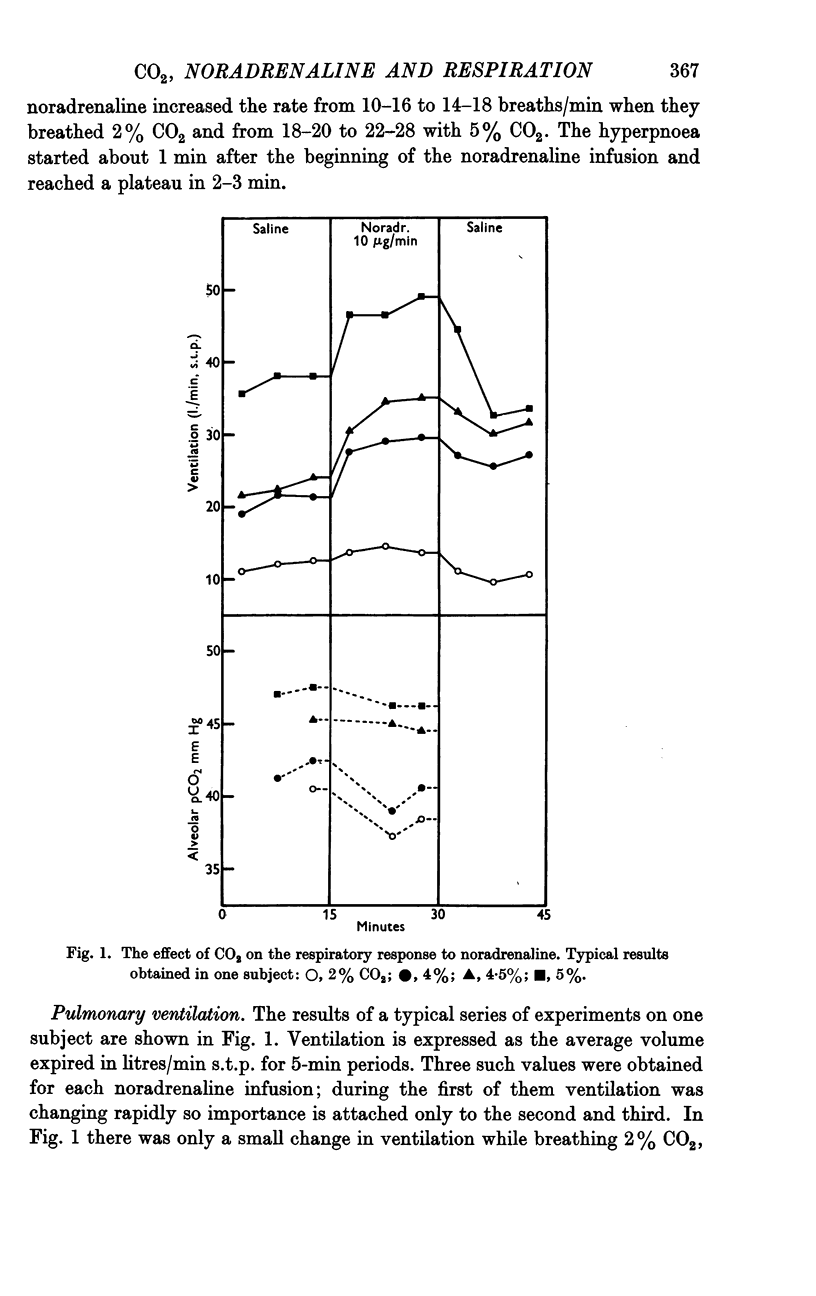
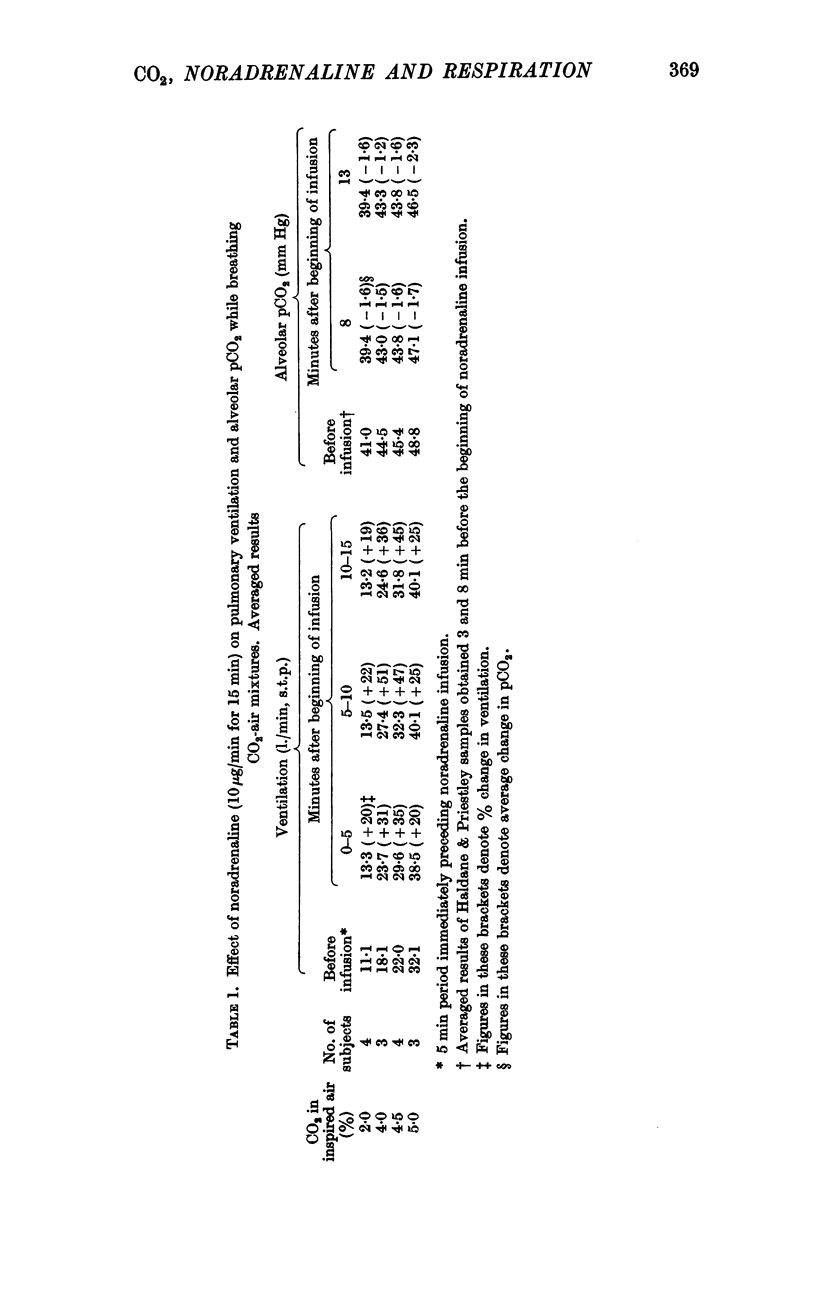
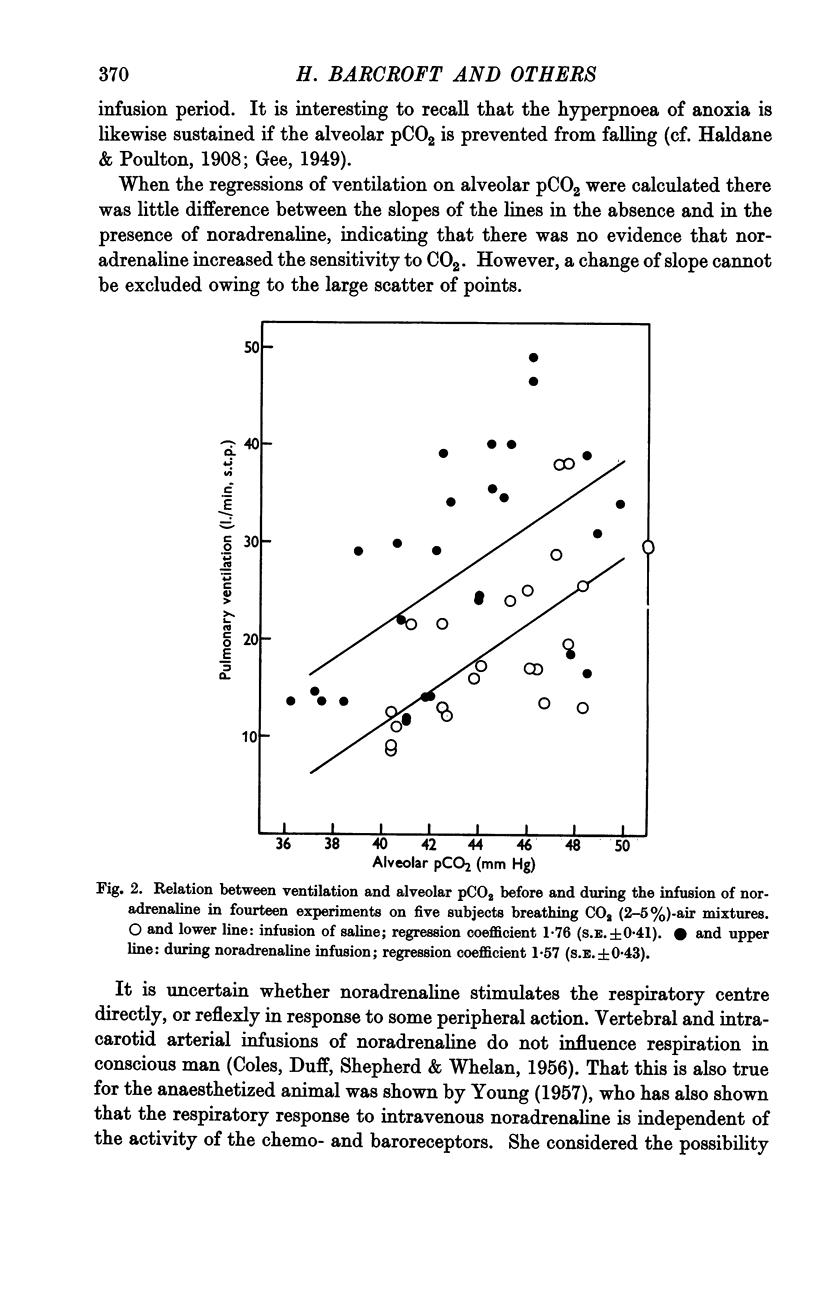
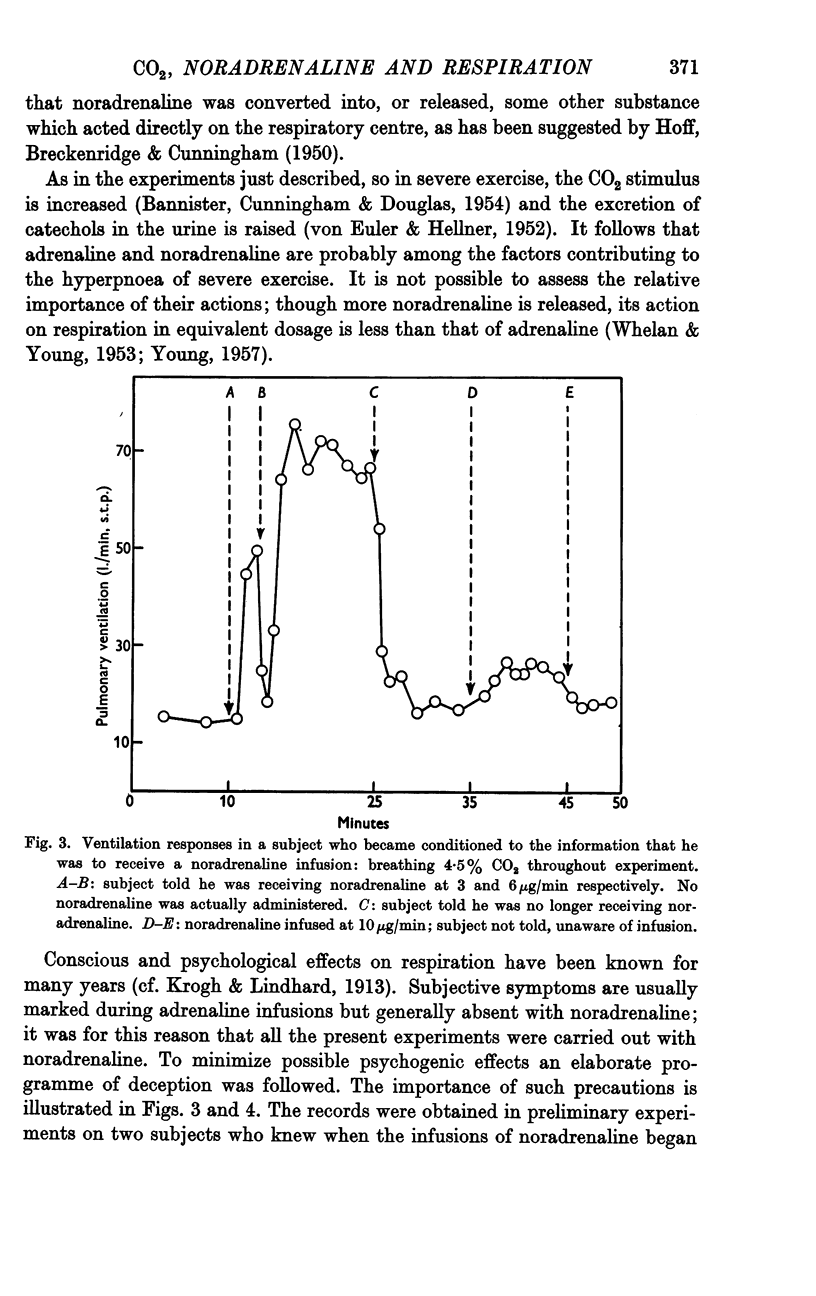
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BANNISTER R. G., CUNNINGHAM D. J., DOUGLAS C. G. The carbon dioxide stimulus to breathing in severe exercise. J Physiol. 1954 Jul 28;125(1):90–117. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLES D. R., DUFF F., SHEPHERD W. H., WHELAN R. F. The effect on respiration of infusions of adrenaline and noradrenaline into the carotid and vertebral arteries in man. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1956 Sep;11(3):346–350. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1956.tb01079.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CORMACK R. S., CUNNINGHAM D. J., GEE J. B. The effect of carbon dioxide on the respiratory response to want of oxygen in man. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1957 Jul;42(3):303–319. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1957.sp001266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CUNNINGHAM D. J., CORMACK R. S., O'RIORDAN J. L., JUKES M. G., LLOYD B. B. An arrangement for studying the respiratory effects in man of various factors. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1957 Jul;42(3):294–303. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1957.sp001265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DORNHORST A. C., SEMPLE S. J. G., YOUNG I. M. Automatic fractional analysis of expired air as a clinical test. Lancet. 1953 Feb 21;1(6756):370–372. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(53)91043-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUFF R. S. Effect of sympathectomy on the response to adrenaline of the blood vessels of the skin in man. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):415–430. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaddum J. H., Peart W. S., Vogt M. The estimation of adrenaline and allied substances in blood. J Physiol. 1949 Jun 15;108(4):467–481. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFF H. E., BRECKENRIDGE C. G., CUNNINGHAM J. E. Adrenaline apnea in the medullary animal. Am J Physiol. 1950 Mar;160(3):485–489. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1950.160.3.485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HULLIN R. P., NOBLE R. L. The determination of lacic acid in microgram quantities. Biochem J. 1953 Sep;55(2):289–291. doi: 10.1042/bj0550289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haldane J. S., Poulton E. P. The effects of want of exygen on respiration. J Physiol. 1908 Dec 15;37(5-6):390–407. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1908.sp001280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VON EULER U. S., HELLNER S. Excretion of noradrenaline and adrenaline in muscular work. Acta Physiol Scand. 1952 Sep 10;26(2-3):183–191. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1952.tb00900.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHELAN R. F., YOUNG I. M. The effect of adrenaline and noradrenaline infusions on respiration in man. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1953 Mar;8(1):98–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1953.tb00759.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUNG I. M. Some observations on the mechanism of adrenaline hyperpnoea. J Physiol. 1957 Aug 6;137(3):374–395. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


