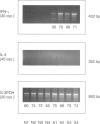
Abstract
We have shown that TAK-603, a new anti-rheumatic drug, is more effective in animal models in which cellular immunity plays a central role. Here, we studied the effect of the drug on Th1 cytokines, which are dominantly produced in this type of immune reaction, in an in vitro system and an in vivo model. We established Th1- and Th2-dominant T-cell lines, and studied the effect of TAK-603 on their cytokine production. Th1 cell lines were BALB/c mouse allo-reactive T cells and C57BL mouse mite antigen-reactive T cells, and the Th2 cell line was BALB/c mouse ovalbumin-reactive T cells. TAK-603 suppressed the production of Th1 cytokines [interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) and interleukin-2 (IL-2)] and not that of Th2 cytokines (IL-4, IL-5) in these cell lines. Furthermore, selective suppression of Th1 cytokine production was also observed in the T-cell clones obtained from the ovalbumin-reactive T-cell line. To investigate the effect on cytokine production in animal models of arthritis, we analysed the expression of cytokine messenger RNA using reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. In adjuvant arthritis rats, Th1-dominant cytokine production was observed both in the arthritic joint and the spleen, and the time-course paralleled the progression of arthritis. On the other hand, in type-II collagen-induced arthritis, in which TAK-603 has little effect, Th1-dominant cytokine production was not observed and Th2 cytokines were shown to be more important. The adjuvant arthritis rats treated with TAK-603 (6.25 mg/kg/day, per os) showed significantly lower cytokine mRNA expression both locally and systemically. These data suggest that TAK-603 selectively suppresses Th1 cytokine production, which is consistent with its effect on cellular immunity in animal models.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Assenmacher M., Schmitz J., Radbruch A. Flow cytometric determination of cytokines in activated murine T helper lymphocytes: expression of interleukin-10 in interferon-gamma and in interleukin-4-expressing cells. Eur J Immunol. 1994 May;24(5):1097–1101. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baba A., Kawamura N., Makino H., Ohta Y., Taketomi S., Sohda T. Studies on disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: synthesis of novel quinoline and quinazoline derivatives and their anti-inflammatory effect. J Med Chem. 1996 Dec 20;39(26):5176–5182. doi: 10.1021/jm9509408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach E. A., Szabo S. J., Dighe A. S., Ashkenazi A., Aguet M., Murphy K. M., Schreiber R. D. Ligand-induced autoregulation of IFN-gamma receptor beta chain expression in T helper cell subsets. Science. 1995 Nov 17;270(5239):1215–1218. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5239.1215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz M., Fox B. S. Prostaglandin E2 inhibits production of Th1 lymphokines but not of Th2 lymphokines. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 1;146(1):108–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y., Inobe J., Marks R., Gonnella P., Kuchroo V. K., Weiner H. L. Peripheral deletion of antigen-reactive T cells in oral tolerance. Nature. 1995 Jul 13;376(6536):177–180. doi: 10.1038/376177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P. A reagent for the single-step simultaneous isolation of RNA, DNA and proteins from cell and tissue samples. Biotechniques. 1993 Sep;15(3):532-4, 536-7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Franco M., Gille-Perramant M. F., Mevel J. C., Couderc J. T helper subset involvement in two high antibody responder lines of mice (Biozzi mice): HI (susceptible) and HII (resistant) to collagen-induced arthritis. Eur J Immunol. 1995 Jan;25(1):132–136. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830250123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkema R., van der Meide P. H., Pouwels P. H., Caspers M., Dubbeld M., Schellekens H. Cloning and expression of the chromosomal immune interferon gene of the rat. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):761–767. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03694.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gajewski T. F., Schell S. R., Fitch F. W. Evidence implicating utilization of different T cell receptor-associated signaling pathways by TH1 and TH2 clones. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 1;144(11):4110–4120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn E. M., Gray J. Adjuvant-induced polyarthritis in rats: biologic and histologic background. Am J Vet Res. 1965 Sep;26(114):1180–1194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn S., Stalder T., Wernli M., Bürgin D., Tschopp J., Nagata S., Erb P. Down-modulation of CD4+ T helper type 2 and type 0 cells by T helper type 1 cells via Fas/Fas-ligand interaction. Eur J Immunol. 1995 Sep;25(9):2679–2685. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830250942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess H., Gately M. K., Rüde E., Schmitt E., Szeliga J., Germann T. High doses of interleukin-12 inhibit the development of joint disease in DBA/1 mice immunized with type II collagen in complete Freund's adjuvant. Eur J Immunol. 1996 Jan;26(1):187–191. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830260129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh C. S., Macatonia S. E., O'Garra A., Murphy K. M. T cell genetic background determines default T helper phenotype development in vitro. J Exp Med. 1995 Feb 1;181(2):713–721. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.2.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimoto M., Fathman C. G. Antigen-reactive T cell clones. I. Transcomplementing hybrid I-A-region gene products function effectively in antigen presentation. J Exp Med. 1980 Oct 1;152(4):759–770. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.4.