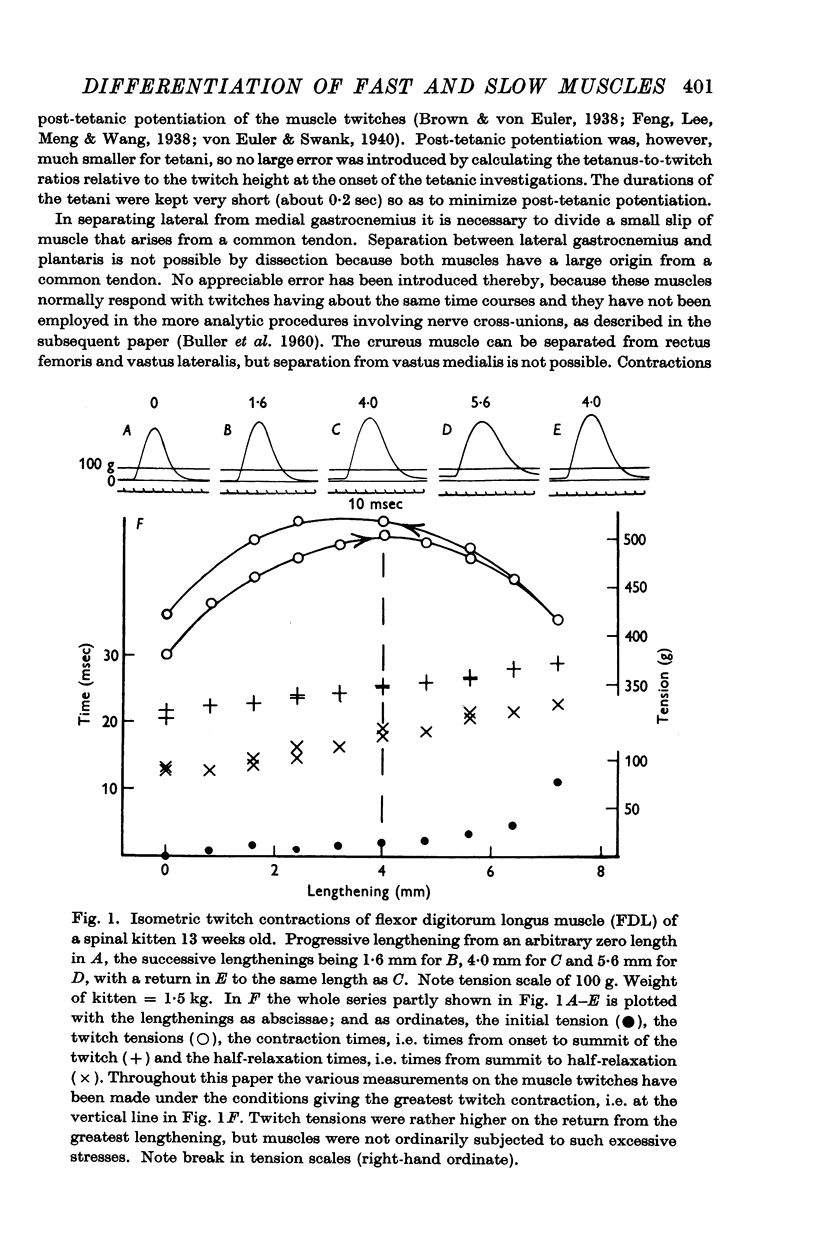
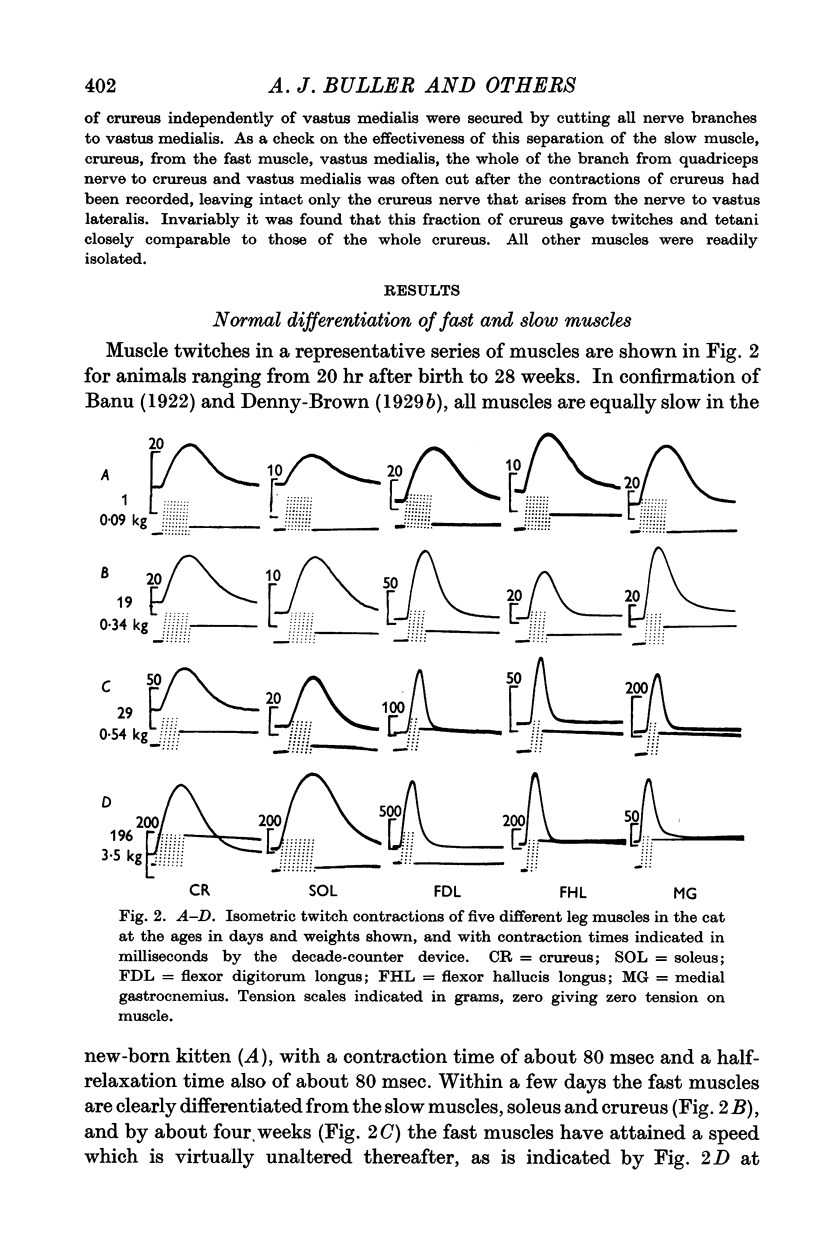
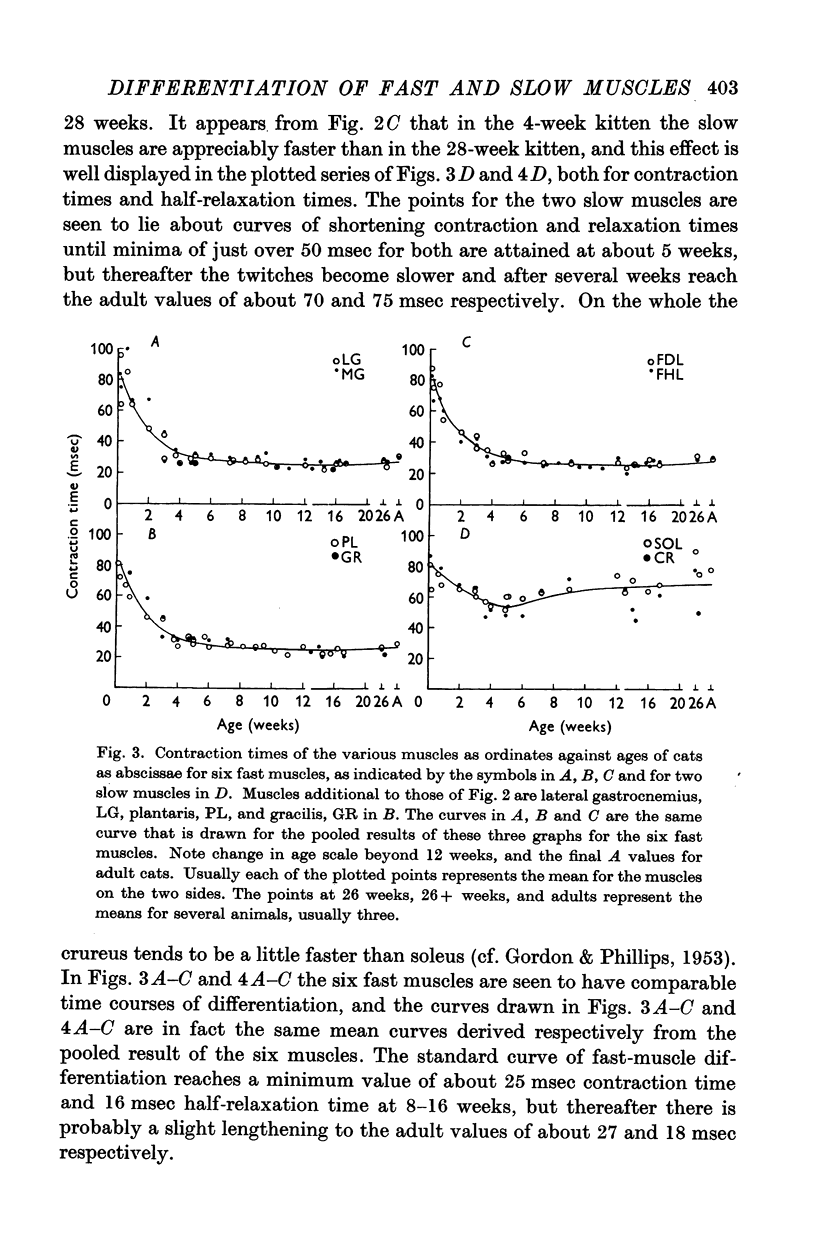
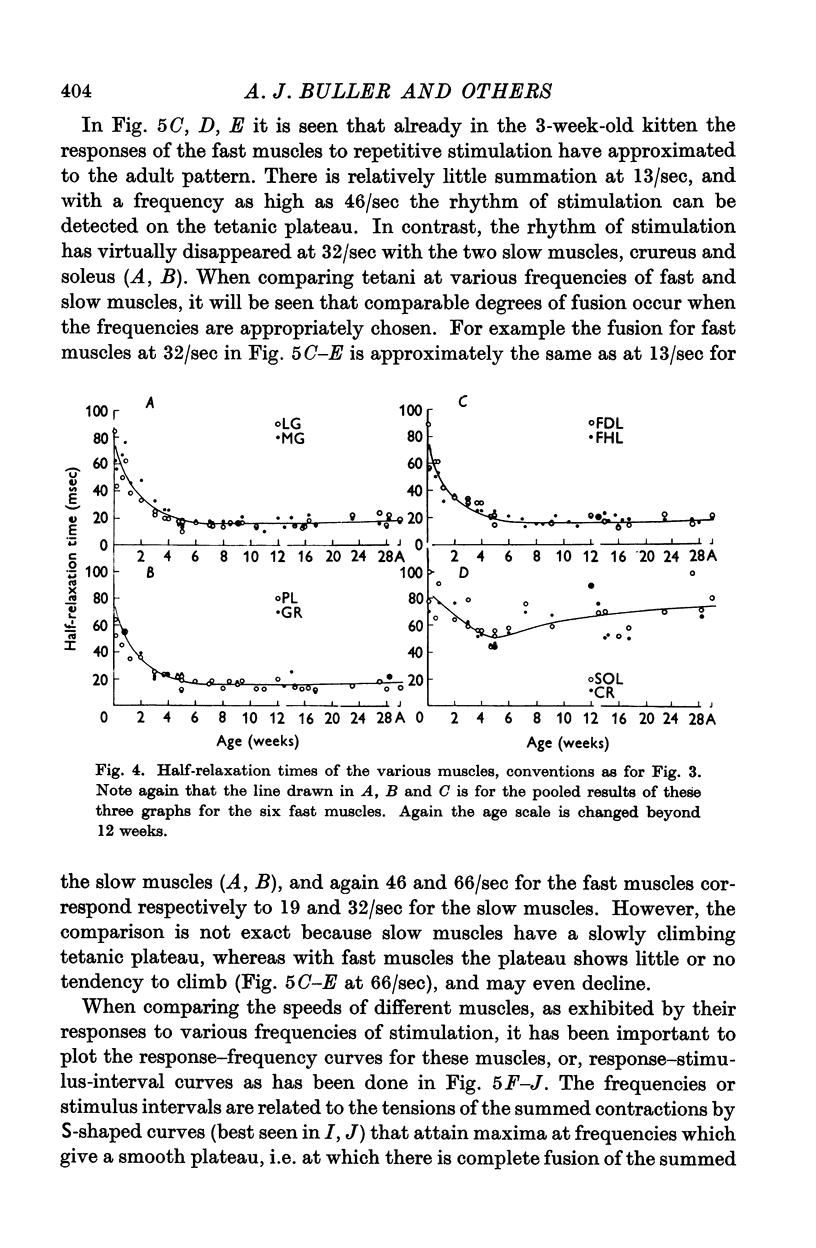
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian E. D., Bronk D. W. The discharge of impulses in motor nerve fibres: Part II. The frequency of discharge in reflex and voluntary contractions. J Physiol. 1929 Mar 20;67(2):i3–151. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BULLER A. J., ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M. Interactions between motoneurones and muscles in respect of the characteristic speeds of their responses. J Physiol. 1960 Feb;150:417–439. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown G. L., von Euler U. S. The after effects of a tetanus on mammalian muscle. J Physiol. 1938 Jun 14;93(1):39–60. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1938.sp003623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper S. The isometric responses of mammalian muscles. J Physiol. 