Abstract
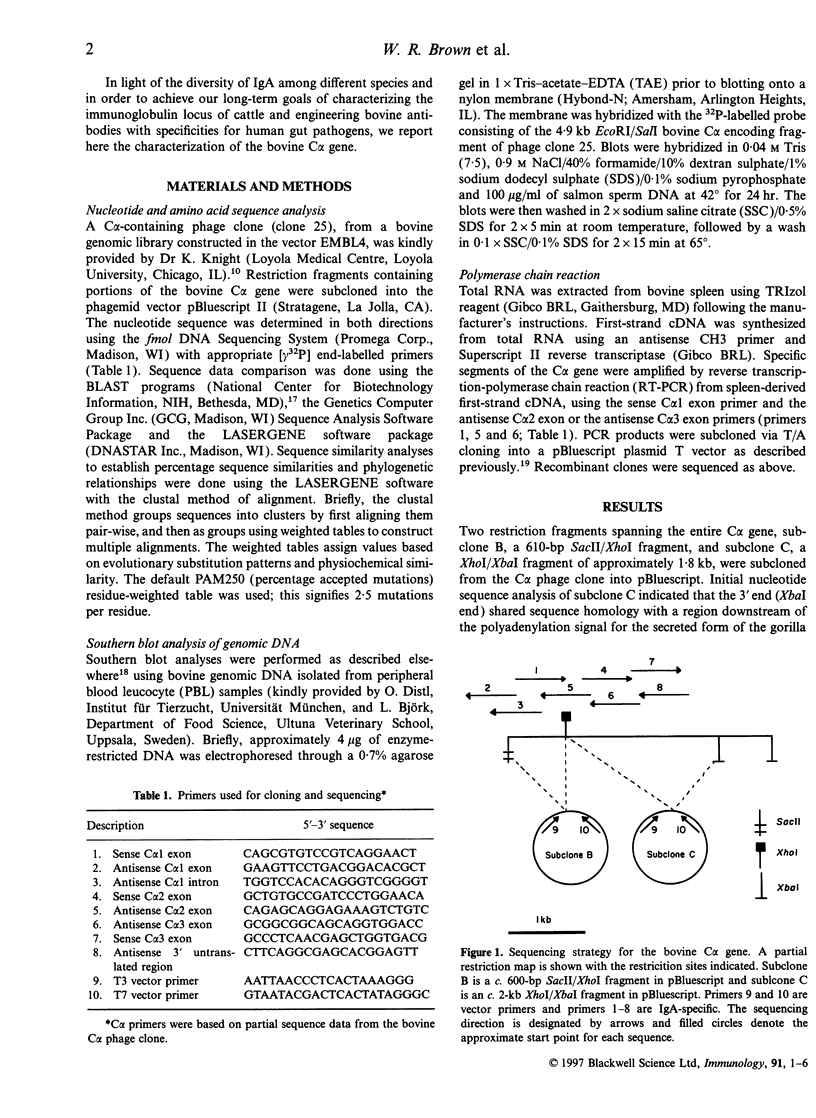
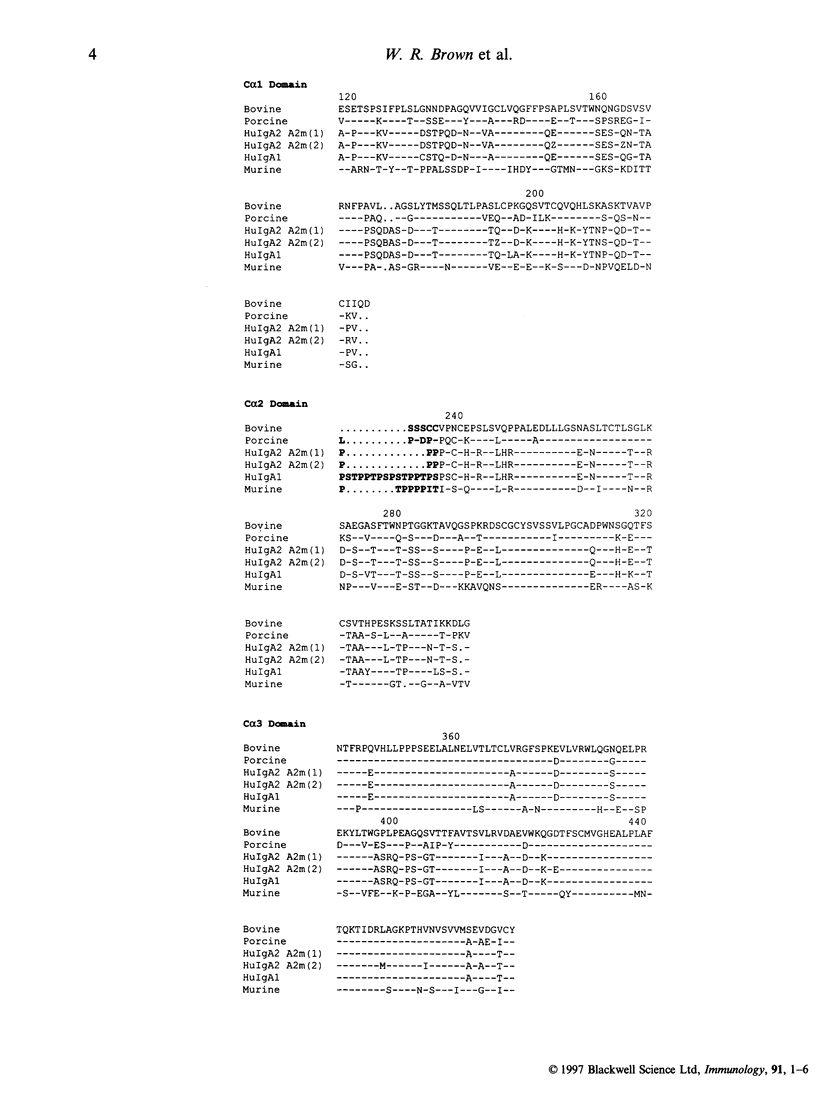
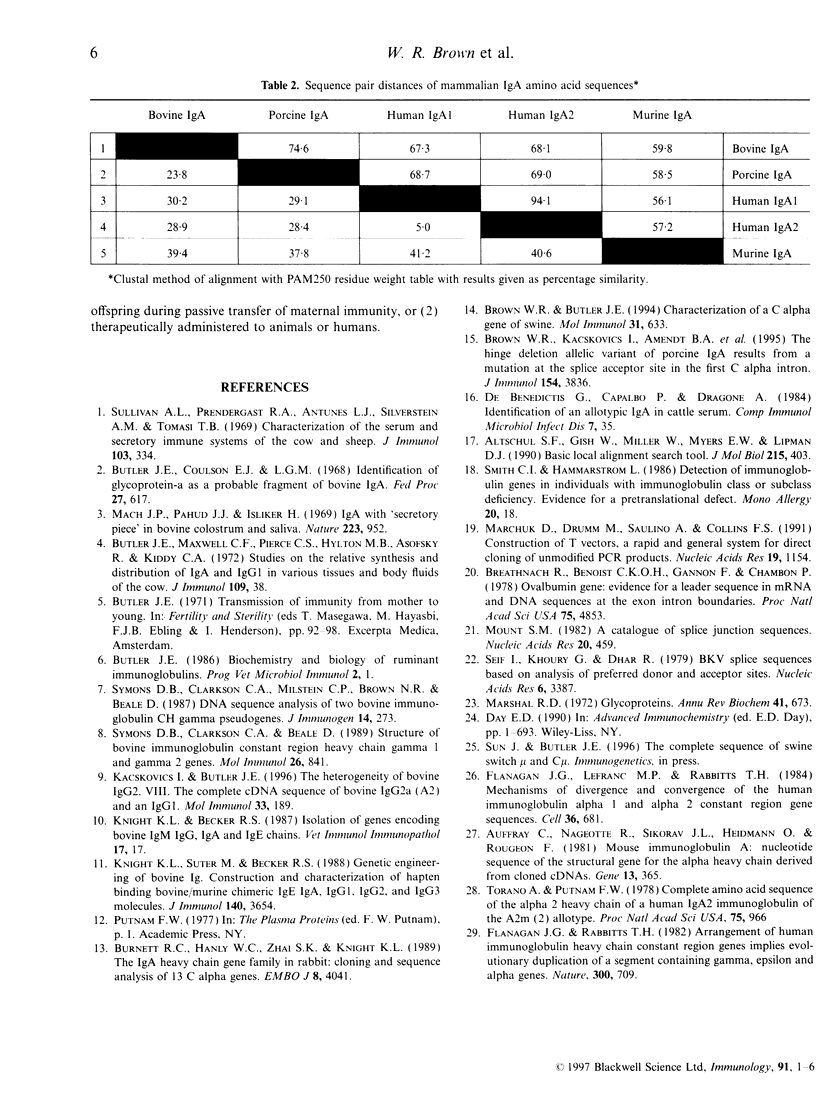
The complete genomic sequence of a bovine C alpha gene is reported here. The genomic sequence was obtained from a C alpha phage clone that had been cloned from a genomic EMBL4 phage vector library. The C alpha sequence had previously been expressed as a chimeric antibody and identified as IgA using IgA-specific antibodies. Intron/exon boundaries were determined by comparison of the genomic sequence with an expressed bovine C alpha sequence obtained from spleen by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Analysis of 50 Swedish bovine genomic DNA samples using genomic blots and five different restriction enzymes failed to detect evidence of polymorphism. However, PstI digests of Brown Swiss DNA showed a restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP), suggesting that at least two allelic variants of bovine IgA exist. Comparison of the deduced amino acid sequence of bovine IgA with sequences available for other species indicated that the highest homology was with that of swine, another artiodactyl. This was the highest homology observed for all mammalian IgA compared except for that between IgA1 and IgA2 in humans. Bovine IgA shares with rabbit IgA3 and IgA4, an additional N-linked glycosylation site at position 282. However, the collective data indicate that cattle are like swine and rodents and unlike rabbits in having a single locus of the gene encoding IgA of this species.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auffray C., Nageotte R., Sikorav J. L., Heidmann O., Rougeon F. Mouse immunoglobulin A: nucleotide sequence of the structural gene for the alpha heavy chain derived from cloned cDNAs. Gene. 1981 May;13(4):365–374. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Benoist C., O'Hare K., Gannon F., Chambon P. Ovalbumin gene: evidence for a leader sequence in mRNA and DNA sequences at the exon-intron boundaries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4853–4857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. R., Butler J. E. Characterization of a C alpha gene of swine. Mol Immunol. 1994 Jun;31(8):633–642. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(94)90171-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. R., Kacskovics I., Amendt B. A., Blackmore N. B., Rothschild M., Shinde R., Butler J. E. The hinge deletion allelic variant of porcine IgA results from a mutation at the splice acceptor site in the first C alpha intron. J Immunol. 