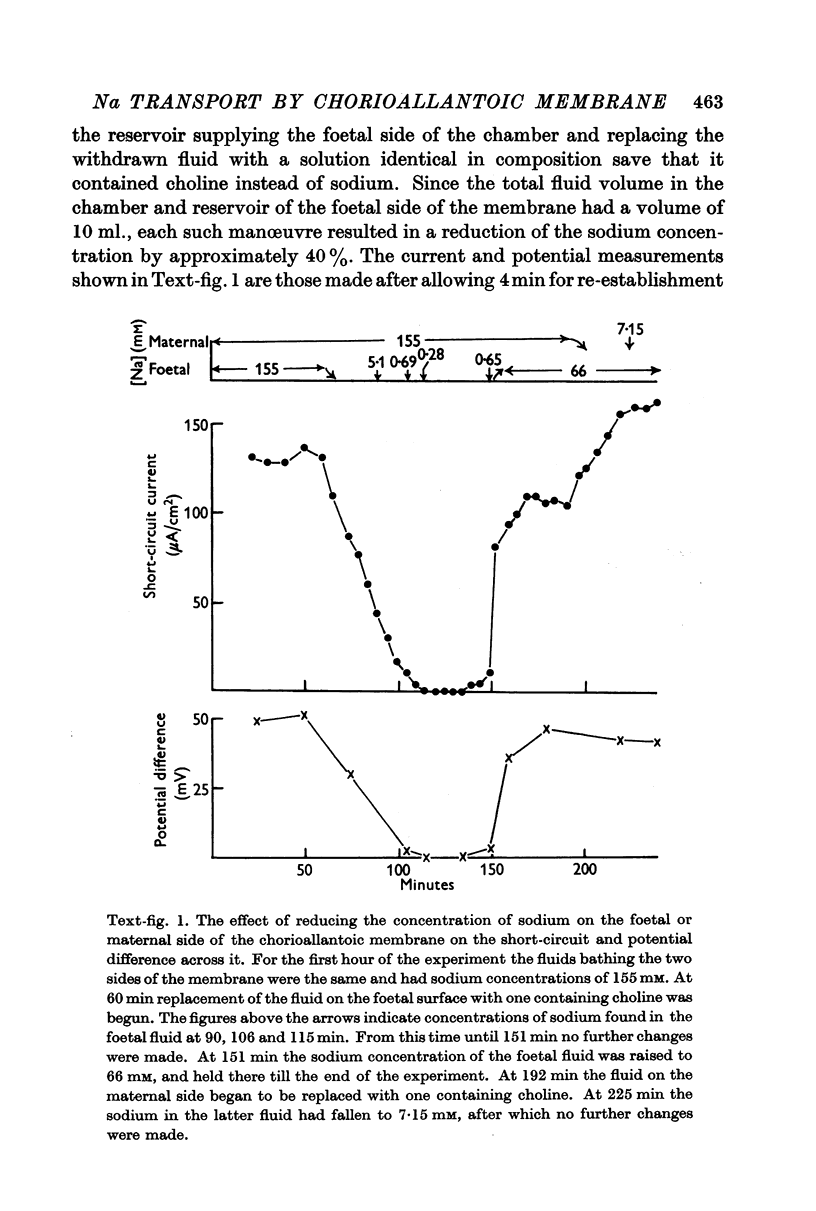
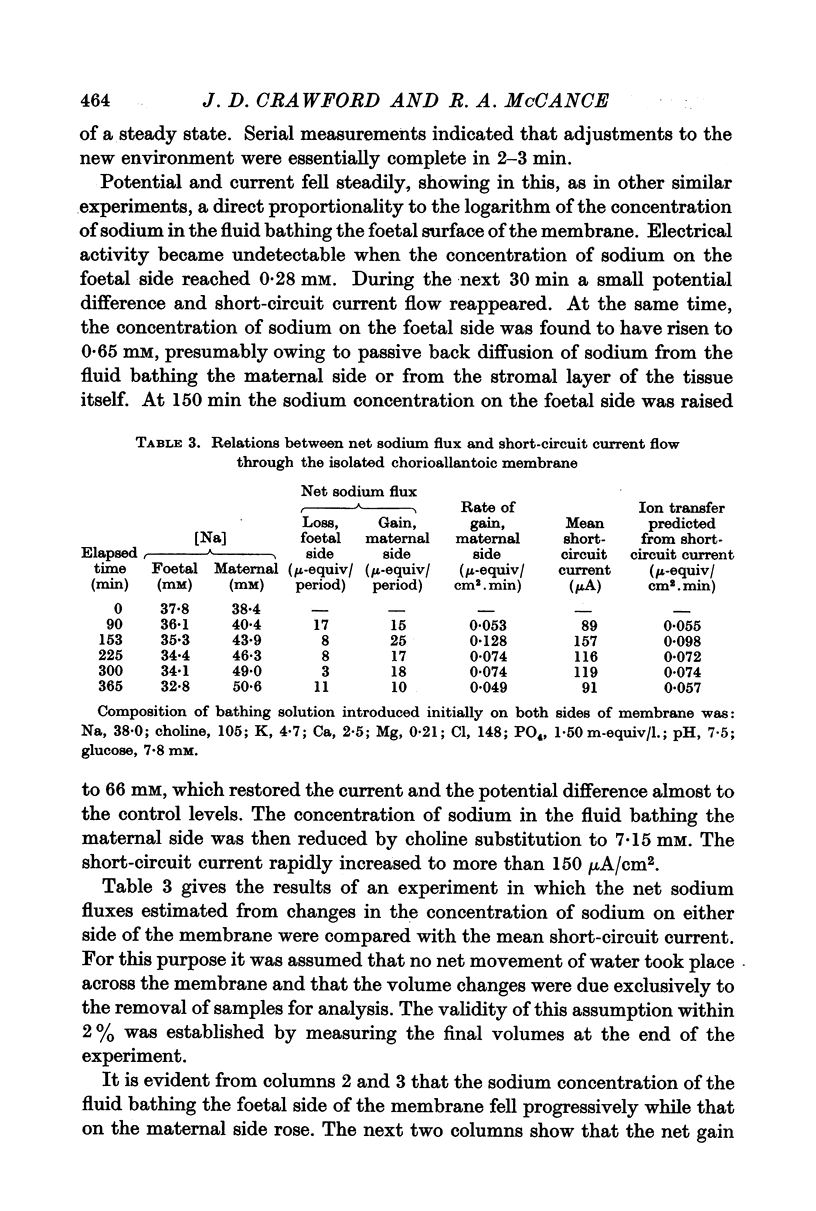
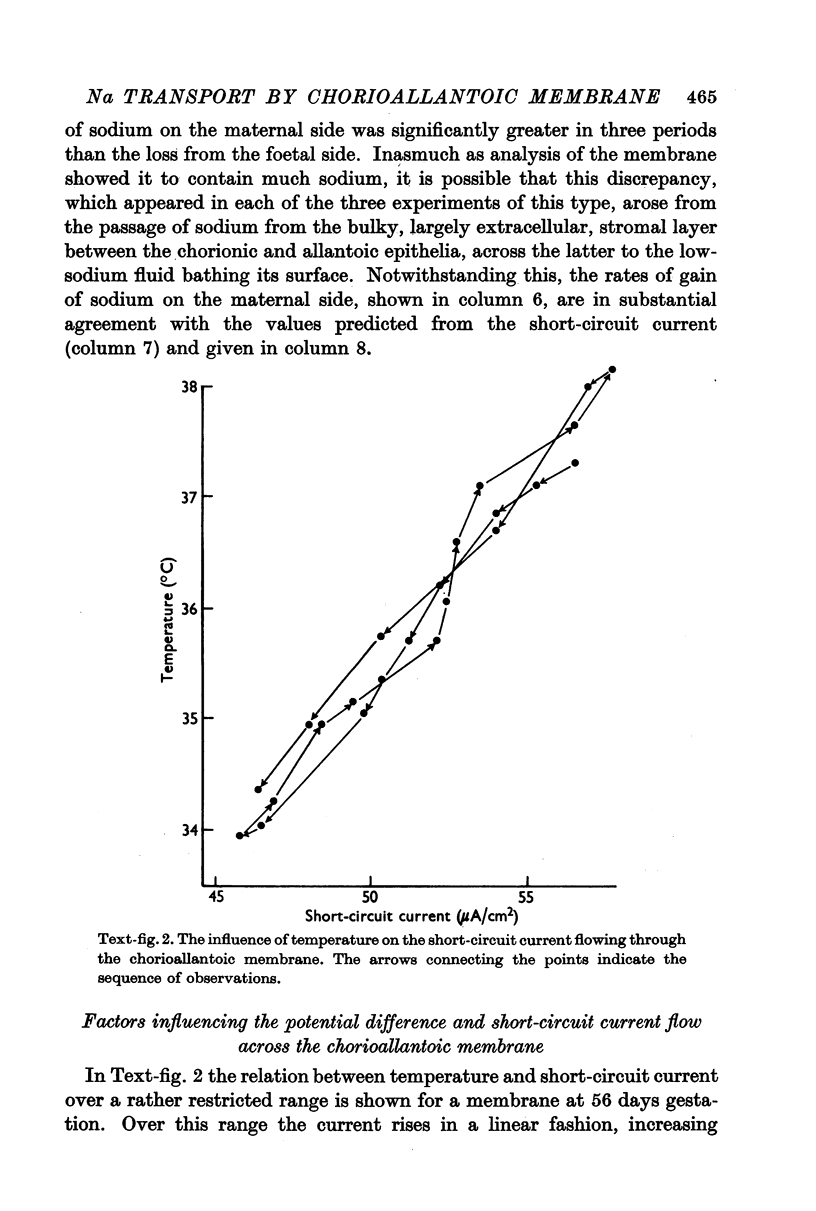
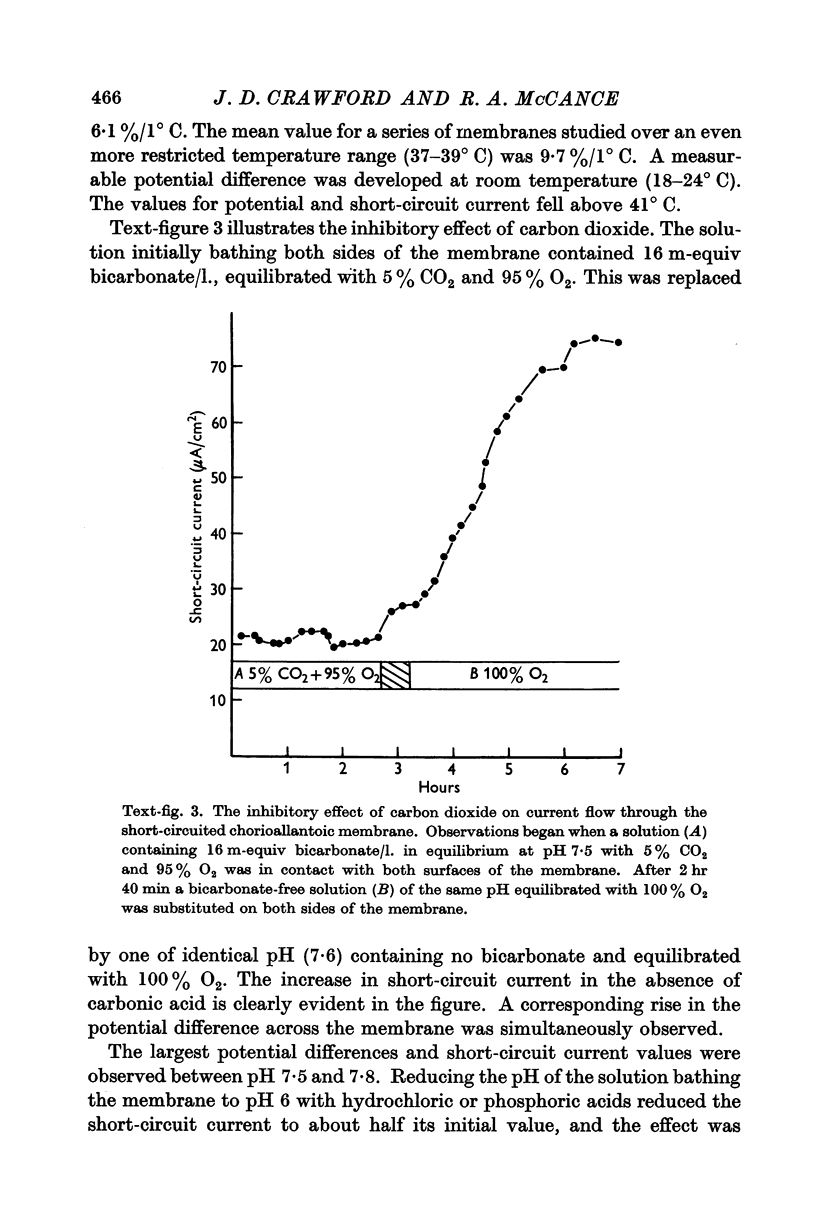
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALEXANDER D. P., NIXON D. A., WIDDAS W. F., WOHLZOGEN F. X. Gestational variations in the composition of the foetal fluids and foetal urine in the sheep. J Physiol. 1958 Jan 23;140(1):1–13. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp005911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENTLEY P. J. The effects of neurohypophysial extracts on the water transfer across the wall of the isolated urinary bladder of the toad Bufo marinus. J Endocrinol. 1958 Sep;17(3):201–209. