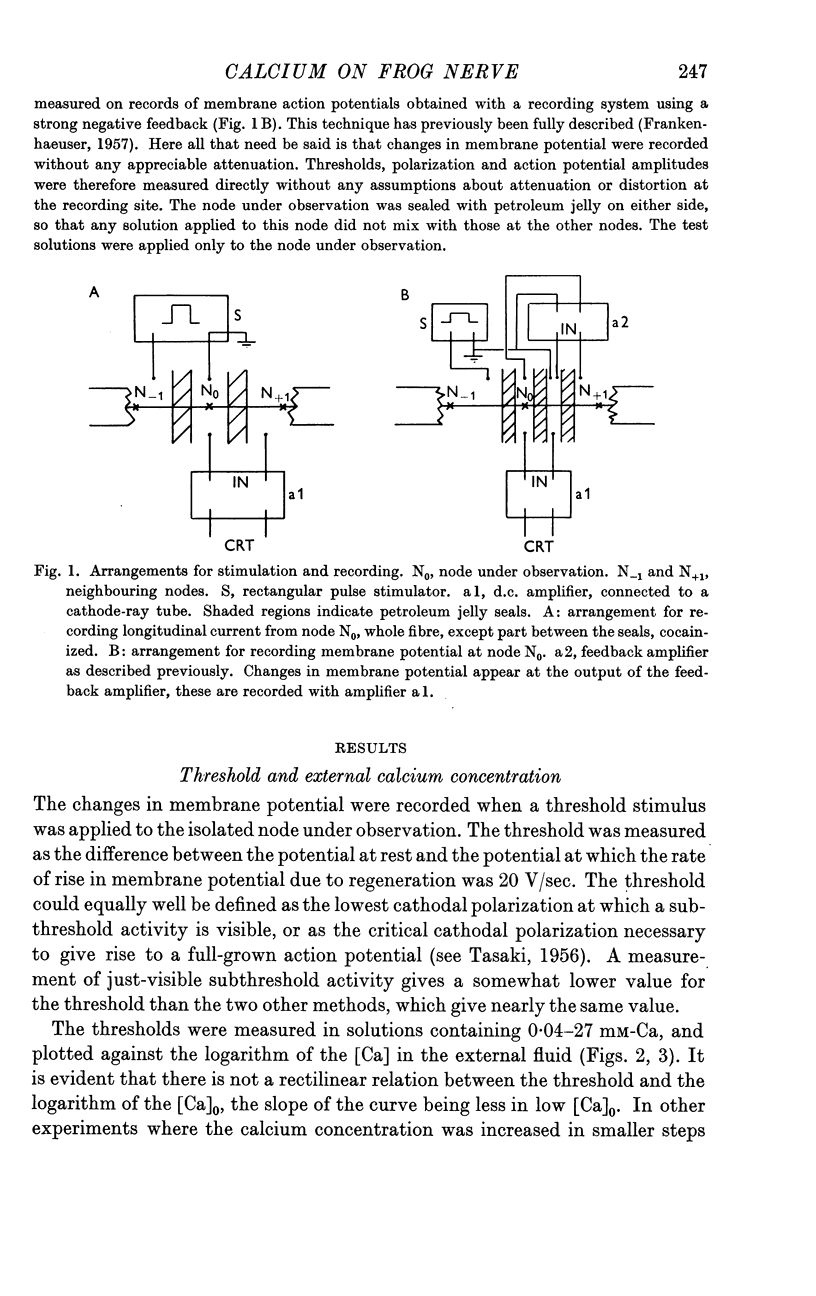
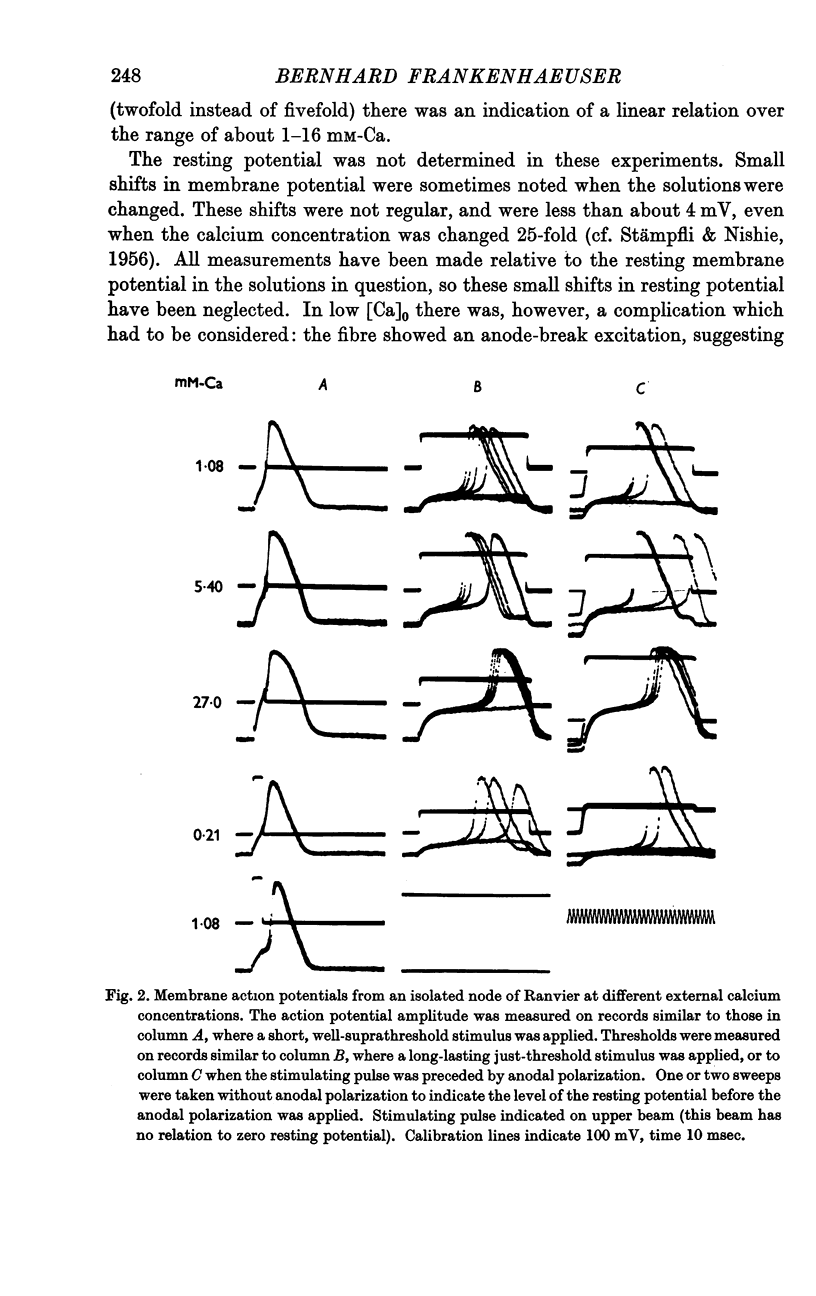
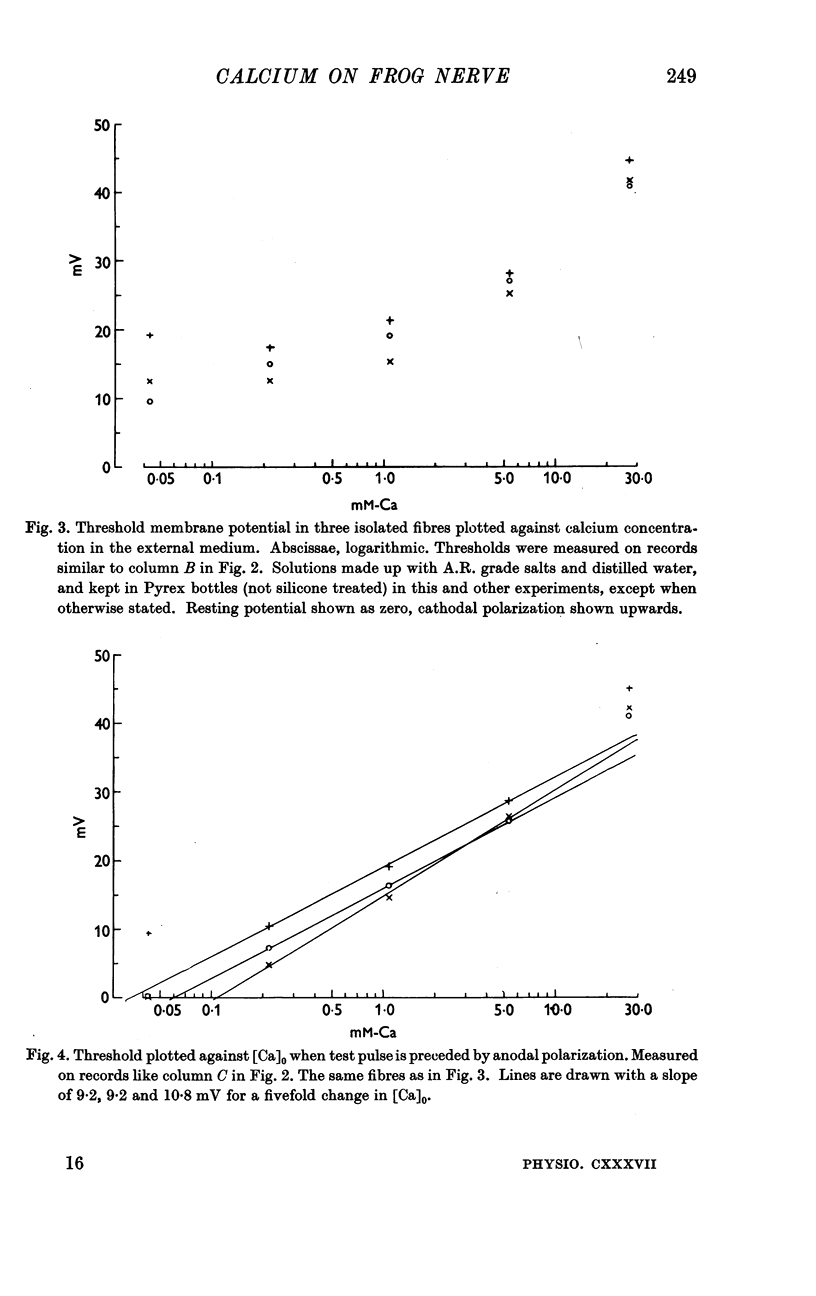
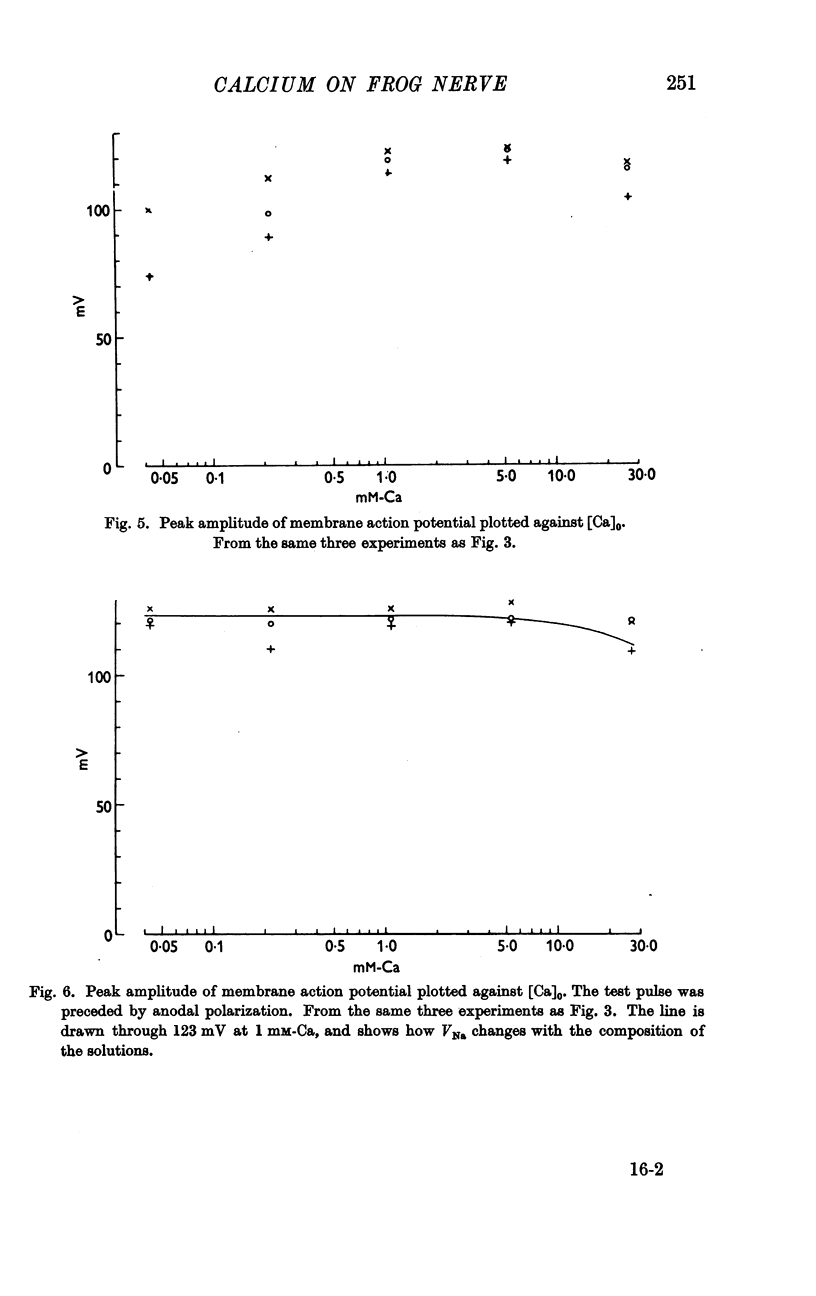
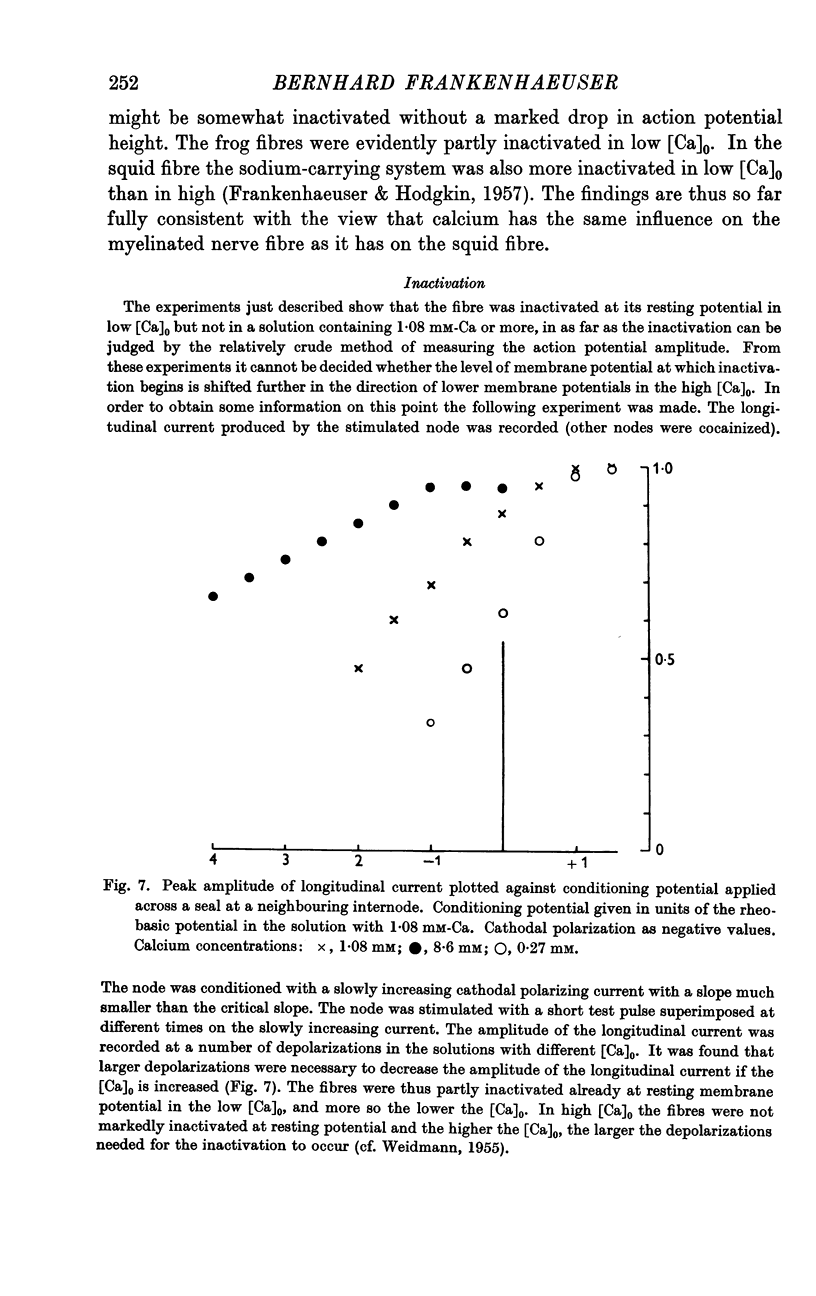
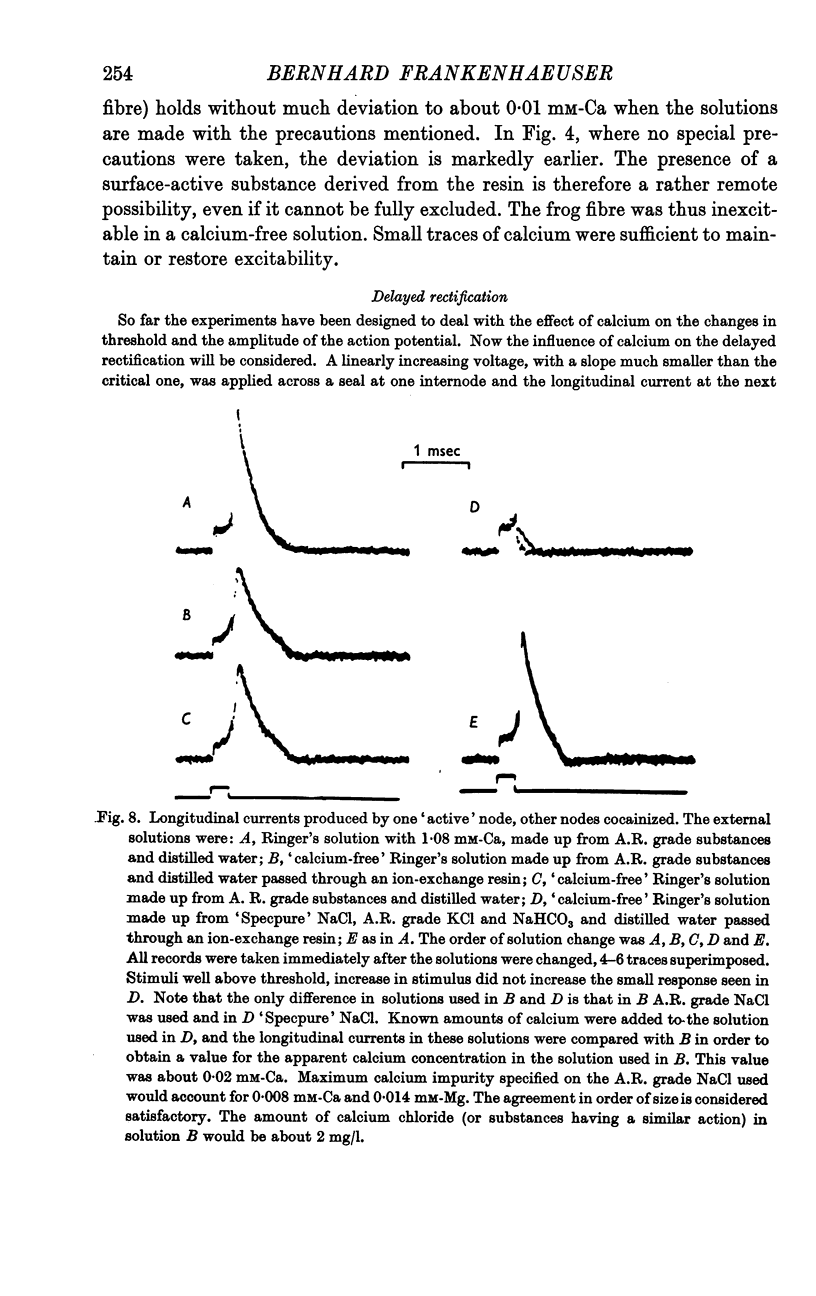
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRINK F. The role of calcium ions in neural processes. Pharmacol Rev. 1954 Sep;6(3):243–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B. A method for recording resting and action potentials in the isolated myelinated nerve fibre of the frog. J Physiol. 