1995 Apr 15;154(8):3836–3842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnett R. C., Hanly W. C., Zhai S. K., Knight K. L. The IgA heavy-chain gene family in rabbit: cloning and sequence analysis of 13 C alpha genes. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4041–4047. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08587.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler J. E. Biochemistry and biology of ruminant immunoglobulins. Prog Vet Microbiol Immunol. 1986;2:1–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler J. E., Maxwell C. F., Pierce C. S., Hylton M. B., Asofsky R., Kiddy C. A. Studies on the relative synthesis and distribution of IgA and IgG1 in various tissues and body fluids of the cow. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):38–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Benedictis G., Capalbo P., Dragone A. Identification of an allotypic IgA in cattle serum. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 1984;7(1):35–42. doi: 10.1016/0147-9571(84)90014-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan J. G., Lefranc M. P., Rabbitts T. H. Mechanisms of divergence and convergence of the human immunoglobulin alpha 1 and alpha 2 constant region gene sequences. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):681–688. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90348-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan J. G., Rabbitts T. H. Arrangement of human immunoglobulin heavy chain constant region genes implies evolutionary duplication of a segment containing gamma, epsilon and alpha genes. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):709–713. doi: 10.1038/300709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kacskovics I., Butler J. E. The heterogeneity of bovine IgG2--VIII. The complete cDNA sequence of bovine IgG2a (A2) and an IgG1. Mol Immunol. 1996 Feb;33(2):189–195. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(95)00107-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight K. L., Becker R. S. Isolation of genes encoding bovine IgM, IgG, IgA and IgE chains. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1987 Dec;17(1-4):17–24. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(87)90123-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight K. L., Suter M., Becker R. S. Genetic engineering of bovine Ig. Construction and characterization of hapten-binding bovine/murine chimeric IgE, IgA, IgG1, IgG2, and IgG3 molecules. J Immunol. 