Abstract
Severe combined immunodeficient (SCID) mice were immunologically reconstituted by the transfer of fetal liver cells (FLC) of BALB/c mice (SCID-FLC mice). In peripheral blood (PB) of SCID-FLC mice, B and T cells started to appear 2 and 5 weeks, respectively, after the transfer of FLC, and had attained normal levels by 7 weeks. Orchidectomy and transplantation of testis under the kidney capsule were conducted at various stages of immunological maturation, and the induction of experimental autoimmune orchitis (EAO) was performed after immunological maturation in SCID-FLC mice. The experimental system was used to establish that the presence of testicular antigens in the early stage of immunological development influences the induction of EAO; grade of EAO was reduced in the presence of the antigens, and enhanced in their absence. In other words, the existence of self tissue antigens in the early stage of immunological development was essential for proper establishment of tolerance to the self tissue. These findings suggested that the SCID-FLC mouse is a suitable model with which to analyse the interaction between self antigens and cells of the developing immune system, which is otherwise observed only in the fetal or perinatal stage in experimental animals.
Full text
PDF

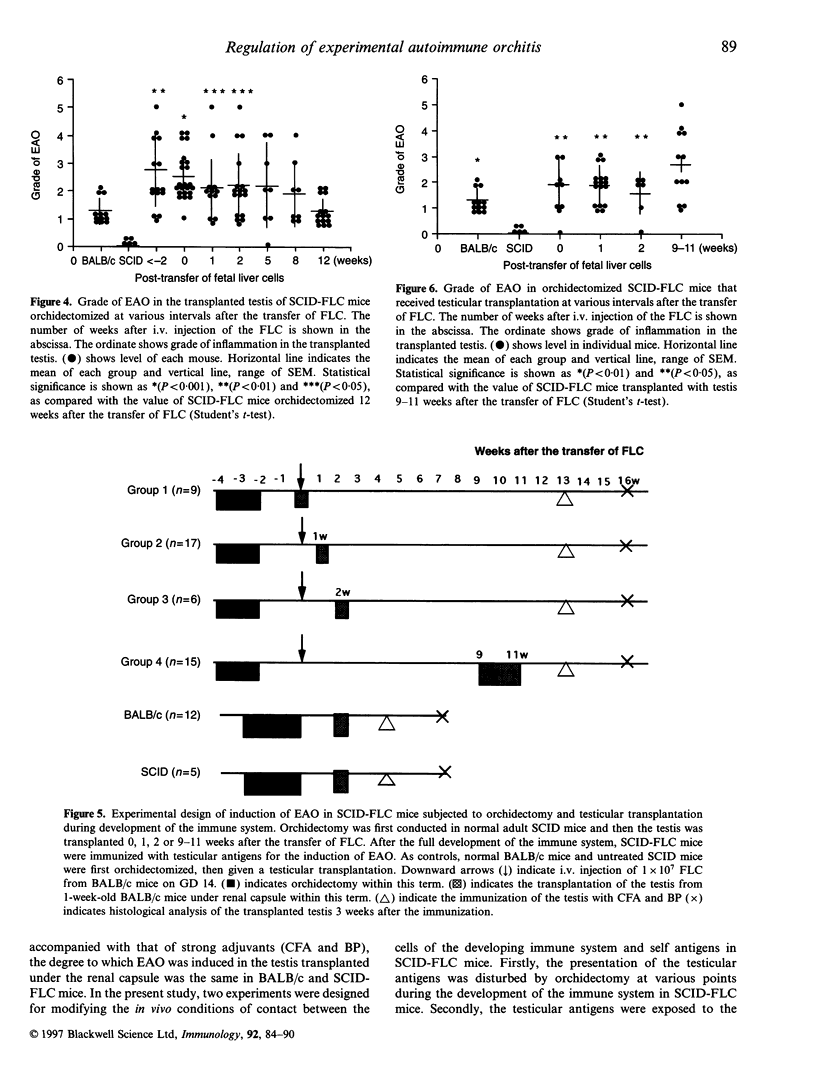

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams T. E., Alpert S., Hanahan D. Non-tolerance and autoantibodies to a transgenic self antigen expressed in pancreatic beta cells. Nature. 1987 Jan 15;325(6101):223–228. doi: 10.1038/325223a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akashi T., Eishi Y. Developmental expression of autoimmune target antigens during organogenesis. Immunology. 1991 Nov;74(3):524–532. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkly L. C., Lo D., Kanagawa O., Brinster R. L., Flavell R. A. T-cell tolerance by clonal anergy in transgenic mice with nonlymphoid expression of MHC class II I-E. Nature. 1989 Nov 30;342(6249):564–566. doi: 10.1038/342564a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen X., Shelton J., McCullagh P. Suppression of anti-thyrocyte autoreactivity by the lymphocytes of normal fetal lambs. J Autoimmun. 1995 Aug;8(4):539–559. doi: 10.1016/0896-8411(95)90007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eishi Y., McCullagh P. Acquisition of immunological self-recognition by the fetal rat. Immunology. 1988 Jun;64(2):319–323. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eishi Y., McCullagh P. Regulation of experimental allergic thyroiditis. Scand J Immunol. 1988 Jun;27(6):629–634. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1988.tb02395.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEDERBERG J. Genes and antibodies. Science. 1959 Jun 19;129(3364):1649–1653. doi: 10.1126/science.129.3364.1649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafaille J. J., Nagashima K., Katsuki M., Tonegawa S. High incidence of spontaneous autoimmune encephalomyelitis in immunodeficient anti-myelin basic protein T cell receptor transgenic mice. Cell. 1994 Aug 12;78(3):399–408. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90419-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakaguchi S., Fukuma K., Kuribayashi K., Masuda T. Organ-specific autoimmune diseases induced in mice by elimination of T cell subset. I. Evidence for the active participation of T cells in natural self-tolerance; deficit of a T cell subset as a possible cause of autoimmune disease. J Exp Med. 1985 Jan 1;161(1):72–87. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.1.72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugihara S., Fujiwara H., Shearer G. M. Autoimmune thyroiditis induced in mice depleted of particular T cell subsets. Characterization of thyroiditis-inducing T cell lines and clones derived from thyroid lesions. J Immunol. 1993 Jan 15;150(2):683–694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugihara S., Izumi Y., Yoshioka T., Yagi H., Tsujimura T., Tarutani O., Kohno Y., Murakami S., Hamaoka T., Fujiwara H. Autoimmune thyroiditis induced in mice depleted of particular T cell subsets. I. Requirement of Lyt-1 dull L3T4 bright normal T cells for the induction of thyroiditis. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 1;141(1):105–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRIPLETT E. L. On the mechanism of immunologic self recognition. J Immunol. 1962 Oct;89:505–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]