Abstract
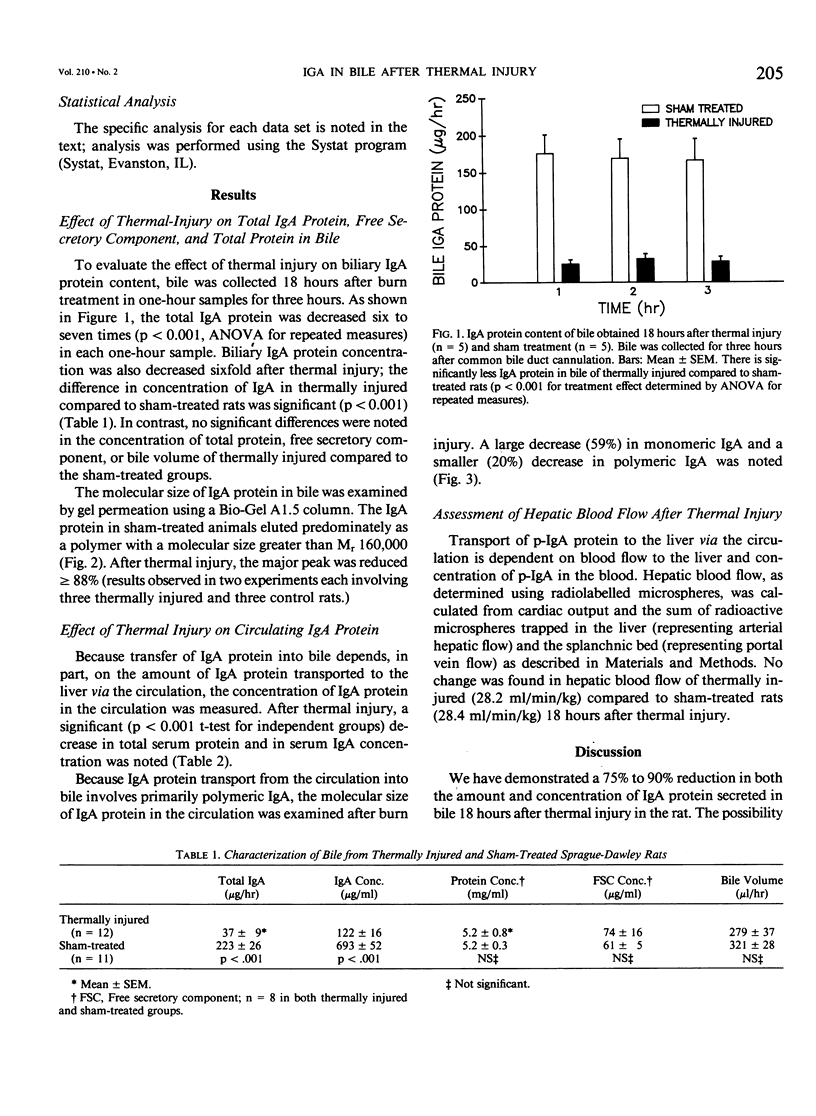
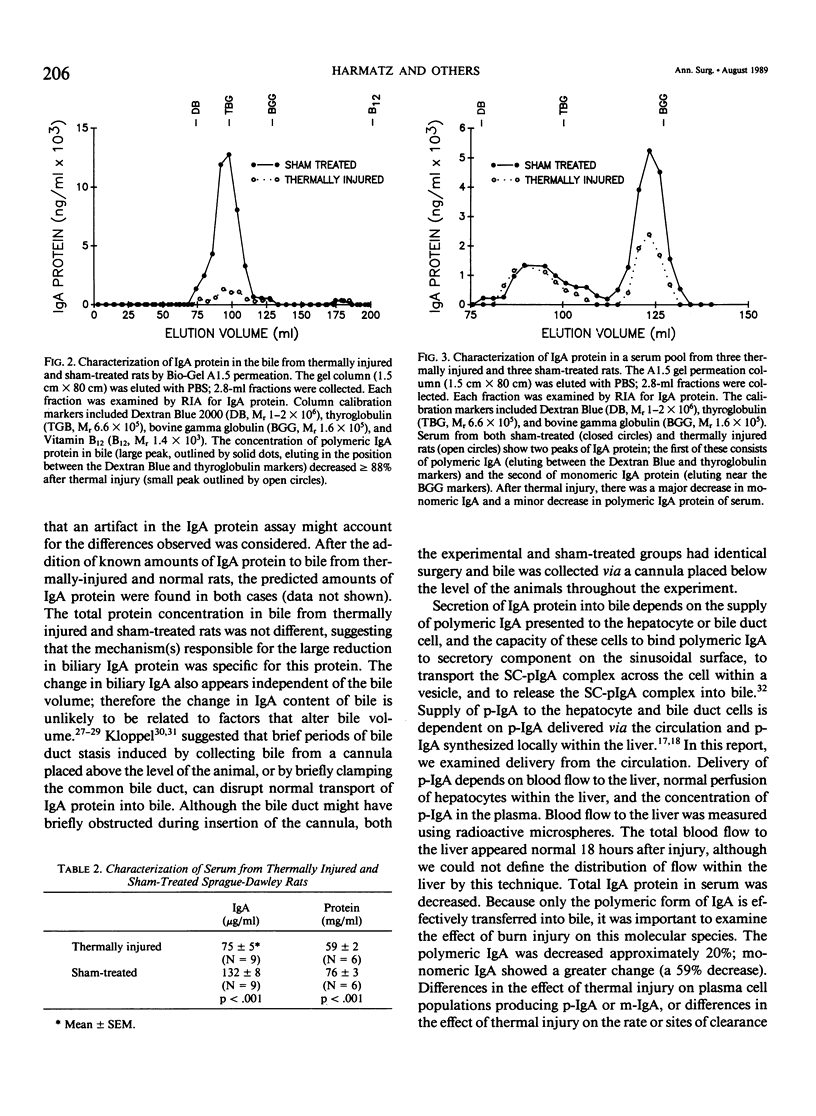
Severe thermal injury is associated with bacterial sepsis; the intestine is considered a likely source of invasive organisms. Because IgA antibody in bile accounts for much of the specific immune defense of the upper intestinal tract in the rat, the effect of thermal injury on the quantity of IgA protein in bile was examined. Sprague-Dawley rats received a 20% to 30% body surface area burn under anesthesia. Eighteen hours later the common bile duct was cannulated and bile was collected for three hours. Total IgA protein in bile decreased 90% after thermal injury. The bile volume, the concentration of bile protein, and free secretory component did not change significantly. Although blood flow to the liver 18 hours after thermal injury was not changed, there was a significant reduction in total IgA concentration in the circulation; both monomeric (m-IgA) and polymeric IgA (p-IgA) were decreased. This finding may explain, in part, the reduced concentration of IgA protein in bile. Although not examined in this study, decreased local hepatic synthesis and/or transport of p-IgA across the hepatocyte may also contribute to the reduced IgA levels in bile.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altorfer J., Hardesty S. J., Scott J. H., Jones A. L. Specific antibody synthesis and biliary secretion by the rat liver after intestinal immunization with cholera toxin. Gastroenterology. 1987 Sep;93(3):539–549. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90917-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg R. D. Inhibition of Escherichia coli translocation from the gastrointestinal tract by normal cecal flora in gnotobiotic or antibiotic-decontaminated mice. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):1073–1081. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.1073-1081.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blitzer B. L., Boyer J. L. Cellular mechanisms of bile formation. Gastroenterology. 1982 Feb;82(2):346–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael F. J., Saldivia V., Israel Y., McKaigney J. P., Orrego H. Ethanol-induced increase in portal hepatic blood flow: interference by anesthetic agents. Hepatology. 1987 Jan-Feb;7(1):89–94. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840070119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter E. A., Udall J. N., Kirkham S. E., Walker W. A. Thermal injury and gastrointestinal function. I. Small intestinal nutrient absorption and DNA synthesis. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1986 Nov-Dec;7(6):469–474. doi: 10.1097/00004630-198611000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curreri P. W., Luterman A., Braun D. W., Jr, Shires G. T. Burn injury. Analysis of survival and hospitalization time for 937 patients. Ann Surg. 1980;192(4):472–478. