Abstract
Recently it was demonstrated that pancreatic islet allografts transplanted to the thymus of rats made diabetic chemically are not rejected and induce specific unresponsiveness to subsequent extrathymic transplants. The authors report that the thymus can also serve as an effective islet transplantation site in spontaneously diabetic BB rats, in which autoimmunity and rejection can destroy islets. Intrathymic Lewis islet grafts consistently reversed hyperglycemia for more than 120 days in these rats, and in three of four recipients the grafts promoted subsequent survival of intraportal islets. In contrast intraportal islet allografts in naive BB hosts all failed rapidly. The authors also show that the immunologically privileged status of the thymus cannot prevent rejection of islet allografts in Wistar Furth (WF) rats sensitized with donor strain skin and that suppressor cells are not likely to contribute to the unresponsive state because adoptive transfer of spleen cells from WF rats bearing established intrathymic Lewis islets fails to prolong islet allograft survival in secondary hosts.
Full text
PDF

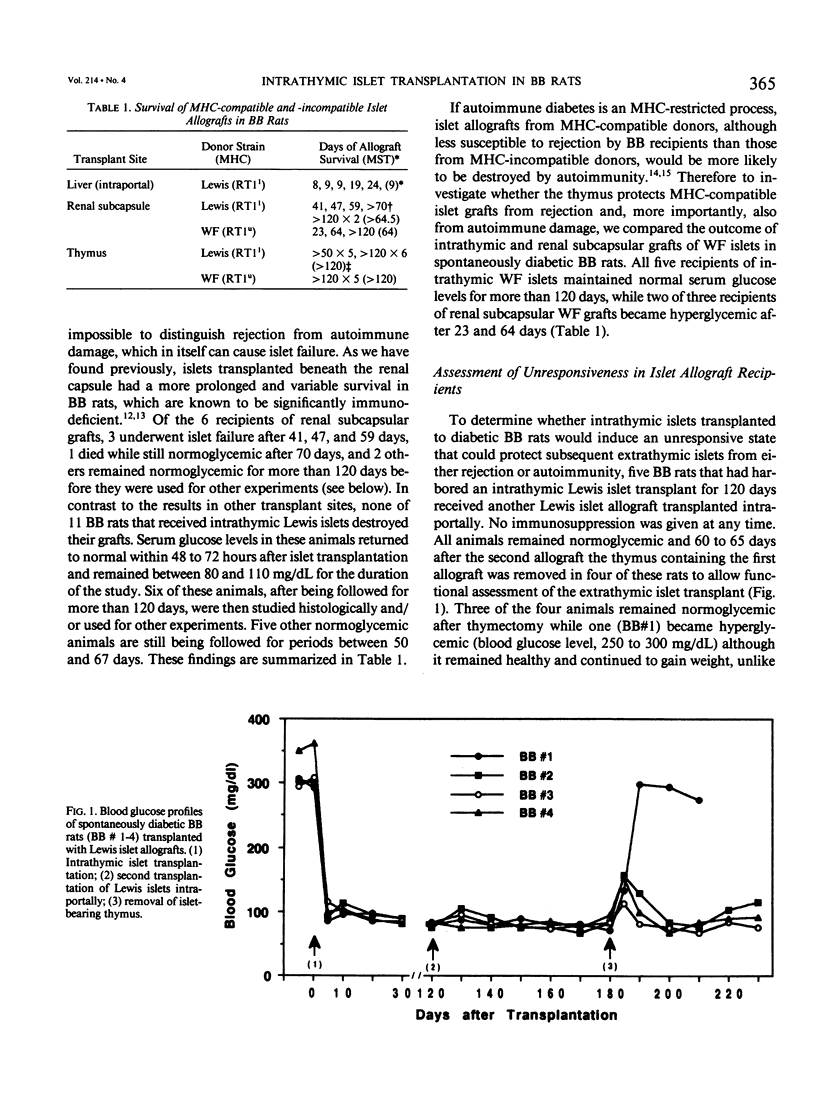
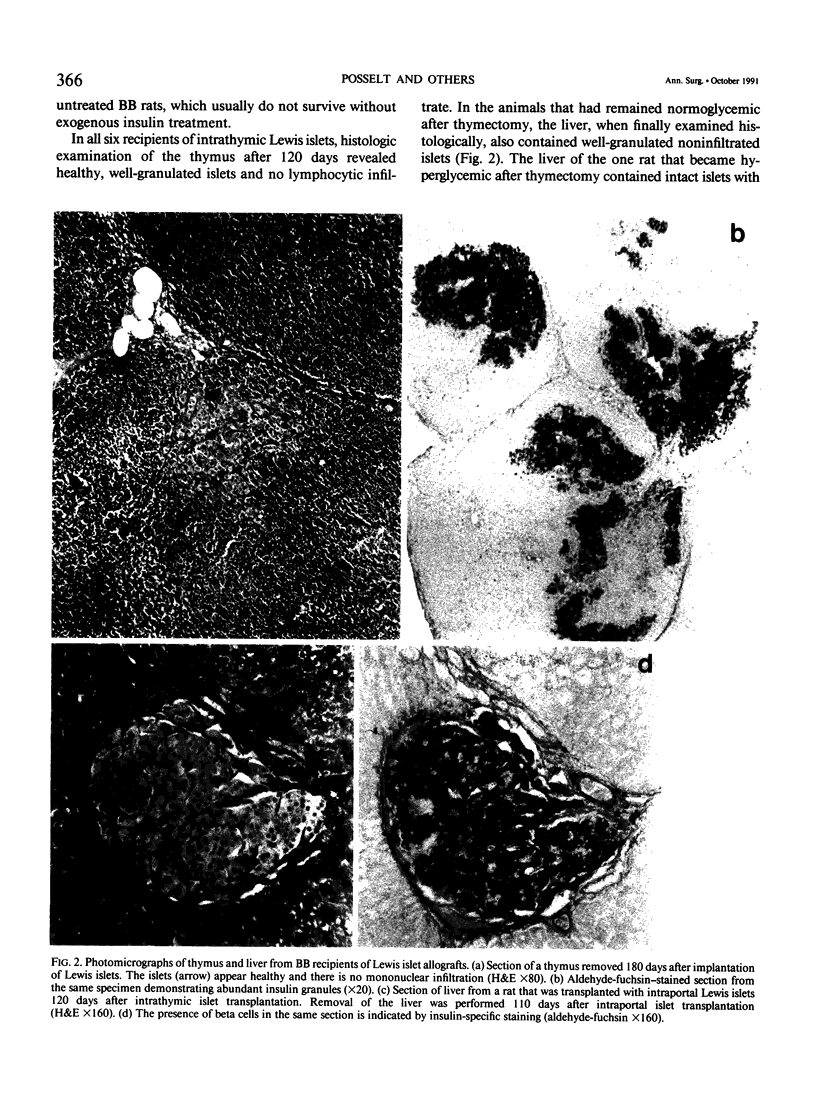

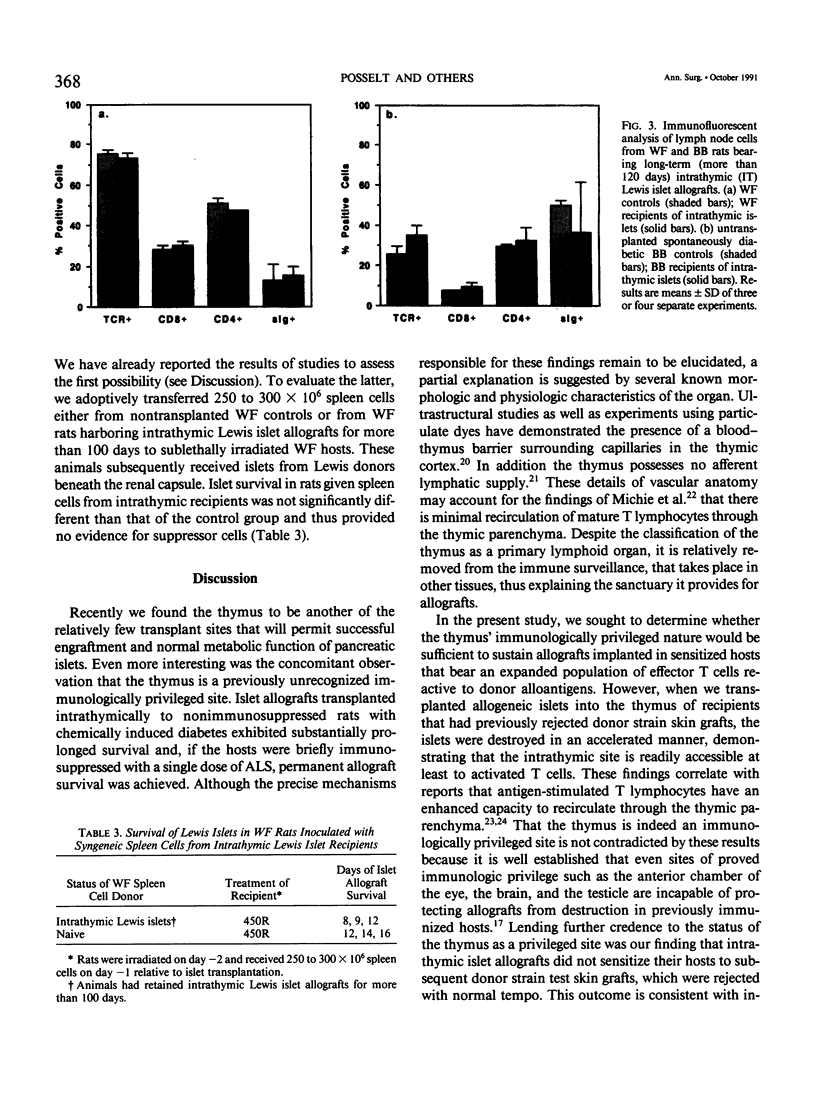



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alinaji, Silvers W. K., Bellgrau D., Anderson A. O., Plotkin S., Barker C. F. Prevention of diabetes in rats by bone marrow transplantation. Ann Surg. 1981 Sep;194(3):328–338. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198109000-00011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BILLINGHAM R. E., BRENT L., MEDAWAR P. B. Actively acquired tolerance of foreign cells. Nature. 1953 Oct 3;172(4379):603–606. doi: 10.1038/172603a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink P. J., Bevan M. J., Weissman I. L. Thymic cytotoxic T lymphocytes are primed in vivo to minor histocompatibility antigens. J Exp Med. 1984 Feb 1;159(2):436–451. