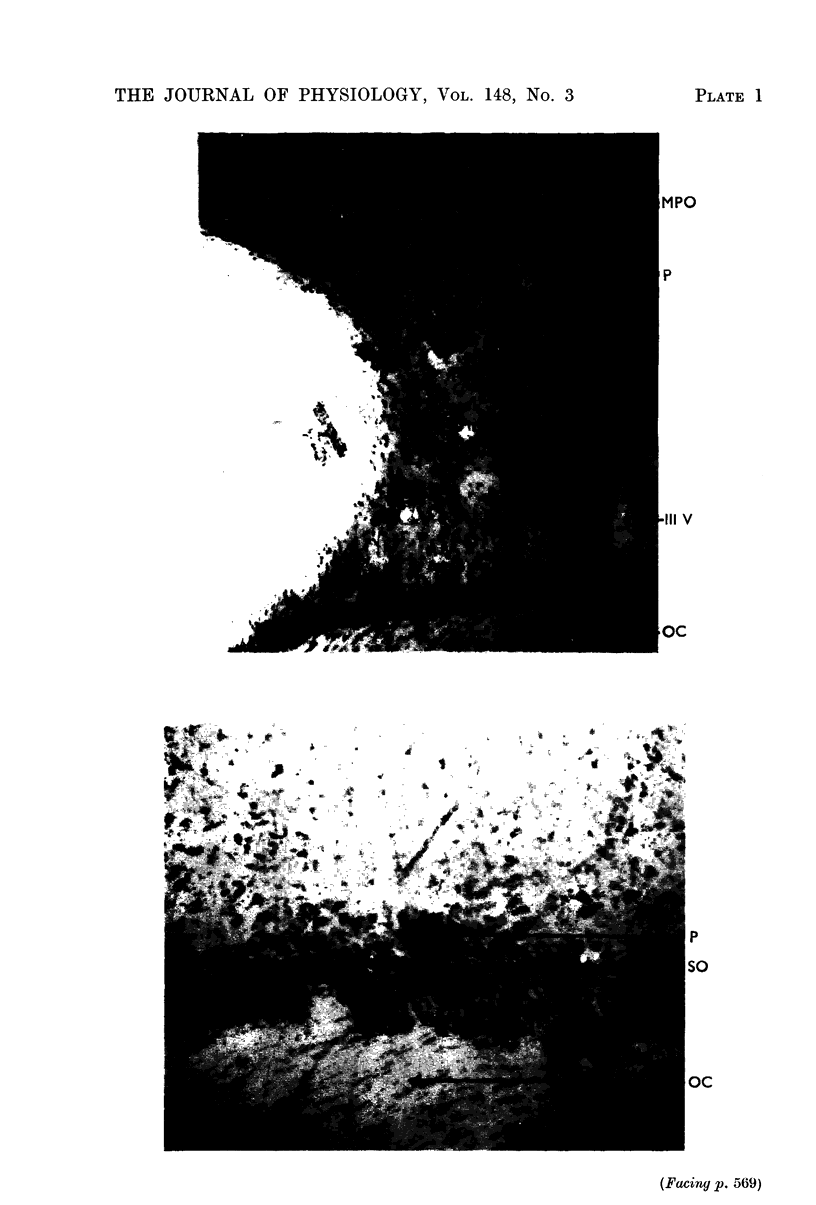
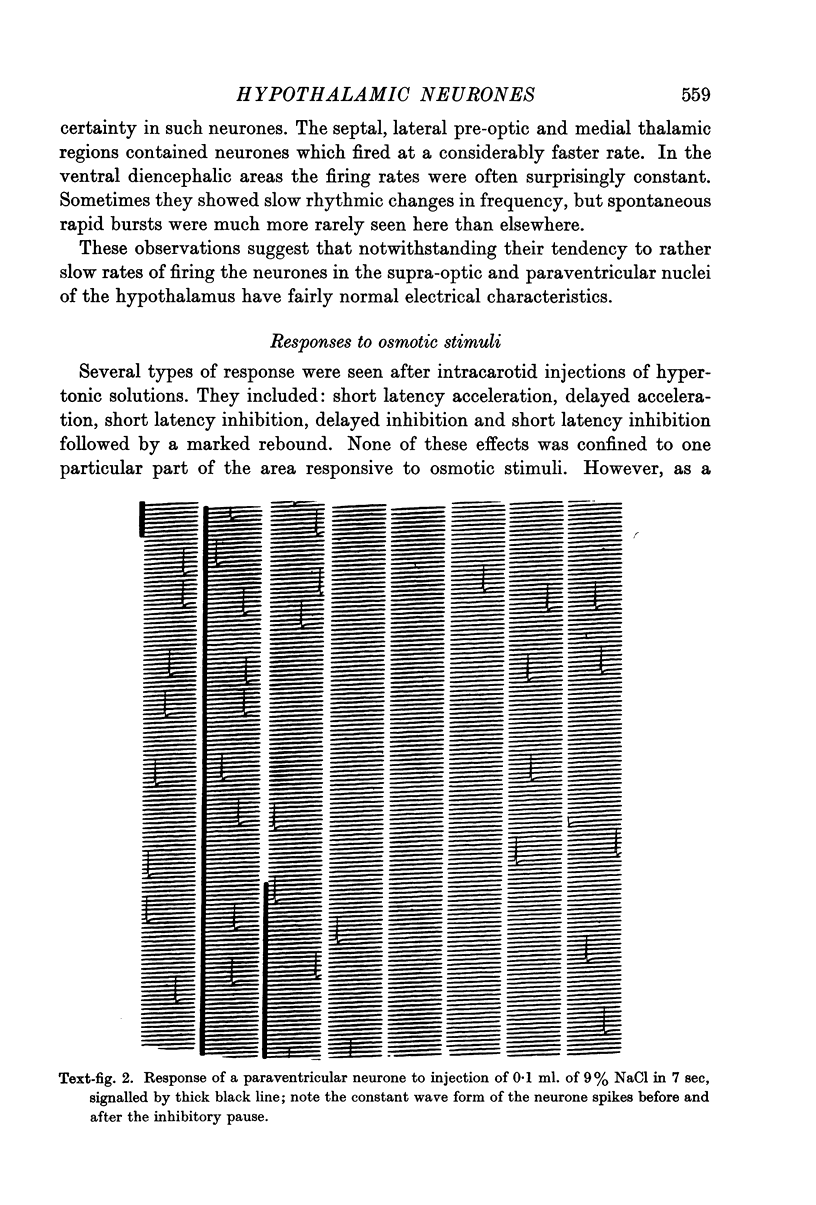
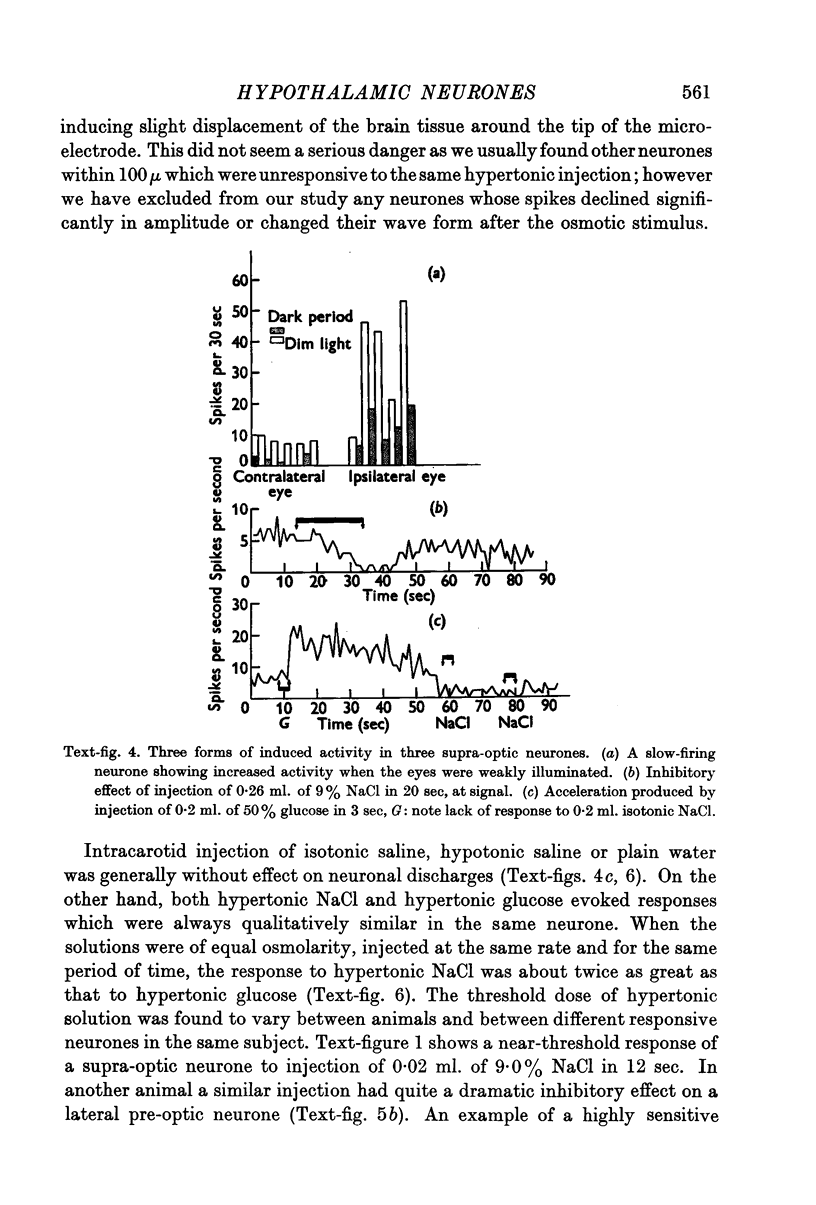
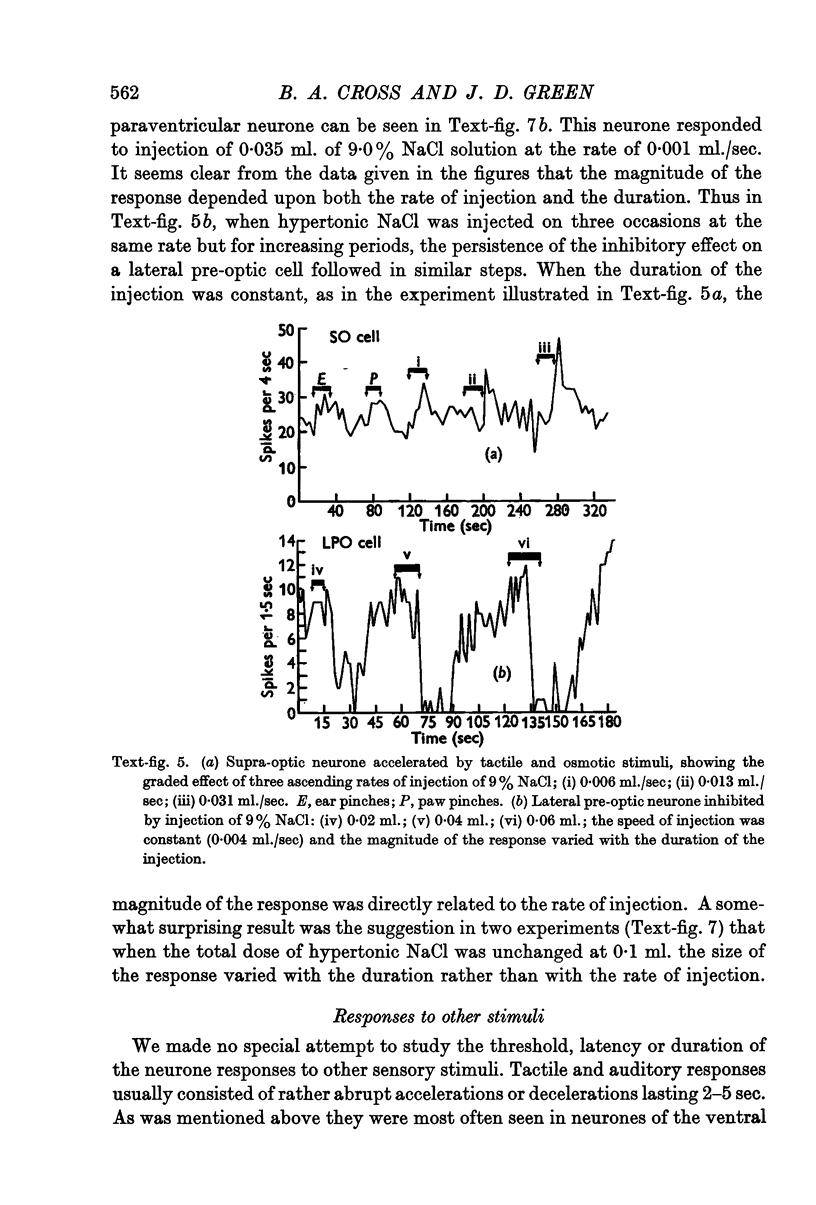
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSSON B., MCCANN S. M. A further study of polydipsia evoked by hypothalamic stimulation in the goat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1955 Aug 19;33(4):333–346. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1955.tb01213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANDERSSON B., MCCANN S. M. Drinking, antidiuresis and milk ejection from electrical stimulation within the hypothalamus of the goat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1955 Dec 31;35(2):191–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1955.tb01277.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANDERSSON B., MCCANN S. M. The effect of hypothalamic lesions on the water intake of the dog. Acta Physiol Scand. 1956 Feb 20;35(3-4):312–320. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1955.tb01288.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROSS B. A., HARRIS G. W. The role of the neurohypophysis in the milk-ejection reflex. J Endocrinol. 