Abstract
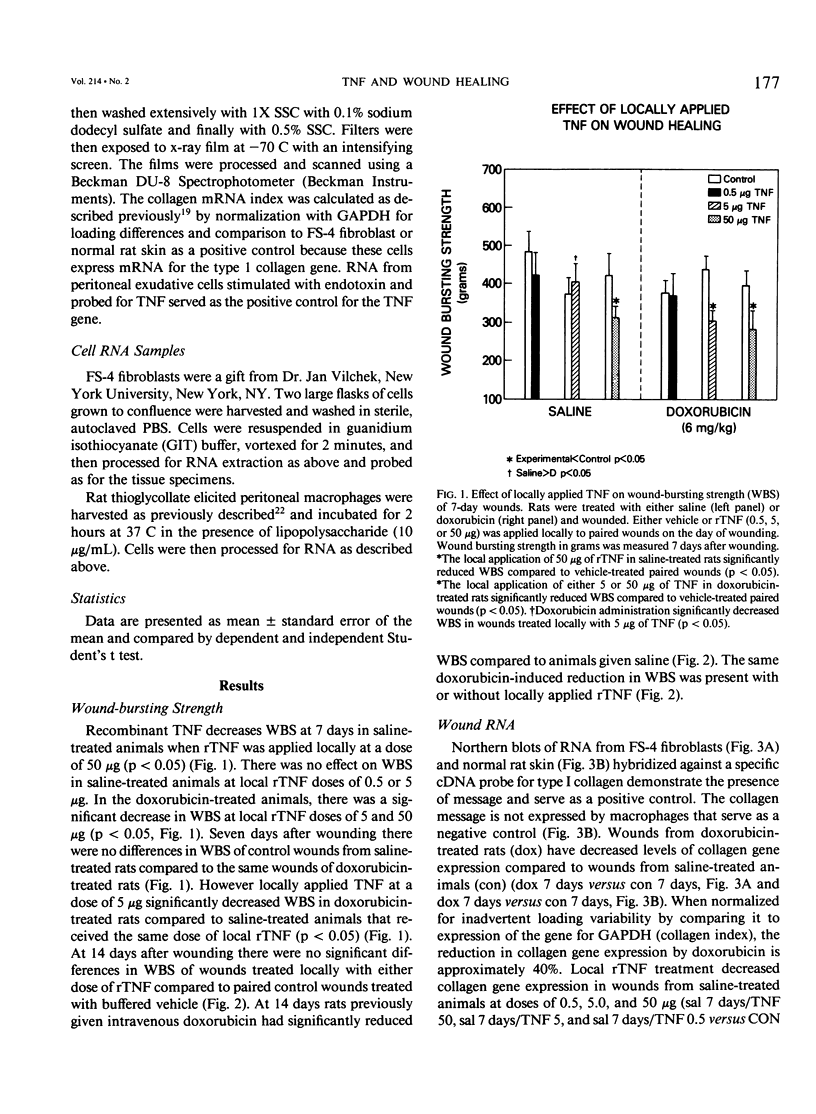
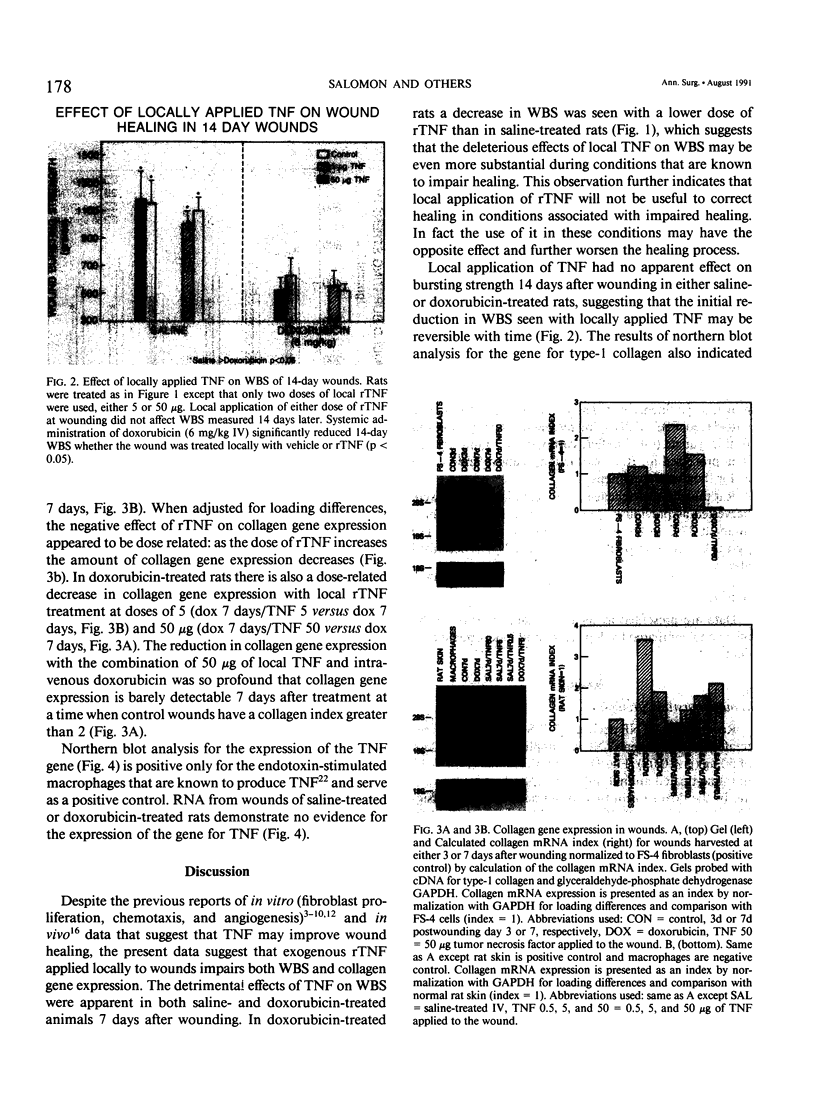
Previous experimental studies have suggested that tumor necrosis factor (TNF) may have either a beneficial or a detrimental role in wound healing. Control and doxorubicin-treated (6 mg/kg, intravenously) rats underwent paired dorsal 5-cm linear wounds and had either vehicle or recombinant (r)TNF (0.5, 5, or 50 micrograms) applied locally to the wound. Paired wounds were harvested at 7 and 14 days after wounding and analyzed for wound-bursting strength (WBS) and activity of the gene for type 1 collagen and TNF. Doxorubicin treatment decreased WBS at 14 days but not at 7 days after wounding. Local application of 50 micrograms of rTNF decreased WBS in saline-treated rats and concentrations of 5 and 50 micrograms decreased WBS in doxorubicin-treated rats when measured 7 days after wounding. These effects dissipated when WBS was measured 14 days after wounding. Doxorubicin decreased wound collagen gene expression and local TNF treatment decreased wound collagen gene expression in saline-treated rats and further decreased it in doxorubicin-treated rats. The decrement in collagen gene expression induced by rTNF increased as the local dose of rTNF increased. The gene for TNF was not detectable in wounds from normal or doxorubicin-treated rats at 3, 7, 10, or 14 days after wounding. These data suggest that the gene for TNF is not expressed in wounds and that the local application of TNF is detrimental to wound healing as it decreases WBS and activity of the gene for collagen.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balkwill F., Osborne R., Burke F., Naylor S., Talbot D., Durbin H., Tavernier J., Fiers W. Evidence for tumour necrosis factor/cachectin production in cancer. Lancet. 1987 Nov 28;2(8570):1229–1232. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91850-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. A., O'Hara M., Angel P., Chojkier M., Karin M. Prolonged activation of jun and collagenase genes by tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Nature. 1989 Feb 16;337(6208):661–663. doi: 10.1038/337661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayer J. M., Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor stimulates collagenase and prostaglandin E2 production by human synovial cells and dermal fibroblasts. J Exp Med. 1985 Dec 1;162(6):2163–2168. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.6.2163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford H. R., Hoffman R. A., Wing E. J., Magee D. M., McIntyre L., Simmons R. L. Characterization of wound cytokines in the sponge matrix model. Arch Surg. 1989 Dec;124(12):1422–1428. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1989.01410120068014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker D. L., Stovroff M. C., Merino M. J., Norton J. A. Tolerance to tumor necrosis factor in rats and the relationship to endotoxin tolerance and toxicity. J Exp Med. 1988 Jul 1;168(1):95–105. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girardin E., Grau G. E., Dayer J. M., Roux-Lombard P., Lambert P. H. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 in the serum of children with severe infectious purpura. N Engl J Med. 1988 Aug 18;319(7):397–400. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198808183190703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajjar K. A., Hajjar D. P., Silverstein R. L., Nachman R. L. Tumor necrosis factor-mediated release of platelet-derived growth factor from cultured endothelial cells. J Exp Med. 1987 Jul 1;166(1):235–245. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.1.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesse D. G., Tracey K. J., Fong Y., Manogue K. R., Palladino M. A., Jr, Cerami A., Shires G. T., Lowry S. F. Cytokine appearance in human endotoxemia and primate bacteremia. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1988 Feb;166(2):147–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasid A., Director E. P., Rosenberg S. A. Induction of endogenous cytokine-mRNA in circulating peripheral blood mononuclear cells by IL-2 administration to cancer patients. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 15;143(2):736–739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohase M., Henriksen-DeStefano D., May L. T., Vilcek J., Sehgal P. B. Induction of beta 2-interferon by tumor necrosis factor: a homeostatic mechanism in the control of cell proliferation. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):659–666. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90780-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibovich S. J., Polverini P. J., Shepard H. M., Wiseman D. M., Shively V., Nuseir N. Macrophage-induced angiogenesis is mediated by tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):630–632. doi: 10.1038/329630a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lähdevirta J., Maury C. P., Teppo A. M., Repo H. Elevated levels of circulating cachectin/tumor necrosis factor in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am J Med. 1988 Sep;85(3):289–291. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(88)90576-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ming W. J., Bersani L., Mantovani A. Tumor necrosis factor is chemotactic for monocytes and polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 1;138(5):1469–1474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philip R., Epstein L. B. Tumour necrosis factor as immunomodulator and mediator of monocyte cytotoxicity induced by itself, gamma-interferon and interleukin-1. Nature. 1986 Sep 4;323(6083):86–89. doi: 10.1038/323086a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Bevilacqua M. P., Mendrick D. L., Lapierre L. A., Fiers W., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Two distinct monokines, interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor, each independently induce biosynthesis and transient expression of the same antigen on the surface of cultured human vascular endothelial cells. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 1;136(5):1680–1687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon G. D., Kasid A., Bernstein E., Buresh C., Director E., Norton J. A. Gene expression in normal and doxorubicin-impaired wounds: importance of transforming growth factor-beta. Surgery. 1990 Aug;108(2):318–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherry B., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor exerts endocrine, paracrine, and autocrine control of inflammatory responses. J Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;107(4):1269–1277. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.4.1269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solis-Herruzo J. A., Brenner D. A., Chojkier M. Tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibits collagen gene transcription and collagen synthesis in cultured human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5841–5845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steenfos H. H., Hunt T. K., Scheuenstuhl H., Goodson W. H., 3rd Selective effects of tumor necrosis factor-alpha on wound healing in rats. Surgery. 1989 Aug;106(2):171–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stovroff M. C., Fraker D. L., Travis W. D., Norton J. A. Altered macrophage activity and tumor necrosis factor: tumor necrosis and host cachexia. J Surg Res. 1989 May;46(5):462–469. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(89)90161-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugarman B. J., Aggarwal B. B., Hass P. E., Figari I. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, Shepard H. M. Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor-alpha: effects on proliferation of normal and transformed cells in vitro. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):943–945. doi: 10.1126/science.3933111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Fong Y., Hesse D. G., Manogue K. R., Lee A. T., Kuo G. C., Lowry S. F., Cerami A. Anti-cachectin/TNF monoclonal antibodies prevent septic shock during lethal bacteraemia. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):662–664. doi: 10.1038/330662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Wei H., Manogue K. R., Fong Y., Hesse D. G., Nguyen H. T., Kuo G. C., Beutler B., Cotran R. S., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor induces cachexia, anemia, and inflammation. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):1211–1227. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.1211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlassara H., Brownlee M., Manogue K. R., Dinarello C. A., Pasagian A. Cachectin/TNF and IL-1 induced by glucose-modified proteins: role in normal tissue remodeling. Science. 1988 Jun 10;240(4858):1546–1548. doi: 10.1126/science.3259727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waage A., Halstensen A., Espevik T. Association between tumour necrosis factor in serum and fatal outcome in patients with meningococcal disease. Lancet. 1987 Feb 14;1(8529):355–357. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91728-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]