Abstract
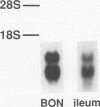
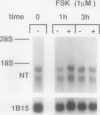
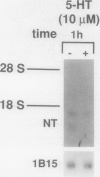
Neurotensin (NT), a distal gut peptide, has important regulatory and trophic effects throughout the gut; however the intracellular mechanisms that regulate the gene expression and release of human NT are not known. The purpose of this endeavor was to study a functioning human pancreatic carcinoid cell line (called BON) in vitro that expresses the NT gene, and to study the effect of the cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) signal-transduction pathway on the expression and release of human NT. RNA was prepared from BON cell line (which has been established in this laboratory); the RNA was analyzed for NT mRNA expression by Northern hybridization with a complementary DNA probe. RNA blot analysis demonstrated that the NT gene is expressed in BON and is transcribed to two mRNAs of 1.0- and 1.5-kb sizes. In the second part of this study, BON cells were treated with either forskolin (FSK), which increases intracellular levels of cAMP, or with serotonin (5-HT), which reduces cAMP in BON cells. Forskolin produced a dose-dependent increase in NT peptide release and, furthermore, FSK (10(-6) mol/L) rapidly increased NT mRNA abundance 1 hour after addition; conversely, 5-HT (10(-5) mol/L) decreased NT mRNA at 1 hour. Neurotensin mRNA levels returned to control values by 3 hours after either FSK or 5-HT, which suggests that the transcript half-life for NT is relatively short. These findings show that the expression and peptide release of human NT is mediated, in part, by the cAMP signal-transduction pathway. Our human carcinoid cell line will provide a useful model to study the in vitro regulation of NT gene expression and peptide release.
Full text
PDF


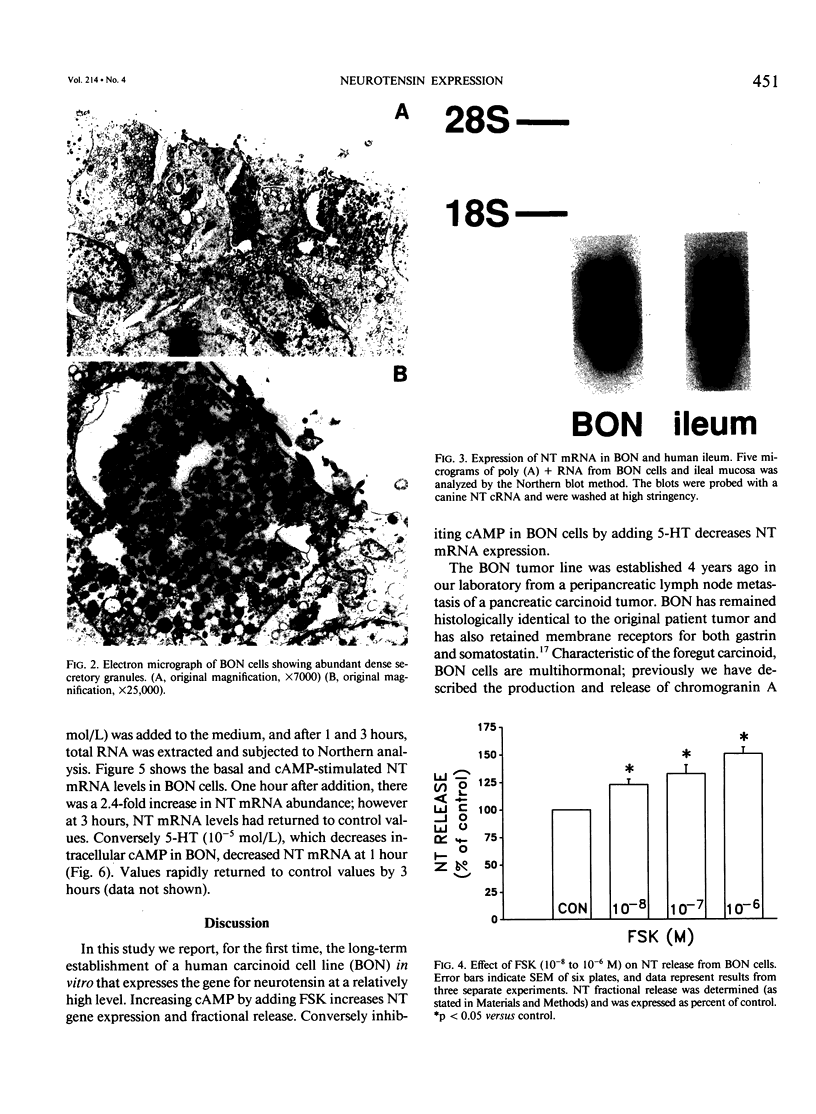
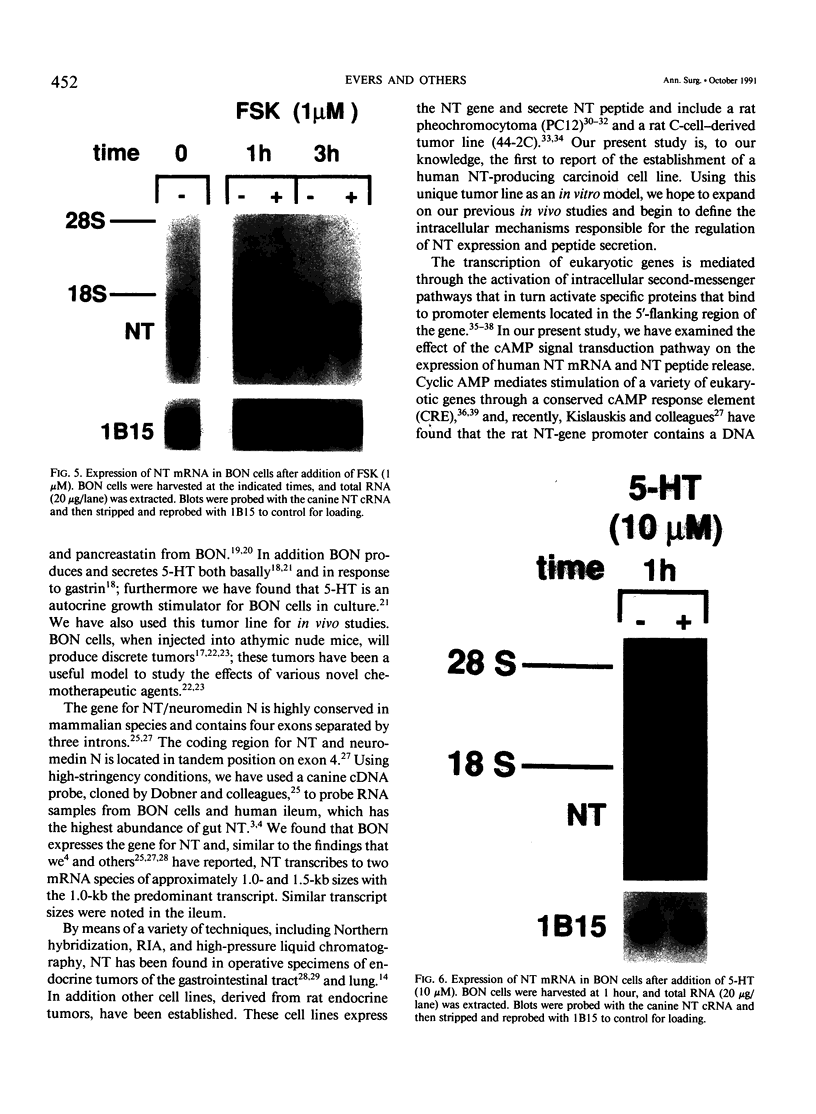


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson S., Rosell S., Hjelmquist U., Chang D., Folkers K. Inhibition of gastric and intestinal motor activity in dogs by (Gln4) neurotensin. Acta Physiol Scand. 1977 Jun;100(2):231–235. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1977.tb05941.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beimling P., Benter T., Sander T., Moelling K. Isolation and characterization of the human cellular myc gene product. Biochemistry. 1985 Nov 5;24(23):6349–6355. doi: 10.1021/bi00344a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn A. M., Fletcher D. R., Bloom S. R., Christofides N. D., Long R. G., Fitzpatrick M. L., Baron J. H. Effect of neurotensin on gastric function in man. Lancet. 1980 May 10;1(8176):987–989. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91434-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Auger K. R., Carpenter C., Duckworth B., Graziani A., Kapeller R., Soltoff S. