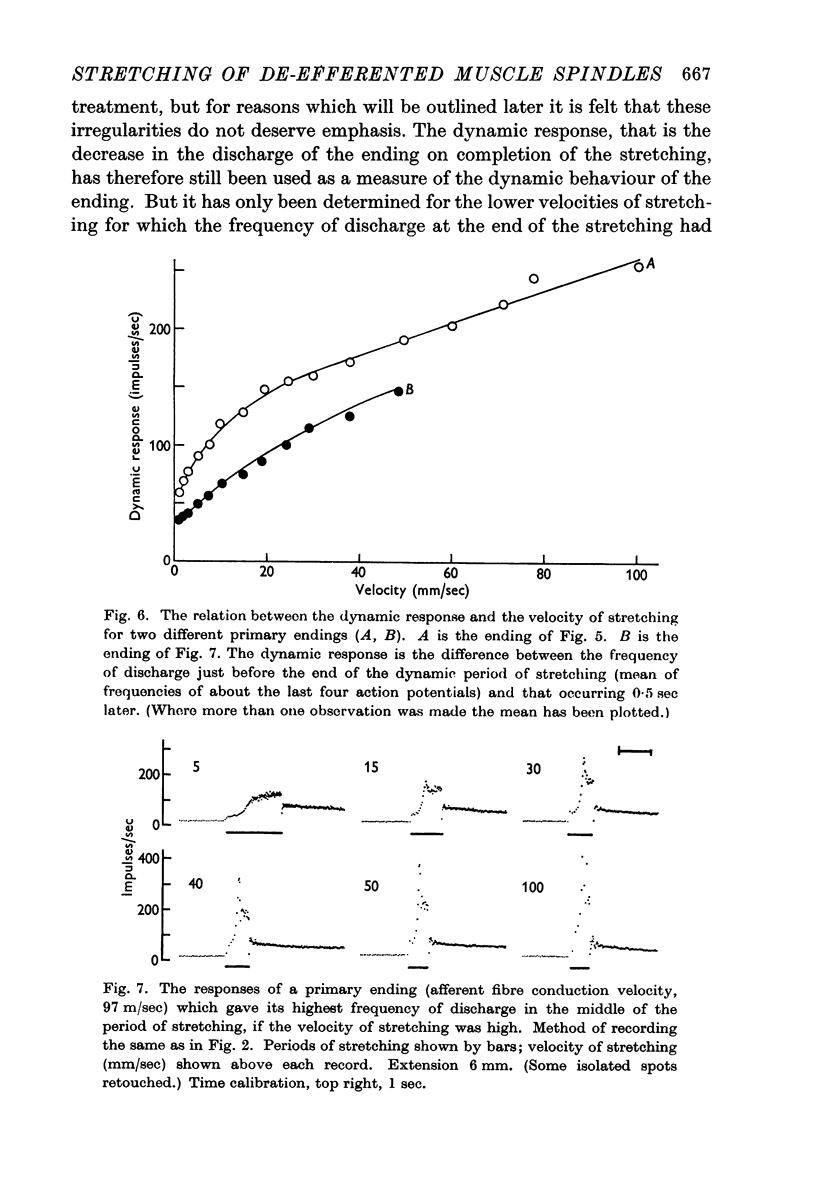
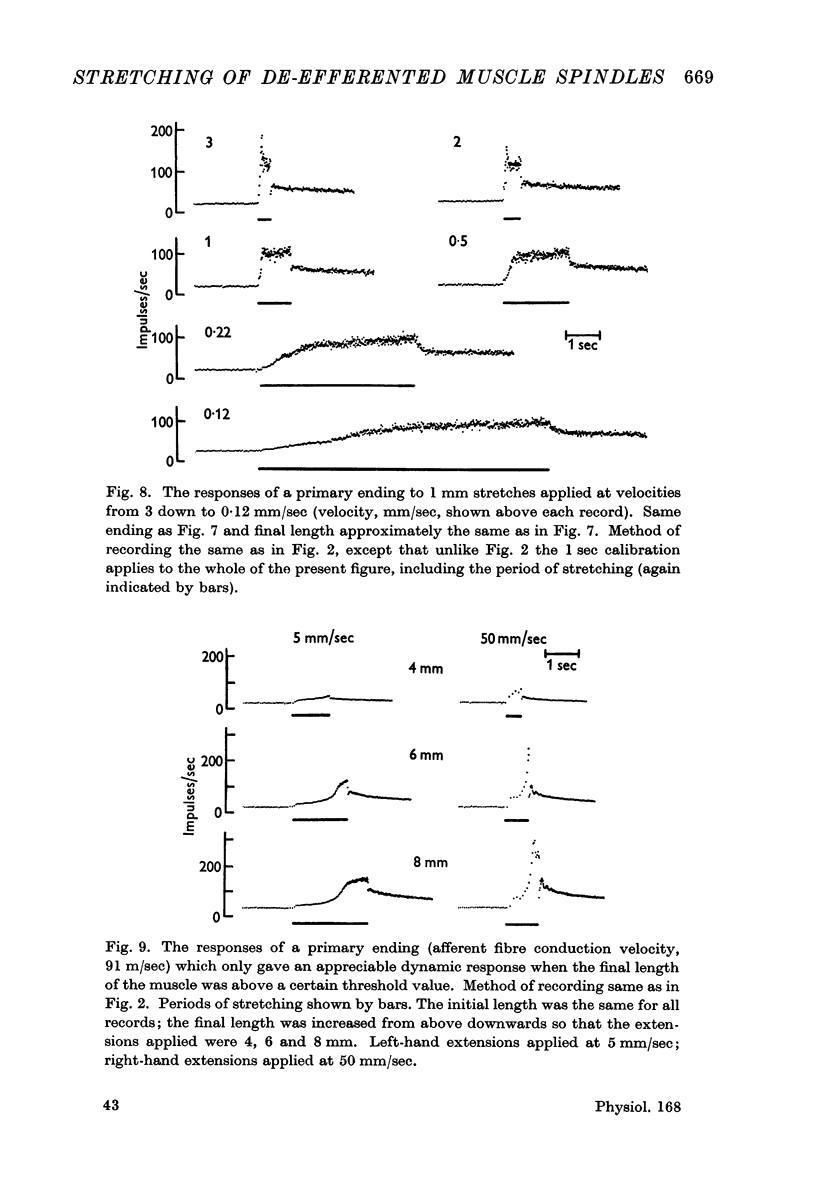
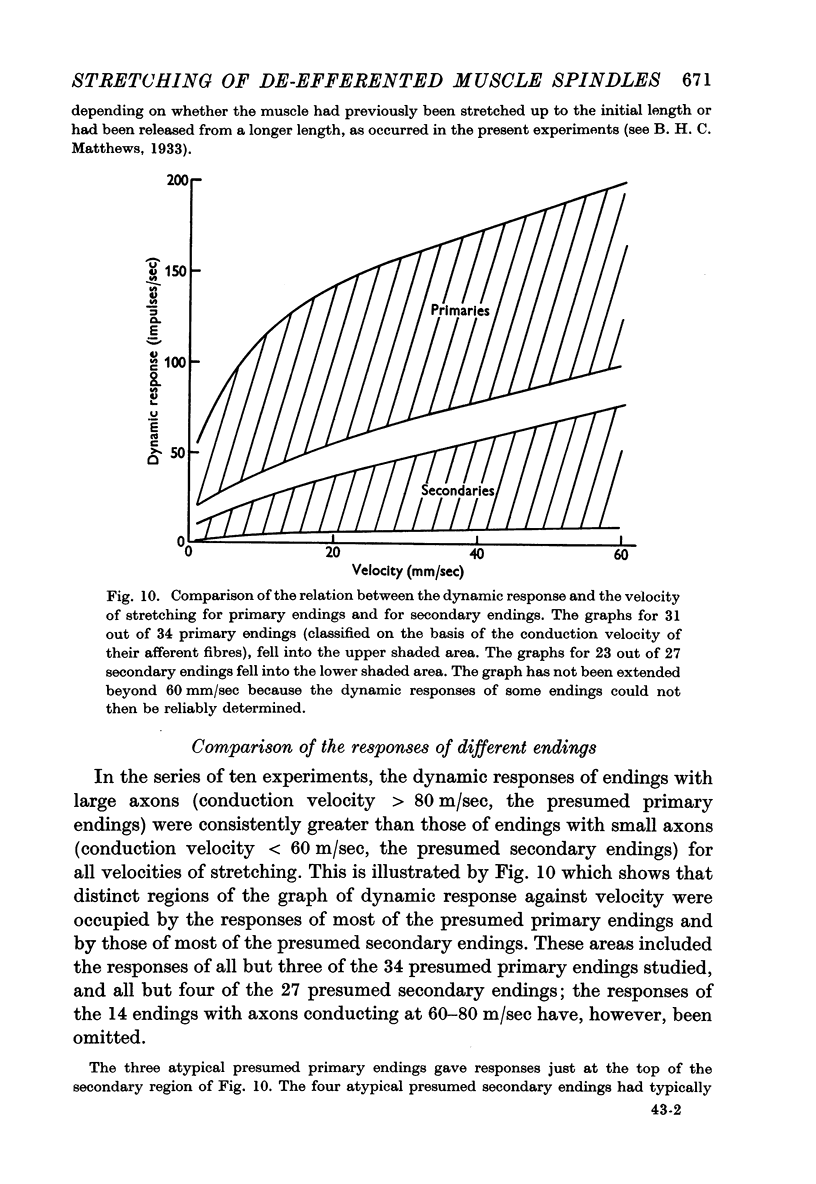
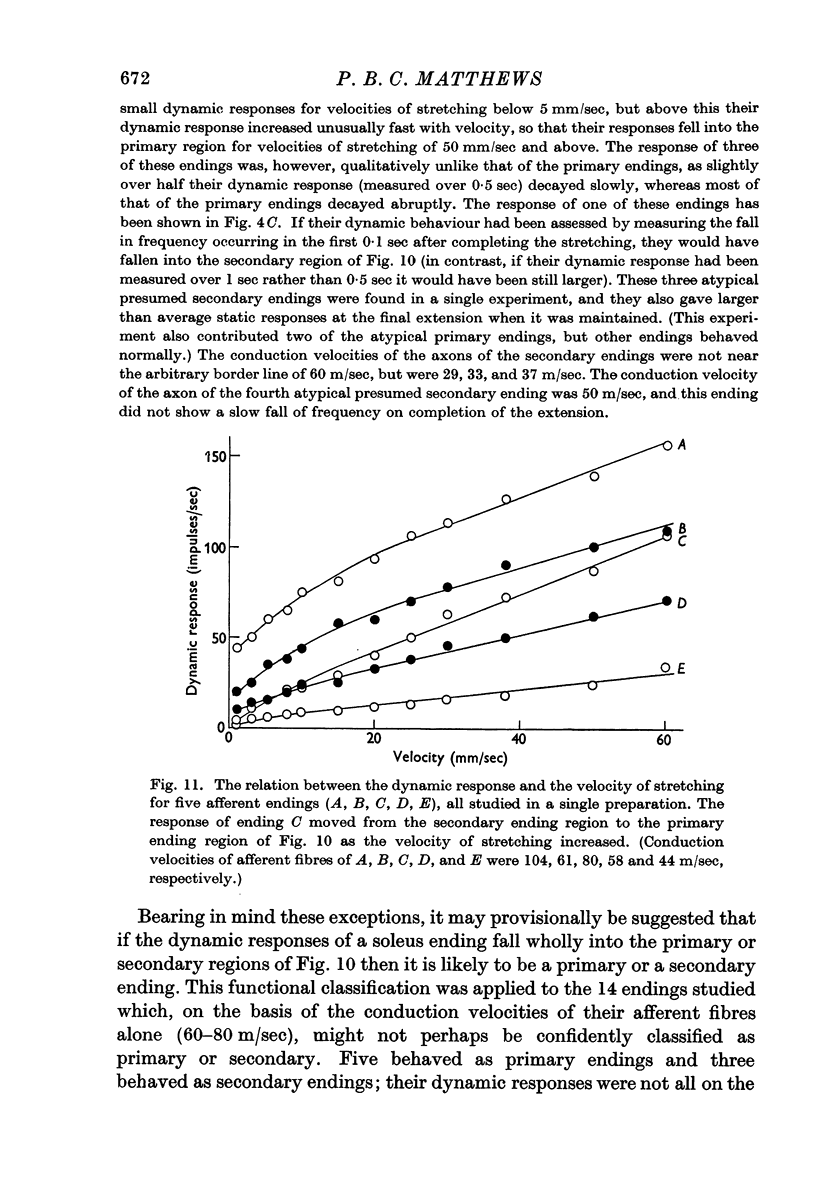
Full text
PDF





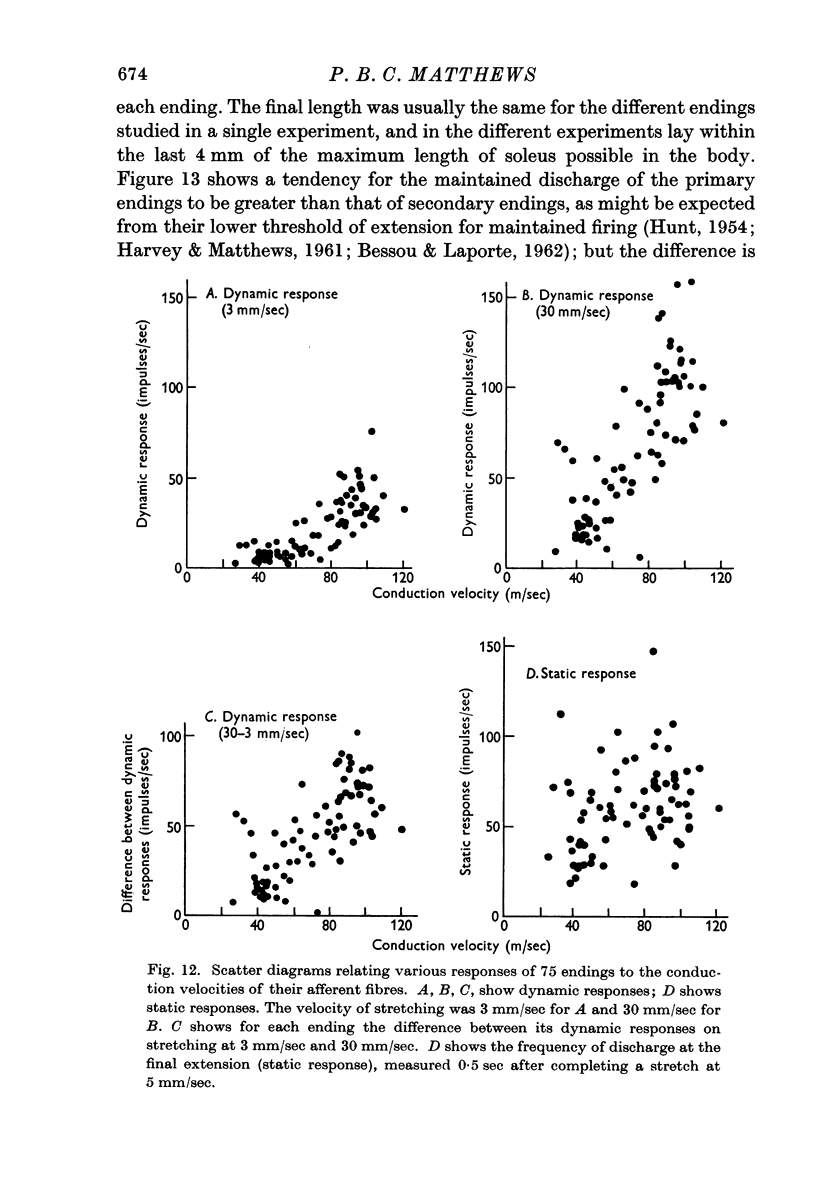




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- APPELBERG B. The effect of electrical stimulation in nucleus ruber on the response to stretch in primary and secondary muscle spindle afferents. Acta Physiol Scand. 1962 Oct;56:140–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1962.tb02491.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPER S. The responses of the primary and secondary endings of muscle spindles with intact motor innervation during applied stretch. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1961 Oct;46:389–398. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1961.sp001558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELDRED E., GRANIT R., MERTON P. A. Supraspinal control of the muscle spindles and its significance. J Physiol. 