1930 Jun 27;69(4):377–385. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1930.sp002657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. The action potentials of the alpha motoneurones supplying fast and slow muscles. J Physiol. 1958 Jul 14;142(2):275–291. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eccles J. C. Investigations on muscle atrophies arising from disuse and tenotomy. J Physiol. 1944 Dec 15;103(3):253–266. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1944.sp004074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORDON G., HOLBOURN A. H. S. The mechanical activity of single motor units in reflex contractions of skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1949 Dec 15;110(1-2):26–35. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORDON G., PHILLIPS C. G. Slow and rapid components in a flexor muscle. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1953;38(1):35–45. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1953.sp001005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANIT R., HENATSCH H. D., STEG G. Tonic and phasic ventral horn cells differentiated by post-tetanic potentiation in cat extensors. Acta Physiol Scand. 1956 Sep 26;37(2-3):114–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1956.tb01347.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANIT R., PHILLIPS C. G., SKOGLUND S., STEG G. Differentiation of tonic from phasic alpha ventral horn cells by stretch, pinna and crossed extensor reflexes. J Neurophysiol. 1957 Sep;20(5):470–481. doi: 10.1152/jn.1957.20.5.470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILL A. V. The mechanics of active muscle. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1953 Mar 11;141(902):104–117. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1953.0027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JEWELL B. R., WILKIE D. R. An analysis of the mechanical components in frog's striated muscle. J Physiol. 1958 Oct 31;143(3):515–540. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACPHERSON L. A method of determining the force-velocity relation of muscle from two isometric contractions. J Physiol. 1953 Oct;122(1):172–177. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACPHERSON L., WILKIE D. R. The duration of the active state in a muscle twitch. J Physiol. 1954 May 28;124(2):292–299. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RITCHE J. M. The duration of the plateau of full activity in frog muscle. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):605–612. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SINGER M. The influence of the nerve in regeneration of the amphibian extremity. Q Rev Biol. 1952 Jun;27(2):169–200. doi: 10.1086/398873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


