Abstract
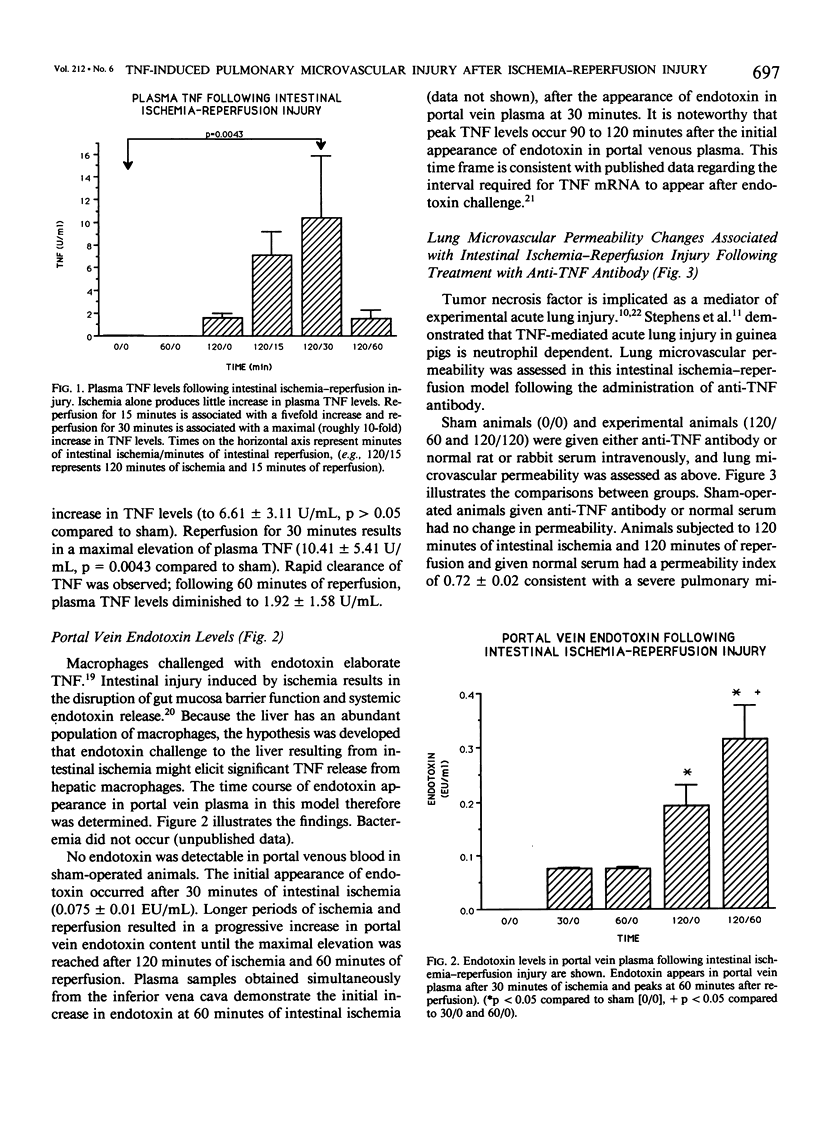
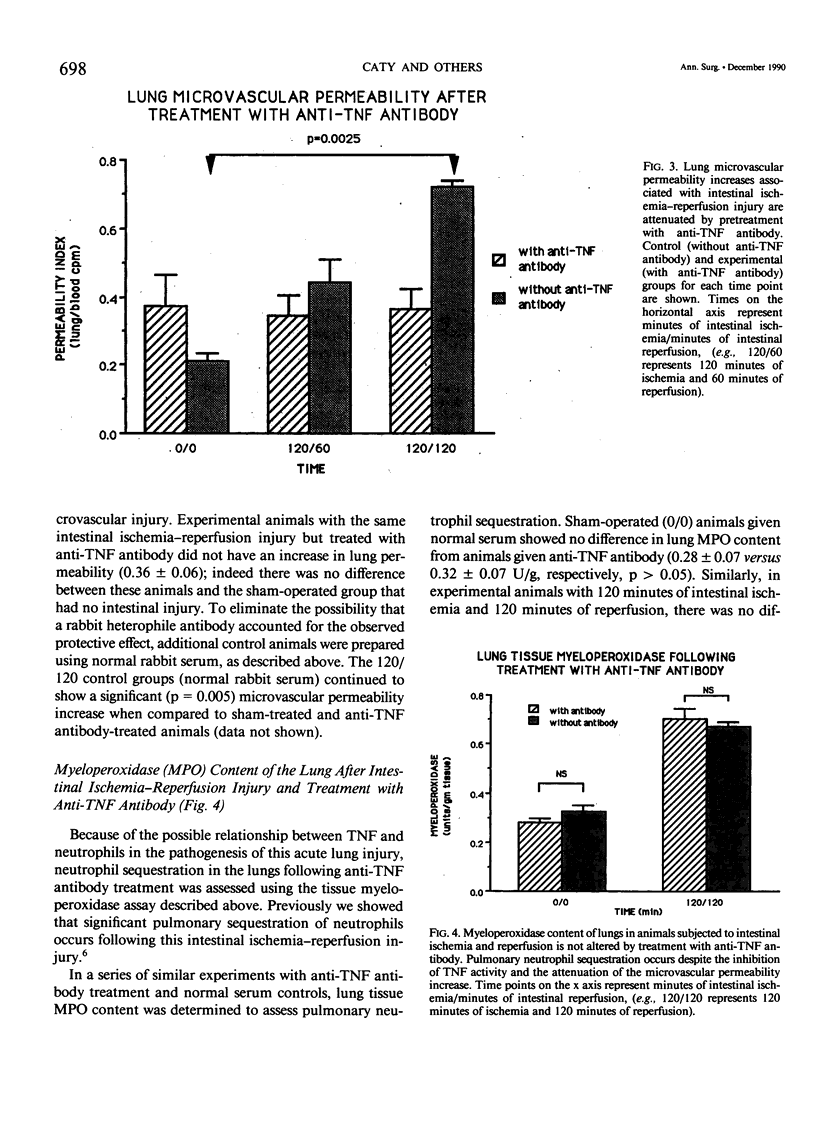
Acute lung injury characterized by increased microvascular permeability is one feature of multiple-organ system failure and the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury has been linked to this type of acute lung injury. The purpose of these experiments was to examine the pathogenic mediators that link the two processes, with particular emphasis on the roles of endotoxin and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF alpha). Previously described characteristics of the acute lung injury in this rat model of intestinal ischemia-reperfusion include pulmonary neutrophil sequestration, depletion of lung tissue ATP, alveolar endothelial cell disruption, and increased microvascular permeability. Plasma levels of TNF in the systemic circulation of sham-operated animals and those with intestinal ischemic injury less than 60 minutes in duration were very low or undetectable. Intestinal ischemia for 120 minutes was associated with TNF elevation to 1.19 +/- 0.50 U/mL. Reperfusion for periods of 15 and 30 minutes generated 5- to 10-fold increases in circulating TNF levels (6.61 +/- 3.11 U/mL, p greater than 0.05 and 10.41 +/- 5.41 U/mL, p = 0.004 compared to sham); however this increase in circulating TNF was transient and largely cleared within 60 minutes after initiating reperfusion. Portal vein endotoxin levels were found to increase significantly before the appearance of TNF in systemic plasma, suggesting that gut-derived endotoxin may induce TNF release from hepatic macrophages into the systemic circulation. Anti-TNF antibody attenuated the increase in pulmonary microvascular permeability in this preparation but did not prevent pulmonary neutrophil sequestration. These observations suggest that endotoxin and TNF have pathogenic roles in this acute lung injury, but that mechanisms of adherence of neutrophils to endothelial cells independent of TNF may be involved. The accumulation of neutrophils in the lung but the prevention of a vascular permeability increase in the presence of antibody to TNF may imply an in vivo role for TNF in the process of neutrophil activation. These studies provide additional evidence of the importance of the endogenous inflammatory mediators in the development of systemic injury in response to local tissue injury.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin: more than a tumor necrosis factor. N Engl J Med. 1987 Feb 12;316(7):379–385. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198702123160705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brigham K. L., Bowers R., Haynes J. Increased sheep lung vascular permeability caused by Escherichia coli endotoxin. Circ Res. 1979 Aug;45(2):292–297. doi: 10.1161/01.res.45.2.292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chensue S. W., Remick D. G., Shmyr-Forsch C., Beals T. F., Kunkel S. L. Immunohistochemical demonstration of cytoplasmic and membrane-associated tumor necrosis factor in murine macrophages. Am J Pathol. 1988 Dec;133(3):564–572. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuevas P., Fine J. Demonstration of a lethal endotoxemia in experimental occlusion of the superior mesenteric artery. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1971 Jul;133(1):81–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espevik T., Nissen-Meyer J. A highly sensitive cell line, WEHI 164 clone 13, for measuring cytotoxic factor/tumor necrosis factor from human monocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Dec 4;95(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90322-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldblum S. E., Wu K. M., Jay M. Lung myeloperoxidase as a measure of pulmonary leukostasis in rabbits. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1985 Dec;59(6):1978–1985. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1985.59.6.1978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger D. N., Höllwarth M. E., Parks D. A. Ischemia-reperfusion injury: role of oxygen-derived free radicals. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1986;548:47–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guice K. S., Oldham K. T., Caty M. G., Johnson K. J., Ward P. A. Neutrophil-dependent, oxygen-radical mediated lung injury associated with acute pancreatitis. Ann Surg. 1989 Dec;210(6):740–747. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198912000-00008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guice K. S., Oldham K. T., Johnson K. J., Kunkel R. G., Morganroth M. L., Ward P. A. Pancreatitis-induced acute lung injury. An ARDS model. Ann Surg. 1988 Jul;208(1):71–77. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198807000-00010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslberger A., Sayers T., Reiter H., Chung J., Schütze E. Reduced release of TNF and PCA from macrophages of tolerant mice. Circ Shock. 1988 Oct;26(2):185–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. J., Fantone J. C., 3rd, Kaplan J., Ward P. A. In vivo damage of rat lungs by oxygen metabolites. J Clin Invest. 1981 Apr;67(4):983–993. doi: 10.1172/JCI110149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer J. D., Yurt R. W., Duhaney R., Hesse D. G., Tracey K. J., Fong Y. M., Verma M., Shires G. T., Dineen P., Lowry S. F. Tumor necrosis factor-enhanced leukotriene B4 generation and chemotaxis in human neutrophils. Arch Surg. 1988 Dec;123(12):1454–1458. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1988.01400360024002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michie H. R., Spriggs D. R., Manogue K. R., Sherman M. L., Revhaug A., O'Dwyer S. T., Arthur K., Dinarello C. A., Cerami A., Wolff S. M. Tumor necrosis factor and endotoxin induce similar metabolic responses in human beings. Surgery. 1988 Aug;104(2):280–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldham K. T., Guice K. S., Gore D., Gourley W. K., Lobe T. E. Treatment of intestinal ischemia with oxygenated intraluminal perfluorocarbons. Am J Surg. 1987 Mar;153(3):291–294. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(87)90606-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohlman T. H., Stanness K. A., Beatty P. G., Ochs H. D., Harlan J. M. An endothelial cell surface factor(s) induced in vitro by lipopolysaccharide, interleukin 1, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha increases neutrophil adherence by a CDw18-dependent mechanism. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4548–4553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remick D. G., Kunkel R. G., Larrick J. W., Kunkel S. L. Acute in vivo effects of human recombinant tumor necrosis factor. Lab Invest. 1987 Jun;56(6):583–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remick D. G., Strieter R. M., Eskandari M. K., Nguyen D. T., Genord M. A., Raiford C. L., Kunkel S. L. Role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in lipopolysaccharide-induced pathologic alterations. Am J Pathol. 1990 Jan;136(1):49–60. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remick D. G., Strieter R. M., Lynch J. P., 3rd, Nguyen D., Eskandari M., Kunkel S. L. In vivo dynamics of murine tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene expression. Kinetics of dexamethasone-induced suppression. Lab Invest. 