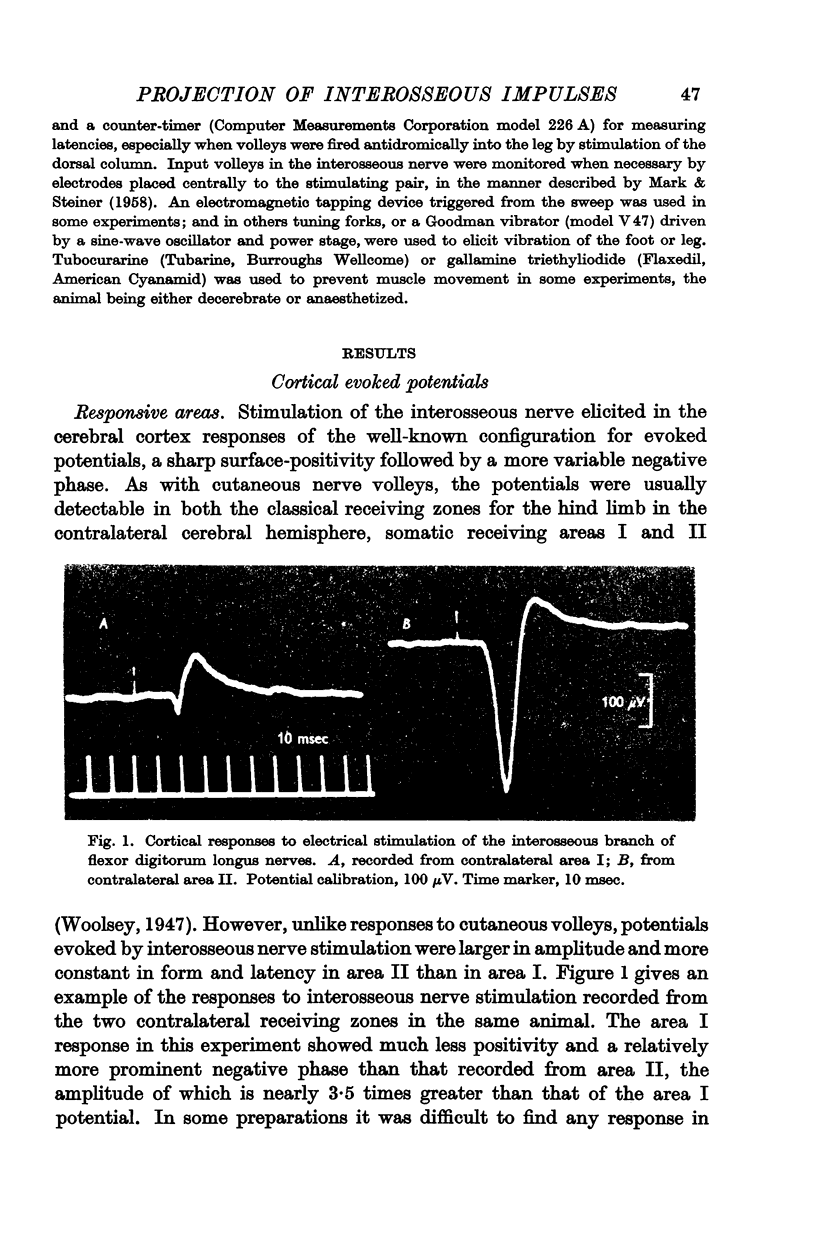
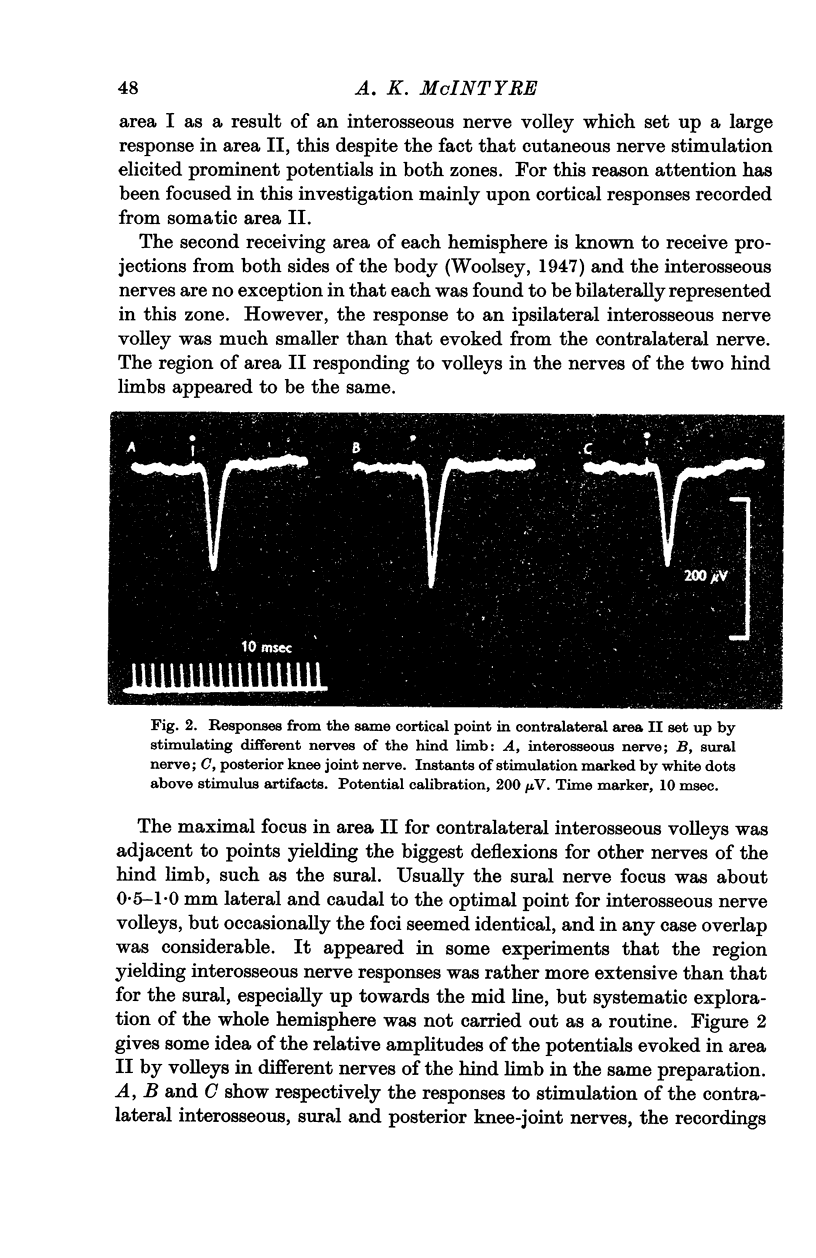
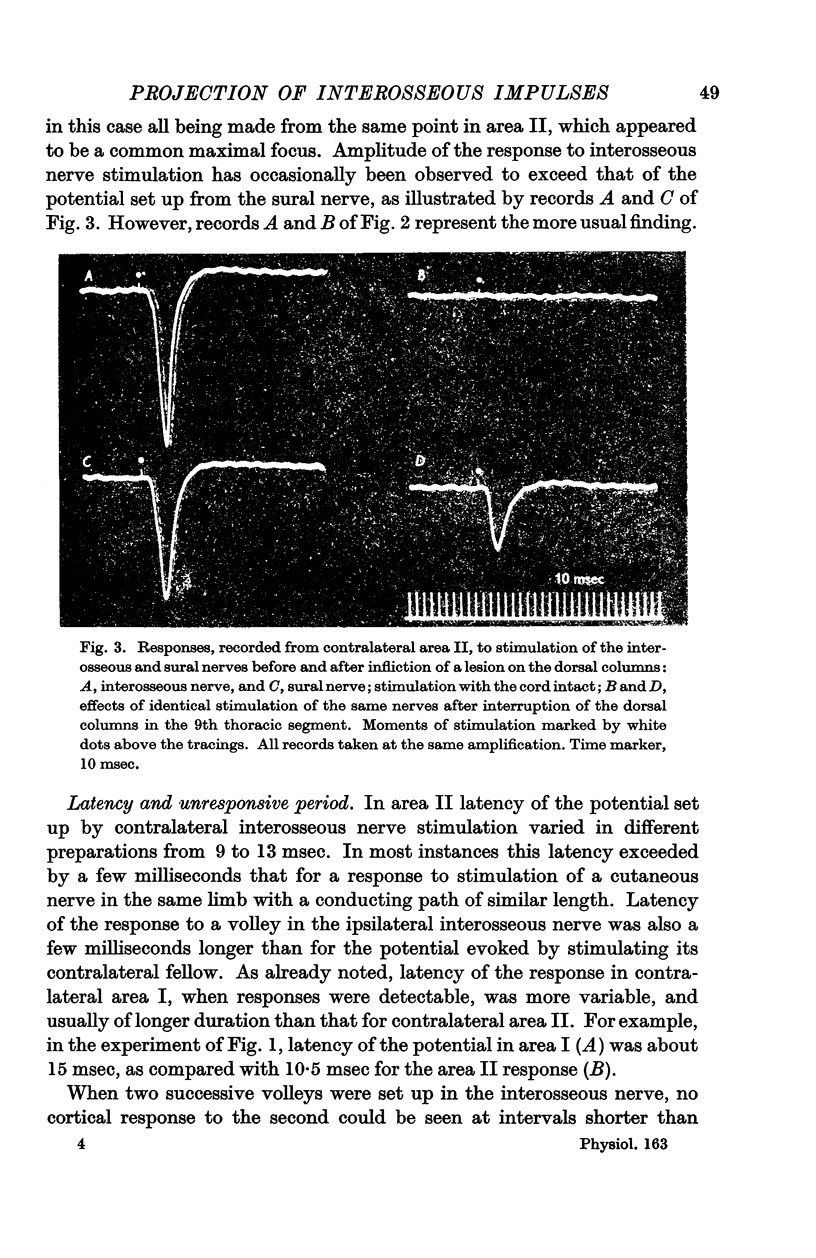
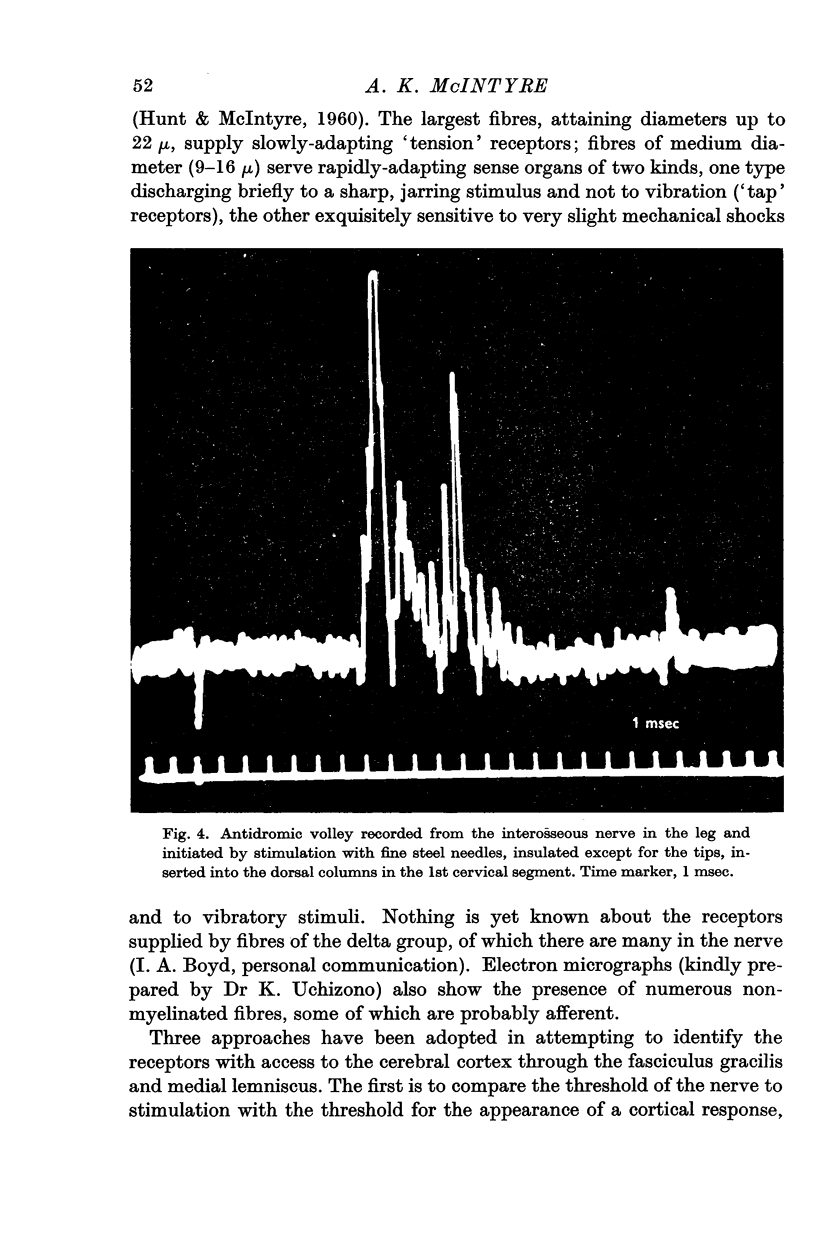
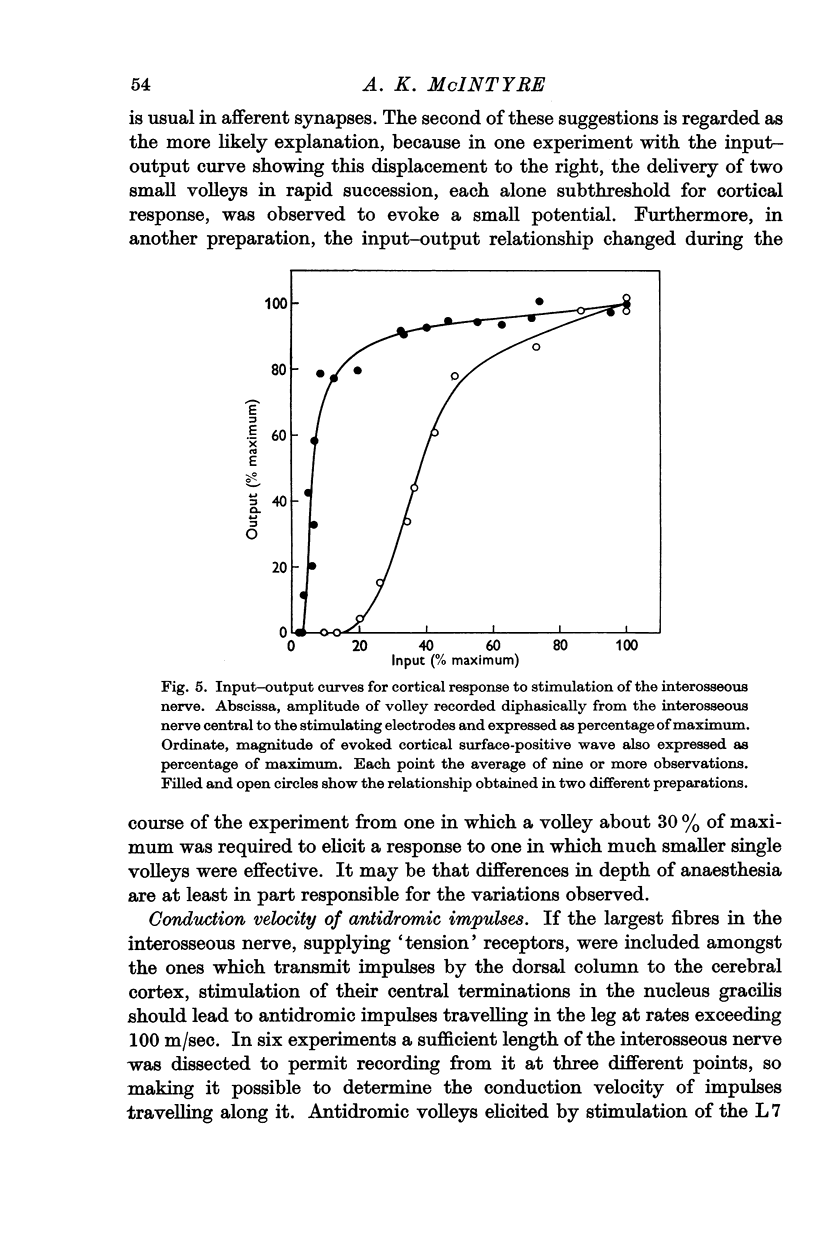
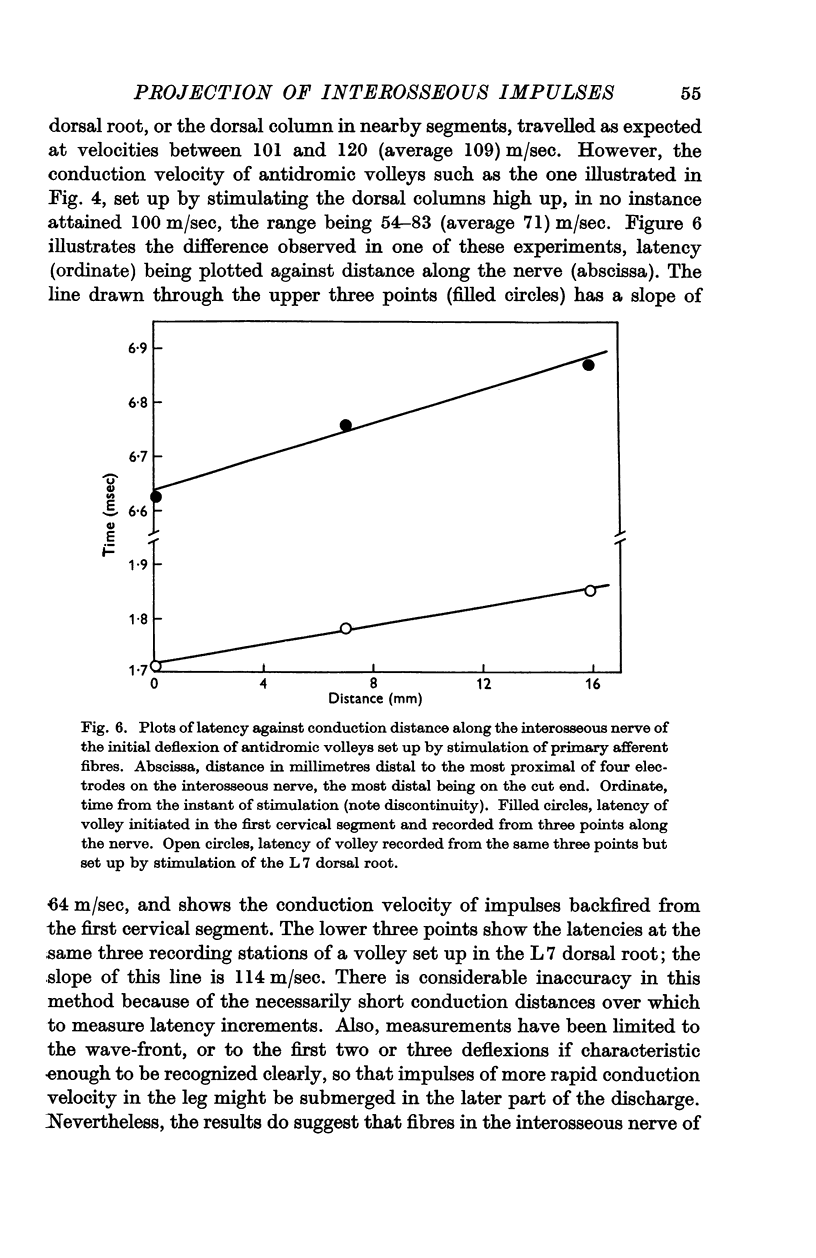
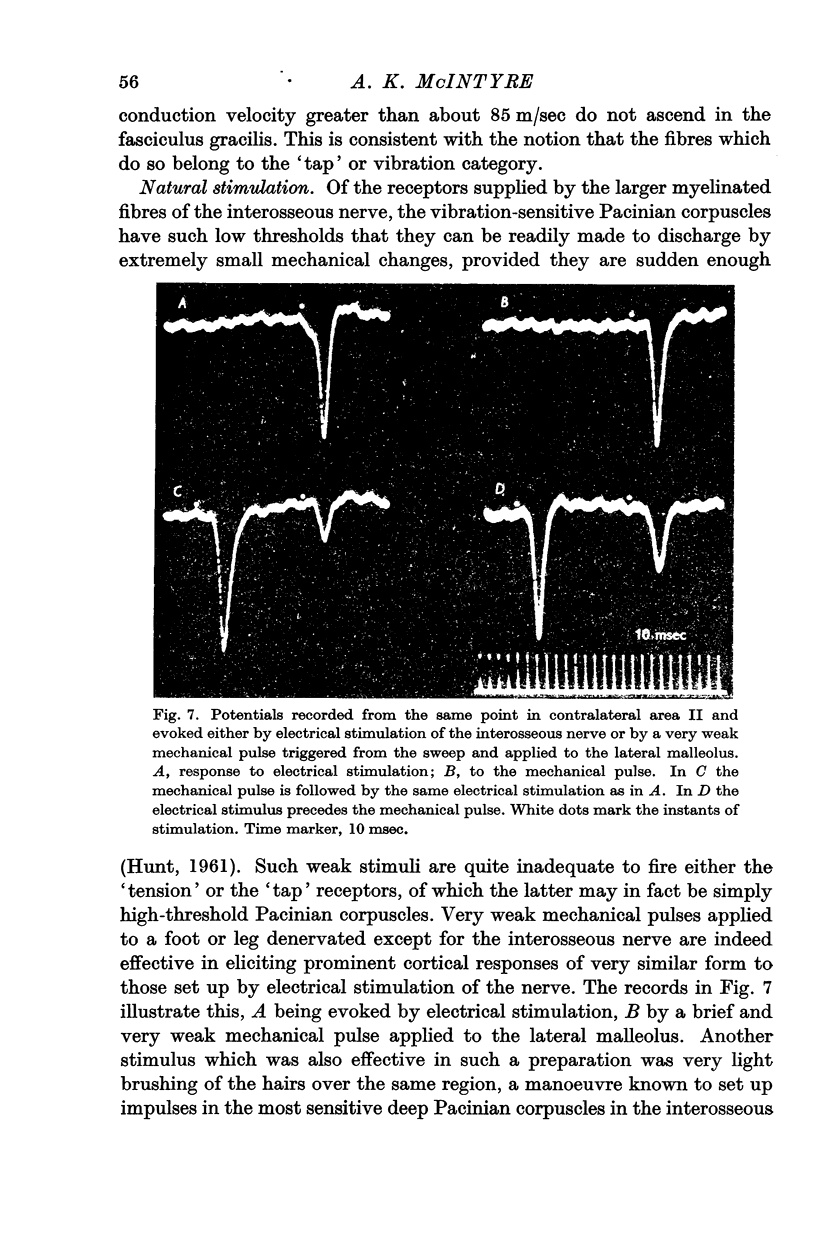
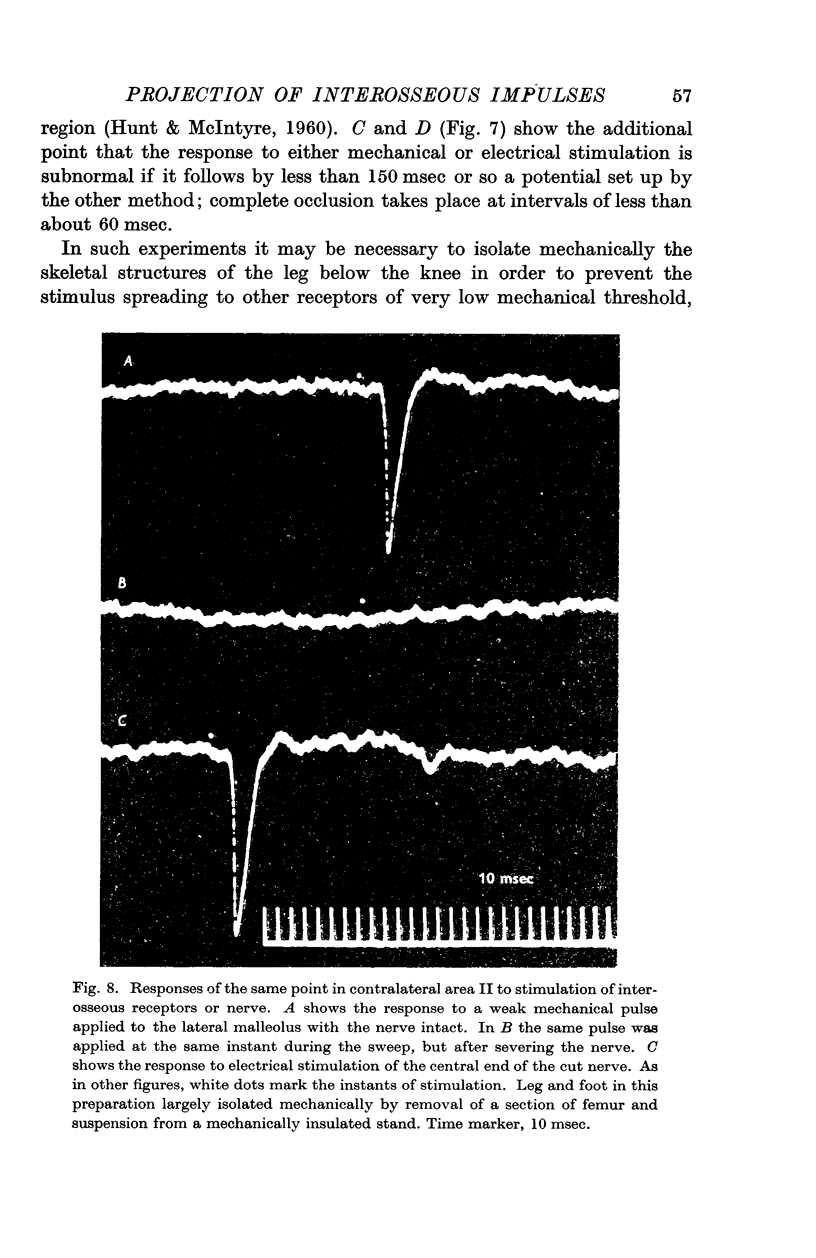
