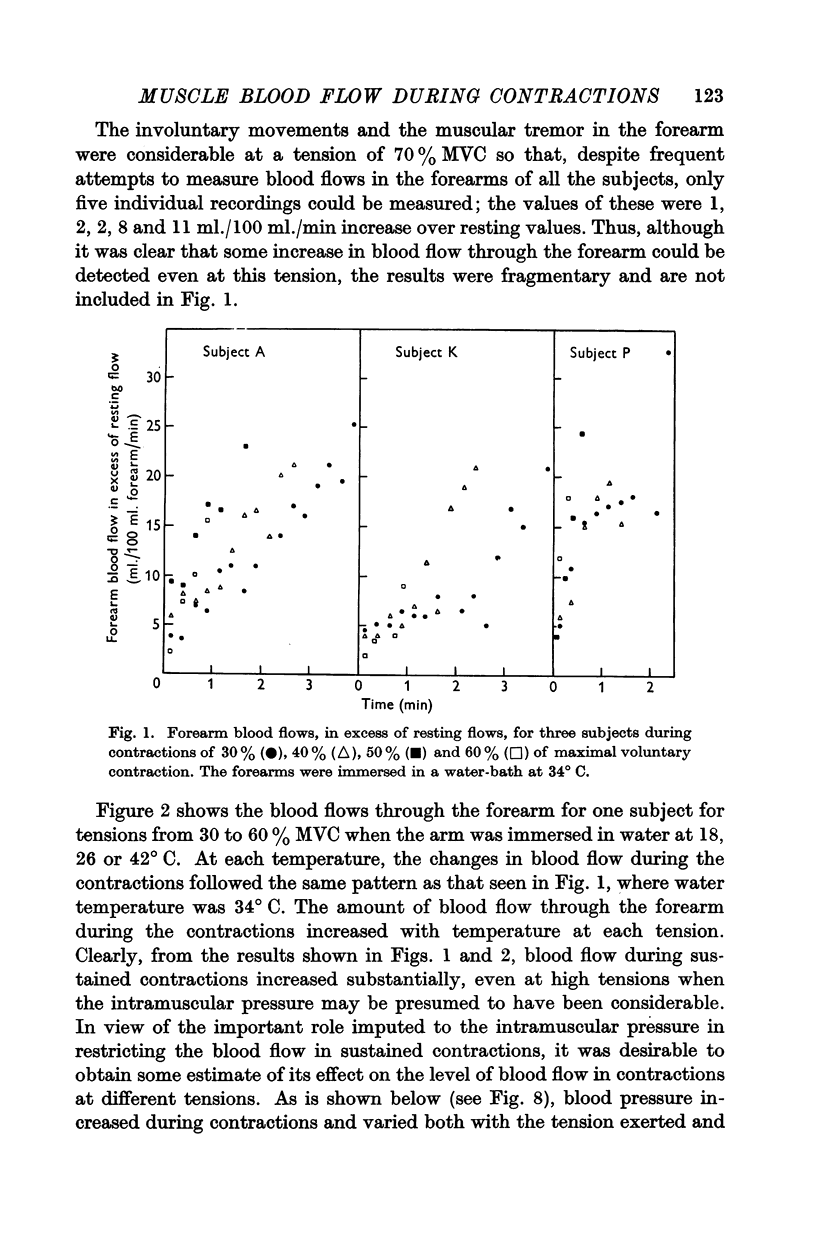
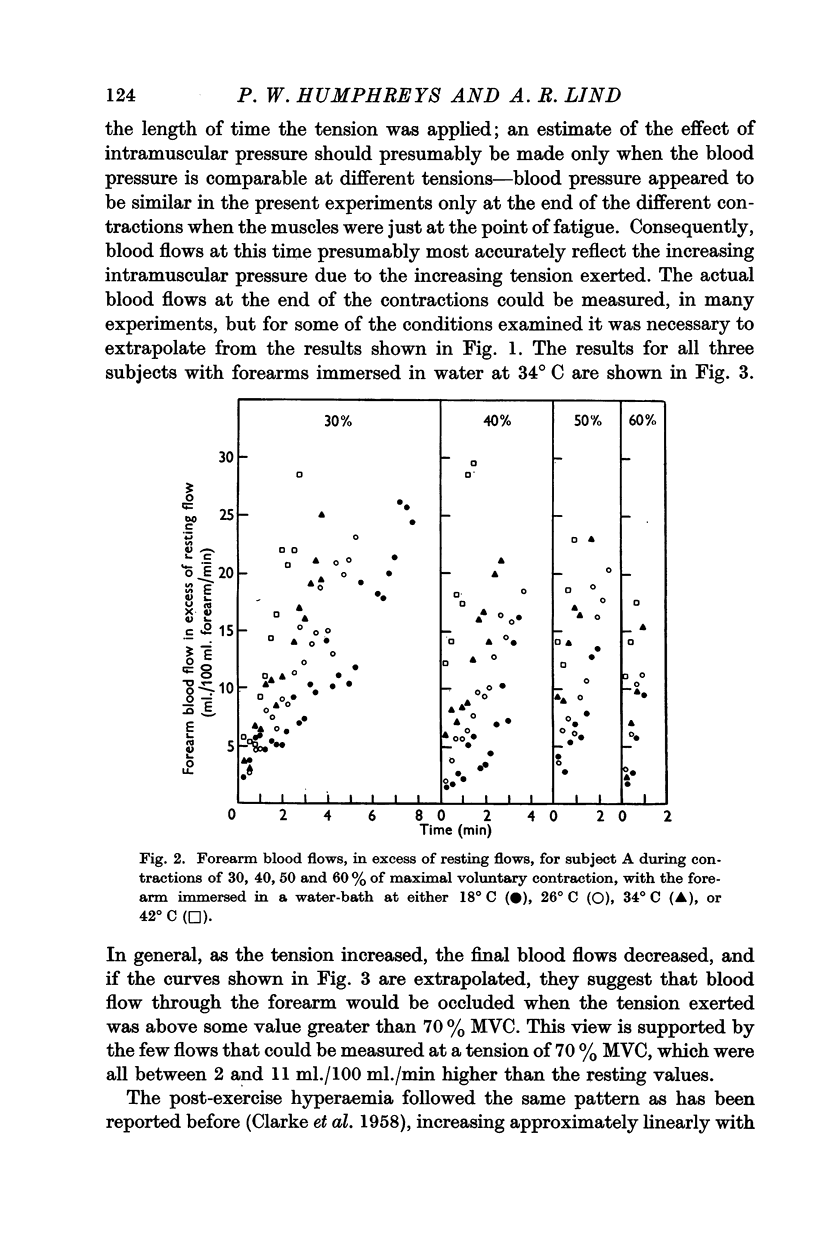
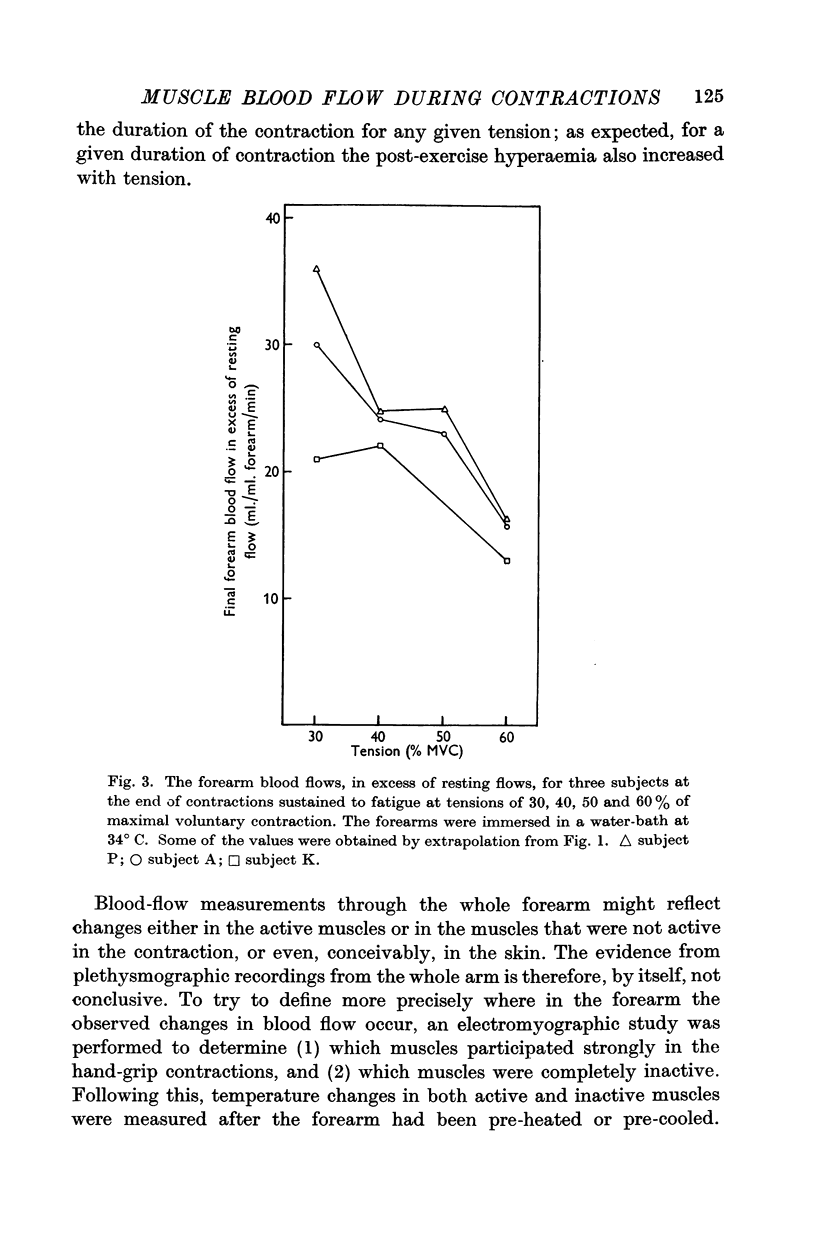
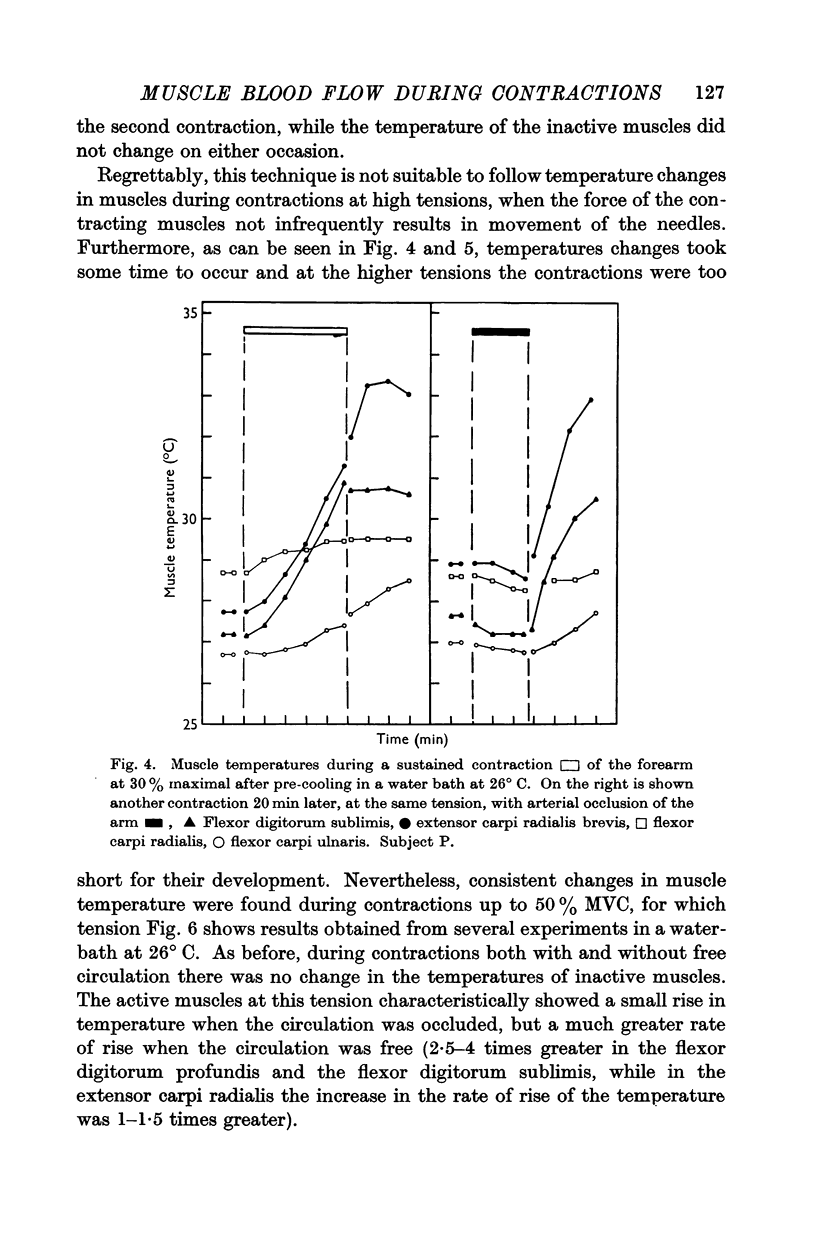
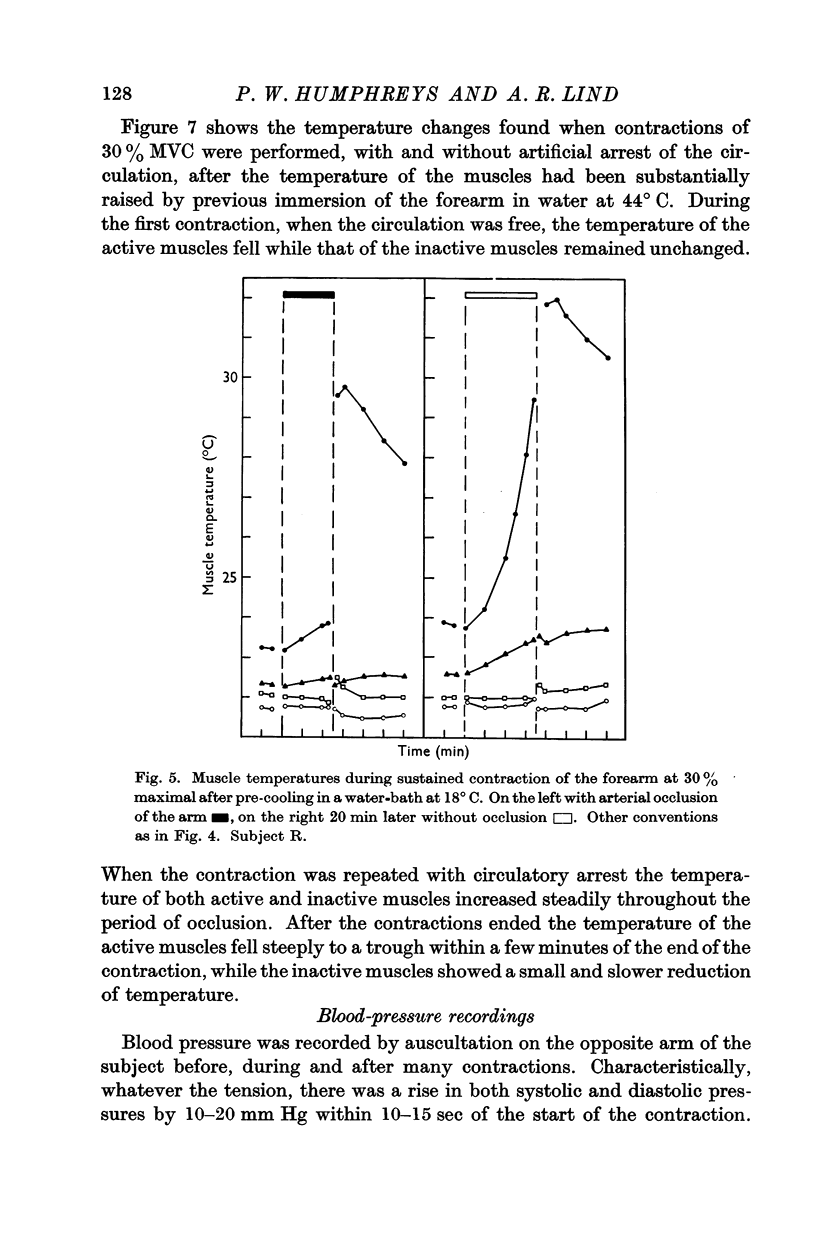
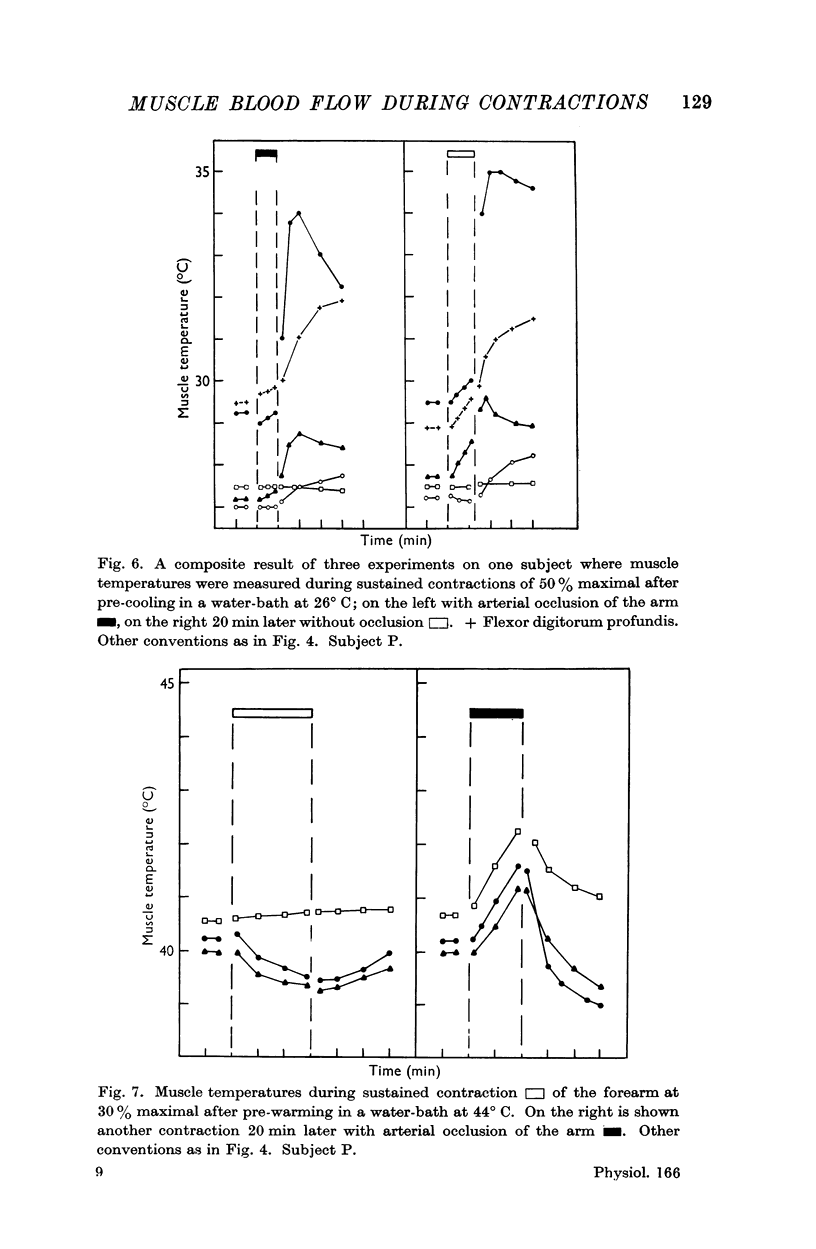
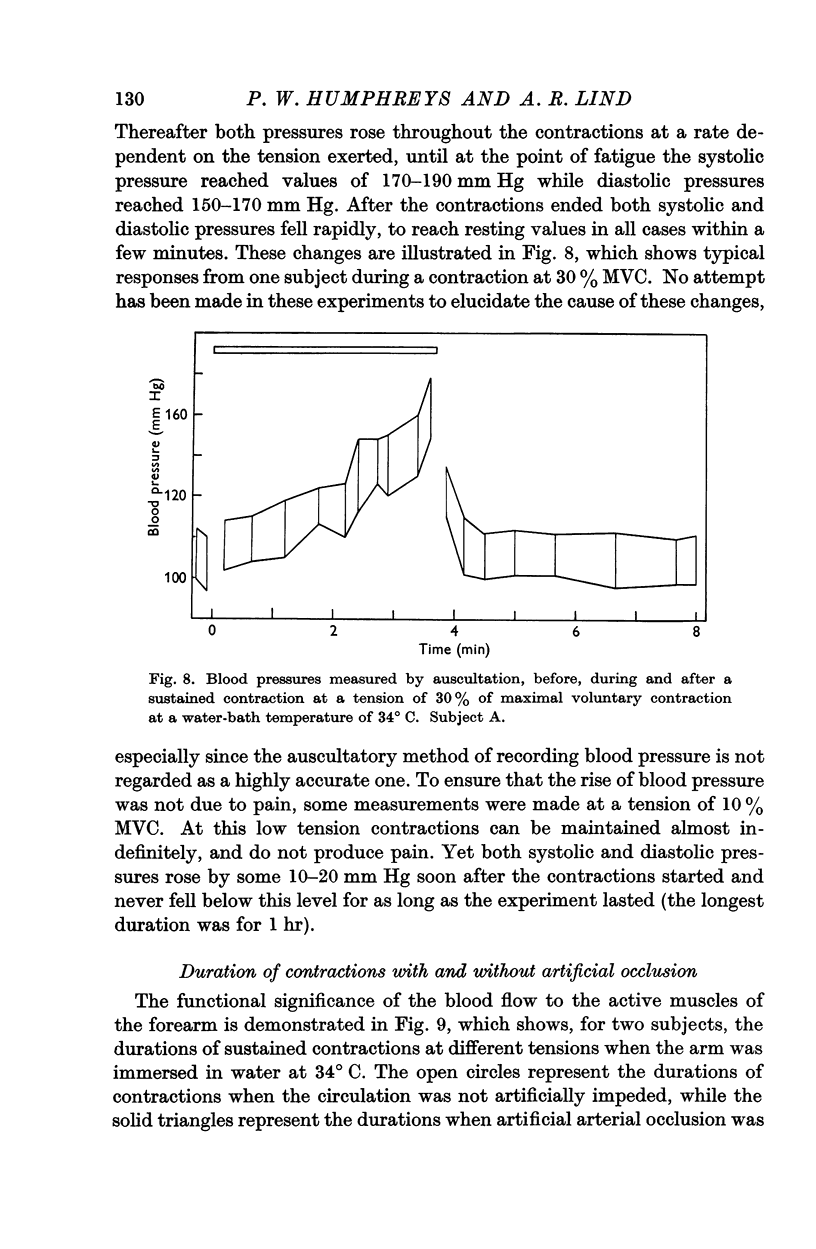