1957 Mar 11;135(3):550–559. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., HODGKIN A. L. The action of calcium on the electrical properties of squid axons. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):218–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., WIDEN L. Anode break excitation in desheathed frog nerve. J Physiol. 1956 Jan 27;131(1):243–247. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY A. F., STAMPFLI R. Direct determination of membrane resting potential and action potential in single myelinated nerve fibers. J Physiol. 1951 Feb;112(3-4):476–495. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY A. F., STAMPFLI R. Effect of potassium and sodium on resting and action potentials of single myelinated nerve fibers. J Physiol. 1951 Feb;112(3-4):496–508. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAMPFLI R., NISHIE K. Effects of calcium-free solutions on membrane-potential of myelinated nerve fibers of the Brazilian frog Leptodactylus ocellatus. Helv Physiol Pharmacol Acta. 1956;14(1):93–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TASAKI I., FRANK K. Measurement of the action potential of myelinated nerve fiber. Am J Physiol. 1955 Sep;182(3):572–578. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1955.182.3.572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TASAKI I., FREYGANG W. H., Jr The parallelism between the action potential, action current, and membrane resistance at a node of Ranvier. J Gen Physiol. 1955 Nov 20;39(2):211–223. doi: 10.1085/jgp.39.2.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TASAKI I. Initiation and abolition of the action potential of a single node of Ranvier. J Gen Physiol. 1956 Jan 20;39(3):377–395. doi: 10.1085/jgp.39.3.377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIDMANN S. Effects of calcium ions and local anesthetics on electrical properties of Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1955 Sep 28;129(3):568–582. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



