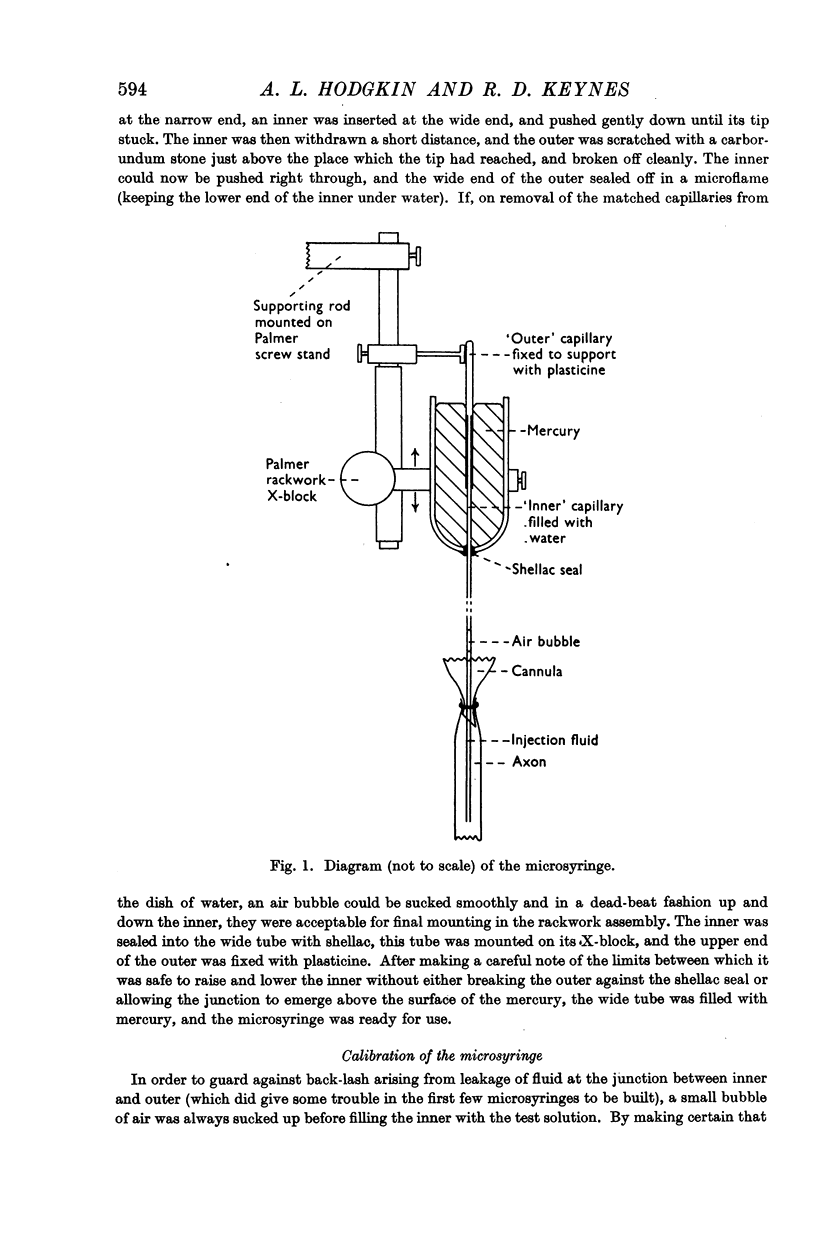
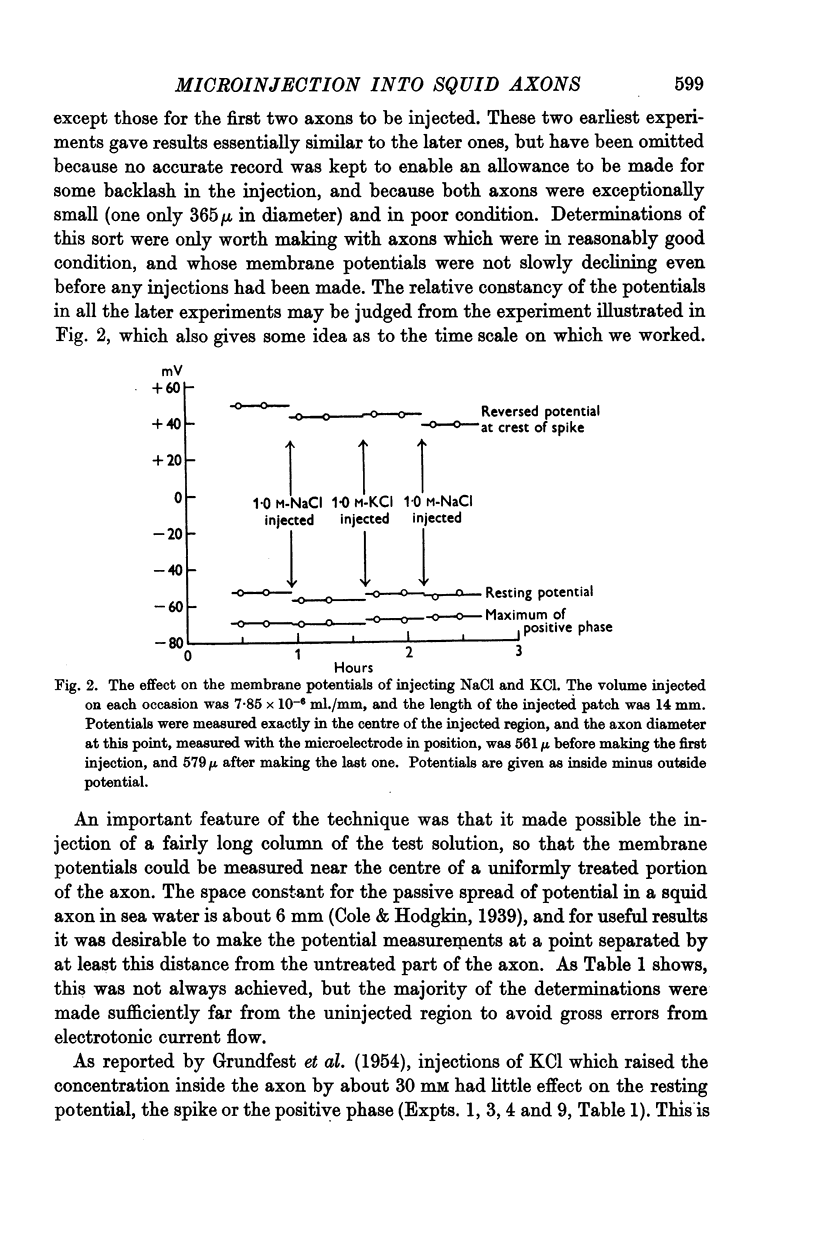
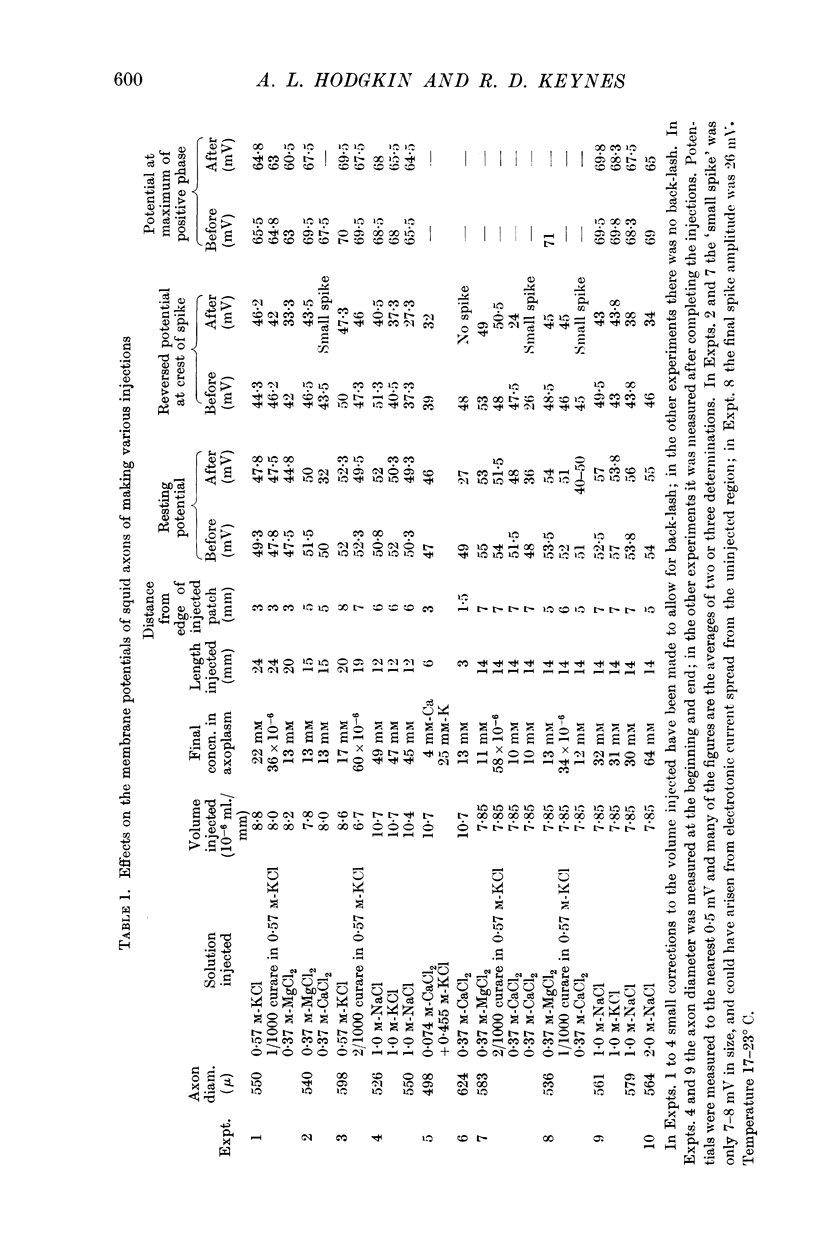
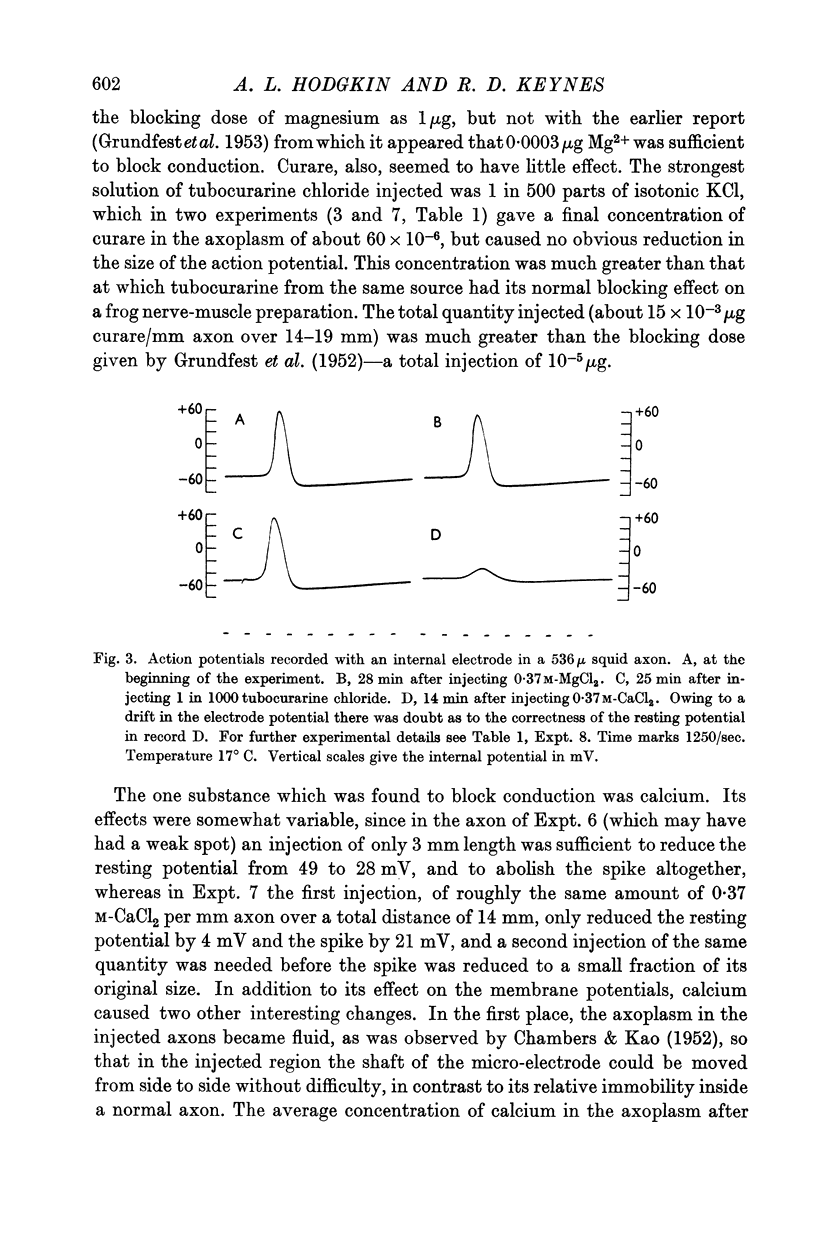
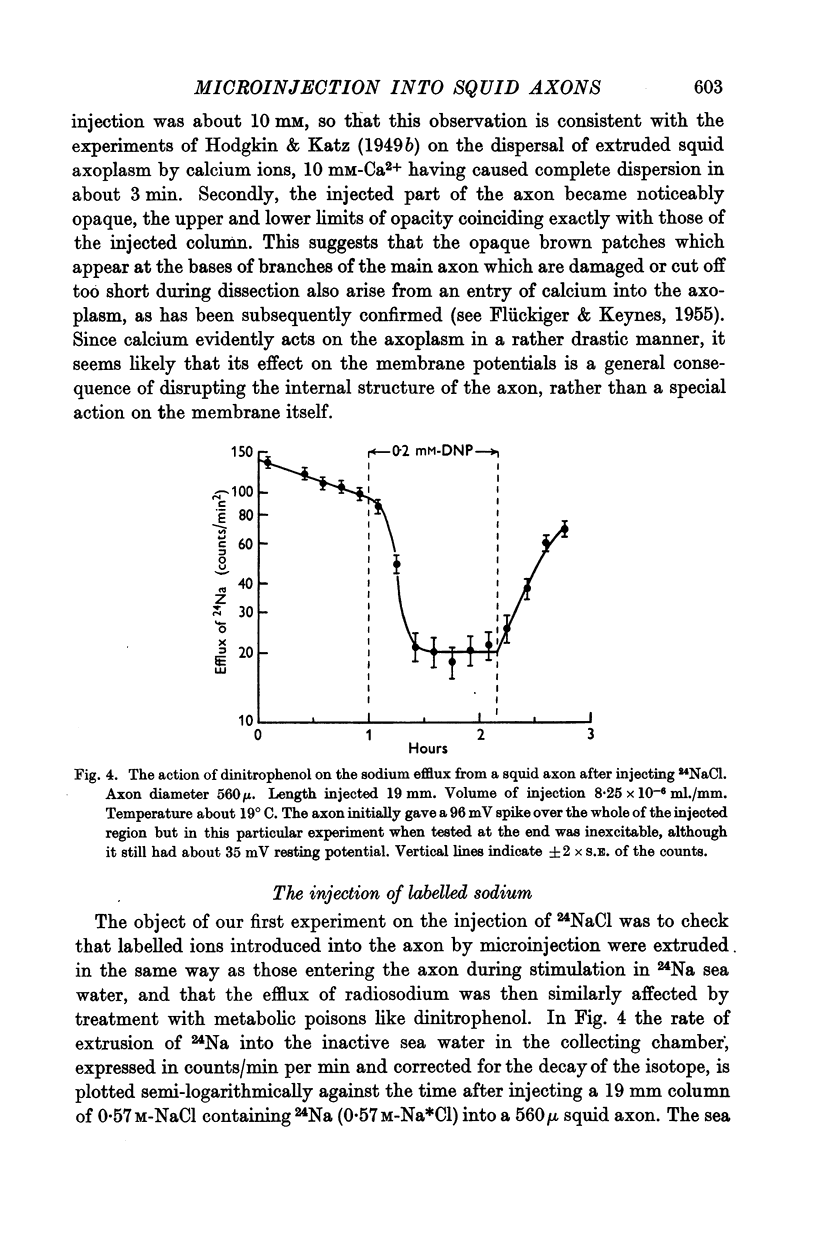
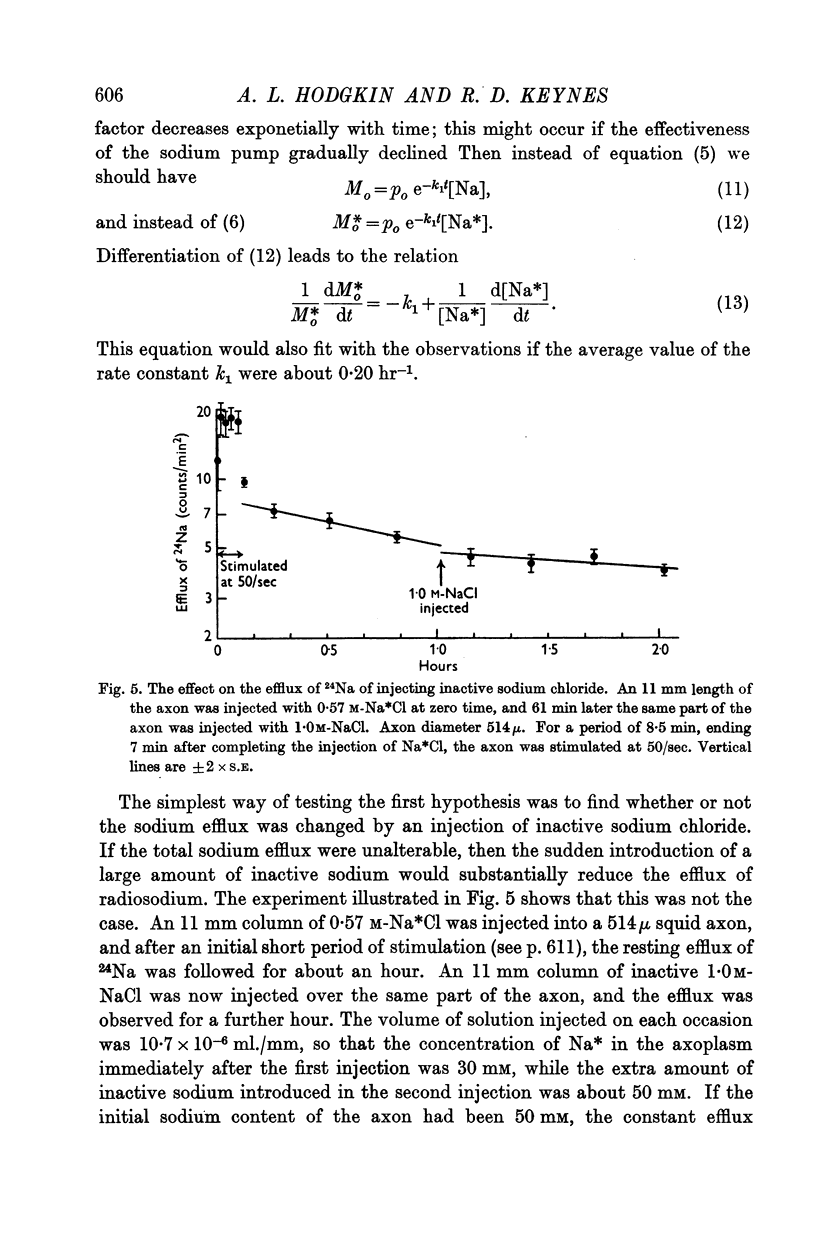
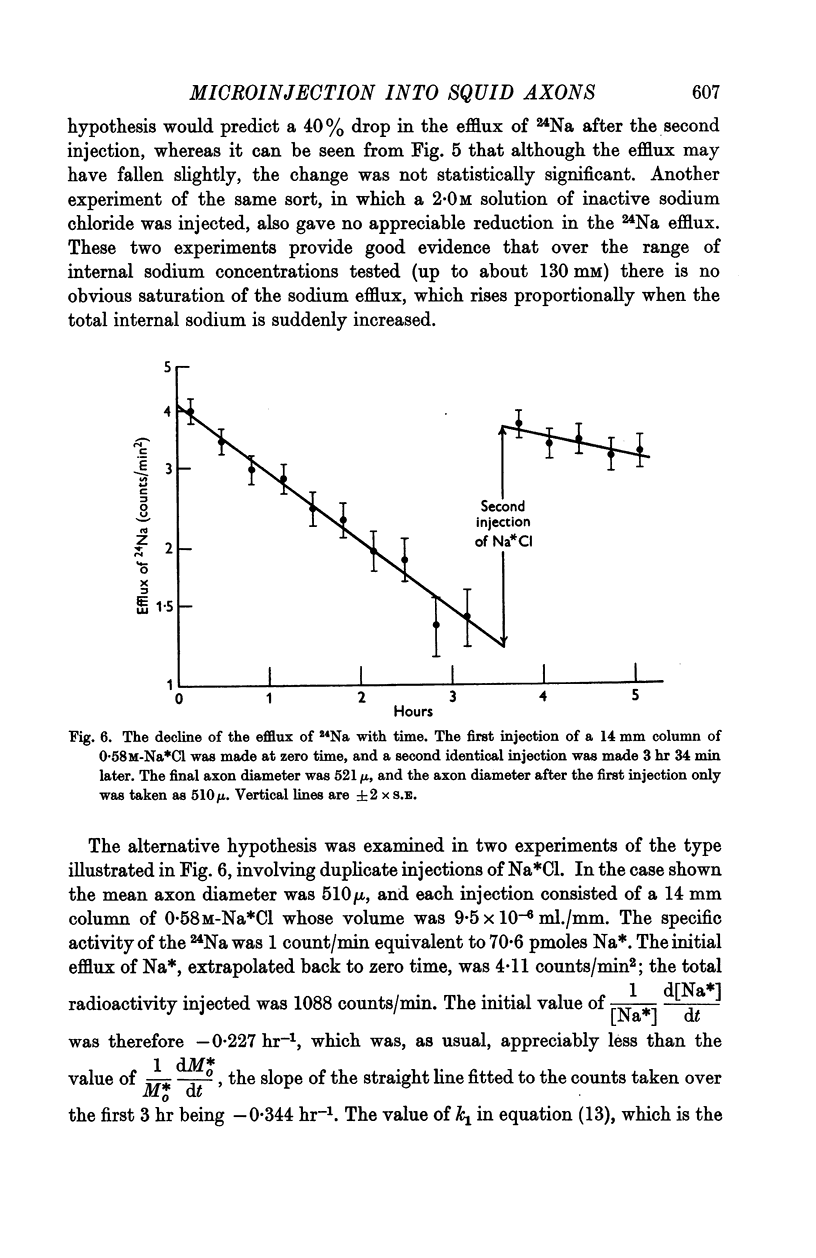
Full text
PDF









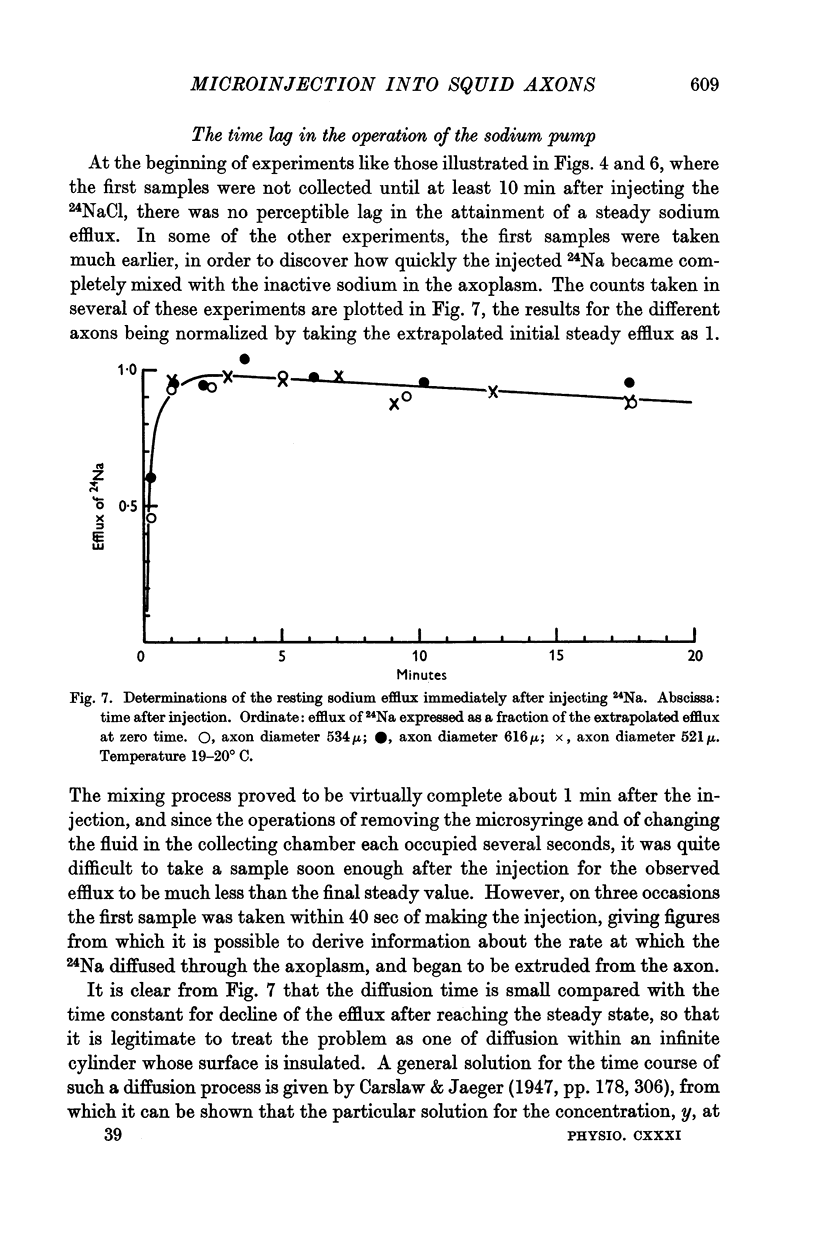







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARVANITAKI A., CHALAZONITIS N. Recherches