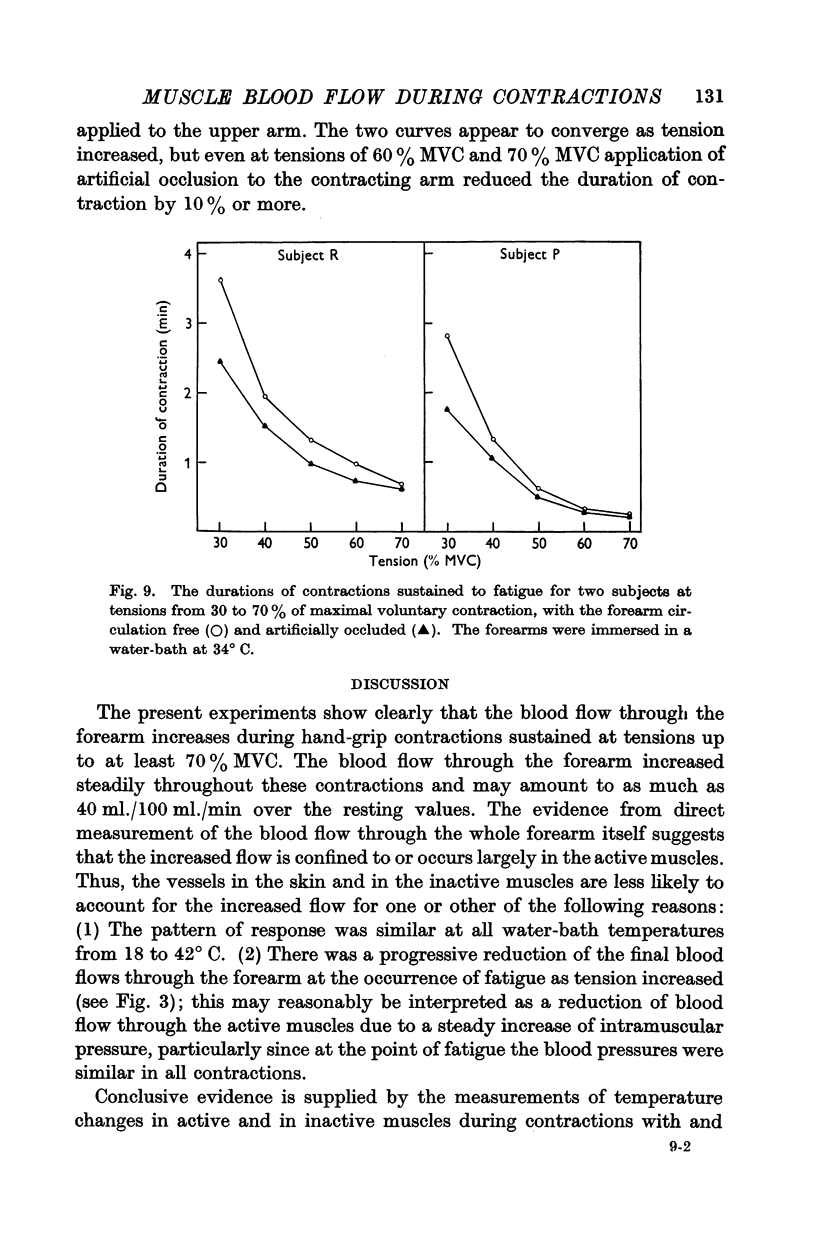
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARCROFT H., DORNHORST A. C. The blood flow through the human calf during rhythmic exercise. J Physiol. 1949 Sep;109(3-4):402-11, pl. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barcroft H., Millen J. L. The blood flow through muscle during sustained contraction. J Physiol. 1939 Nov 14;97(1):17–31. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1939.sp003789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKE R. S., HELLON R. F., LIND A. R. The duration of sustained contractions of the human forearm at different muscle temperatures. J Physiol. 1958 Oct 31;143(3):454–473. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaskell W H. The Changes of the Blood-stream in Muscles through Stimulation of their Nerves. J Anat Physiol. 1877 Apr;11(Pt 3):360–402.3. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILTON S. M. A peripheral arterial conducting mechanism underlying dilatation of the femoral artery and concerned in functional vasodilatation in skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1959 Dec;149:93–111. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill A. V. The pressure developed in muscle during contraction. J Physiol. 1948 Sep 30;107(4):518–526. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1948.sp004296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIND A. R. Muscle fatigue and recovery from fatigue induced by sustained contractions. J Physiol. 1959 Jun 23;147(1):162–171. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