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMASSIAN V. E. Cortical representation of visceral afferents. J Neurophysiol. 1951 Nov;14(6):433–444. doi: 10.1152/jn.1951.14.6.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOWNMAN C. B. B. Cerebral destination of splanchnic afferent impulses. J Physiol. 1951 May;113(4):434–441. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT C. C., McINTYRE A. K. Characteristics of responses from receptors from the flexor longus digitorum muscle and the adjoining interosseous region of the cat. J Physiol. 1960 Aug;153:74–87. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT C. C. On the nature of vibration receptors in the hind limb of the cat. J Physiol. 1961 Jan;155:175–186. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LLOYD D. P. C., McINTYRE A. K. Dorsal column conduction of group I muscle afferent impulses and their relay through Clarke's column. J Neurophysiol. 1950 Jan;13(1):39–54. doi: 10.1152/jn.1950.13.1.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARK R. F., STEINER J. Cortical projection of impulses in myelinated cutaneous afferent nerve fibres of the cat. J Physiol. 1958 Aug 6;142(3):544–562. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCINTYRE A. K., MARK R. F. Synaptic linkage between afferent fibres of the cat's hind limb and ascending fibres in the dorsolateral funiculus. J Physiol. 1960 Sep;153:306–330. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOUNTCASTLE V. B., COVIAN M. R., HARRISON C. R. The central representation of some forms of deep sensibility. Res Publ Assoc Res Nerv Ment Dis. 1952;30:339–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOUNTCASTLE V. B., POWELL T. P. Central nervous mechanisms subserving position sense and kinesthesis. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1959 Oct;105:173–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