sur la répartition de quelques catalyseurs respiratoires dans l'espace cellulaire. (Axone géant et soma neuronique de Sepia). Arch Sci Physiol (Paris) 1951;5(3):207–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOMBS J. S., ECCLES J. C., FATT P. The electrical properties of the motoneurone membrane. J Physiol. 1955 Nov 28;130(2):291–325. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. On the localization of acetylcholine receptors. J Physiol. 1955 Apr 28;128(1):157–181. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DESMEDT J. E. Electrical activity and intracellular sodium concentration in frog muscle. J Physiol. 1953 Jul;121(1):191–205. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLUCKIGER E., KEYNES R. D. The calcium permeability of Loligo axons. J Physiol. 1955 May 27;128(2):41–2P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLYNN F., MAIZELS M. Cation control in human erythrocytes. J Physiol. 1949 Dec;110(3-4):301–318. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRUNDFEST H., KAO C. Y., ALTAMIRANO M. Bioelectric effects of ions microinjected into the giant axon of Loligo. J Gen Physiol. 1954 Nov 20;38(2):245–282. doi: 10.1085/jgp.38.2.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRUNDFEST H., NACHMANSOHN D., KAO C. Y., CHAMBERS R. Mode of blocking of axonal activity by curare and inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase. Nature. 1952 Feb 2;169(4292):190–190. doi: 10.1038/169190a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KATZ B. The effect of calcium on the axoplasm of giant nerve fibers. J Exp Biol. 1949 Oct;26(3):292-4, pl. doi: 10.1242/jeb.26.3.292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KATZ B. The effect of sodium ions on the electrical activity of giant axon of the squid. J Physiol. 1949 Mar 1;108(1):37–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KEYNES R. D. Active transport of cations in giant axons from Sepia and Loligo. J Physiol. 1955 Apr 28;128(1):28–60. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KEYNES R. D. The mobility and diffusion coefficient of potassium in giant axons from Sepia. J Physiol. 1953 Mar;119(4):513–528. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin A. L., Huxley A. F. Resting and action potentials in single nerve fibres. J Physiol. 1945 Oct 15;104(2):176–195. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1945.sp004114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYNES R. D. The ionic fluxes in frog muscle. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1954 May 27;142(908):359–382. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1954.0030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]