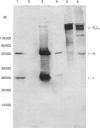
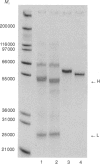
Abstract
The cloning and production of a human anti-rhesus (Rh) D monoclonal antibody (mAb) using the baculovirus-insect cell expression system is described. This monoclonal recombinant antibody R.D7C2 derived from a human parental IgM lambda immunoglobulin was obtained after immortalization of lymphocytes by Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). The human heavy (VH) and light (VL) variable regions were cloned from the parental cell line and genetically fused to the human constant IgG1 heavy (H) and light (L) chain genes (gamma 1 and lambda, respectively). A recombinant baculovirus was constructed that directs the co-expression of genes encoding both genetically fused heavy and light chains under the control of two late and strong baculovirus promoters. After infecting the Spodoptera frugiperda (Sf9) insect cell line with this baculovector, a complete IgG1 mAb was secreted in the culture medium indicating that each immunoglobulin chain was correctly processed and assembled with a functional glycosylation into a tetrameric form. In vitro analysis showed that the functional properties of R.D7C2 using agglutination tests were efficient for the specific recognition of Rh-D-positive red blood cells (RBC). In addition, R.D7C2 showed effector functions of the gamma 1 heavy chain resulting in the lysis of Rh+ papain RBC by an antibody-directed cellular cytotoxicity mechanism. These results demonstrate that R.D7C2 can be produced in the baculovirus-insect cell expression system as a source for potential therapeutic application in the treatment of the haemolytic disease of the newborn.
Full text
PDF