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):281–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90639-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway R. E., Mitra S. P., Feurle G. E., Hacki W. H. Presence of neurotensin and neuromedin-N within a common precursor from a human pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988 Jun;66(6):1323–1328. doi: 10.1210/jcem-66-6-1323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cimbala M. A., Lamers W. H., Nelson K., Monahan J. E., Yoo-Warren H., Hanson R. W. Rapid changes in the concentration of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase mRNA in rat liver and kidney. Effects of insulin and cyclic AMP. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7629–7636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielson P. E., Forss-Petter S., Brow M. A., Calavetta L., Douglass J., Milner R. J., Sutcliffe J. G. p1B15: a cDNA clone of the rat mRNA encoding cyclophilin. DNA. 1988 May;7(4):261–267. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Jr Variety in the level of gene control in eukaryotic cells. Nature. 1982 Jun 3;297(5865):365–371. doi: 10.1038/297365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis T. P., Burgess H. S., Crowell S., Moody T. W., Culling-Berglund A., Liu R. H. Beta-endorphin and neurotensin stimulate in vitro clonal growth of human SCLC cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Feb 28;161(2-3):283–285. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90862-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobner P. R., Barber D. L., Villa-Komaroff L., McKiernan C. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for the canine neurotensin/neuromedin N precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3516–3520. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobner P. R., Tischler A. S., Lee Y. C., Bloom S. R., Donahue S. R. Lithium dramatically potentiates neurotensin/neuromedin N gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):13983–13986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle H., Greeley G. H., Jr, Mate L., Sakamoto T., Townsend C. M., Jr, Thompson J. C. Distribution of neurotensin in the canine gastrointestinal tract. Surgery. 1985 Mar;97(3):337–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evers B. M., Beauchamp R. D., Ishizuka J., Townsend C. M., Jr, Alam T., Papaconstantinou J., Thompson J. C. Posttranscriptional regulation of neurotensin in the gut. Surgery. 1991 Aug;110(2):247–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evers B. M., Hurlbut S. C., Tyring S. K., Townsend C. M., Jr, Uchida T., Thompson J. C. Novel therapy for the treatment of human carcinoid. Ann Surg. 1991 May;213(5):411–416. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199105000-00005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evers B. M., Izukura M., Townsend C. M., Jr, Uchida T., Thompson J. C. Differential effects of gut hormones on pancreatic and intestinal growth during administration of an elemental diet. Ann Surg. 1990 May;211(5):630–638. