Abstract
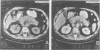
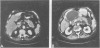
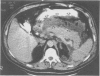
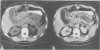
Parenchymal necrosis has recently been recognized as the principal determinant of the incidence of secondary infection in acute pancreatitis. Because secondary infection of pancreatic necrosis accounts for more than 80% of all deaths from acute pancreatitis, a method for determining the presence or absence of parenchymal necrosis would offer considerable prognostic and therapeutic information. Thirty seven patients with unequivocal acute pancreatitis and five normal controls were prospectively studied with intravenous bolus, contrast-enhanced computed tomography (dynamic pancreatography). In the absence of pancreatic necrosis, there were no significant differences in parenchymal enhancement between any of the following patient groups: controls (5), uncomplicated pancreatitis (20), pancreatic abscess (7), or peripancreatic necrosis (4)(p less than 0.05). On the other hand, pancreatic parenchymal enhancement was significantly reduced or absent in all six patients with segmental or diffuse pancreatic necrosis (p less than 0.05). Postcontrast pancreatic parenchymal enhancement was also found to be inversely correlated with the number of Ranson signs (p less than 0.001). Dynamic pancreatography offers prognostic information and is a safe and reliable technique for predicting the presence or absence of pancreatic parenchymal necrosis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. R., Spence R. A., Laird J. D., Ferguson W. R., Kennedy T. L. Indium-111 autologous leukocyte imaging in pancreatitis. J Nucl Med. 1986 Mar;27(3):345–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks P. A., Gerzof S. G., Sullivan J. G. Central cavitary necrosis: differentiation from pancreatic pseudocyst on CT scan. Pancreas. 1988;3(1):83–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker H., Vinten-Johansen J., Buckberg G. D., Bugyi H. I. Correlation of pancreatic blood flow and high-energy phosphates during experimental pancreatitis. Eur Surg Res. 1982;14(3):203–210. doi: 10.1159/000128290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beger H. G., Krautzberger W., Bittner R., Block S., Büchler Results of surgical treatment of necrotizing pancreatitis. World J Surg. 1985 Dec;9(6):972–979. doi: 10.1007/BF01655406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block S., Maier W., Bittner R., Büchler M., Malfertheiner P., Beger H. G. Identification of pancreas necrosis in severe acute pancreatitis: imaging procedures versus clinical staging. Gut. 1986 Sep;27(9):1035–1042. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.9.1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buggy B. P., Nostrant T. T. Lethal pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1983 Dec;78(12):810–814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büchler M., Malfertheiner P., Schoetensack C., Uhl W., Beger H. G. Sensitivity of antiproteases, complement factors and C-reactive protein in detecting pancreatic necrosis. Results of a prospective clinical study. Int J Pancreatol. 1986 Oct;1(3-4):227–235. doi: 10.1007/BF02795248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean P. B., Kormano M. Intra-arterial bolus of 125I labeled meglumine diatrizoate. Early extravascular distribution. Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh) 1977 Jul;18(4):425–432. doi: 10.1177/028418517701800408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulis A. K., Murray W. R., Galloway D., McCartney A. C., Lang E., Veitch J., Whaley K. Endotoxaemia and complement activation in acute pancreatitis in man. Gut. 1982 Aug;23(8):656–661. doi: 10.1136/gut.23.8.656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeny P. C. Computed tomography of the pancreas. Clin Gastroenterol. 1984 Sep;13(3):791–818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey C. F., Bradley E. L., 3rd, Beger H. G. Progress in acute pancreatitis. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1988 Oct;167(4):282–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodhead B. Acute pancreatitis and pancreatic blood flow. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1969 Aug;129(2):331–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollender L. F., Meyer C., Marrie A., Costa J. da S., Castellanos J. G. Role of surgery in the management of acute pancreatitis. World J Surg. 1981 May;5(3):361–368. doi: 10.1007/BF01657998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isikoff M. B., Hill M. C., Silverstein W., Barkin J. The clinical significance of acute pancreatic hemorrhage. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1981 Apr;136(4):679–684. doi: 10.2214/ajr.136.4.679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffrey R. B., Federle M. P., Cello J. P., Crass R. A. Early computed tomographic scanning in acute severe pancreatitis. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1982 Feb;154(2):170–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kivilaakso E., Lempinen M., Mäkeläinen A., Nikki P., Schröder T. Pancreatic resection versus peritoneal lavation for acute fulminant pancreatitis. A randomized prospective study. Ann Surg. 1984 Apr;199(4):426–431. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198404000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kivisaari L., Somer K., Standertskjöld-Nordenstam C. G., Schröder T., Kivilaakso E., Lempinen M. A new method for the diagnosis of acute hemorrhagic-necrotizing pancreatitis using contrast-enhanced CT. Gastrointest Radiol. 1984;9(1):27–30. doi: 10.1007/BF01887796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kivisaari L., Somer K., Standertskjöld-Nordenstam C. G., Schröder T., Kivilaakso E., Lempinen M. Early detection of acute fulminant pancreatitis by contrast-enhanced computed tomography. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1983 Jan;18(1):39–41. doi: 10.3109/00365528309181556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knol J. A., Edgcomb L. P., Inman M. G., Eckhauser F. E. Low molecular weight dextran in experimental pancreatitis: effects on pancreatic microcirculation. J Surg Res. 1983 Jul;35(1):73–82. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(83)90128-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson T. L. Acute pancreatitis and its complications. Computed tomography and sonography. Radiol Clin North Am. 1983 Sep;21(3):495–513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leger L., Chiche B., Louvel A. Pancreatic necrosis and acute pancreatitis. World J Surg. 1981 May;5(3):315–317. doi: 10.1007/BF01657985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon M. J., Playforth M. J., Pickford I. R. A compaative study of methods for the prediction of severity of attacks of acute pancreatitis. Br J Surg. 1980 Jan;67(1):22–25. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800670107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordback I., Pessi T., Auvinen O., Autio V. Determination of necrosis in necrotizing pancreatitis. Br J Surg. 1985 Mar;72(3):225–227. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800720329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordestgaard A. G., Wilson S. E., Williams R. A. Early computerized tomography as a predictor of outcome in acute pancreatitis. Am J Surg. 1986 Jul;152(1):127–132. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(86)90162-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuutinen P., Kivisaari L., Lehtola A., Talja M., Standertskjöld-Nordenstam C. G., Lempinen M., Schröder T. Hypovolemic shock and contrast-enhanced computed tomography of the pancreas. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1986 May;21(4):483–486. doi: 10.3109/00365528609015166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuutinen P., Kivisaari L., Schröder T. Contrast-enhanced computed tomography and microangiography of the pancreas in acute human hemorrhagic/necrotizing pancreatitis. Pancreas. 1988;3(1):53–60. doi: 10.1097/00006676-198802000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuutinen P., Kivisaari L., Standertskjöld-Nordenstam C. G., Lempinen M., Schröder T. Microangiography of the pancreas in experimental hemorrhagic pancreatitis. Eur J Radiol. 1986 Aug;6(3):187–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PFEFFER R. B., LAZZARINI-ROBERTSON A., Jr, SAFADI D., MIXTER G., Jr, SECOY C. F., HINTON J. W. Gradations of pancreatitis, edematous, through hemorrhagic, experimentally produced by controlled injection of microspheres into blood vessels in dogs. Surgery. 1962 Jun;51:764–769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranson J. H., Balthazar E., Caccavale R., Cooper M. Computed tomography and the prediction of pancreatic abscess in acute pancreatitis. Ann Surg. 1985 May;201(5):656–665. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198505000-00016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranson J. H., Spencer F. C. Prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of pancreatic abscess. Surgery. 1977 Jul;82(1):99–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renner I. G., Savage W. T., 3rd, Pantoja J. L., Renner V. J. Death due to acute pancreatitis. A retrospective analysis of 405 autopsy cases. Dig Dis Sci. 1985 Oct;30(10):1005–1018. doi: 10.1007/BF01308298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotman N., Bonnet F., Lardé D., Fagniez P. L. Computerized tomography in the evaluation of the late complications of acute pancreatitis. Am J Surg. 1986 Sep;152(3):286–289. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(86)90259-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smadja C., Bismuth H. Pancreatic debridement in acute necrotizing pancreatitis: an obsolete procedure? Br J Surg. 1986 May;73(5):408–410. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800730532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THAL A., BRACKNEY E. Acute hemorrhagic pancreatic necrosis produced by local Shwartzman reaction: experimental study on pancreatitis. J Am Med Assoc. 1954 Jun 5;155(6):569–574. doi: 10.1001/jama.1954.73690240003011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teerenhovi O., Nordback I., Isolauri J. Influence of pancreatic resection on systemic complications in acute necrotizing pancreatitis. Br J Surg. 1988 Aug;75(8):793–795. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800750823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warshaw A. L., Jin G. L. Improved survival in 45 patients with pancreatic abscess. Ann Surg. 1985 Oct;202(4):408–417. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198510000-00002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warshaw A. L., Lee K. H. Serum ribonuclease elevations and pancreatic necrosis in acute pancreatitis. Surgery. 1979 Aug;86(2):227–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whicher J. T., Barnes M. P., Brown A., Cooper M. J., Read R., Walters G., Williamson R. C. Complement activation and complement control proteins in acute pancreatitis. Gut. 1982 Nov;23(11):944–950. doi: 10.1136/gut.23.11.944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White E. M., Wittenberg J., Mueller P. R., Simeone J. F., Butch R. J., Warshaw A. L., Neff C. C., Nardi G. L., Ferrucci J. T., Jr Pancreatic necrosis: CT manifestations. Radiology. 1986 Feb;158(2):343–346. doi: 10.1148/radiology.158.2.3510442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White T. T., Heimbach D. M. Sequestrectomy and hyperalimentation in the treatment of hemorrhagic pancreatitis. Am J Surg. 1976 Aug;132(2):270–275. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(76)90059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]