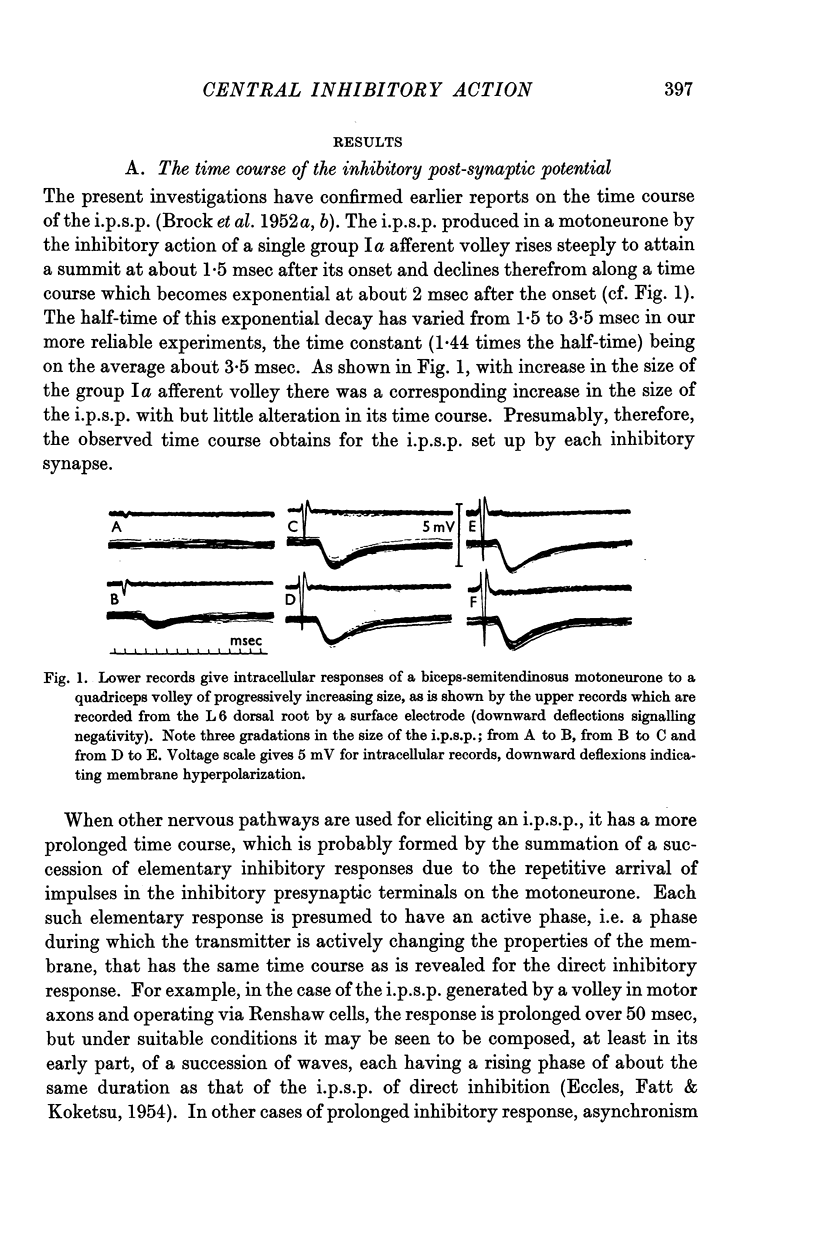
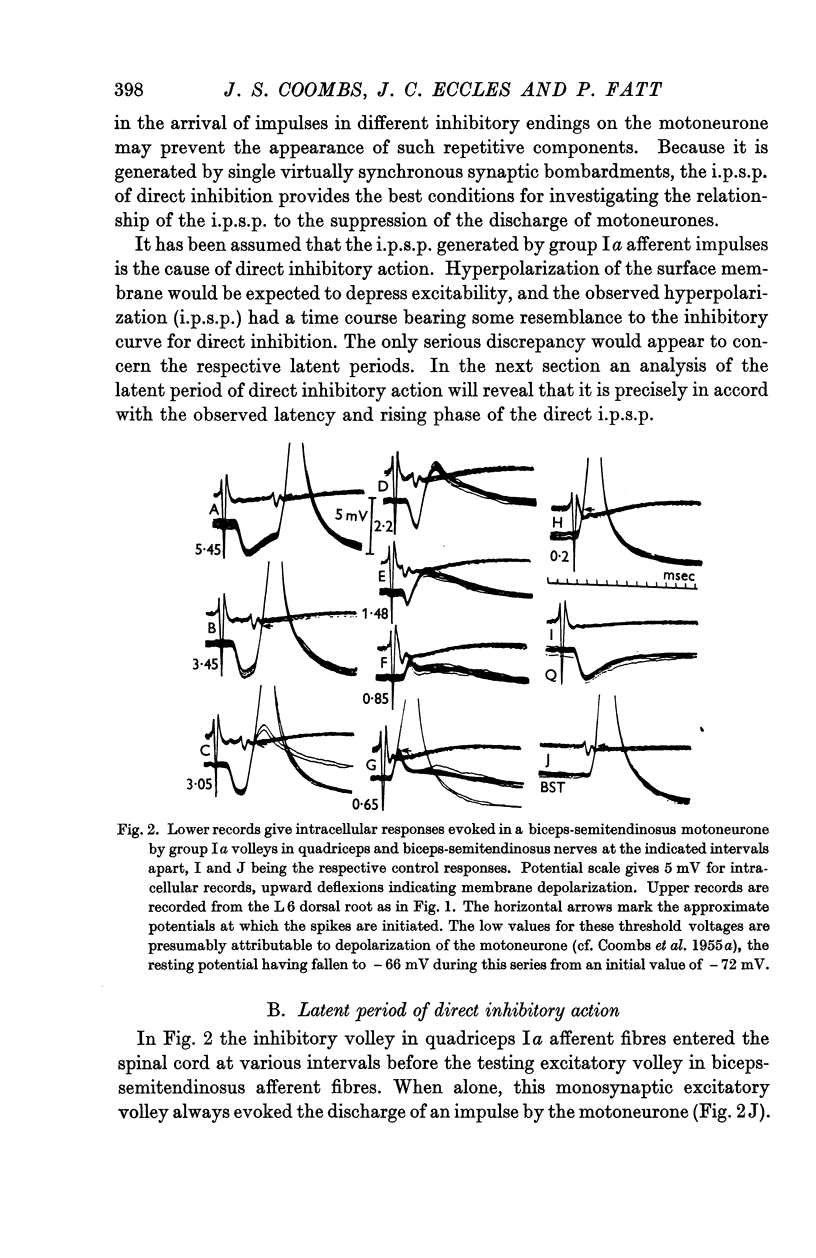
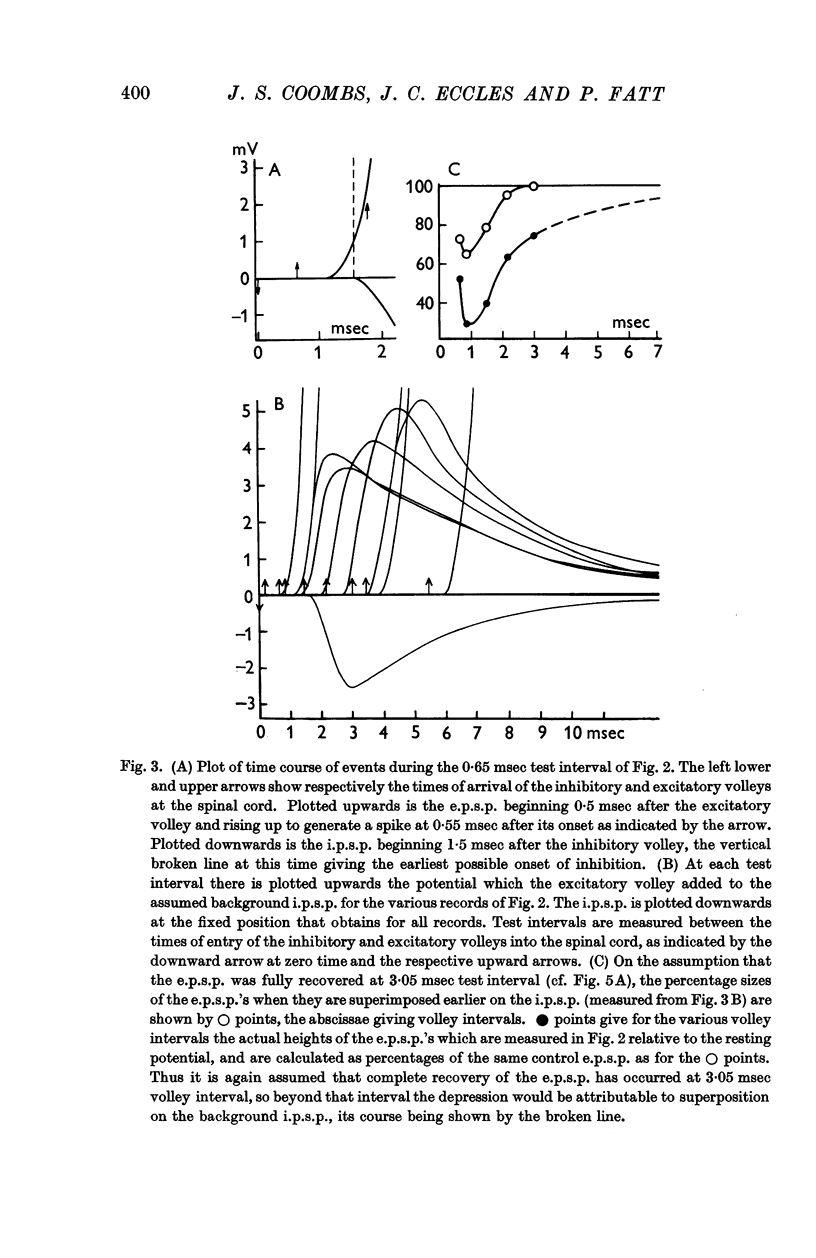
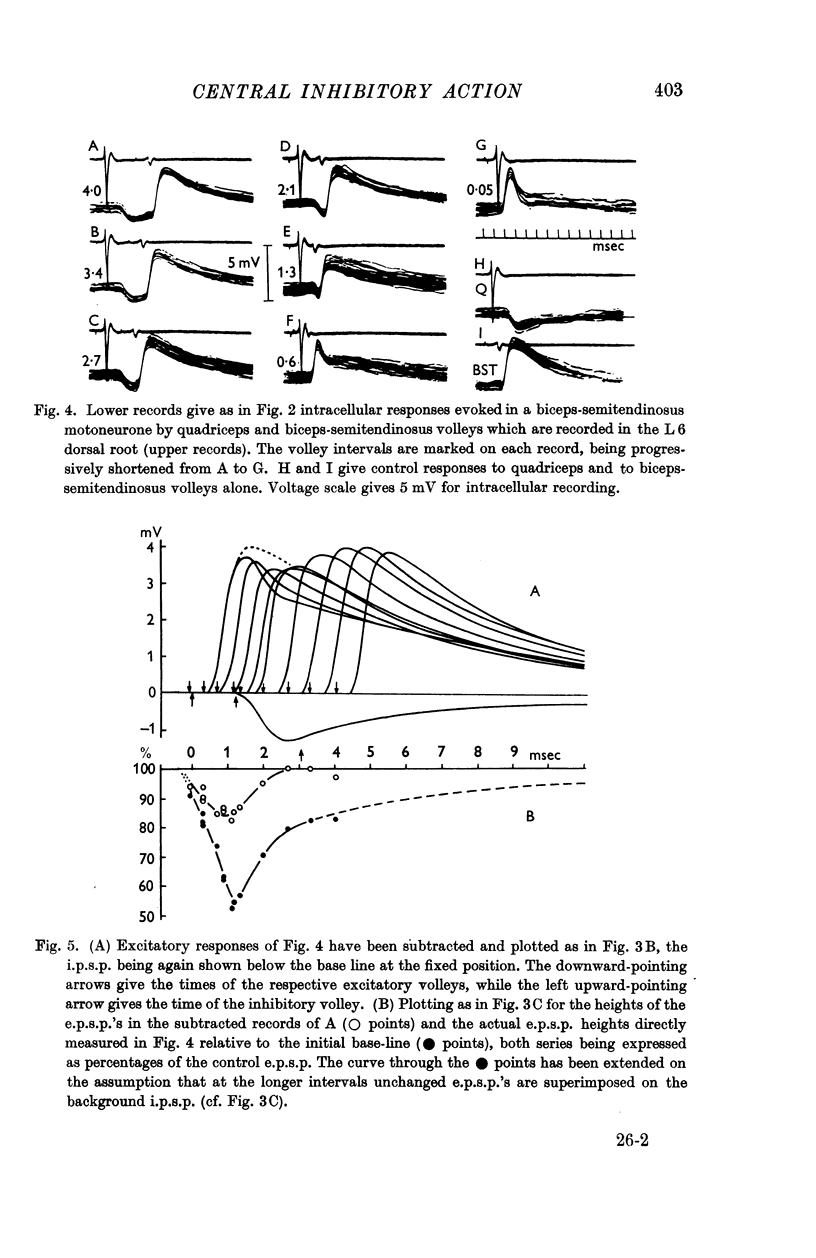
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRADLEY K., EASTON D. M., ECCLES J. C. An investigation of primary or direct inhibition. J Physiol. 1953 Dec 29;122(3):474–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp005015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROCK L. G., COOMBS J. S., ECCLES J. C. The nature of the monosynaptic excitatory and inhibitory processes in the spinal cord. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1952 Oct 16;140(899):170–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROCK L. G., COOMBS J. S., ECCLES J. C. The recording of potentials from motoneurones with an intracellular electrode. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):431–460. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOMBS J. S., ECCLES J. C., FATT P. Excitatory synaptic action in motoneurones. J Physiol. 1955 Nov 28;130(2):374–395. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOMBS J. S., ECCLES J. C., FATT P. The electrical properties of the motoneurone membrane. J Physiol. 1955 Nov 28;130(2):291–325. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOMBS J. S., ECCLES J. C., FATT P. The specific ionic conductances and the ionic movements across the motoneuronal membrane that produce the inhibitory post-synaptic potential. J Physiol. 1955 Nov 28;130(2):326–374. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., FATT P., KOKETSU K. Cholinergic and inhibitory synapses in a pathway from motor-axon collaterals to motoneurones. J Physiol. 1954 Dec 10;126(3):524–562. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., FATT P., LANDGREN S., WINSBURY G. J. Spinal cord potentials generated by volleys in the large muscle afferents. J Physiol. 1954 Sep 28;125(3):590–606. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C. The electrophysiological properties of the motoneurone. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1952;17:175–183. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1952.017.01.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., KATZ B. An analysis of the end-plate potential recorded with an intracellular electrode. J Physiol. 1951 Nov 28;115(3):320–370. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., KATZ B. The effect of inhibitory nerve impulses on a crustacean muscle fibre. J Physiol. 1953 Aug;121(2):374–389. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAPORTE Y., LLOYD D. P. C. Nature and significance of the reflex connections established by large afferent fibers of muscular origin. Am J Physiol. 1952 Jun;169(3):609–621. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1952.169.3.609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



