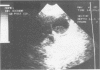
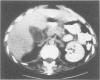
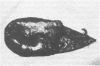
Abstract
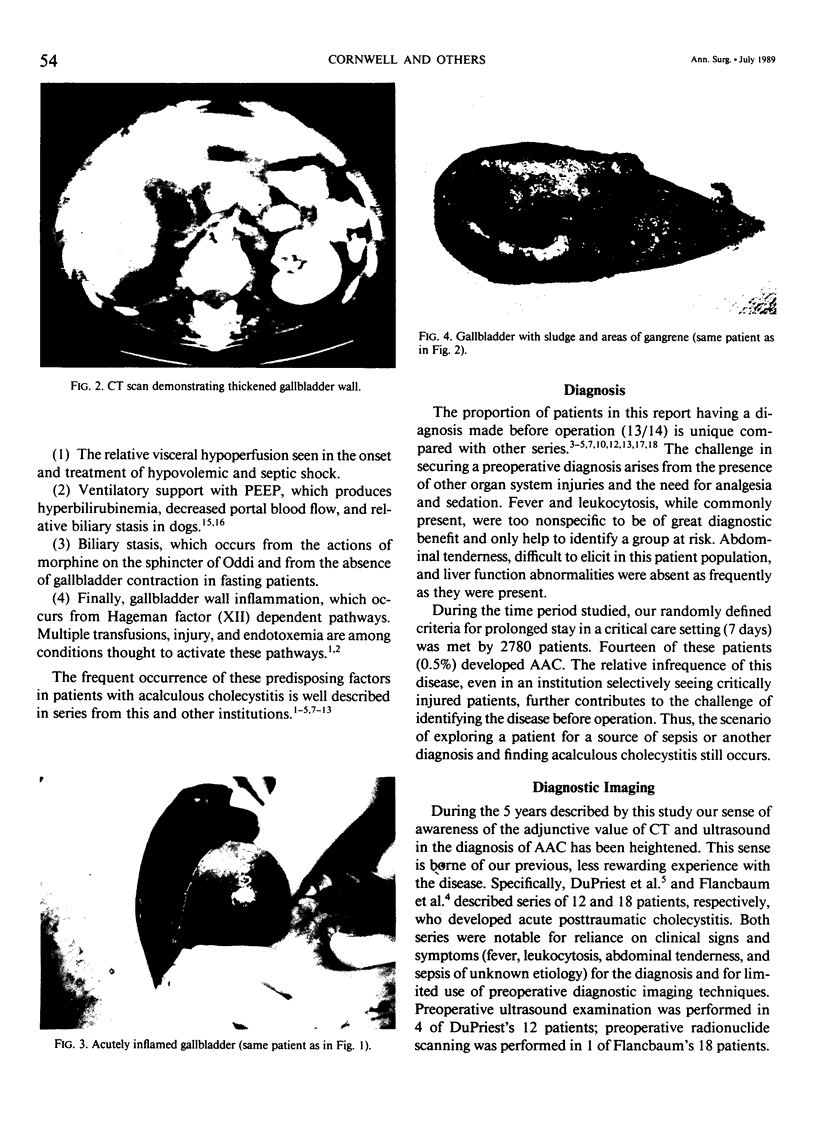
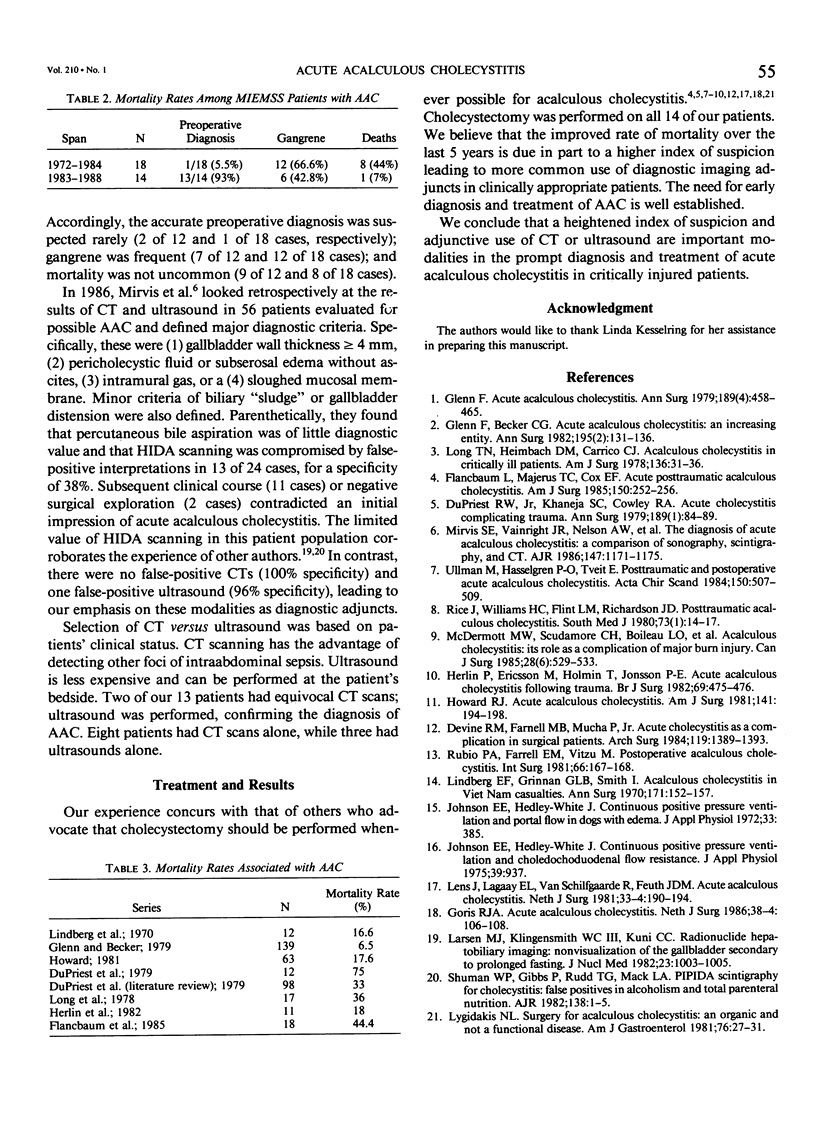
The potential lethality and predisposing factors of acute acalculous cholecystitis (AAC) are well established; however, preoperative diagnosis remains a challenge. This update of a previous report of 30 cases of AAC at a Level I trauma center describes 14 multiply injured patients who developed AAC and underwent cholecystectomy. All 14 patients had acutely inflamed gallbladders; 6 (42.8%) had areas of necrosis or gangrene. The mortality rate was 7% (1 patient). While the percentage of patients receiving prolonged intensive care (100%), narcotic analgesics (100%), and TPN (93%) correlates with the experience cited previously, the percentage undergoing preoperative diagnostic imaging is unusually high, reflecting a heightened suspicion for AAC. Computed tomographic or sonographic evidence of gallbladder wall thickness greater than or equal to 4 mm, pericholecystic fluid or subserosal edema without ascites, intramural gas, or a sloughed mucosal membrane was considered diagnostic criteria for AAC. We conclude that preoperative computed tomogram or ultrasound imaging leads to earlier recognition of this life-threatening problem.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Devine R. M., Farnell M. B., Mucha P., Jr Acute cholecystitis as a complication in surgical patients. Arch Surg. 1984 Dec;119(12):1389–1393. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1984.01390240027005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuPriest R. W., Jr, Khaneja S. C., Cowley R. A. Acute cholecystitis complicating trauma. Ann Surg. 1979 Jan;189(1):84–89. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197901000-00016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flancbaum L., Majerus T. C., Cox E. F. Acute posttraumatic acalculous cholecystitis. Am J Surg. 1985 Aug;150(2):252–256. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(85)90131-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn F. Acute acalculous cholecystitis. Ann Surg. 1979 Apr;189(4):458–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn F., Becker C. G. Acute acalculous cholecystitis. An increasing entity. Ann Surg. 1982 Feb;195(2):131–136. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198202000-00002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goris R. J. Acute acalculous cholecystitis. Neth J Surg. 1986 Aug;38(4):106–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herlin P., Ericsson M., Holmin T., Jönsson P. E. Acute acalculous cholecystitis following trauma. Br J Surg. 1982 Aug;69(8):475–476. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800690815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard R. J. Acute acalculous cholecystitis. Am J Surg. 1981 Feb;141(2):194–198. