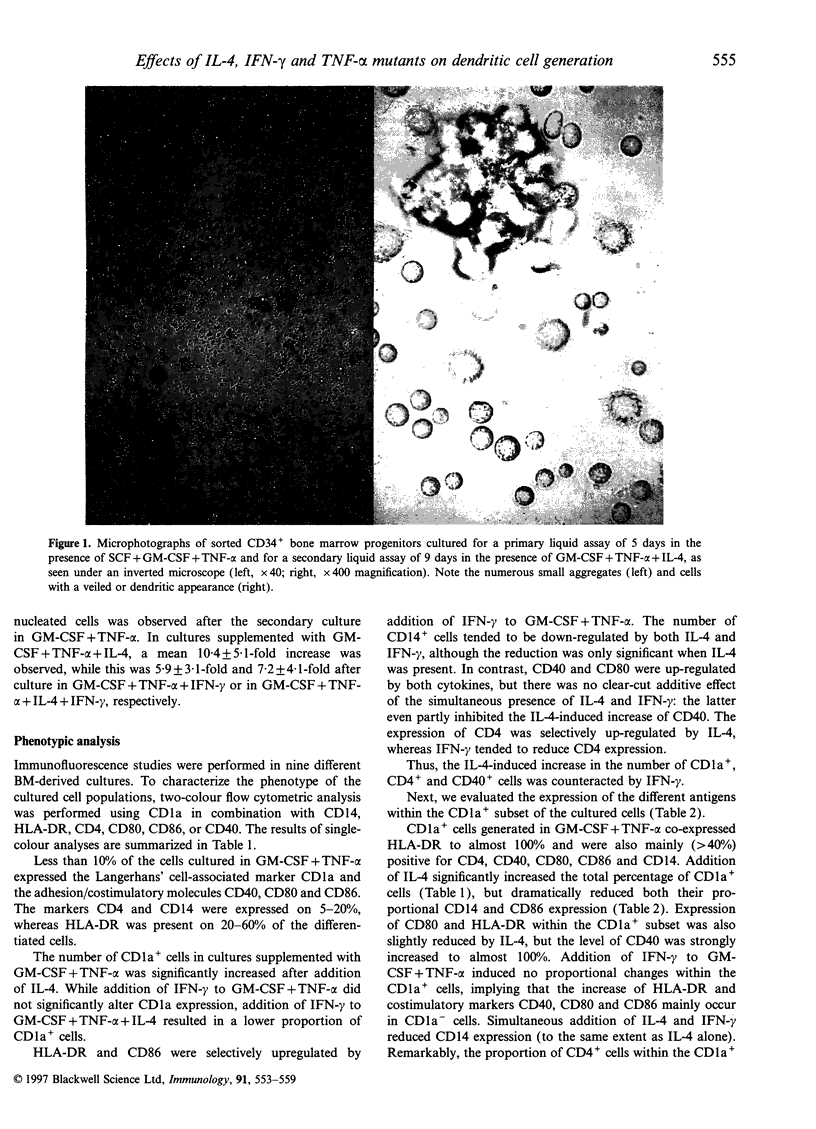
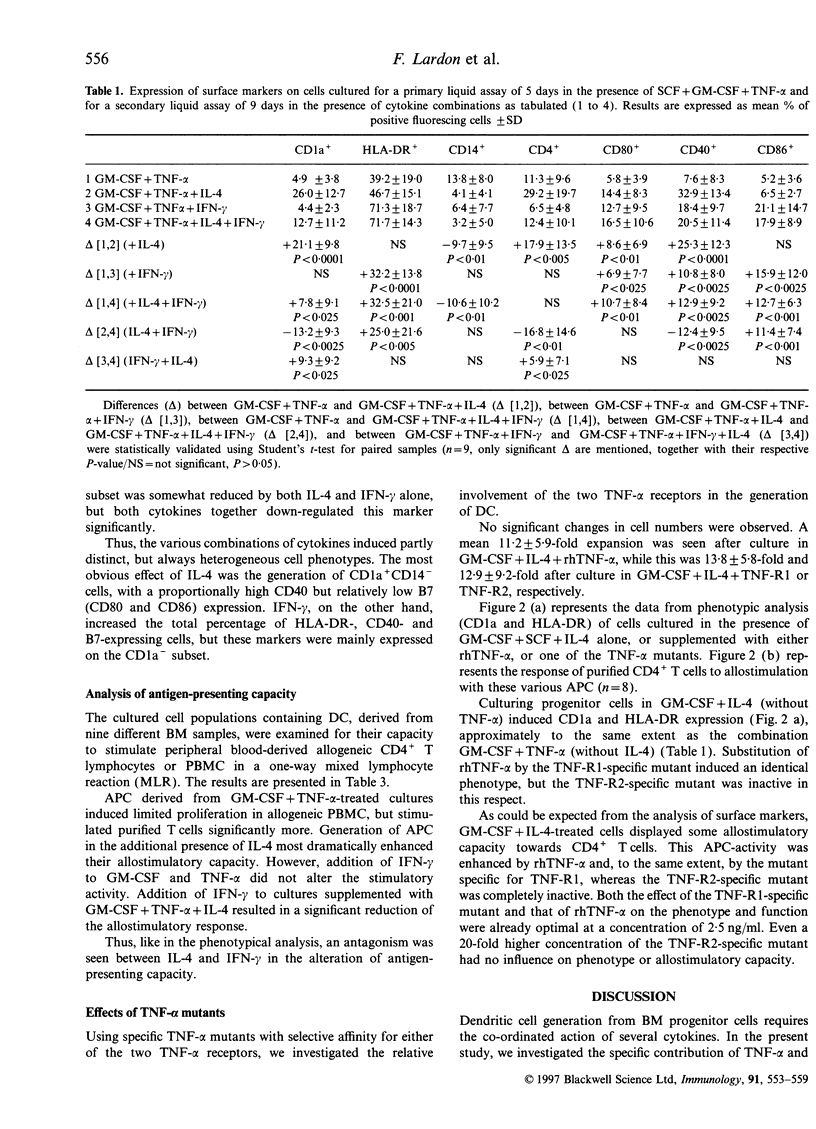
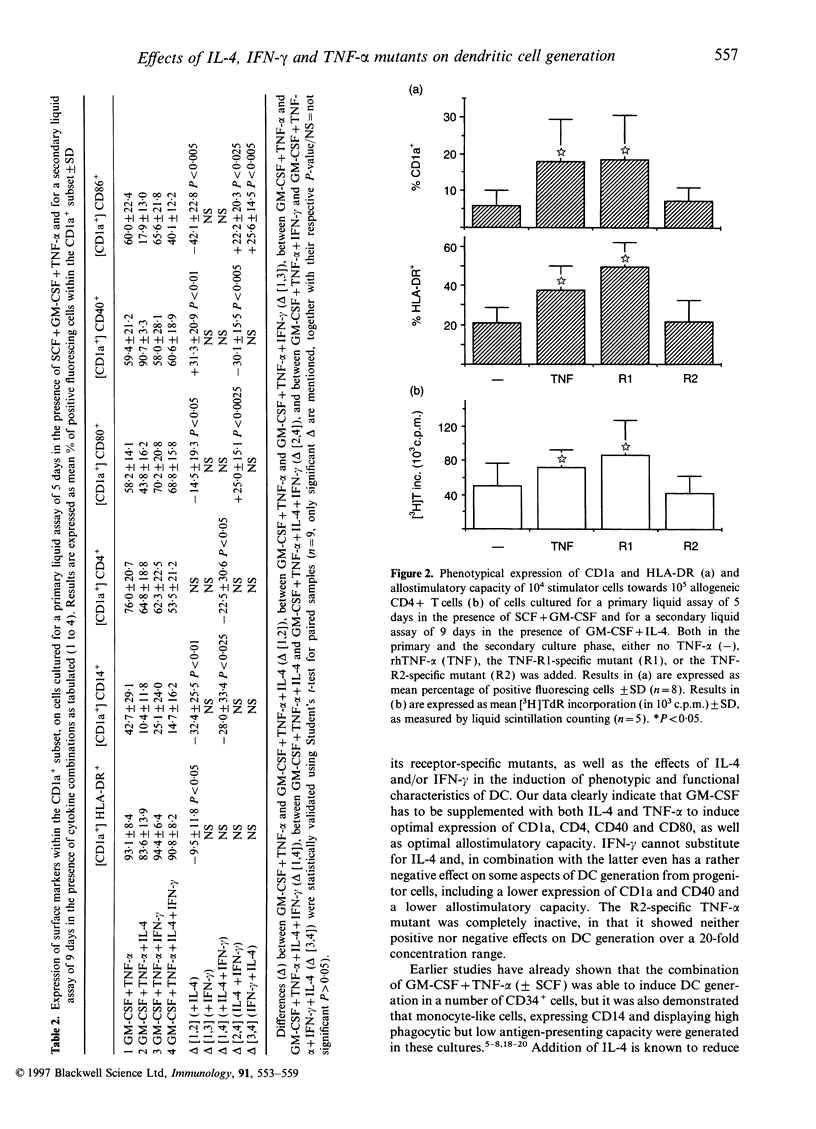
Abstract
We report the generation of dendritic cells (DC) starting from CD34+ bone marrow (BM) progenitor cells, using a two-stage culture system in which, besides granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) and tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), stem-cell factor (SCF) was added during the first 5 days, while interleukin-4 (IL-4) and/or interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) were added during the secondary culture period of 9 days. Addition of IL-4 favoured the outgrowth of CD1a+, HLA-DR+, CD4+, CD40+, CD80+ but CD14- cells with dendritic morphology and strong antigen-presenting capacity. Addition of IFN-gamma selectively induced HLA-DR and CD86 but did not up-regulate CD1a expression or antigen-presenting capacity of the differentiated cells. An antagonism between IL-4 and IFN-gamma could further be confirmed in that, as compared with IL-4 alone, the simultaneous addition of IL-4 and IFN-gamma to GM-CSF plus TNF-alpha during maturation reduced both the phenotypical (CD1a, CD4, CD40) and functional characteristics of DC. Using receptor-specific TNF-alpha mutants, we investigated the relative involvement of TNF-alpha receptors R1 and R2 in the generation of DC. The induction of CD1a and HLA-DR, as well as the increase in allostimulatory capacity were dependent on TNF-R1 triggering, whereas triggering through TNF-R2 had no measurable effect. We conclude first, that the expansion of DC from BM progenitors could most effectively be enhanced in a two-stage culture assay using SCF, GM-CSF, TNF-alpha and IL-4; second, that the effect of TNF-alpha in DC generation involves signalling via the TNF-R1 receptor; and third, that IFN-gamma counteracts some of the effects of IL-4 in DC generation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbas A. K., Murphy K. M., Sher A. Functional diversity of helper T lymphocytes. Nature. 1996 Oct 31;383(6603):787–793. doi: 10.1038/383787a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bühring H. J., Ullrich A., Schaudt K., Müller C. A., Busch F. W. The product of the proto-oncogene c-kit (P145c-kit) is a human bone marrow surface antigen of hemopoietic precursor cells which is expressed on a subset of acute non-lymphoblastic leukemic cells. Leukemia. 1991 Oct;5(10):854–860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caux C., Dezutter-Dambuyant C., Schmitt D., Banchereau J. GM-CSF and TNF-alpha cooperate in the generation of dendritic Langerhans cells. Nature. 