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liblau R. S., Singer S. M., McDevitt H. O. Th1 and Th2 CD4+ T cells in the pathogenesis of organ-specific autoimmune diseases. Immunol Today. 1995 Jan;16(1):34–38. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(95)80068-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsky P. E., Davis L. S., Cush J. J., Oppenheimer-Marks N. The role of cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1989;11(2):123–162. doi: 10.1007/BF00197186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauri C., Williams R. O., Walmsley M., Feldmann M. Relationship between Th1/Th2 cytokine patterns and the arthritogenic response in collagen-induced arthritis. Eur J Immunol. 1996 Jul;26(7):1511–1518. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830260716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight A. J., Barclay A. N., Mason D. W. Molecular cloning of rat interleukin 4 cDNA and analysis of the cytokine repertoire of subsets of CD4+ T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1991 May;21(5):1187–1194. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble A., Staynov D. Z., Kemeny D. M. Generation of rat Th2-like cells in vitro is interleukin-4-dependent and inhibited by interferon-gamma. Immunology. 1993 Aug;79(4):562–567. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novak T. J., Rothenberg E. V. cAMP inhibits induction of interleukin 2 but not of interleukin 4 in T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9353–9357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEARSON C. M., WOOD F. D. PASSIVE TRANSFER OF ADJUVANT ARTHRITIS BY LYMPH NODE OR SPLEEN CELLS. J Exp Med. 1964 Oct 1;120:547–560. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.4.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul W. E., Seder R. A. Lymphocyte responses and cytokines. Cell. 1994 Jan 28;76(2):241–251. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90332-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pernis A., Gupta S., Gollob K. J., Garfein E., Coffman R. L., Schindler C., Rothman P. Lack of interferon gamma receptor beta chain and the prevention of interferon gamma signaling in TH1 cells. Science. 1995 Jul 14;269(5221):245–247. doi: 10.1126/science.7618088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racke M. K., Bonomo A., Scott D. E., Cannella B., Levine A., Raine C. S., Shevach E. M., Röcken M. Cytokine-induced immune deviation as a therapy for inflammatory autoimmune disease. J Exp Med. 1994 Nov 1;180(5):1961–1966. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.5.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez F., Fowell D. J., Puklavec M., Simmonds S., Mason D. Glucocorticoids promote a TH2 cytokine response by CD4+ T cells in vitro. J Immunol. 1996 Apr 1;156(7):2406–2412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rott O., Cash E., Fleischer B. Phosphodiesterase inhibitor pentoxifylline, a selective suppressor of T helper type 1- but not type 2-associated lymphokine production, prevents induction of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in Lewis rats. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Aug;23(8):1745–1751. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sander B., Andersson J., Andersson U. Assessment of cytokines by immunofluorescence and the paraformaldehyde-saponin procedure. Immunol Rev. 1991 Feb;119:65–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1991.tb00578.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze-Koops H., Lipsky P. E., Kavanaugh A. F., Davis L. S. Elevated Th1- or Th0-like cytokine mRNA in peripheral circulation of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Modulation by treatment with anti-ICAM-1 correlates with clinical benefit. J Immunol. 1995 Nov 15;155(10):5029–5037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon A. K., Seipelt E., Sieper J. Divergent T-cell cytokine patterns in inflammatory arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 30;91(18):8562–8566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.18.8562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart J. M., Dixon F. J. Serum transfer of collagen-induced arthritis in mice. J Exp Med. 1983 Aug 1;158(2):378–392. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.2.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura T., Nakano H., Nagase H., Morokata T., Igarashi O., Oshimi Y., Miyazaki S., Nariuchi H. Early activation signal transduction pathways of Th1 and Th2 cell clones stimulated with anti-CD3. Roles of protein tyrosine kinases in the signal for IL-2 and IL-4 production. J Immunol. 1995 Nov 15;155(10):4692–4701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura T., Yanagida T., Nariuchi H. Difference in signal transduction pathway for IL-2 and IL-4 production in T helper 1 and T helper 2 cell clones in response to anti-CD3. J Immunol. 1993 Dec 1;151(11):6051–6061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson A. W., Phillips R. S. Expression of the IL-1 receptor discriminates Th2 from Th1 cloned CD4+ T cells specific for Plasmodium chabaudi. Immunology. 1994 Feb;81(2):216–221. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson A. W., Phillips R. S. Functional characterization of protective CD4+ T-cell clones reactive to the murine malaria parasite Plasmodium chabaudi. Immunology. 1992 Sep;77(1):99–105. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trentham D. E., Dynesius-Trentham R. A., Orav E. J., Combitchi D., Lorenzo C., Sewell K. L., Hafler D. A., Weiner H. L. Effects of oral administration of type II collagen on rheumatoid arthritis. Science. 1993 Sep 24;261(5129):1727–1730. doi: 10.1126/science.8378772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Yasumizu R., Sugiura K., Hashimoto F., Amoh Y., Lian Z., Cherry, Nishio N., Ikehara S. Fate of allogeneic or syngeneic cells in intravenous or portal vein injection: possible explanation for the mechanism of tolerance induction by portal vein injection. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Jul;24(7):1558–1565. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]