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(81)90155-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. E., Hedley-Whyte J. Continuous positive-pressure ventilation and choledochoduodenal flow resistance. J Appl Physiol. 1975 Dec;39(6):937–942. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1975.39.6.937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. E., Hedley-Whyte J. Continuous positive-pressure ventilation and portal flow in dogs with pulmonary edema. J Appl Physiol. 1972 Sep;33(3):385–389. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1972.33.3.385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen M. J., Klingensmith W. C., 3rd, Kuni C. C. Radionuclide hepatobiliary imaging: nonvisualization of the gallbladder secondary to prolonged fasting. J Nucl Med. 1982 Nov;23(11):1003–1005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lens J., Lagaay E. L., van Schilfgaarde R., Feuth J. D. Acute acalculous cholecystitis. Neth J Surg. 1981 Oct;33(4):190–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg E. F., Grinnan G. L., Smith L. Acalculous cholecystitis in Viet Nam casualties. Ann Surg. 1970 Jan;171(1):152–157. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197001000-00022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long T. N., Heimbach D. M., Carrico C. J. Acalculous cholecystitis in critically ill patients. Am J Surg. 1978 Jul;136(1):31–36. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(78)90196-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lygidakis N. J. Surgery for acalculous cholecystitis. An organic and not a functional disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 1981 Jul;76(1):27–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDermott M. W., Scudamore C. H., Boileau L. O., Snelling C. F., Kramer T. A. Acalculous cholecystitis: its role as a complication of major burn injury. Can J Surg. 1985 Nov;28(6):529–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirvis S. E., Vainright J. R., Nelson A. W., Johnston G. S., Shorr R., Rodriguez A., Whitley N. O. The diagnosis of acute acalculous cholecystitis: a comparison of sonography, scintigraphy, and CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1986 Dec;147(6):1171–1175. doi: 10.2214/ajr.147.6.1171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice J., Williams H. C., Flint L. M., Richardson J. D. Posttraumatic acalculous cholecystitis. South Med J. 1980 Jan;73(1):14–17. doi: 10.1097/00007611-198001000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman W. P., Gibbs P., Rudd T. G., Mack L. A. PIPIDA scintigraphy for cholecystitis: false positives in alcoholism and total parenteral nutrition. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1982 Jan;138(1):1–5. doi: 10.2214/ajr.138.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullman M., Hasselgren P. O., Tveit E. Posttraumatic and postoperative acute acalculous cholecystitis. Acta Chir Scand. 1984;150(6):507–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]