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.2.436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freitas A. A., Rocha B., Coutinho A. A. Lymphocyte population kinetics in the mouse. Immunol Rev. 1986 Jun;91:5–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1986.tb01482.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgiou H. M., Bellgrau D. Thymus transplantation and disease prevention in the diabetes-prone Bio-Breeding rat. J Immunol. 1989 May 15;142(10):3400–3405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall B. M., Pearce N. W., Gurley K. E., Dorsch S. E. Specific unresponsiveness in rats with prolonged cardiac allograft survival after treatment with cyclosporine. III. Further characterization of the CD4+ suppressor cell and its mechanisms of action. J Exp Med. 1990 Jan 1;171(1):141–157. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.1.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegre O. D., Enriquez A. J., Ketchum R. J., Weinhaus A. J., Serie J. R. Islet transplantation in spontaneously diabetic BB/Wor rats. Diabetes. 1989 Sep;38(9):1148–1154. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.9.1148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hünig T., Wallny H. J., Hartley J. K., Lawetzky A., Tiefenthaler G. A monoclonal antibody to a constant determinant of the rat T cell antigen receptor that induces T cell activation. Differential reactivity with subsets of immature and mature T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1989 Jan 1;169(1):73–86. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy P. E., Kostianovsky M. Method for the isolation of intact islets of Langerhans from the rat pancreas. Diabetes. 1967 Jan;16(1):35–39. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason D. W., Arthur R. P., Dallman M. J., Green J. R., Spickett G. P., Thomas M. L. Functions of rat T-lymphocyte subsets isolated by means of monoclonal antibodies. Immunol Rev. 1983;74:57–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb01084.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michie S. A., Kirkpatrick E. A., Rouse R. V. Rare peripheral T cells migrate to and persist in normal mouse thymus. J Exp Med. 1988 Nov 1;168(5):1929–1934. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.5.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naji A., Silvers W. K., Kimura H., Bellgrau D., Markmann J. F., Barker C. F. Analytical and functional studies on the T cells of untreated and immunologically tolerant diabetes-prone BB rats. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2168–2172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naparstek Y., Holoshitz J., Eisenstein S., Reshef T., Rappaport S., Chemke J., Ben-Nun A., Cohen I. R. Effector T lymphocyte line cells migrate to the thymus and persist there. Nature. 1982 Nov 18;300(5889):262–264. doi: 10.1038/300262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posselt A. M., Barker C. F., Tomaszewski J. E., Markmann J. F., Choti M. A., Naji A. Induction of donor-specific unresponsiveness by intrathymic islet transplantation. Science. 1990 Sep 14;249(4974):1293–1295. doi: 10.1126/science.2119056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prowse S. J., Bellgrau D., Lafferty K. J. Islet allografts are destroyed by disease occurrence in the spontaneously diabetic BB rat. Diabetes. 1986 Jan;35(1):110–114. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.1.110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raviola E., Karnovsky M. J. Evidence for a blood-thymus barrier using electron-opaque tracers. J Exp Med. 1972 Sep 1;136(3):466–498. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.3.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roser B. J. Cellular mechanisms in neonatal and adult tolerance. Immunol Rev. 1989 Feb;107:179–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1989.tb00009.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selawry H. P., Whittington K. Extended allograft survival of islets grafted into intra-abdominally placed testis. Diabetes. 1984 Apr;33(4):405–406. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.4.405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selawry H., Fajaco R., Whittington K. Intratesticular islet allografts in the spontaneously diabetic BB/W rat. Diabetes. 1985 Oct;34(10):1019–1024. doi: 10.2337/diab.34.10.1019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selawry H., Fojaco R., Whittington K. Extended survival of MHC-compatible islet grafts from diabetes-resistant donors in spontaneously diabetic BB/W rat. Diabetes. 1987 Sep;36(9):1061–1067. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.9.1061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terasaka R., Lacy P. E., Hauptfeld V., Bucy R. P., Davie J. M. The effect of cyclosporin-A, low-temperature culture, and anti-Ia antibodies on prevention of rejection of rat islet allografts. Diabetes. 1986 Jan;35(1):83–88. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.1.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tze W. J., Tai J. Allotransplantation of dispersed single pancreatic endocrine cells in diabetic rats. Diabetes. 1988 Apr;37(4):383–392. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.4.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weringer E. J., Like A. A. Immune attack on pancreatic islet transplants in the spontaneously diabetic BioBreeding/Worcester (BB/W) rat is not MHC restricted. J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2383–2386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woehrle M. F., Markmann J. F., Armstrong J., Naji A. Effect of transplant site on islet allograft survival in BB rats. Transplant Proc. 1987 Feb;19(1 Pt 2):925–927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woehrle M., Markman J. F., Beyer K., Naji A., Bretzel R. G., Federlin K. The influence of the implantation site (kidney capsule vs. portal vein) on islet survival. Horm Metab Res Suppl. 1990;25:163–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woehrle M., Markmann J. F., Silvers W. K., Barker C. F., Naji A. Transplantation of cultured pancreatic islets to BB rats. Surgery. 1986 Aug;100(2):334–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]