1988 May 15;140(10):3654–3659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mach J. P., Pahud J. J., Isliker H. IgA with "secretory piece" in bovine colostrum and saliva. Nature. 1969 Aug 30;223(5209):952–955. doi: 10.1038/223952a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchuk D., Drumm M., Saulino A., Collins F. S. Construction of T-vectors, a rapid and general system for direct cloning of unmodified PCR products. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 11;19(5):1154–1154. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.5.1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall R. D. Glycoproteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1972;41:673–702. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.41.070172.003325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seif I., Khoury G., Dhar R. BKV splice sequences based on analysis of preferred donor and acceptor sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jul 25;6(10):3387–3398. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.10.3387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. I., Hammarström L. Detection of immunoglobulin genes in individuals with immunoglobulin class or subclass deficiency. Evidence for a pretranslational defect. Monogr Allergy. 1986;20:18–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan A. L., Prendergast R. A., Antunes L. J., Silverstein A. M., Tomasi T. B., Jr Characterization of the serum and secretory immune systems of the cow and sheep. J Immunol. 1969 Aug;103(2):334–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symons D. B., Clarkson C. A., Beale D. Structure of bovine immunoglobulin constant region heavy chain gamma 1 and gamma 2 genes. Mol Immunol. 1989 Sep;26(9):841–850. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(89)90140-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symons D. B., Clarkson C. A., Milstein C. P., Brown N. R., Beale D. DNA sequence analysis of two bovine immunoglobulin CH gamma pseudogenes. J Immunogenet. 1987 Dec;14(6):273–283. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-313x.1987.tb00392.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toraño A., Putnam F. W. Complete amino acid sequence of the alpha 2 heavy chain of a human IgA2 immunoglobulin of the A2m (2) allotype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):966–969. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




