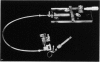
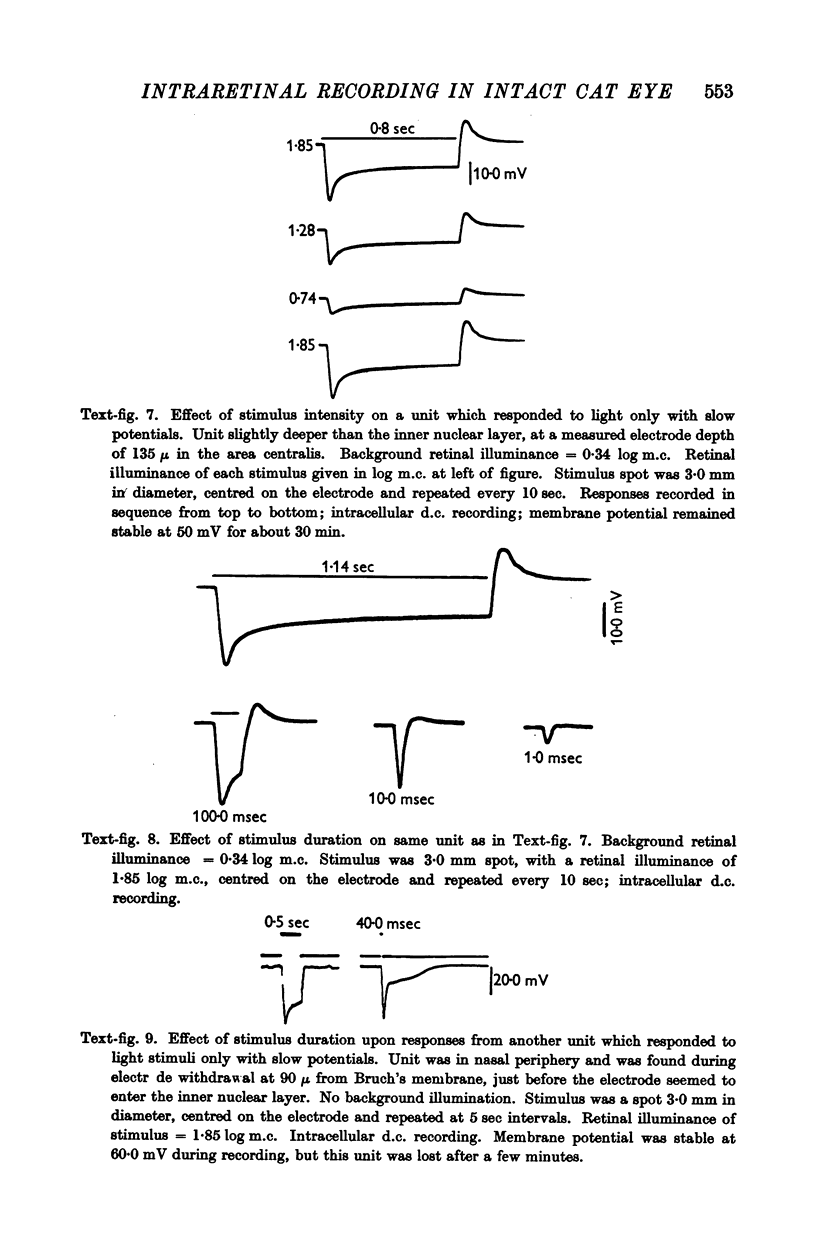
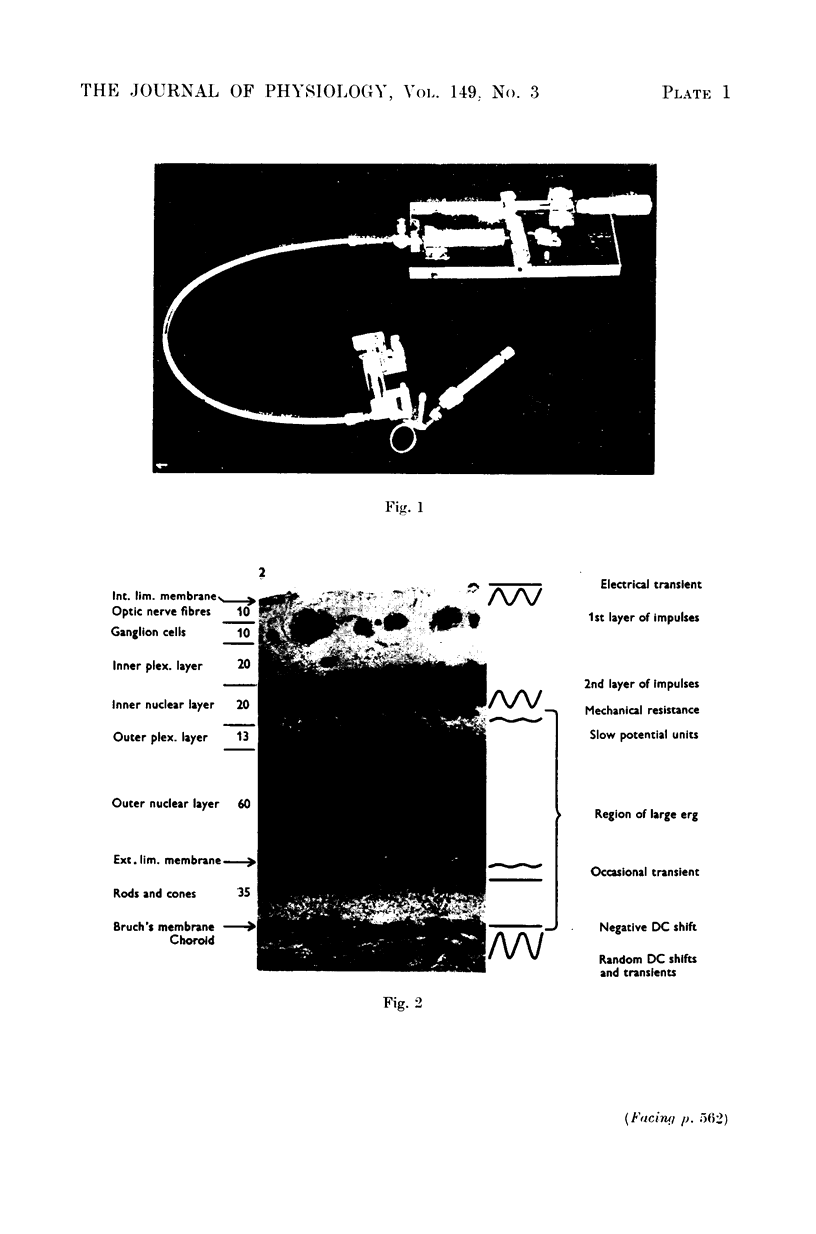
Full text
PDF
























Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADRIAN R. H. The effect of internal and external potassium concentration on the membrane potential of frog muscle. J Physiol. 1956 Sep 27;133(3):631–658. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AEBI H. Kationenmilieu und Gewebsatmung. Helv Physiol Pharmacol Acta. 1950;8(4):525–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARLOW H. B., FITZHUGH R., KUFFLER S. W. Dark adaptation, absolute threshold and Purkinje shift in single units of the cat's retina. J Physiol. 1957 Aug 6;137(3):327–337. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERNSTEIN M. H., PEASE D. C. Electron microscopy of the tapetum lucidum of the cat. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1959 Jan 25;5(1):35–40. doi: 10.1083/jcb.5.1.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRINDLEY G. S. The passive electrical properties of the frog's retina, choroid and sclera for radial fields and currents. J Physiol. 1956 Nov 28;134(2):339–352. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRINDLEY G. S. The sources of slow electrical activity in the frog's retina. J Physiol. 1958 Feb 17;140(2):247–261. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp005931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN K. T., WIESEL T. N. Intraretinal recording in the unopened cat eye. Am J Ophthalmol. 1958 Sep;46(3 Pt 2):91–98. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(58)90058-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKSON E. M., MAIZELS M. Sodium transfer in human and chicken erythrocytes. J Physiol. 1955 Sep 28;129(3):476–503. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKSON E. M., MAIZELS M. Sodium transfer in the erythrocytes of sickle-cell anaemia. J Physiol. 1955 Sep 28;129(3):504–512. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES P. W. Chamber for microelectrode studies in the cerebral cortex. Science. 1956 Jul 27;124(3213):179–180. doi: 10.1126/science.124.3213.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Local activity at a depolarized nerve-muscle junction. J Physiol. 1955 May 27;128(2):396–411. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DICK D. A., LOWENSTEIN L. M. Osmotic equilibria in human erythrocytes studied by immersion refractometry. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1958 Feb 18;148(931):241–256. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1958.0016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DRABKIN D. L. Spectrophotometric studies. XV. Hydration of macro sized crystals of human hemoglobin, and osmotic concentrations in red cells. J Biol Chem. 1950 Jul;185(1):231–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davson H. Studies on the permeability of erythrocytes. Biochem J. 1934;28(2):676–683. doi: 10.1042/bj0280676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLYNN I. M. Sodium and potassium movements in human red cells. J Physiol. 1956 Nov 28;134(2):278–310. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRUNDFEST H., PURPURA D. P. Nature of dendritic potentials and synaptic mechanisms in cerebral cortex of cat. J Neurophysiol. 1956 Nov;19(6):573–595. doi: 10.1152/jn.1956.19.6.573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS E. J., MAIZELS M. Distribution of ions in suspensions of human erythrocytes. J Physiol. 1952 Sep;118(1):40–53. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS E. J., PRANKERD T. A. Diffusion and permeation of cations in human and dog erythrocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1957 Sep 20;41(1):197–218. doi: 10.1085/jgp.41.1.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARTLINE H. K., WAGNER H. G., RATLIFF F. Inhibition in the eye of Limulus. J Gen Physiol. 1956 May 20;39(5):651–673. doi: 10.1085/jgp.39.5.651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JUNG R., CREUTZFELDT O., GRUSSER O. J. Die Mikrophysiologie kortikaler Neurone und ihre Bedeutung für die Sinnes- und Hirnfunktionen. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1957 Jun 28;82(26):1050–1059. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1114837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOLMODIN G. M., SKOGLUND C. R. Slow membrane potential changes accompanying excitation and inhibition in spinal moto- and interneurons in the cat during natural activation. Acta Physiol Scand. 1958 Oct 28;44(1):11–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1958.tb01607.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUFFLER S. W. Discharge patterns and functional organization of mammalian retina. J Neurophysiol. 1953 Jan;16(1):37–68. doi: 10.1152/jn.1953.16.1.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LI C. L. Action and resting potentials of cortical neurones. J Physiol. 1955 Oct 28;130(1):96–108. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINCOFF H. A., BREININ G. M., DE VOE A. G. The effect of succinylcholine on the extraocular muscles. Am J Ophthalmol. 1957 Mar;43(3):440–444. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(57)92344-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACNICHOL E. J., SVAETICHIN G. Electric responses from the isolated retinas of fishes. Am J Ophthalmol. 1958 Sep;46(3 Pt 2):26–46. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(58)90053-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACRI F. J., GRIMES P. A. The effects of succinylcholine on the extraocular striate muscles and on the intraocular pressure. Am J Ophthalmol. 1957 Oct;44(4 Pt 2):221–230. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(57)90450-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAIZELS M. Calcium ions and the permeability of human red cells. Nature. 1959 Aug 1;184(Suppl 6):366–366. doi: 10.1038/184366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAIZELS M., REMINGTON M. Cation exchanges of human erythrocytes. J Physiol. 1959 Mar 12;145(3):641–657. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAIZELS M., REMINGTON M. Percentage of intercellular medium in human erythrocytes centrifuged from albumin and other media. J Physiol. 1959 Mar 12;145(3):658–666. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAIZELS M. Sodium transfer in tortoise erythrocytes. J Physiol. 