Full text
PDF

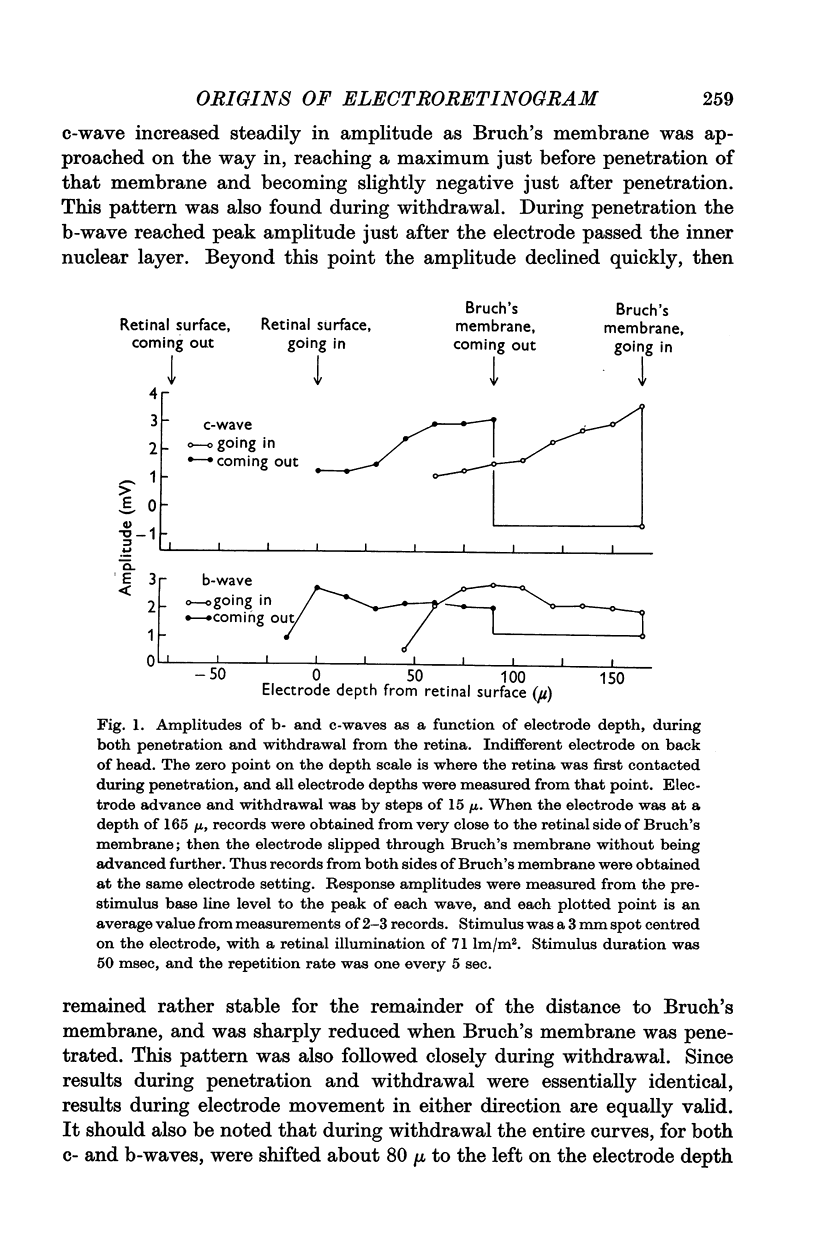

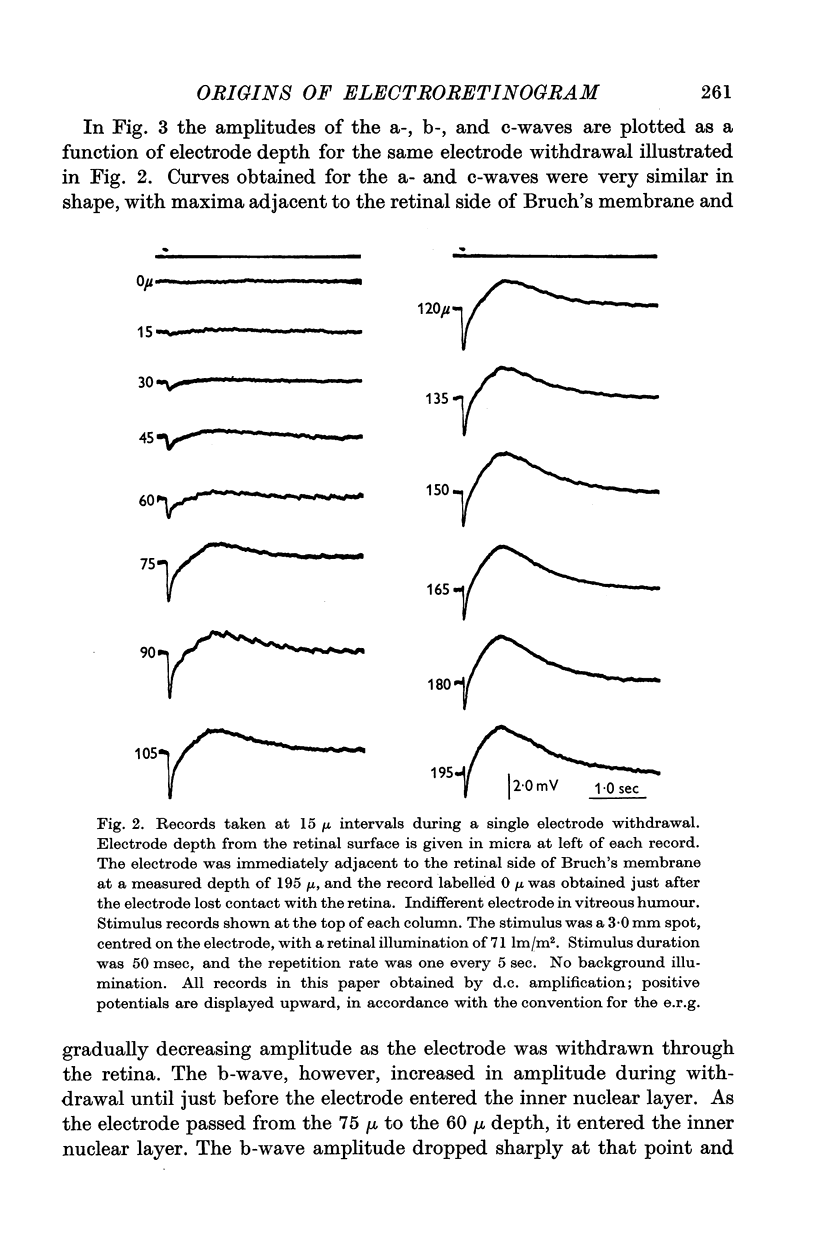
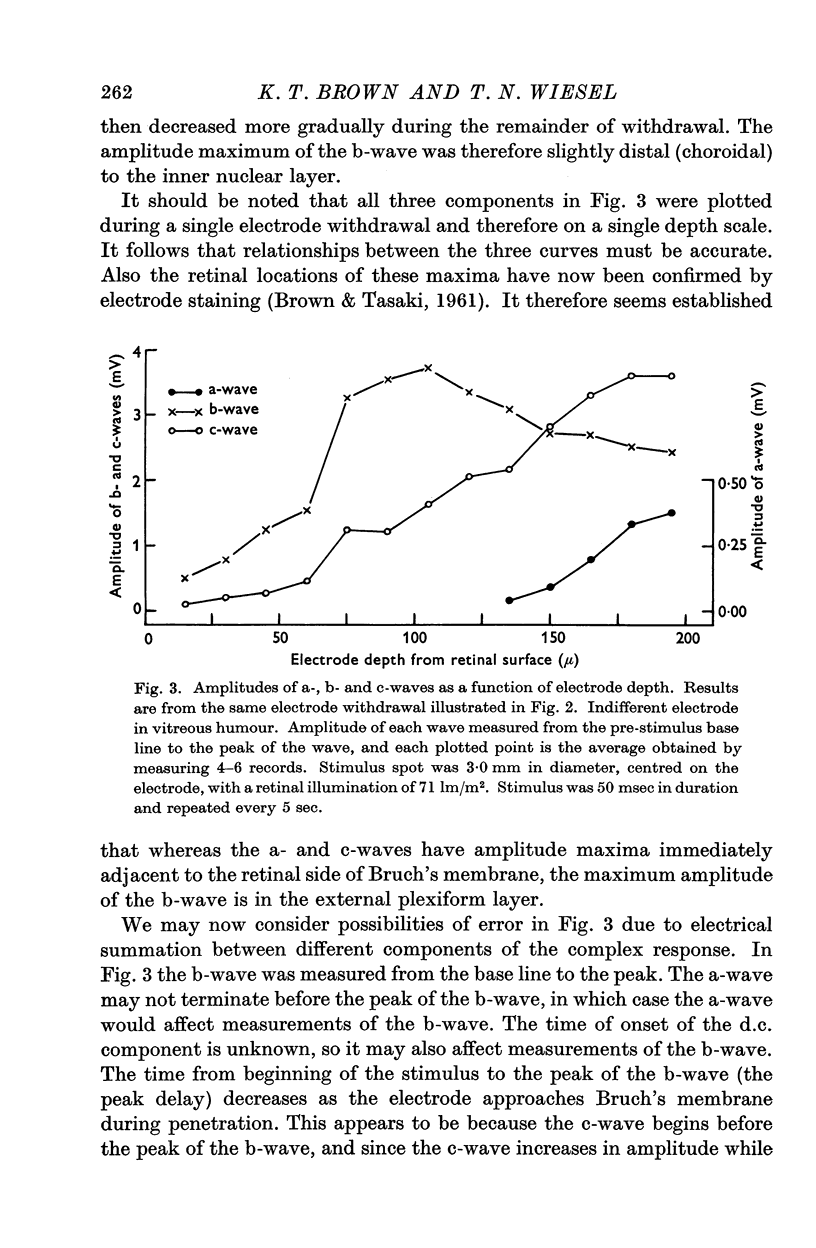
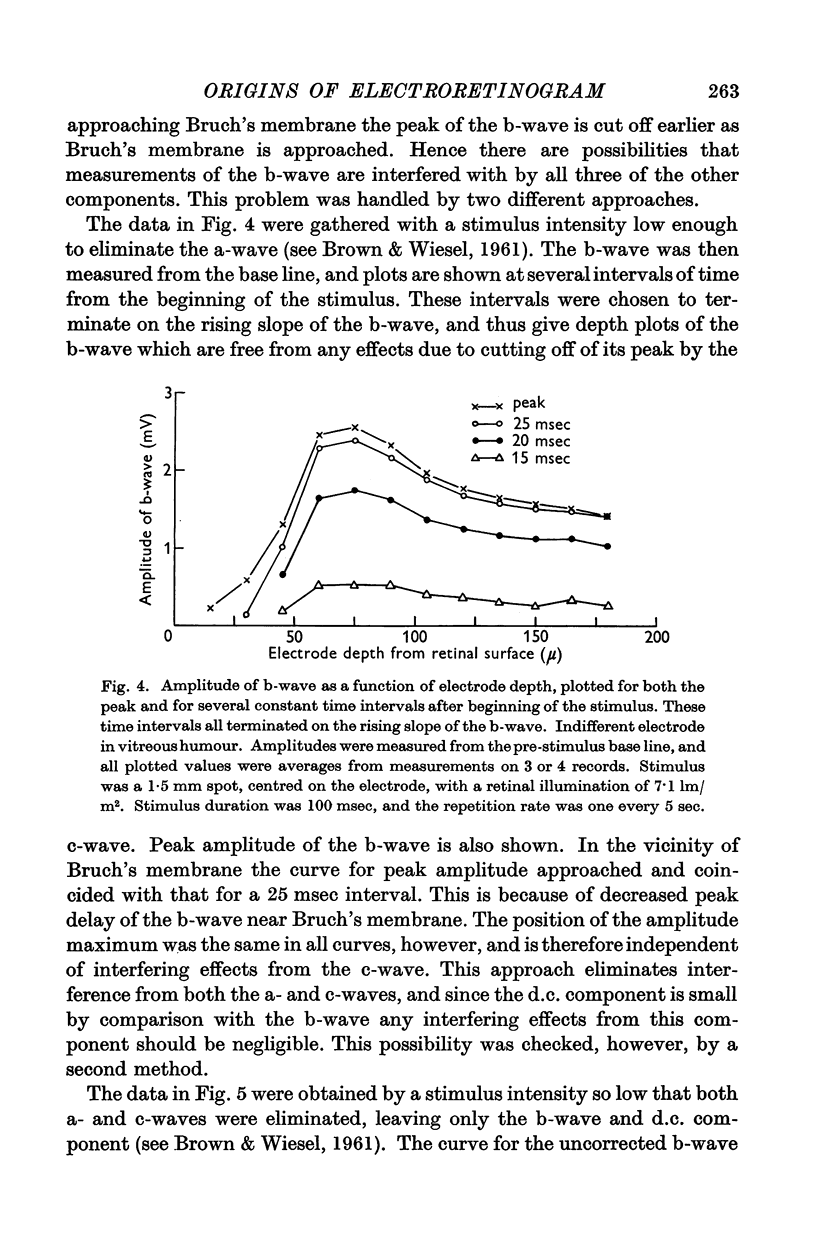














Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRINDLEY G. S. Responses to illumination recorded by microelectrodes from the frog's retina. J Physiol. 1956 Nov 28;134(2):360–384. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRINDLEY G. S. The sources of slow electrical activity in the frog's retina. J Physiol. 1958 Feb 17;140(2):247–261. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp005931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN K. T., TASAKI K. Localization of electrical activity in the cat retina by an electrode marking method. J Physiol. 1961 Sep;158:281–295. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN K. T., WIESEL T. N. Analysis of the intraretinal electroretinogram in the intact cat eye. J Physiol. 1961 Sep;158:229–256. