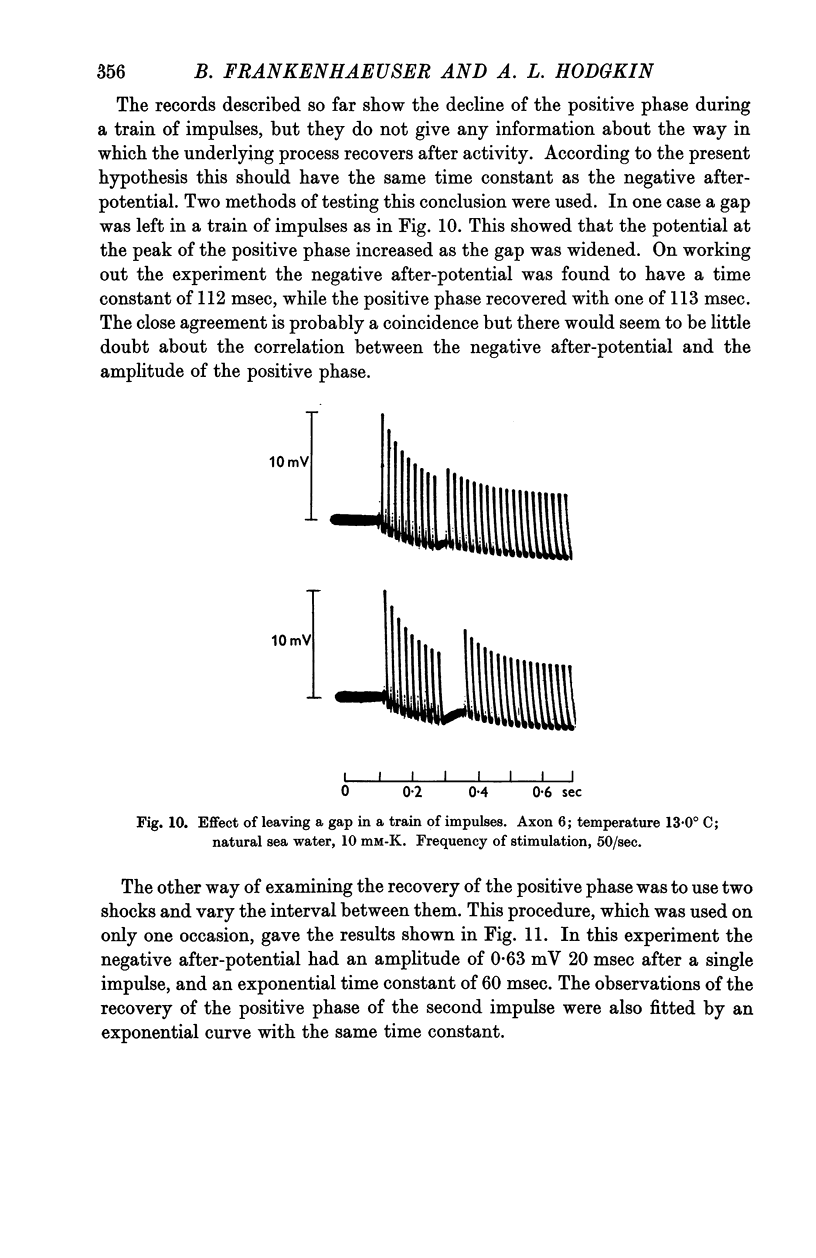
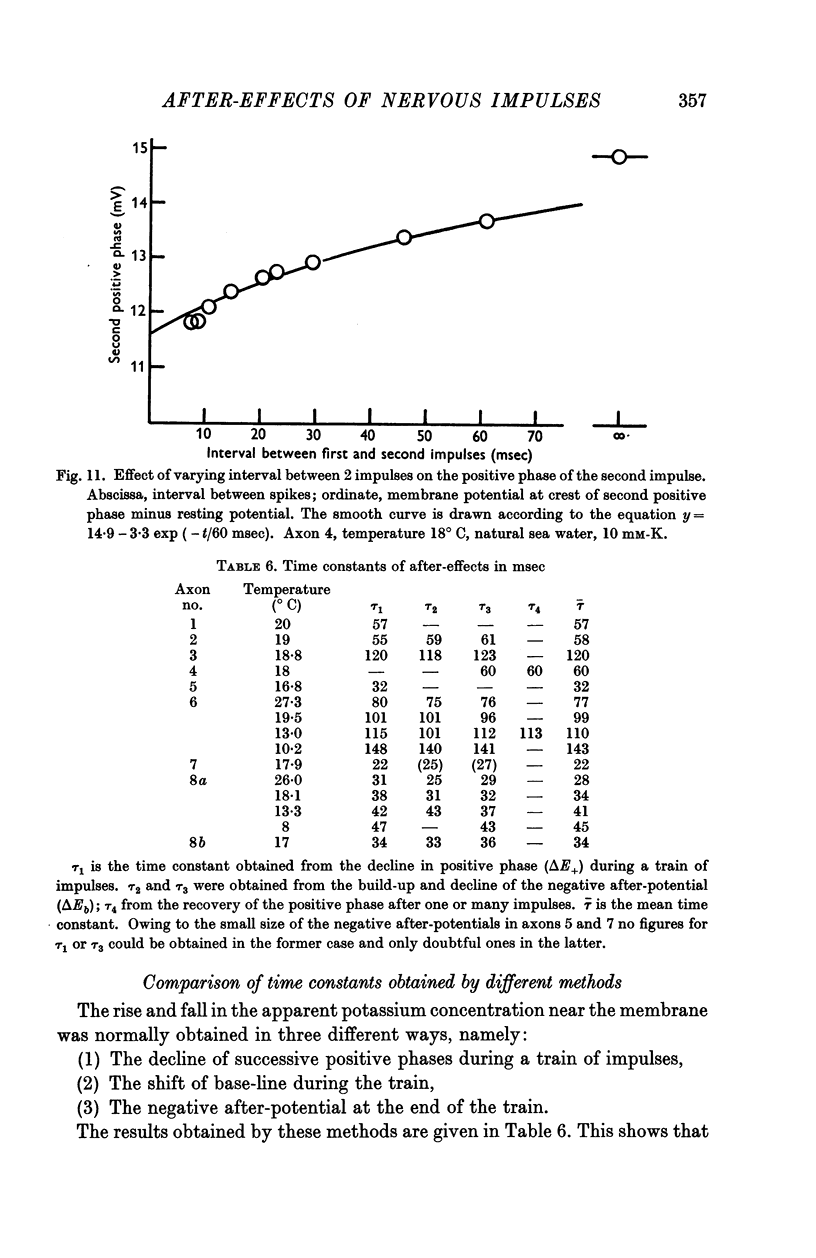
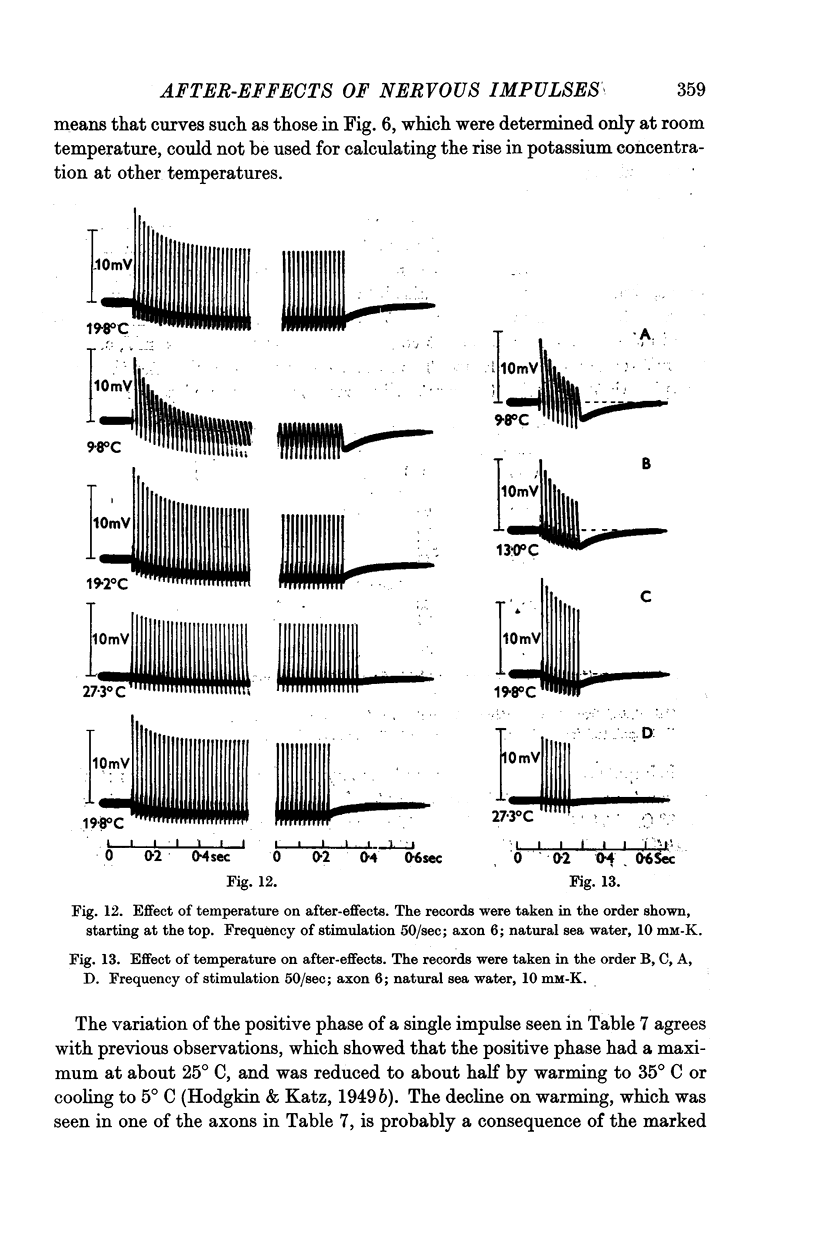
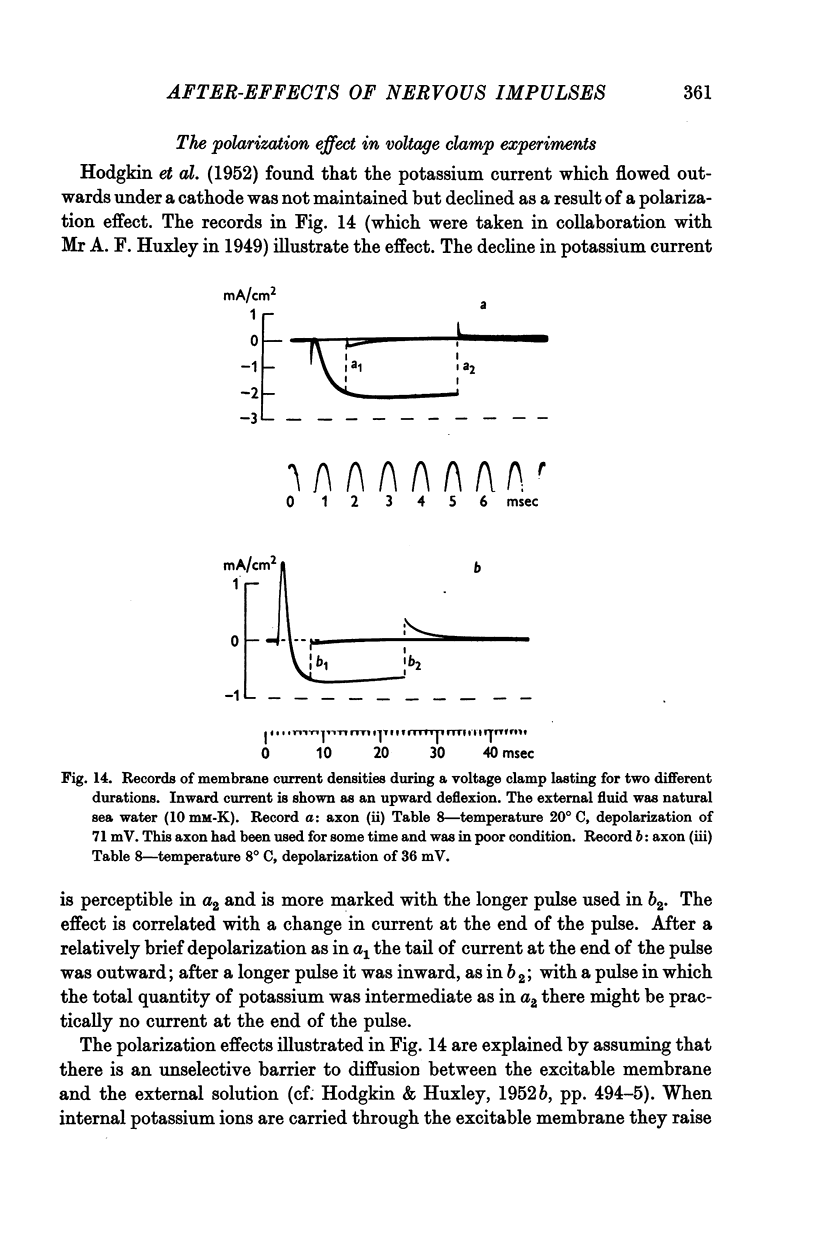
Full text
PDF


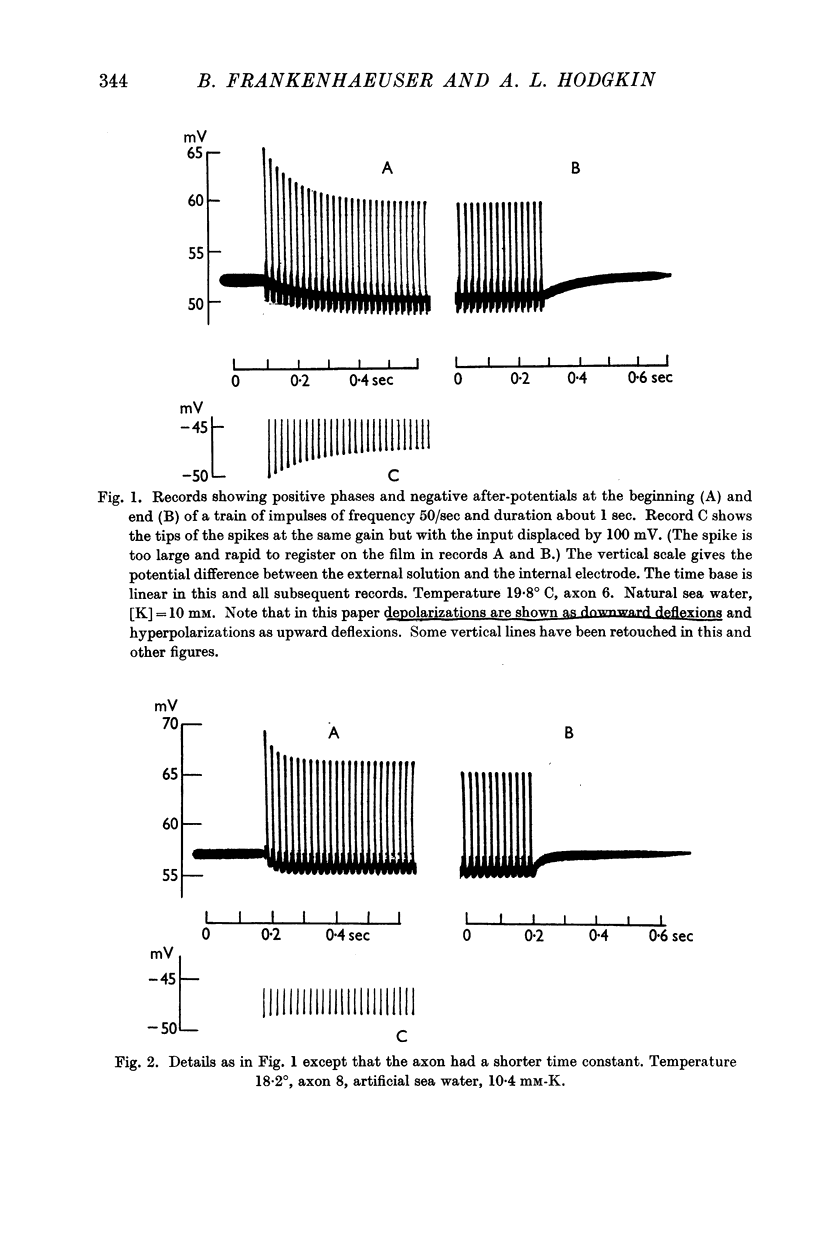
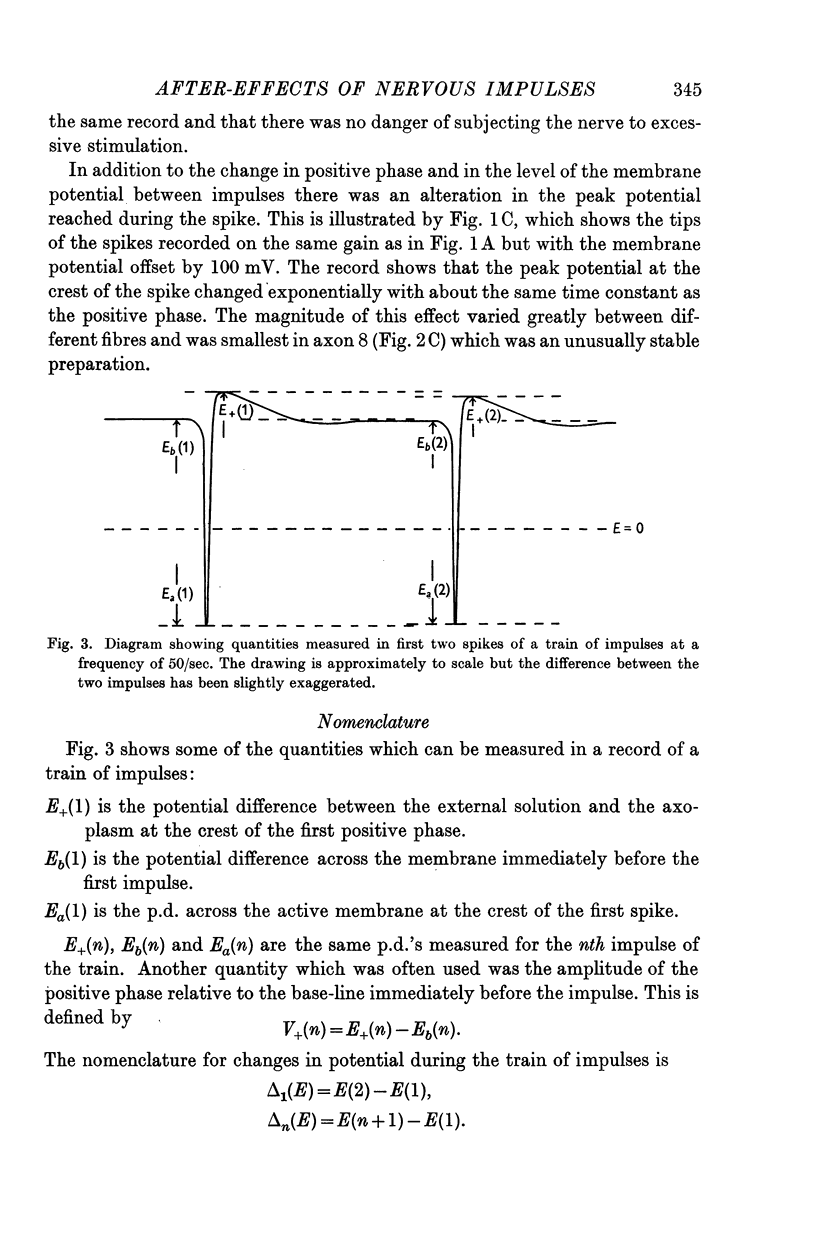
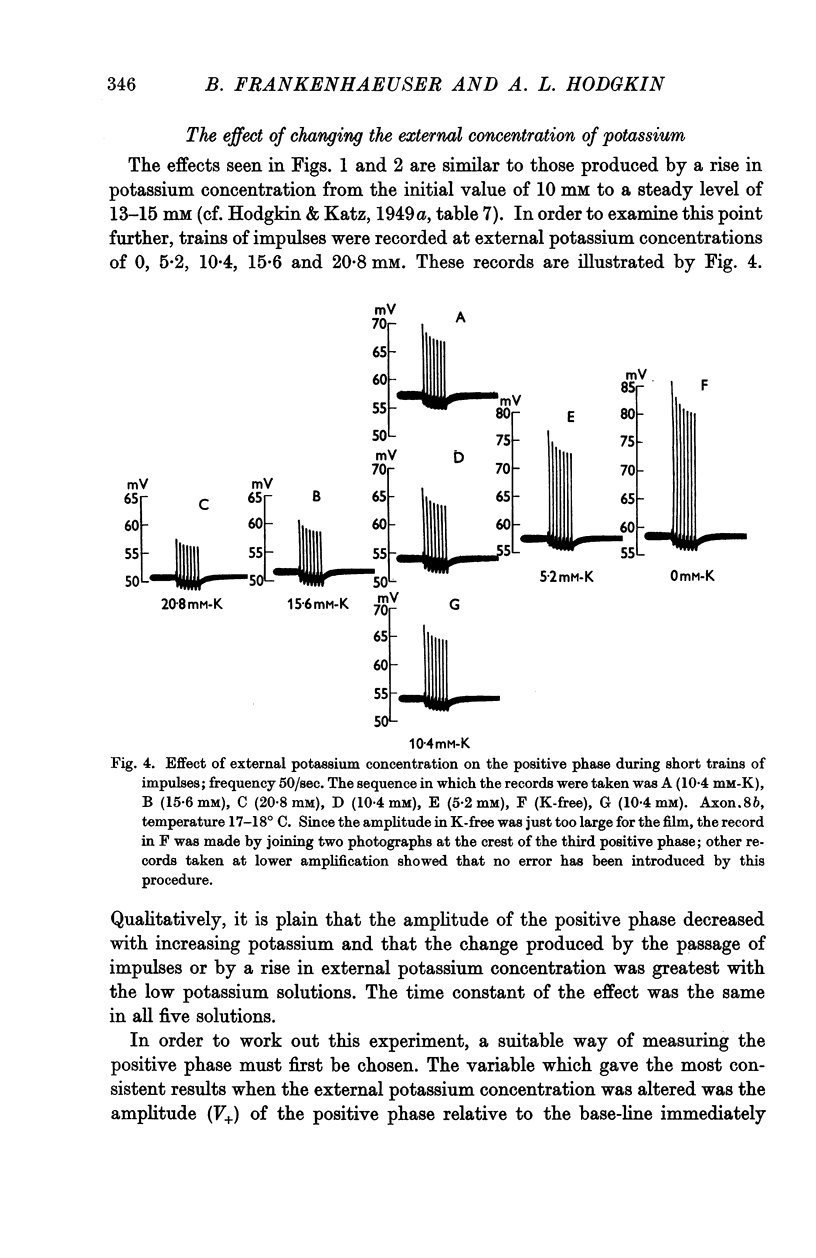


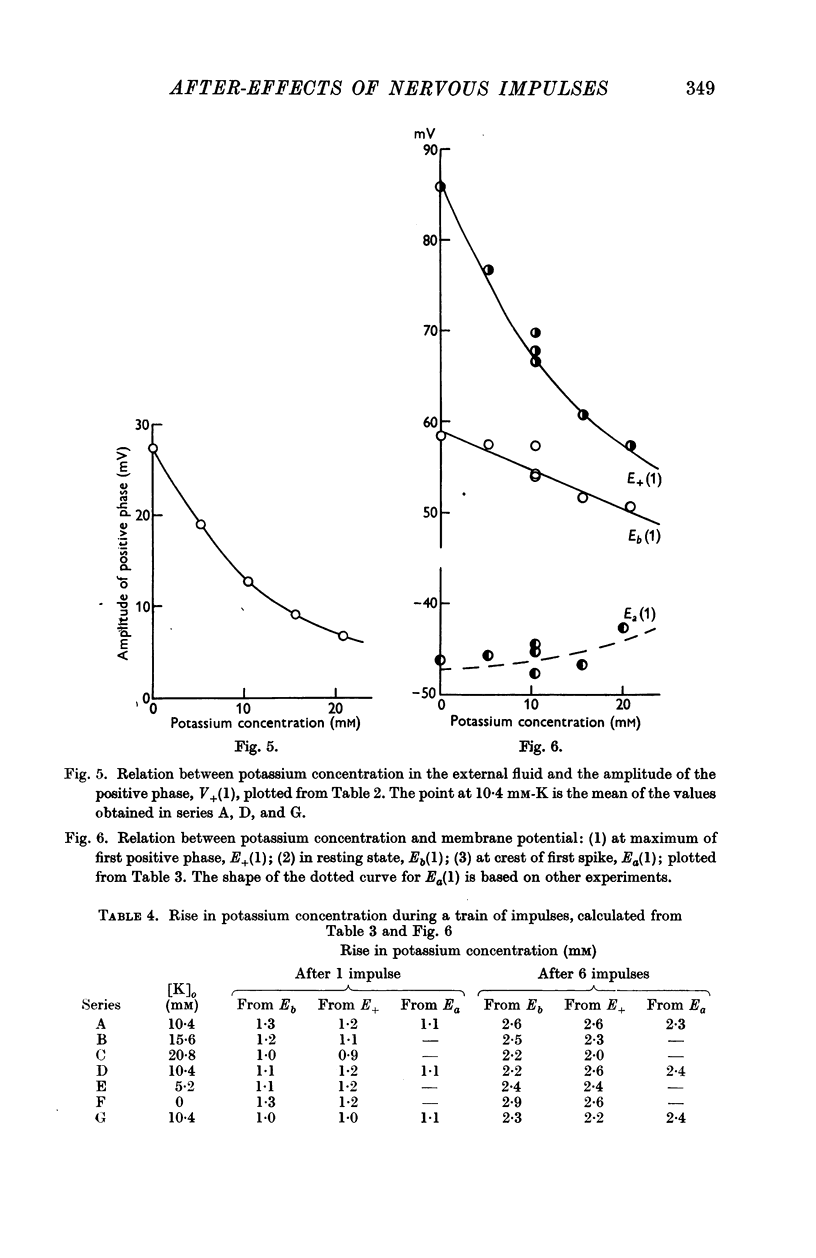
















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Geren B. B., Schmitt F. O. THE STRUCTURE OF THE SCHWANN CELL AND