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198010000-00006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deitch E. A., Berg R. Bacterial translocation from the gut: a mechanism of infection. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1987 Nov-Dec;8(6):475–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlinger S. Hepatocyte bile secretion: current views and controversies. Hepatology. 1981 Jul-Aug;1(4):352–359. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840010413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher M. M., Nagy B., Bazin H., Underdown B. J. Biliary transport of IgA: role of secretory component. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):2008–2012. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardison W. G., Wood C. A. Importance of bicarbonate in bile salt independent fraction of bile flow. Am J Physiol. 1978 Aug;235(2):E158–E164. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.235.2.E158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartford C. E. The bequests of Moncrief and Moyer: an appraisal of topical therapy of burns- 1981 American Burn Association Presidential Address. J Trauma. 1981 Oct;21(10):827–834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartree E. F. Determination of protein: a modification of the Lowry method that gives a linear photometric response. Anal Biochem. 1972 Aug;48(2):422–427. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90094-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson G. D., Lemaître-Coelho I., Vaerman J. P., Bazin H., Beckers A. Rapid disappearance from serum of intravenously injected rat myeloma IgA and its secretion into bile. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Feb;8(2):123–126. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloppel T. M., Hoops T. C., Brown W. R. Advances in the cellular mechanisms of secretory component synthesis and secretion and the transport of IgA. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1987;216B:1061–1069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloppel T. M., Hoops T. C., Gaskin D., Le M. Uncoupling of the secretory pathways for IgA and secretory component by cholestasis. Am J Physiol. 1987 Aug;253(2 Pt 1):G232–G240. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1987.253.2.G232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaitre-Coelho I., Jackson G. D., Vaerman J. P. Relevance of biliary IgA antibodies in rat intestinal immunity. Scand J Immunol. 1978;8(5):459–463. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00542.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maejima K., Deitch E. A., Berg R. D. Bacterial translocation from the gastrointestinal tracts of rats receiving thermal injury. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):6–10. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.6-10.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malik A. B., Kaplan J. E., Saba T. M. Reference sample method for cardiac output and regional blood flow determinations in the rat. J Appl Physiol. 1976 Mar;40(3):472–475. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1976.40.3.472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning R. J., Walker P. G., Carter L., Barrington P. J., Jackson G. D. Studies on the origins of biliary immunoglobulins in rats. Gastroenterology. 1984 Jul;87(1):173–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestecky J., Russell M. W., Jackson S., Brown T. A. The human IgA system: a reassessment. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1986 Jul;40(1):105–114. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(86)90073-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morehouse J. L., Specian R. D., Stewart J. J., Berg R. D. Translocation of indigenous bacteria from the gastrointestinal tract of mice after oral ricinoleic acid treatment. Gastroenterology. 1986 Sep;91(3):673–682. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90638-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlans E., Peppard J., Reynolds J., Hall J. Rapid active transport of immunoglobulin A from blood to bile. J Exp Med. 1978 Feb 1;147(2):588–592. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.2.588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens W. E., Berg R. D. Bacterial translocation from the gastrointestinal tract of athymic (nu/nu) mice. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):461–467. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.461-467.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quie P. G. "Walk-in" bacteremia. Pediatrics. 1976 Jun;57(6):827–828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan D. A., Allansmith M. R. Source of IgA in tears of rats. Immunology. 1984 Dec;53(4):791–799. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan D. A., Wira C. R. Variations in free secretory component levels in mucosal secretions of the rat. J Immunol. 1983 Mar;130(3):1330–1335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi I., Nakane P. K., Brown W. R. Ultrastructural events in the translocation of polymeric IgA by rat hepatocytes. J Immunol. 1982 Mar;128(3):1181–1187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Underdown B. J., Schiff J. M. Immunoglobulin A: strategic defense initiative at the mucosal surface. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:389–417. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.002133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker H. L., Mason A. D., Jr A standard animal burn. J Trauma. 1968 Nov;8(6):1049–1051. doi: 10.1097/00005373-196811000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