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evers B. M., Townsend C. M., Jr, Upp J. R., Allen E., Hurlbut S. C., Kim S. W., Rajaraman S., Singh P., Reubi J. C., Thompson J. C. Establishment and characterization of a human carcinoid in nude mice and effect of various agents on tumor growth. Gastroenterology. 1991 Aug;101(2):303–311. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90004-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feurle G. E., Müller B., Rix E. Neurotensin induces hyperplasia of the pancreas and growth of the gastric antrum in rats. Gut. 1987;28 (Suppl):19–23. doi: 10.1136/gut.28.suppl.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., Tischler A. S. Establishment of a noradrenergic clonal line of rat adrenal pheochromocytoma cells which respond to nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2424–2428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habener J. F. Cyclic AMP response element binding proteins: a cornucopia of transcription factors. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Aug;4(8):1087–1094. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-8-1087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmstaedter V., Taugner C., Feurle G. E., Forssmann W. G. Localization of neurotensin-immunoreactive cells in the small intestine of man and various mammals. Histochemistry. 1977 Jul 18;53(1):35–41. doi: 10.1007/BF00511208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeng Y. J., Townsend C. M., Jr, Nagasawa S., Chuo S., Kern K., Yanaihara N., Ferrar R. S., Hill F. L., Thompson J. C., Greeley G. H., Jr Regulation of pancreastatin release from a human pancreatic carcinoid cell line in vitro. Endocrinology. 1991 Jan;128(1):220–225. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-1-220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapuscinski M., Shulkes A., Read D., Hardy K. J. Expression of neurotensin in endocrine tumors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990 Jan;70(1):100–106. doi: 10.1210/jcem-70-1-100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kislauskis E., Bullock B., McNeil S., Dobner P. R. The rat gene encoding neurotensin and neuromedin N. Structure, tissue-specific expression, and evolution of exon sequences. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 5;263(10):4963–4968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kislauskis E., Dobner P. R. Mutually dependent response elements in the cis-regulatory region of the neurotensin/neuromedin N gene integrate environmental stimuli in PC12 cells. Neuron. 1990 May;4(5):783–795. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90205-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montminy M. R., Sevarino K. A., Wagner J. A., Mandel G., Goodman R. H. Identification of a cyclic-AMP-responsive element within the rat somatostatin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6682–6686. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody T. W., Carney D. N., Korman L. Y., Gazdar A. F., Minna J. D. Neurotensin is produced by and secreted from classic small cell lung cancer cells. Life Sci. 1985 May 6;36(18):1727–1732. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(85)90555-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polak J. M., Sullivan S. N., Bloom S. R., Buchan A. M., Facer P., Brown M. R., Pearse A. G. Specific localisation of neurotensin to the N cell in human intestine by radioimmunoassay and immunocytochemistry. Nature. 1977 Nov 10;270(5633):183–184. doi: 10.1038/270183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roesler W. J., Vandenbark G. R., Hanson R. W. Cyclic AMP and the induction of eukaryotic gene transcription. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9063–9066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto T., Newman J., Fujimura M., Greeley G. H., Jr, Townsend C. M., Jr, Thompson J. C. Role of neurotensin in pancreatic secretion. Surgery. 1984 Aug;96(2):146–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staley J., Fiskum G., Davis T. P., Moody T. W. Neurotensin elevates cytosolic calcium in small cell lung cancer cells. Peptides. 1989 Nov-Dec;10(6):1217–1221. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(89)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thor K., Rosell S. Neurotensin increases colonic motility. Gastroenterology. 1986 Jan;90(1):27–31. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90070-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Transient accumulation of c-fos RNA following serum stimulation requires a conserved 5' element and c-fos 3' sequences. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):889–902. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90285-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. G., Hoang H. D., Bussjaeger L. J., Solomon T. E. Effect of neurotensin on pancreatic and gastric secretion and growth in rats. Pancreas. 1988;3(3):332–339. doi: 10.1097/00006676-198805000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. G., Hoang H. D., Bussjaeger L. J., Solomon T. E. Neurotensin stimulates growth of small intestine in rats. Am J Physiol. 1988 Dec;255(6 Pt 1):G813–G817. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1988.255.6.G813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeytin F. N., Delellis R. The neuropeptide-synthesizing rat 44-2C cell line: regulation of peptide synthesis, secretion, 3,'5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate efflux, and adenylate cyclase activation. Endocrinology. 1987 Jul;121(1):352–360. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-1-352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeytin F. N., Rusk S. F., Baird A., Raymond V., Leff S. E., Haaparanta T., Mandell A. J. Induction of c-fos, calcitonin gene expression, and acidic fibroblast growth factor production in a multipeptide-secreting neuroendocrine cell line. Endocrinology. 1988 Mar;122(3):1114–1120. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-3-1114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]