ITS RELATION TO THE AXON IN CERTAIN INVERTEBRATE NERVE FIBERS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1954 Sep;40(9):863–870. doi: 10.1073/pnas.40.9.863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. Currents carried by sodium and potassium ions through the membrane of the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):449–472. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F., KATZ B. Measurement of current-voltage relations in the membrane of the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):424–448. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. The components of membrane conductance in the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):473–496. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. The dual effect of membrane potential on sodium conductance in the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):497–506. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KATZ B. The effect of sodium ions on the electrical activity of giant axon of the squid. J Physiol. 1949 Mar 1;108(1):37–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KATZ B. The effect of temperature on the electrical activity of the giant axon of the squid. J Physiol. 1949 Aug;109(1-2):240–249. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KEYNES R. D. The potassium permeability of a giant nerve fibre. J Physiol. 1955 Apr 28;128(1):61–88. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYNES R. D., LEWIS P. R. The sodium and potassium content of cephalopod nerve fibers. J Physiol. 1951 Jun;114(1-2):151–182. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHANES A. M. Effect of temperature on potassium liberation during nerve activity. Am J Physiol. 1954 Jun;177(3):377–382. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1954.177.3.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHANES A. M., GRUNDFEST H., FREYGANG W. Low level impedance changes following the spike in the squid giant axon before and after treatment with "veratrine" alkaloids. J Gen Physiol. 1953 Sep;37(1):39–51. doi: 10.1085/jgp.37.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHANES A. M. Potassium movement in relation to nerve activity. J Gen Physiol. 1951 Jul;34(6):795–807. doi: 10.1085/jgp.34.6.795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHANES A. M. The ultraviolet spectra and neurophysiological effects of "veratrine" alkaloids. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1952 Jun;105(2):216–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIDMANN S. Electrical characteristics of Sepia axons. J Physiol. 1951 Jul;114(3):372–381. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIDMANN S. The effect of the cardiac membrane potential on the rapid availability of the sodium-carrying system. J Physiol. 1955 Jan 28;127(1):213–224. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



