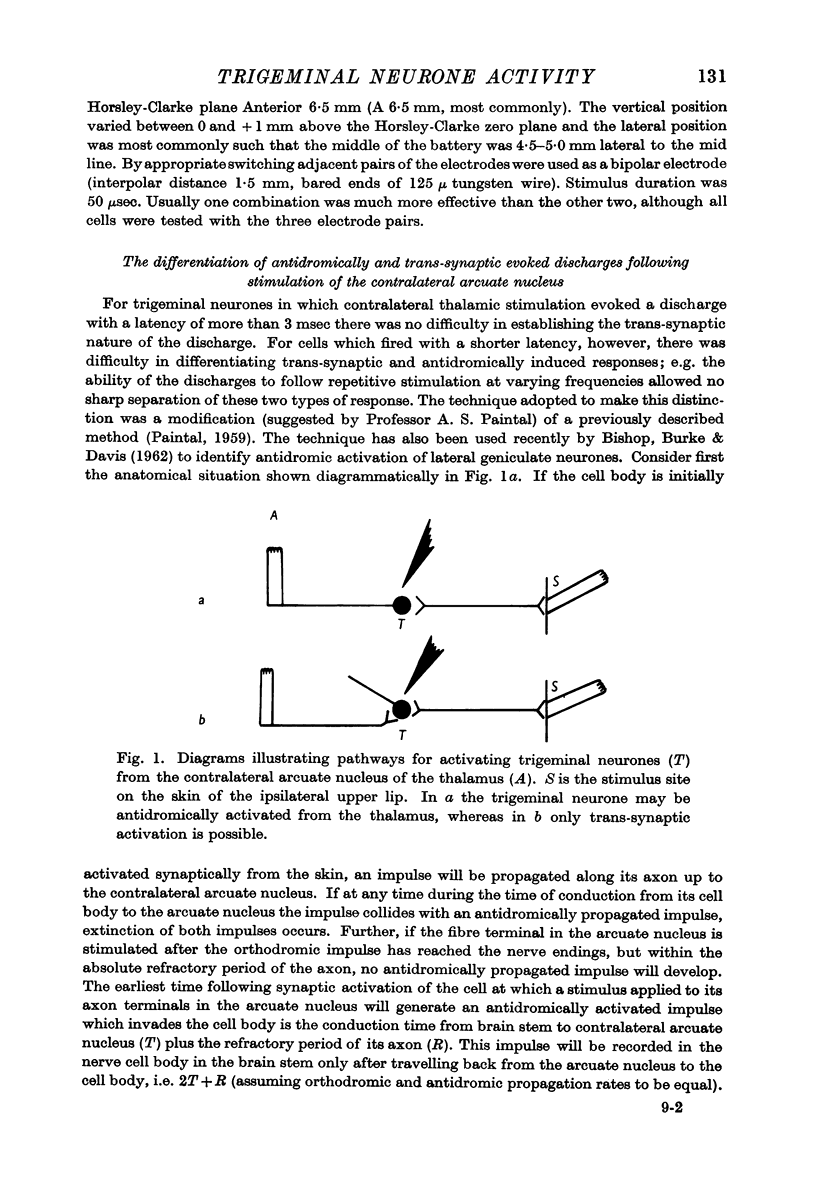
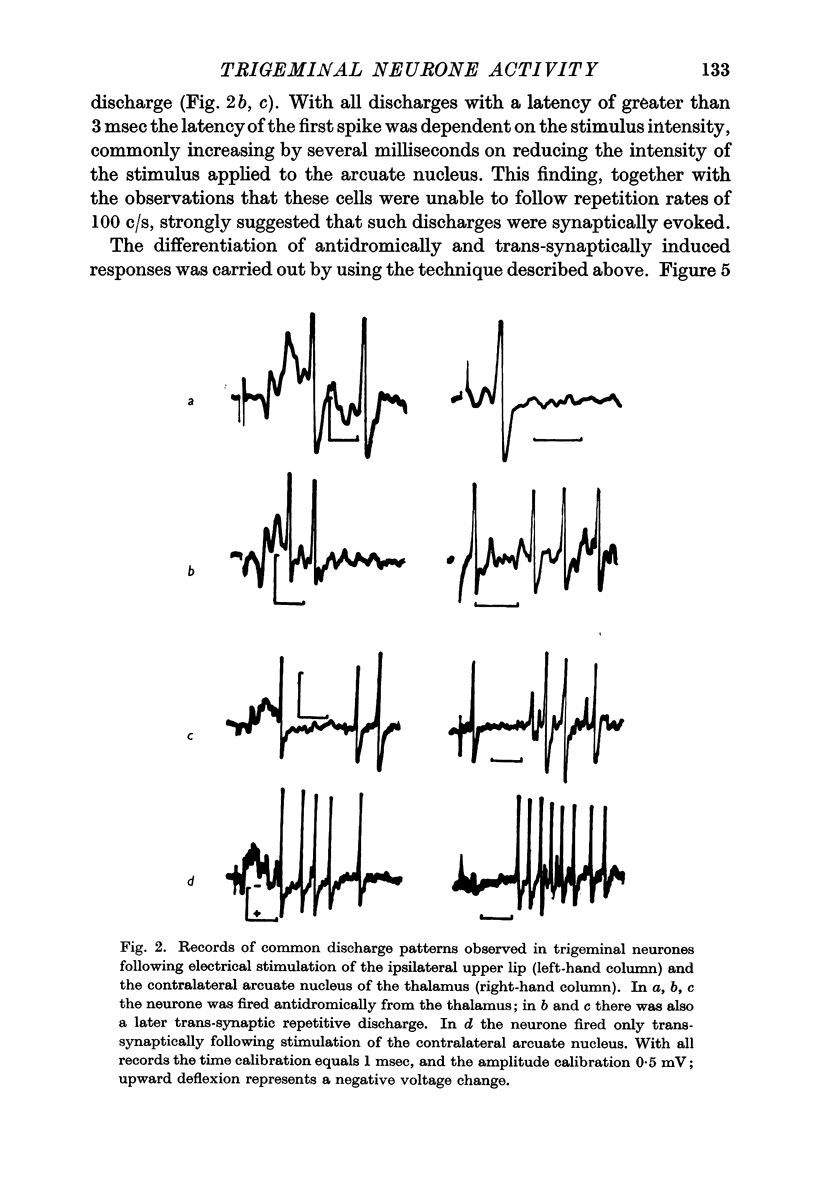
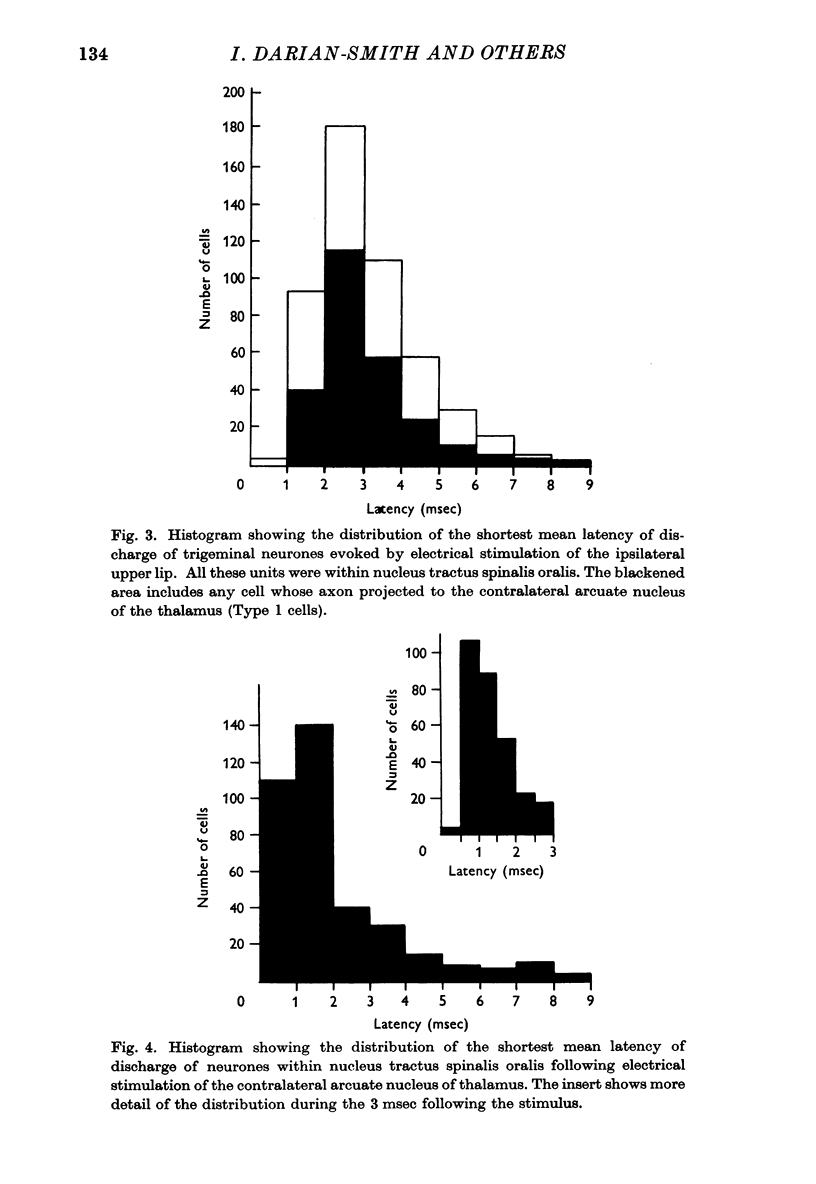
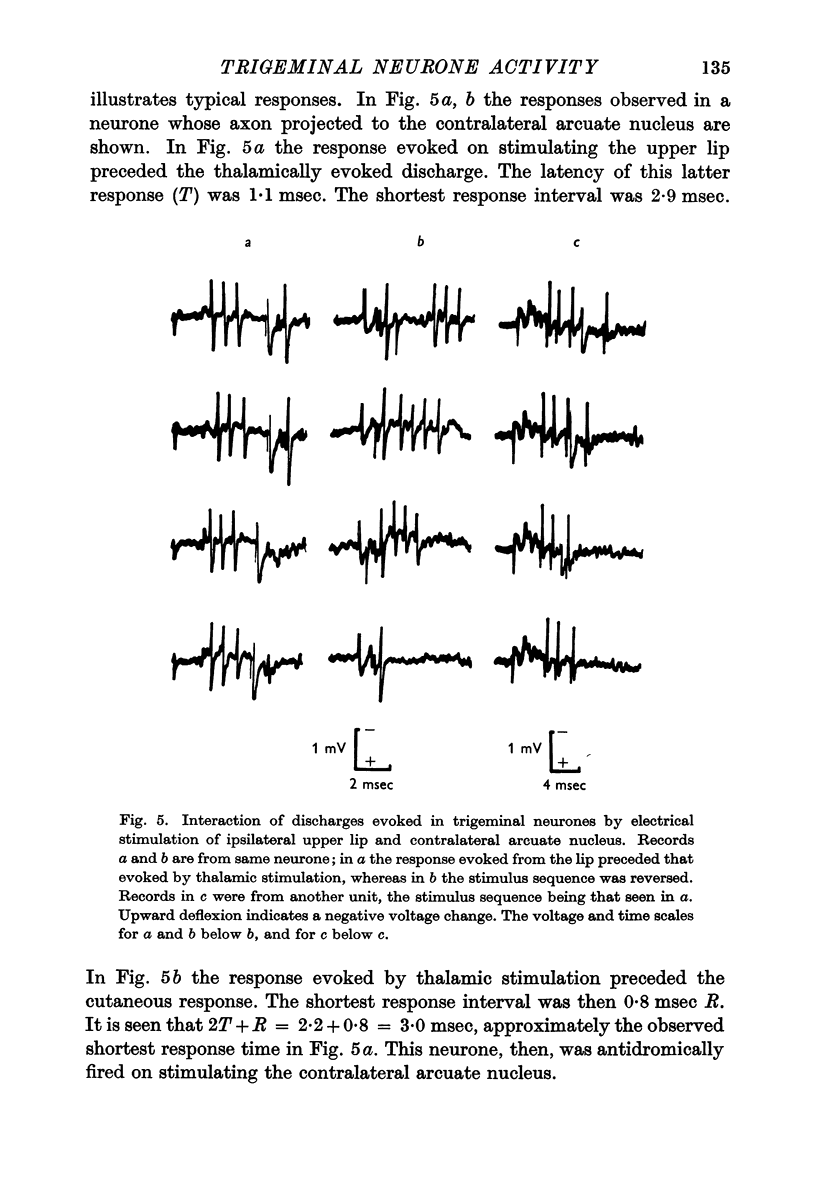
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BISHOP P. O., BURKE W., DAVIS R. Single-unit recording from antidromically activated optic radiation neurones. J Physiol. 1962 Aug;162:432–450. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRODAL A., SZABO T., TORVIK A. Corticofugal fibers to sensory trigeminal nuclei and nucleus of solitary tract; an experimental study in the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1956 Dec;106(2):527–555. doi: 10.1002/cne.901060215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARPENTER M. B., HANNA G. R. Fiber projections from the spinal trigeminal nucleus in the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1961 Aug;117:117–131. doi: 10.1002/cne.901170110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DARIAN-SMITH I., MAYDAY G. Somatotopic organization within the brain-stem trigeminal complex of the cat. Exp Neurol. 1960 Jun;2:290–309. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(60)90015-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DARIAN-SMITH I. Neurone activity in the cat's trigeminal main sensory nucleus elicited by graded afferent stimulation. J Physiol. 1960 Aug;153:52–73. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DARIAN-SMITH I., PROCTOR R., RYAN R. D. A SINGLE-NEURONE INVESTIGATION OF SOMATOTOPIC ORGANIZATION WITHIN THE CAT'S TRIGEMINAL BRAIN-STEM NUCLEI. J Physiol. 1963 Aug;168:147–157. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einarson L. A Method for Progressive Selective Staining of Nissl and Nuclear Substance in Nerve Cells. Am J Pathol. 1932 May;8(3):295–308.5. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORDON G., LANDGREN S., SEED W. A. The functional characteristics of single cells in the caudal part of the spinal nucleus of the trigeminal nerve of the cat. J Physiol. 1961 Oct;158:544–559. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORDON G., PAINE C. H. Functional organization in nucleus gracilis of the cat. J Physiol. 1960 Sep;153:331–349. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORDON G., SEED W. A. An investigation of nucleus gracilis of the cat by antidromic stimulation. J Physiol. 1961 Mar;155:589–601. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT C. C., McINTYRE A. K. An analysis of fibre diameter and receptor characteristics of myelinated cutaneous afferent fibres in cat. J Physiol. 1960 Aug;153:99–112. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubel D. H. Tungsten Microelectrode for Recording from Single Units. Science. 1957 Mar 22;125(3247):549–550. doi: 10.1126/science.125.3247.549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRUGER L., SIMINOFF R., WITKOVSKY P. Single neuron analysis of dorsal column nuclei and spinal nucleus of trigeminal in cat. J Neurophysiol. 1961 Jul;24:333–349. doi: 10.1152/jn.1961.24.4.333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLSZEWSKI J. On the anatomical and functional organization of the spinal trigeminal nucleus. J Comp Neurol. 1950 Jun;92(3):401–413. doi: 10.1002/cne.900920305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAINTAL A. S. Intramuscular propagation of sensory impulses. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:240–251. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERL E. R., WHITLOCK D. G., GENTRY J. R. Cutaneous projection to second-order neurons of the dorsal column system. J Neurophysiol. 1962 May;25:337–358. doi: 10.1152/jn.1962.25.3.337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SNIDER R. S. Recent contributions to the anatomy and physiology of the cerebellum. Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1950 Aug;64(2):196–219. doi: 10.1001/archneurpsyc.1950.02310260034002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TORVIK A. The ascending fibers from the main trigeminal sensory nucleus; an experimental study in the cat. Am J Anat. 1957 Jan;100(1):1–15. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001000102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALL P. D., TAUB A. Four aspects of trigeminal nucleus and a paradox. J Neurophysiol. 1962 Jan;25:110–126. doi: 10.1152/jn.1962.25.1.110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