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN K. T., WIESEL T. N. Intraretinal recording in the unopened cat eye. Am J Ophthalmol. 1958 Sep;46(3 Pt 2):91–98. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(58)90058-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN K. T., WIESEL T. N. Intraretinal recording with micropipette electrodes in the intact cat eye. J Physiol. 1959 Dec;149:537–562. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRESCITELLI F. Physiology of vision. Annu Rev Physiol. 1960;22:525–578. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.22.030160.002521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granit R. The components of the retinal action potential in mammals and their relation to the discharge in the optic nerve. J Physiol. 1933 Feb 8;77(3):207–239. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1933.sp002964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOELL W. K. The origin of the electroretinogram. Am J Ophthalmol. 1954 Jul;38(12):78–90. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(54)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTER K. R. The submicroscopic morphology of protoplasm. Harvey Lect. 1955;51:175–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOMITA T., FUNAISHI A. Studies on the intraretinal action potential. II. Effects of some chemical agents upon it. Jpn J Physiol. 1951 Nov;2(2):147–153. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.2.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOMITA T., MIZUNO H. B., IDA T. Studies on the intraretinal action potential. III. Intraretinal negative potential as compared with b wave in the ERG. Jpn J Physiol. 1952 Feb;2(3):171–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOMITA T., MURAKAMI M., HASHIMOTO Y. On the R membrane in the frog's eye: its localization, and relation to the retinal action potential. J Gen Physiol. 1960 Jul;43(6 Suppl):81–94. doi: 10.1085/jgp.43.6.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOMITA T., TORIHAMA Y. Further study on the intraretinal action potentials and on the site of ERG generation. Jpn J Physiol. 1956 Jun 15;6(2):118–136. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.6.118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATANABE K., TOSAKA T., YOKOTA T. Effects of extrinsic electric current on the cyprinid fish EIRG (S-potential). Jpn J Physiol. 1960 Apr 29;10:132–141. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.10.132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAMADA E. A peculiar lamellated body observed in the cells of the pigment epithelium of the retina of the bat, Pipistrellus abramus. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 May 25;4(3):329–330. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.3.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAMASHITA E. Some analyses of slow potentials of toad's retina. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1959 Aug 25;70:221–233. doi: 10.1620/tjem.70.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


