Abstract
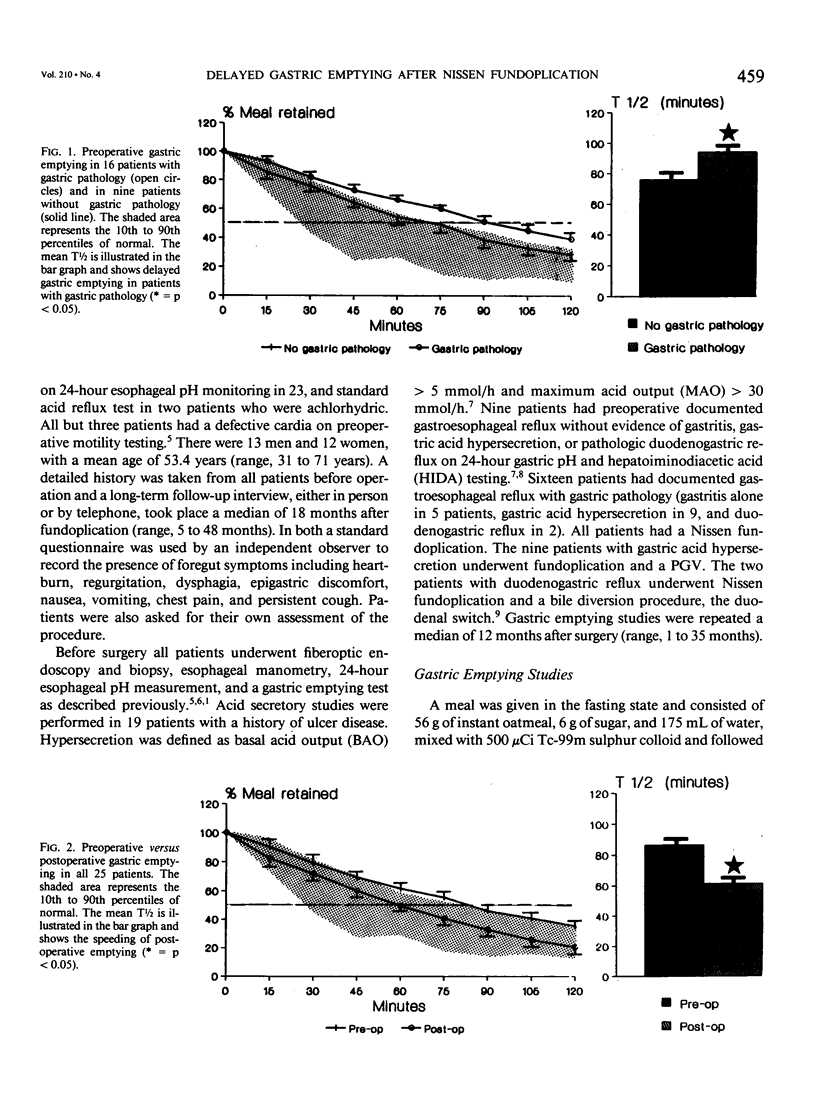
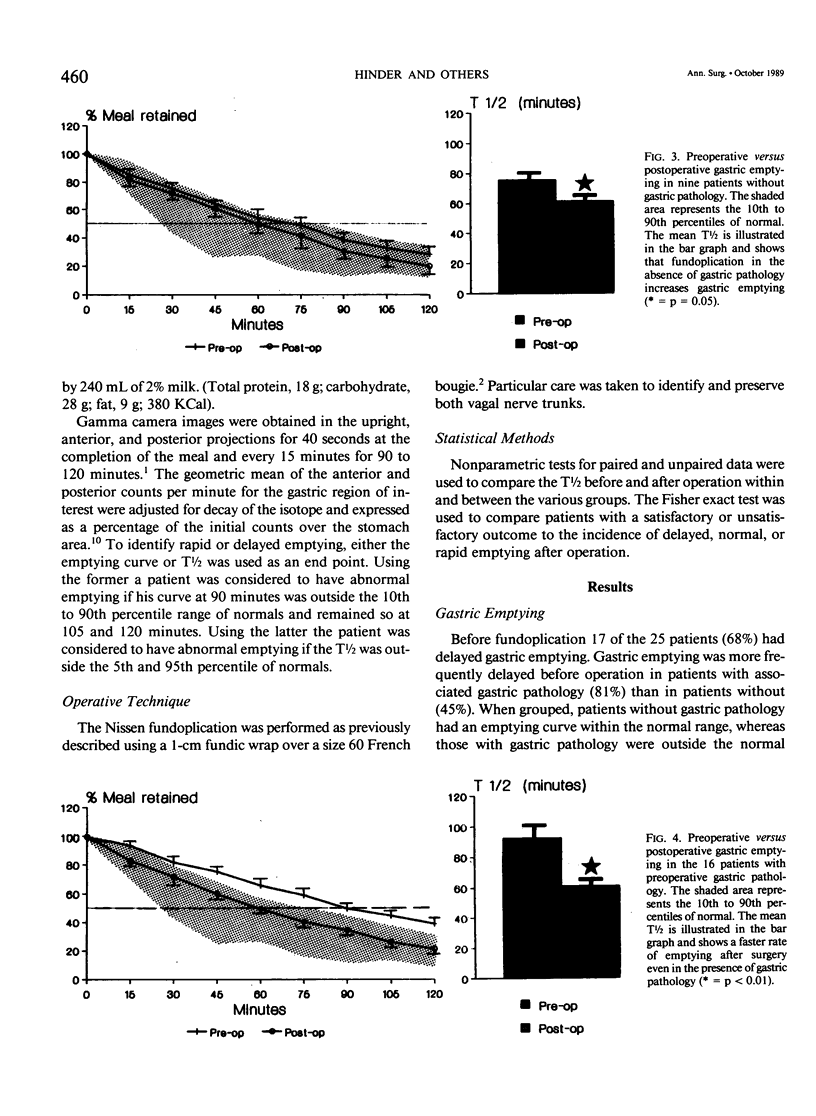
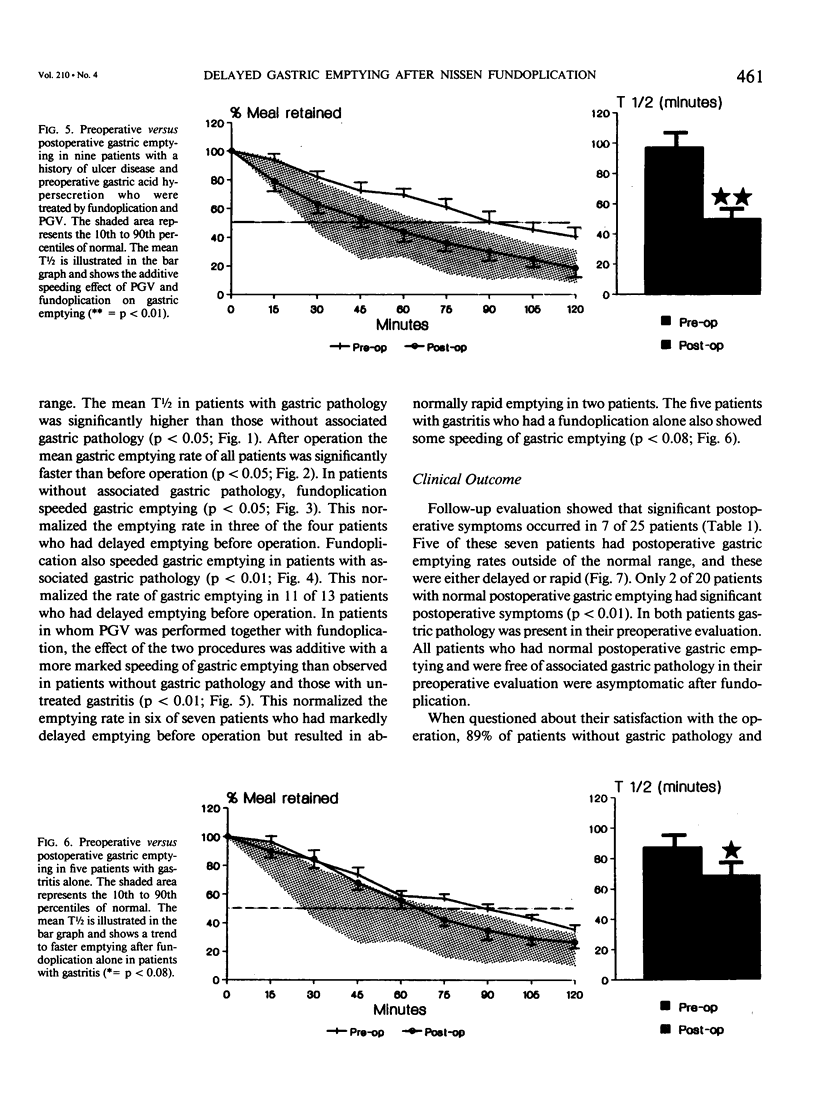
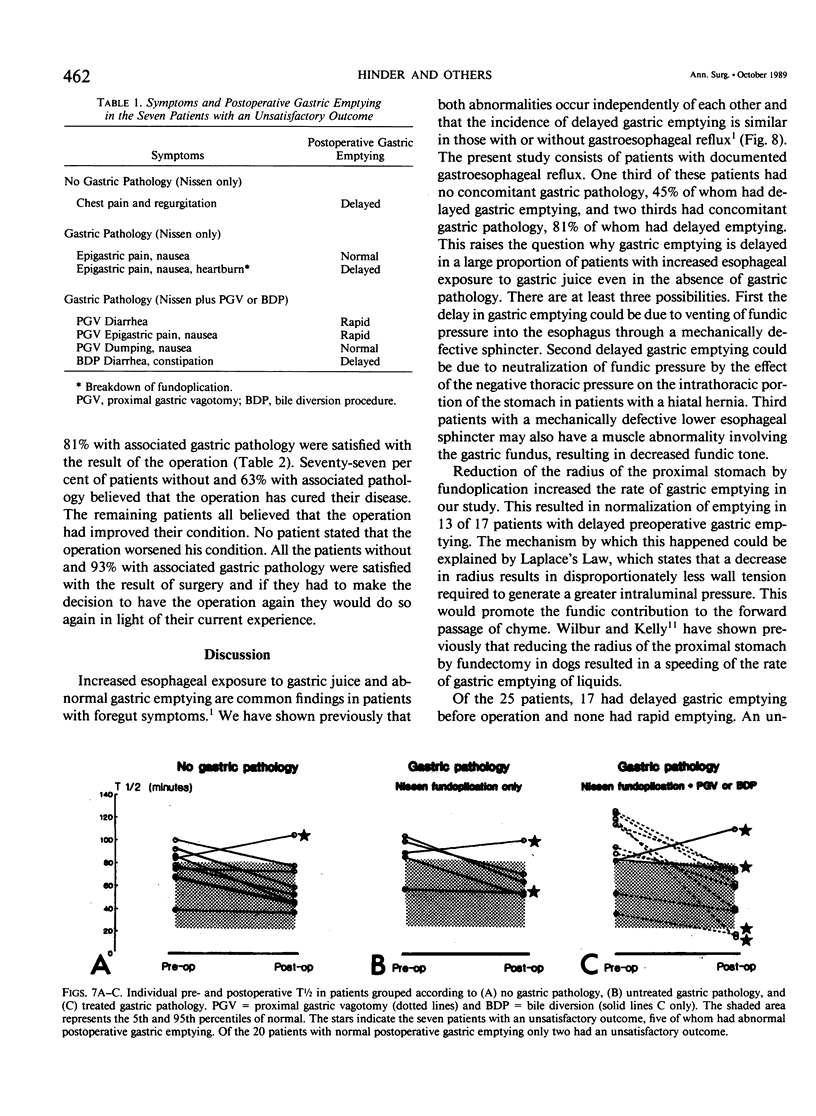
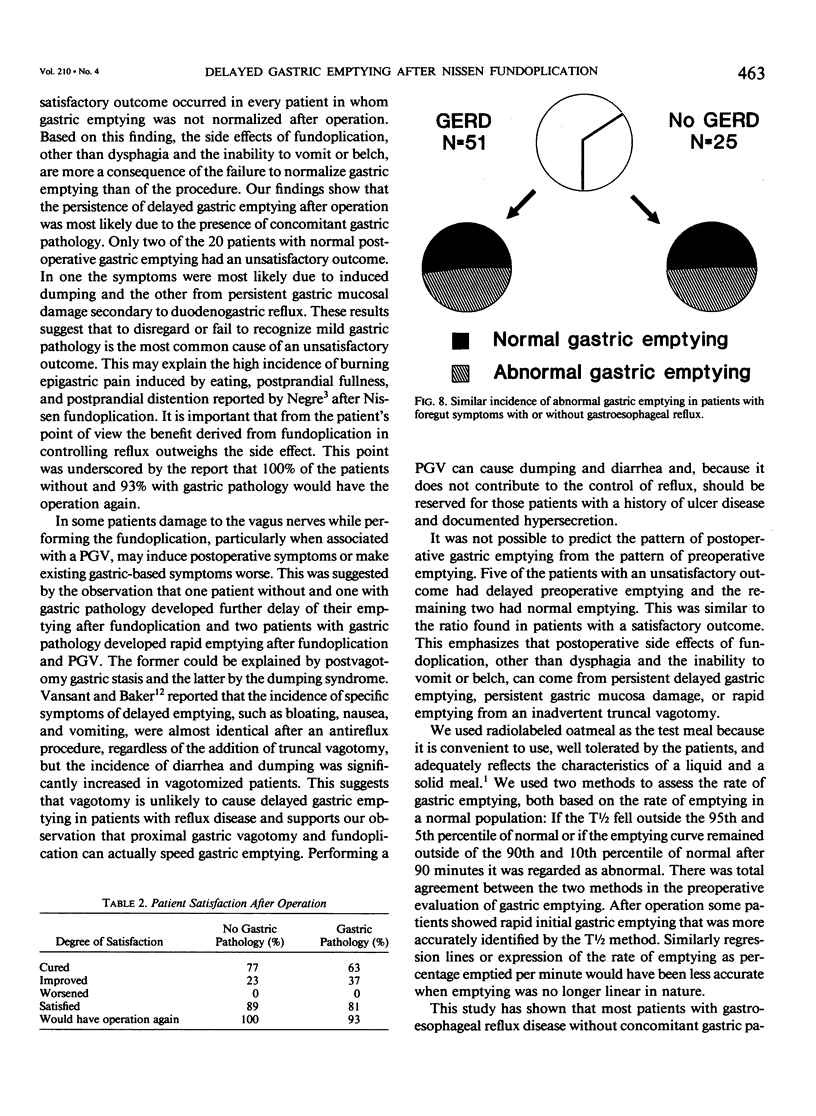
Delayed gastric emptying in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease may be due to an incompetent distal esophageal sphincter and/or a gastric abnormality. To determine the influence of the Nissen fundoplication on gastric emptying we studied the rate of gastric emptying before and after operation in 25 patients with proved gastroesophageal reflux disease. Nine patients had no gastric pathology, 9 had gastric acid hypersecretion, 5 had gastritis, and 2 had evidence of significant duodenogastric reflux. All were treated by Nissen fundoplication. Those with gastric acid hypersecretion also had a proximal gastric vagotomy (PGV) and the two patients with pathologic duodenogastric reflux were treated by a bile diversion procedure. We found that in gastroesophageal reflux disease with associated gastric pathology there was a higher prevalence of delayed gastric emptying before operation than in patients without gastric pathology. Nissen fundoplication