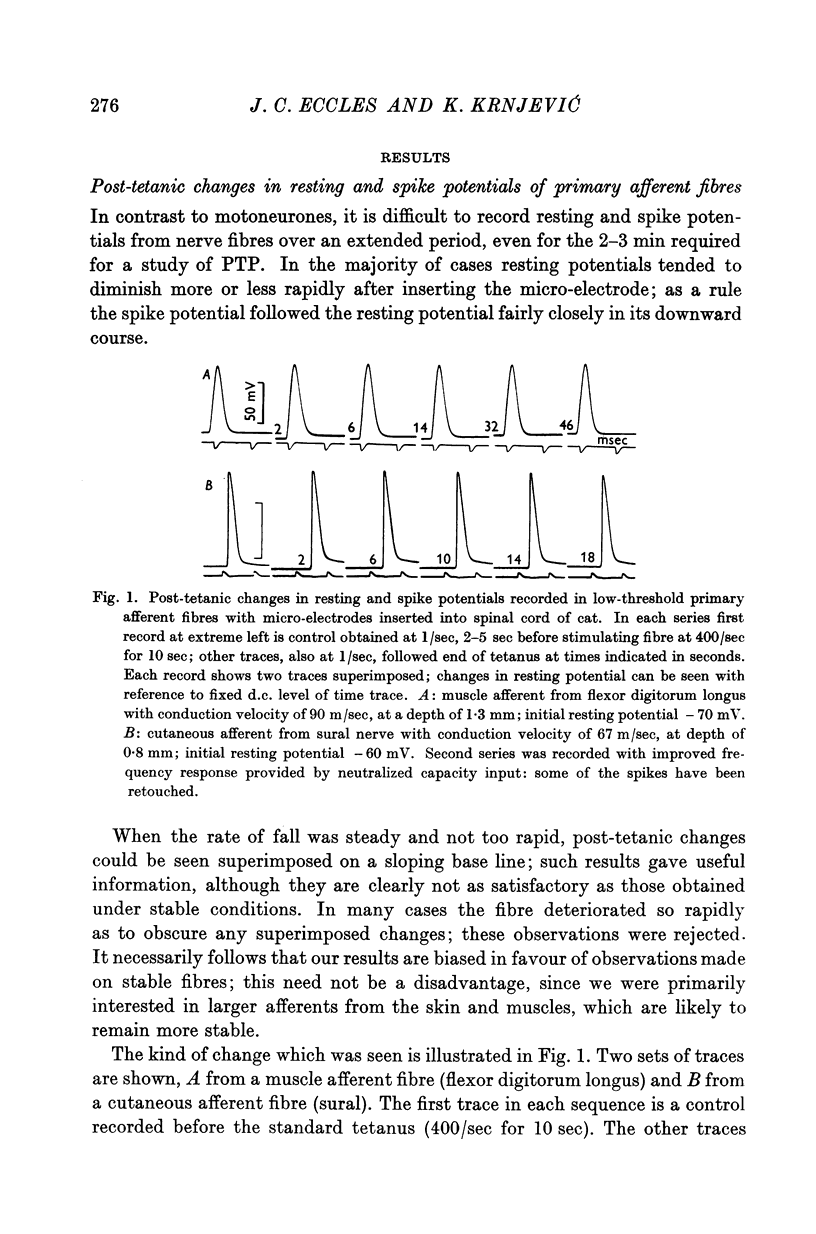
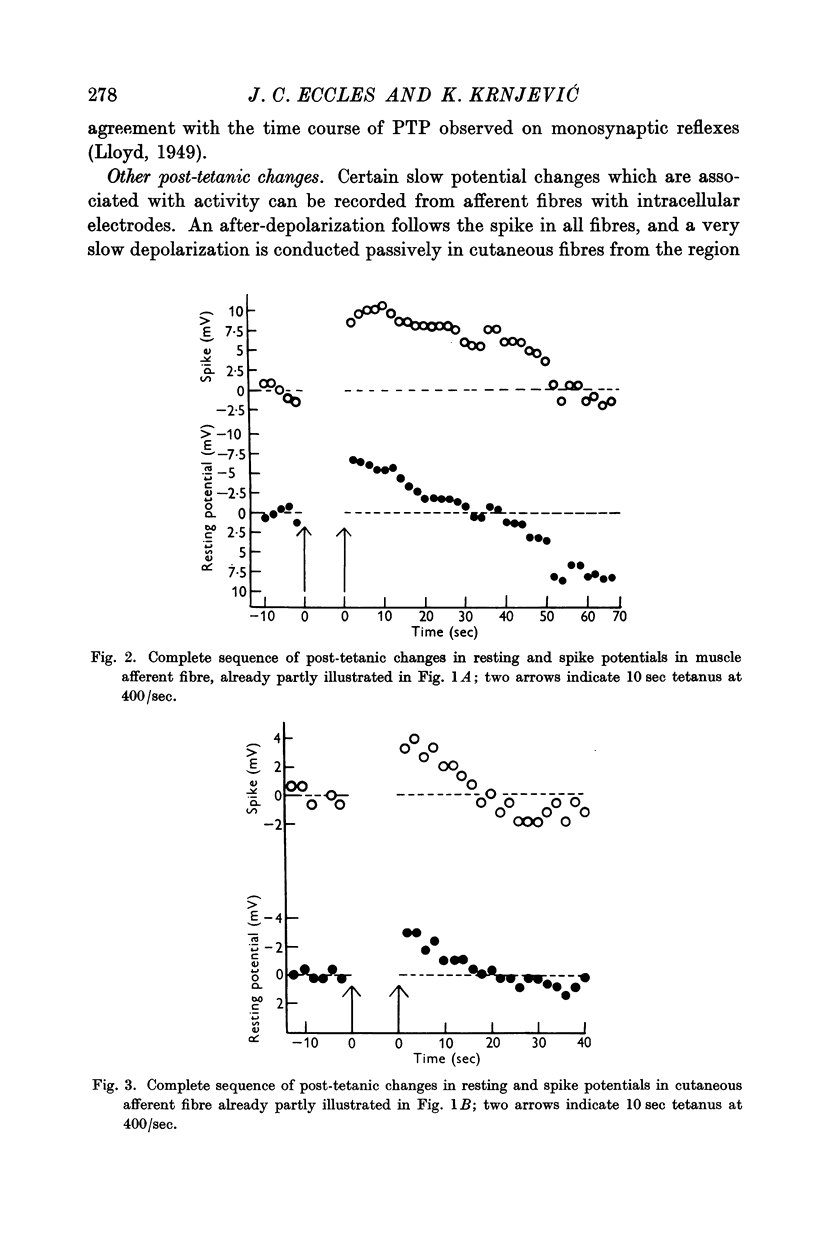
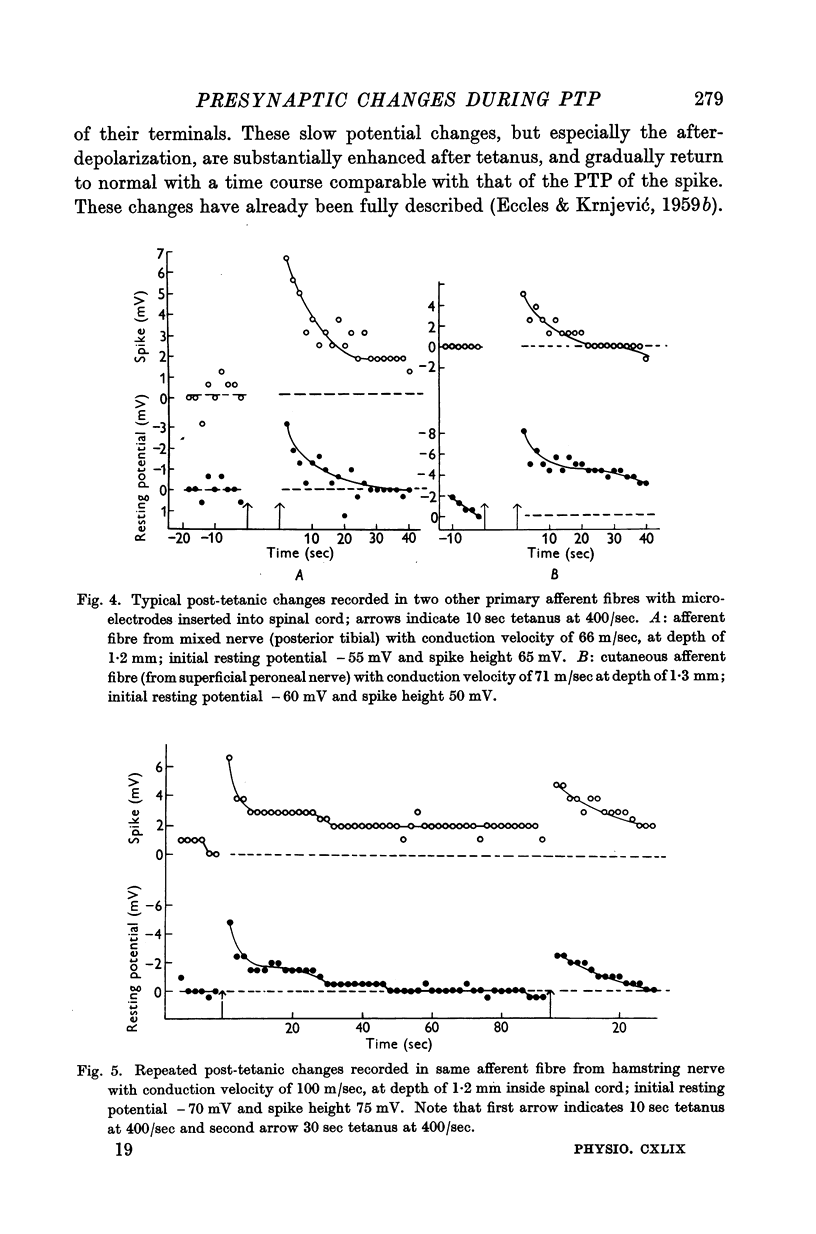
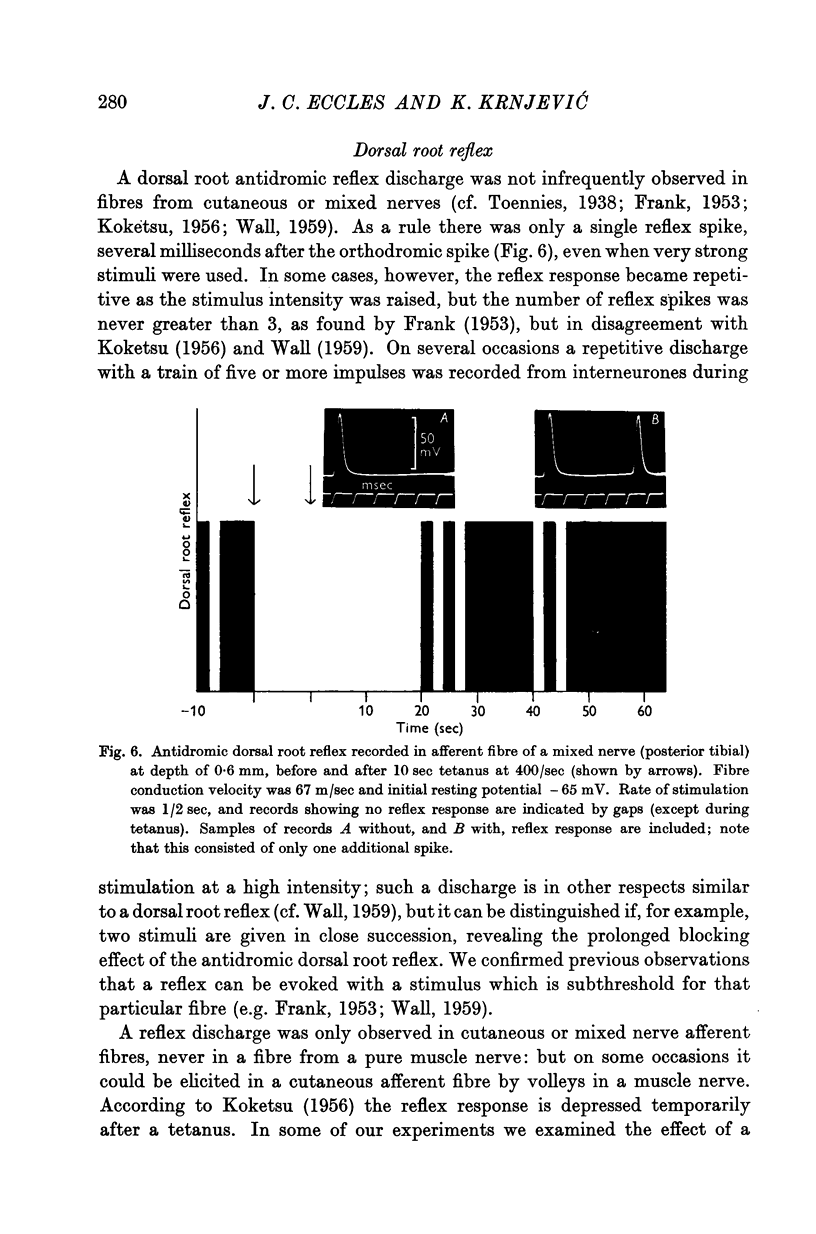
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian E. D. On the summation of propagated disturbances in nerve and muscle. J Physiol. 1912 Mar 29;44(1-2):68–124. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1912.sp001503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown G. L., Harvey A. M. Neuro-muscular conduction in the fowl. J Physiol. 1938 Aug 15;93(3):285–300. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1938.sp003640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Changes in end-plate activity produced by presynaptic polarization. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):586–604. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., KRNJEVIC K., MILEDI R. Delayed effects of peripheral severance of afferent nerve fibres on the efficacy of their central synapses. J Physiol. 1959 Jan 28;145(1):204–220. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., KRNJEVIC K. Potential changes recorded inside primary afferent fibres within the spinal cord. J Physiol. 1959 Dec;149:250–273. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., RALL W. Effects induced in a monosynaptic reflex path by its activation. J Neurophysiol. 1951 Sep;14(5):353–376. doi: 10.1152/jn.1951.14.5.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANK K., FUORTES M. G. Potentials recorded from the spinal cord with microelectrodes. J Physiol. 1955 Dec 29;130(3):625–654. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GASSER H. S. The postspike positivity of unmedullated fibers of dorsal root origin. J Gen Physiol. 1958 Mar 20;41(4):613–632. doi: 10.1085/jgp.41.4.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAGIWARA S., TASAKI I. A study on the mechanism of impulse transmission across the giant synapse of the squid. J Physiol. 1958 Aug 29;143(1):114–137. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOKETSU K. Intracellular potential changes of primary afferent nerve fibers in spinal cords of cats. J Neurophysiol. 1956 Sep;19(5):375–392. doi: 10.1152/jn.1956.19.5.375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LILEY A. W., NORTH K. A. An electrical investigation of effects of repetitive stimulation on mammalian neuromuscular junction. J Neurophysiol. 1953 Sep;16(5):509–527. doi: 10.1152/jn.1953.16.5.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LILEY A. W. The effects of presynaptic polarization on the spontaneous activity at the mammalian neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1956 Nov 28;134(2):427–443. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LILEY A. W. The quantal components of the mammalian end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1956 Sep 27;133(3):571–587. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LLOYD D. P. C. Electrotonus in dorsal nerve roots. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1952;17:203–219. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1952.017.01.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LLOYD D. P. C. Post-tetanic potentiation of response in monosynaptic reflex pathways of the spinal cord. J Gen Physiol. 1949 Nov;33(2):147–170. doi: 10.1085/jgp.33.2.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUDIN D. O., EISENMAN G. On the role of the spinal afferent neuron as a generator of extracellular current. J Gen Physiol. 1954 Jul 20;37(6):795–812. doi: 10.1085/jgp.37.6.795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHOEPFLE G. M. Kinetics of slow changes in membrane potential induced by direct current polarization of single nerve fibers. Am J Physiol. 1959 Jan;196(1):1–7. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1958.196.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALL P. D. Excitability changes in afferent fibre terminations and their relation to slow potentials. J Physiol. 1958 Jun 18;142(1):1–21. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp005997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALL P. D., JOHNSON A. R. Changes associated with post-tetanic potentiation of a monosynaptic reflex. J Neurophysiol. 1958 Mar;21(2):148–158. doi: 10.1152/jn.1958.21.2.148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALL P. D. Repetitive discharge of neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1959 May;22(3):305–320. doi: 10.1152/jn.1959.22.3.305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOODBURY J. W., PATTON H. D. Electrical activity of single spinal cord elements. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1952;17:185–188. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1952.017.01.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