1956 May 28;132(2):414–441. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOTOKAWA K., OIKAWA T., TASAKI K. Receptor potential of vertebrate retina. J Neurophysiol. 1957 Mar;20(2):186–199. doi: 10.1152/jn.1957.20.2.186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOUNTCASTLE V. B., DAVIES P. W., BERMAN A. L. Response properties of neurons of cat's somatic sensory cortex to peripheral stimuli. J Neurophysiol. 1957 Jul;20(4):374–407. doi: 10.1152/jn.1957.20.4.374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maizels M. The permeation of erythrocytes by cations. Biochem J. 1935 Aug;29(8):1970–1982. doi: 10.1042/bj0291970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OIKAWA T., OGAWA T., MOTOKAWA K. Origin of so-called cone action potential. J Neurophysiol. 1959 Jan;22(1):102–111. doi: 10.1152/jn.1959.22.1.102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUSHTON W. A. H. The structure responsible for action potential spikes in the cat's retina. Nature. 1949 Oct 29;164(4174):743–743. doi: 10.1038/164743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SVAETICHIN G. Spectral response curves from single cones. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1956;39(134):17–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TALBOT S. A., KUFFLER S. W. A multibeam ophthalmoscope for the study of retinal physiology. J Opt Soc Am. 1952 Dec;42(12):931–936. doi: 10.1364/josa.42.000931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TASAKI I., POLLEY E. H., ORREGO F. Action potentials from individual elements in cat geniculate and striate cortex. J Neurophysiol. 1954 Sep;17(5):454–474. doi: 10.1152/jn.1954.17.5.454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOMITA T. A study on the origin of intraretinal action potential of the cyprinid fish by means of pencil-type microelectrode. Jpn J Physiol. 1957 Mar 15;7(1):80–85. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.7.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOMITA T., TORIHAMA Y. Further study on the intraretinal action potentials and on the site of ERG generation. Jpn J Physiol. 1956 Jun 15;6(2):118–136. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.6.118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOMITA T., TOSAKA T., WATANABE K., SATO Y. The fish EIRG in response to different types of illumination. Jpn J Physiol. 1958 Mar 30;8(1):41–50. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.8.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIESEL T. N., BROWN K. T. Analysis of receptive fields in the cat's retina. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1959 Nov 12;74(2):405–406. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1958.tb39561.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIESEL T. N. Recording inhibition and excitation in the cat's retinal ganglion cells with intracellular electrodes. Nature. 1959 Jan 24;183(4656):264–265. doi: 10.1038/183264a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WISLOCKI G. B., SIDMAN R. L. The chemical morphology of the retina. J Comp Neurol. 1954 Aug;101(1):53–99. doi: 10.1002/cne.901010104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]