was associated with speeding of gastric emptying in patients with or without gastric pathology. Proximal gastric vagotomy performed in association with Nissen fundoplication augmented the speeding of gastric emptying, which was advantagenous in most cases but detrimental in two. Every patient in whom gastric emptying was not normalized had postoperative symptoms. Only two of 20 patients with normal postoperative gastric emptying had postoperative symptoms. Both patients had preexisting gastric pathology. Based on these findings, the side effects associated with Nissen fundoplication are due to the failure to normalize gastric emptying rather than the operation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Christian P. E., Moore J. G., Sorenson J. A., Coleman R. E., Weich D. M. Effects of meal size and correction technique on gastric emptying time: studies with two tracers and opposed detectors. J Nucl Med. 1980 Sep;21(9):883–885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMeester T. R., Bonavina L., Albertucci M. Nissen fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Evaluation of primary repair in 100 consecutive patients. Ann Surg. 1986 Jul;204(1):9–20. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198607000-00002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMeester T. R., Fuchs K. H., Ball C. S., Albertucci M., Smyrk T. C., Marcus J. N. Experimental and clinical results with proximal end-to-end duodenojejunostomy for pathologic duodenogastric reflux. Ann Surg. 1987 Oct;206(4):414–426. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198710000-00003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMeester T. R., Wang C. I., Wernly J. A., Pellegrini C. A., Little A. G., Klementschitsch P., Bermudez G., Johnson L. F., Skinner D. B. Technique, indications, and clinical use of 24 hour esophageal pH monitoring. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1980 May;79(5):656–670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddern G. J., Jamieson G. G. Fundoplication enhances gastric emptying. Ann Surg. 1985 Mar;201(3):296–299. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198503000-00006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negre J. B. Post-fundoplication symptoms. Do they restrict the success of Nissen fundoplication? Ann Surg. 1983 Dec;198(6):698–700. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198312000-00005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwizer W., Hinder R. A., DeMeester T. R. Does delayed gastric emptying contribute to gastroesophageal reflux disease? Am J Surg. 1989 Jan;157(1):74–81. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(89)90422-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vansant J. H., Baker J. W., Jr Complications of vagotomy in the treatment of hiatal hernia. Ann Surg. 1976 Jun;183(6):629–635. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197606000-00003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilbur B. G., Kelly K. A. Effect of proximal gastric, complete gastric, and truncal vagotomy on canine gastric electric activity, motility, and emptying. Ann Surg. 1973 Sep;178(3):295–303. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197309000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaninotto G., DeMeester T. R., Schwizer W., Johansson K. E., Cheng S. C. The lower esophageal sphincter in health and disease. Am J Surg. 1988 Jan;155(1):104–111. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(88)80266-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