1953 Dec 29;122(3):498–523. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp005017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANIT R., HOMMA S. Phasic stretch and 'spindle constant' in slow and fast rabbit muscle. Acta Physiol Scand. 1959 Jun 24;46:174–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1959.tb01746.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARVEY R. J., MATTHEWS P. B. The response of de-efferented muscle spindle endings in the cat's soleus to slow extension of the muscle. J Physiol. 1961 Jul;157:370–392. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT C. C. Relation of function to diameter in afferent fibers of muscle nerves. J Gen Physiol. 1954 Sep 20;38(1):117–131. doi: 10.1085/jgp.38.1.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JANSEN J. K., MATTHEWS P. B. The central control of the dynamic response of muscle spindle receptors. J Physiol. 1962 May;161:357–378. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JANSEN J. K., MATTHEWS P. B. The effects of fusimotor activity on the static responsiveness of primary and secondary endings of muscle spindles in the decerebrate cat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1962 Aug;55:376–386. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1962.tb02451.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUNDBERG A., WINSBURY G. Selective adequate activation of large afferents from muscle spindles and Golgi tendon organs. Acta Physiol Scand. 1960 Jul 15;49:155–164. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1960.tb01939.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTHEWS P. B. The differentiation of two types of fusimotor fibre by their effects on the dynamic response of muscle spindle primary endings. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1962 Oct;47:324–333. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1962.sp001616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERTON P. A. The silent period in a muscle of the human hand. J Physiol. 1951 Jun;114(1-2):183–198. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews B. H. Nerve endings in mammalian muscle. J Physiol. 1933 Apr 13;78(1):1–53. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1933.sp002984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARTRIDGE L. D., GLASER G. H. Adaptation in regulation of movement and posture. A study of stretch responses in spastic animals. J Neurophysiol. 1960 May;23:257–268. doi: 10.1152/jn.1960.23.3.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruffini A. On the Minute Anatomy of the Neuromuscular Spindles of the Cat, and on their Physiological Significance. J Physiol. 1898 Jul 26;23(3):190–208.3. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1898.sp000723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