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0170201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECONOMOU-MAVROU C., McCANCE R. A. Calcium, magnesium and phosphorus in foetal tissues. Biochem J. 1958 Apr;68(4):573–580. doi: 10.1042/bj0680573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUHRMAN F. A., USSING H. H. A characteristic response of the isolated frog skin potential to neurohypophysial principles and its relation to the transport of sodium and water. J Cell Physiol. 1951 Aug;38(1):109–130. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030380109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUF E. G., PARRISH J., WEATHERFORD C. Active salt and water uptake by isolated frog skin. Am J Physiol. 1951 Jan;164(1):137–142. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1950.164.1.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOEFOED-JOHNSEN V., USSING H. H. The nature of the frog skin potential. Acta Physiol Scand. 1958 Jun 2;42(3-4):298–308. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1958.tb01563.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCance R. A., Widdowson E. M. The acid-base relationships of the foetal fluids of the pig. J Physiol. 1960 Jun;151(3):484–490. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKAY D. G., ROBY C. C., HERTIG A. T., RICHARDSON M. V. Studies of the function of early human trophoblast. I. Observations on the chemical composition of the fluid of hydatidiform moles. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1955 Apr;69(4):722–734. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(16)38072-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKAY D. G., ROBY C. C., HERTIG A. T., RICHARDSON M. V. Studies of the function of early human trophoblast. II. Preliminary observations on certain chemical constituents of chorionic and early amniotic fluid. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1955 Apr;69(4):735–741. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(16)38073-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RADDE I. C., McCANCE R. A. Glutaminase activity of the foetal membranes and kidneys of pigs. Nature. 1959 Jan 10;183(4654):115–116. doi: 10.1038/183115a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STANIER M. W. The function of the mammalian mesonephros. J Physiol. 1960 Jun;151:472–478. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