1992 Nov 19;360(6401):258–261. doi: 10.1038/360258a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cella M., Scheidegger D., Palmer-Lehmann K., Lane P., Lanzavecchia A., Alber G. Ligation of CD40 on dendritic cells triggers production of high levels of interleukin-12 and enhances T cell stimulatory capacity: T-T help via APC activation. J Exp Med. 1996 Aug 1;184(2):747–752. doi: 10.1084/jem.184.2.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Maeyer E., De Maeyer-Guignard J. Interferon-gamma. Curr Opin Immunol. 1992 Jun;4(3):321–326. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(92)90083-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman A. S., Freeman G. J., Rhynhart K., Nadler L. M. Selective induction of B7/BB-1 on interferon-gamma stimulated monocytes: a potential mechanism for amplification of T cell activation through the CD28 pathway. Cell Immunol. 1991 Oct 15;137(2):429–437. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(91)90091-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loetscher H., Stueber D., Banner D., Mackay F., Lesslauer W. Human tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF alpha) mutants with exclusive specificity for the 55-kDa or 75-kDa TNF receptors. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 15;268(35):26350–26357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu L., Hsieh M., Oriss T. B., Morel P. A., Starzl T. E., Rao A. S., Thomson A. W. Generation of DC from mouse spleen cell cultures in response to GM-CSF: immunophenotypic and functional analyses. Immunology. 1995 Jan;84(1):127–134. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maciejewski J., Selleri C., Anderson S., Young N. S. Fas antigen expression on CD34+ human marrow cells is induced by interferon gamma and tumor necrosis factor alpha and potentiates cytokine-mediated hematopoietic suppression in vitro. Blood. 1995 Jun 1;85(11):3183–3190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa H., Aiba S., Nakagawa, Tagami H. Interferon-gamma and interleukin-10 inhibit antigen presentation by Langerhans cells for T helper type 1 cells by suppressing their CD80 (B7-1) expression. Eur J Immunol. 1996 Mar;26(3):648–652. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830260321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters J. H., Gieseler R., Thiele B., Steinbach F. Dendritic cells: from ontogenetic orphans to myelomonocytic descendants. Immunol Today. 1996 Jun;17(6):273–278. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(96)80544-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenzwajg M., Canque B., Gluckman J. C. Human dendritic cell differentiation pathway from CD34+ hematopoietic precursor cells. Blood. 1996 Jan 15;87(2):535–544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusten L. S., Jacobsen F. W., Lesslauer W., Loetscher H., Smeland E. B., Jacobsen S. E. Bifunctional effects of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF alpha) on the growth of mature and primitive human hematopoietic progenitor cells: involvement of p55 and p75 TNF receptors. Blood. 1994 Jun 1;83(11):3152–3159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santiago-Schwarz F., Divaris N., Kay C., Carsons S. E. Mechanisms of tumor necrosis factor-granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor-induced dendritic cell development. Blood. 1993 Nov 15;82(10):3019–3028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santiago-Schwarz F., Rappa D. A., Laky K., Carsons S. E. Stem cell factor augments tumor necrosis factor-granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor-mediated dendritic cell hematopoiesis. Stem Cells. 1995 Mar;13(2):186–197. doi: 10.1002/stem.5530130210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schall T. J., Lewis M., Koller K. J., Lee A., Rice G. C., Wong G. H., Gatanaga T., Granger G. A., Lentz R., Raab H. Molecular cloning and expression of a receptor for human tumor necrosis factor. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):361–370. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90816-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snoeck H. W., Lardon F., Lenjou M., Nys G., Van Bockstaele D. R., Peetermans M. E. Interferon-gamma and interleukin-4 reciprocally regulate the production of monocytes/macrophages and neutrophils through a direct effect on committed monopotential bone marrow progenitor cells. Eur J Immunol. 1993 May;23(5):1072–1077. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snoeck H. W., Lenjou M., Nys G., Lardon F., Peetermans M. E., Van Bockstaele D. R., Moulijn A., Haenen L., Berneman Z. N. Interleukin 4 and interferon gamma costimulate the expansion of early human myeloid colony-forming cells. Proposal of a model for the regulation of myelopoiesis by interleukin 4 and interferon gamma and its integration with the regulation of the immune response. Leukemia. 1996 Jan;10(1):117–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M. The dendritic cell system and its role in immunogenicity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:271–296. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.001415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabolcs P., Avigan D., Gezelter S., Ciocon D. H., Moore M. A., Steinman R. M., Young J. W. Dendritic cells and macrophages can mature independently from a human bone marrow-derived, post-colony-forming unit intermediate. Blood. 1996 Jun 1;87(11):4520–4530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabolcs P., Moore M. A., Young J. W. Expansion of immunostimulatory dendritic cells among the myeloid progeny of human CD34+ bone marrow precursors cultured with c-kit ligand, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, and TNF-alpha. J Immunol. 1995 Jun 1;154(11):5851–5861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartaglia L. A., Goeddel D. V. Two TNF receptors. Immunol Today. 1992 May;13(5):151–153. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90116-O. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Ostade X., Vandenabeele P., Everaerdt B., Loetscher H., Gentz R., Brockhaus M., Lesslauer W., Tavernier J., Brouckaert P., Fiers W. Human TNF mutants with selective activity on the p55 receptor. Nature. 1993 Jan 21;361(6409):266–269. doi: 10.1038/361266a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Ostade X., Vandenabeele P., Tavernier J., Fiers W. Human tumor necrosis factor mutants with preferential binding to and activity on either the R55 or R75 receptor. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Mar 15;220(3):771–779. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb18678.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenabeele P., Declercq W., Beyaert R., Fiers W. Two tumour necrosis factor receptors: structure and function. Trends Cell Biol. 1995 Oct;5(10):392–399. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(00)89088-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams L. A., Egner W., Hart D. N. Isolation and function of human dendritic cells. Int Rev Cytol. 1994;153:41–103. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62188-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. W., Szabolcs P., Moore M. A. Identification of dendritic cell colony-forming units among normal human CD34+ bone marrow progenitors that are expanded by c-kit-ligand and yield pure dendritic cell colonies in the presence of granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor and tumor necrosis factor alpha. J Exp Med. 1995 Oct 1;182(4):1111–1119. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.4.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]