1952 Apr;8(2):148–161. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0080148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROSS B. A. Neurohormonal mechanisms in emotional inhibition of milk ejection. J Endocrinol. 1955 Jan;12(1):29–37. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0120029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROSS B. A. On the mechanism of labour in the rabbit. J Endocrinol. 1958 Feb;16(3):261–276. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0160261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROSS B. A. The hypothalamus and the mechanism of sympathetico-adrenal inhibition of milk ejection. J Endocrinol. 1955 Jan;12(1):15–28. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0120015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROSS B. A., VAN DYKE H. B. The effects of highly purified posterior pituitary principles on the lactating mammary gland of the rabbit. J Endocrinol. 1953 Apr;9(2):232–235. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0090232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISKE V. M., GREEP R. O. Neurosecretory activity in rats under conditions of continuous light or darkness. Endocrinology. 1959 Feb;64(2):175–185. doi: 10.1210/endo-64-2-175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN J. D. A simple microelectrode for recording from the central nervous system. Nature. 1958 Oct 4;182(4640):962–962. doi: 10.1038/182962a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN J. D., ARDUINI A. A. Hippocampal electrical activity in arousal. J Neurophysiol. 1954 Nov;17(6):533–557. doi: 10.1152/jn.1954.17.6.533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYS R. L., VANDEMARK N. L. Effect of stimulation of the reproductive organs of the cow on the release of an oxytocin-like substance. Endocrinology. 1953 Jun;52(6):634–637. doi: 10.1210/endo-52-6-634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND R. C., CROSS B. A., SAWYER C. H. EEG correlates of osmotic activation of the neurohypophyseal milk-ejection mechanism. Am J Physiol. 1959 Apr;196(4):796–802. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1959.196.4.796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JEWELL P. A. The occurrence of vesiculated neurones in the hypothalamus of the dog. J Physiol. 1953 Jul;121(1):167–181. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELSALL A. R. The inhibition of water diuresis in man by ischaemic muscle pain. J Physiol. 1949 Aug;109(1-2):150–161. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAWYER C. H., EVERETT J. W., GREEN J. D. The rabbit diencephalon in stereotaxic coordinates. J Comp Neurol. 1954 Dec;101(3):801–824. doi: 10.1002/cne.901010307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAWYER C. H., GERNANDT B. E. Effects of intracarotid and intraventricular injections of hypertonic solutions on electrical activity of the rabbit brain. Am J Physiol. 1956 Apr;185(1):209–216. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1956.185.1.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VON EULER C. A preliminary note on slow hypothalamic osmo-potentials. Acta Physiol Scand. 1953 Jun 26;29(1):133–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1953.tb01011.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]