1989 Jun;60(6):766–771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldo J. E., Rogers R. M. Adult respiratory-distress syndrome: changing concepts of lung injury and repair. N Engl J Med. 1982 Apr 15;306(15):900–909. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198204153061504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmeling D. J., Caty M. G., Oldham K. T., Guice K. S., Hinshaw D. B. Evidence for neutrophil-related acute lung injury after intestinal ischemia-reperfusion. Surgery. 1989 Aug;106(2):195–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalaby M. R., Aggarwal B. B., Rinderknecht E., Svedersky L. P., Finkle B. S., Palladino M. A., Jr Activation of human polymorphonuclear neutrophil functions by interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factors. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):2069–2073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starnes H. F., Jr, Warren R. S., Jeevanandam M., Gabrilove J. L., Larchian W., Oettgen H. F., Brennan M. F. Tumor necrosis factor and the acute metabolic response to tissue injury in man. J Clin Invest. 1988 Oct;82(4):1321–1325. doi: 10.1172/JCI113733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens K. E., Ishizaka A., Wu Z. H., Larrick J. W., Raffin T. A. Granulocyte depletion prevents tumor necrosis factor-mediated acute lung injury in guinea pigs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Nov;138(5):1300–1307. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/138.5.1300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Till G. O., Beauchamp C., Menapace D., Tourtellotte W., Jr, Kunkel R., Johnson K. J., Ward P. A. Oxygen radical dependent lung damage following thermal injury of rat skin. J Trauma. 1983 Apr;23(4):269–277. doi: 10.1097/00005373-198304000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Till G. O., Hatherill J. R., Tourtellotte W. W., Lutz M. J., Ward P. A. Lipid peroxidation and acute lung injury after thermal trauma to skin. Evidence of a role for hydroxyl radical. Am J Pathol. 1985 Jun;119(3):376–384. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Beutler B., Lowry S. F., Merryweather J., Wolpe S., Milsark I. W., Hariri R. J., Fahey T. J., 3rd, Zentella A., Albert J. D. Shock and tissue injury induced by recombinant human cachectin. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):470–474. doi: 10.1126/science.3764421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Fong Y., Hesse D. G., Manogue K. R., Lee A. T., Kuo G. C., Lowry S. F., Cerami A. Anti-cachectin/TNF monoclonal antibodies prevent septic shock during lethal bacteraemia. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):662–664. doi: 10.1038/330662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto M., Yokota S., Vilcek J., Weissmann G. Tumor necrosis factor provokes superoxide anion generation from neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jun 30;137(3):1094–1100. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90337-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wankowicz Z., Megyeri P., Issekutz A. Synergy between tumour necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-1 in the induction of polymorphonuclear leukocyte migration during inflammation. J Leukoc Biol. 1988 Apr;43(4):349–356. doi: 10.1002/jlb.43.4.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiland J. E., Davis W. B., Holter J. F., Mohammed J. R., Dorinsky P. M., Gadek J. E. Lung neutrophils in the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Clinical and pathophysiologic significance. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Feb;133(2):218–225. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.133.2.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