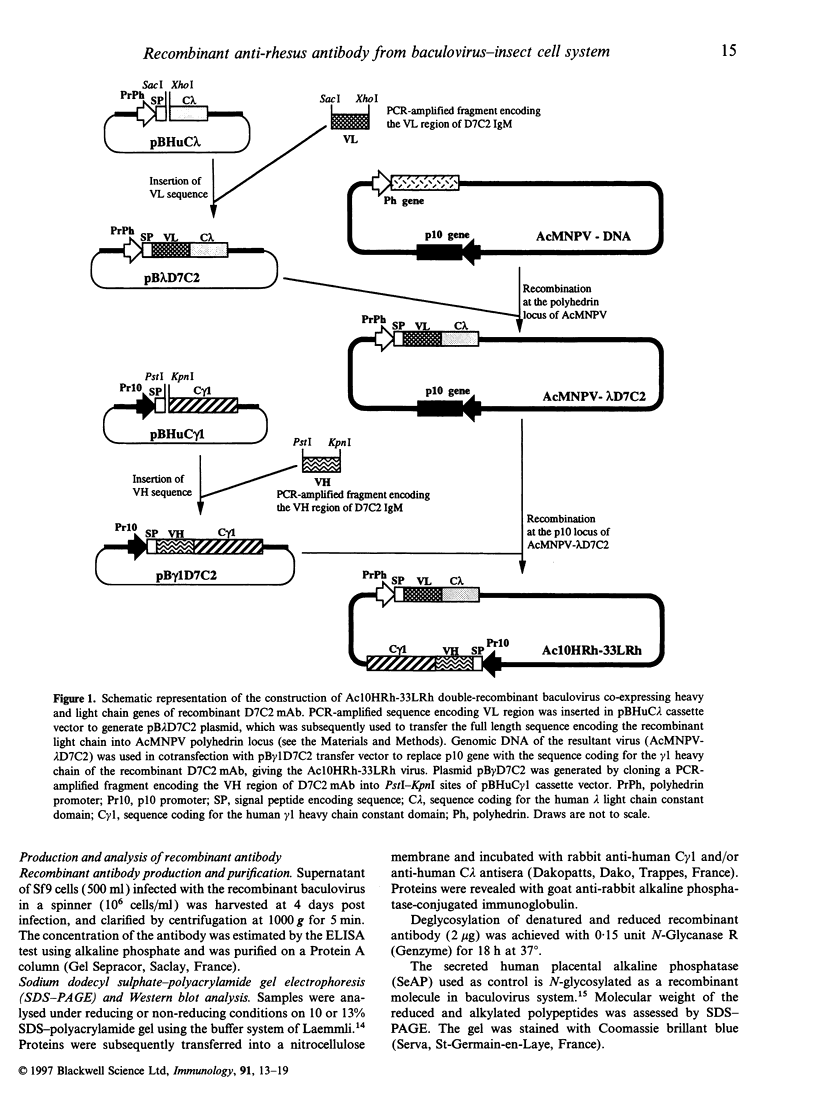

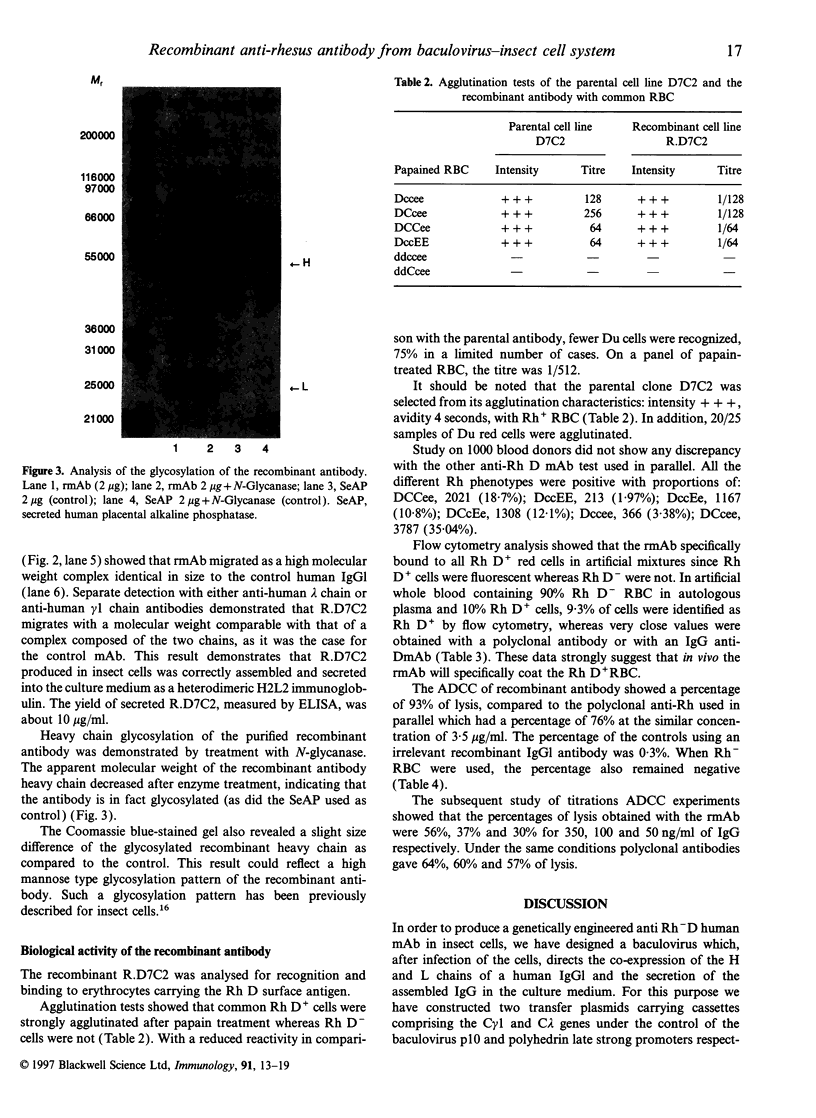


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bird R. E., Hardman K. D., Jacobson J. W., Johnson S., Kaufman B. M., Lee S. M., Lee T., Pope S. H., Riordan G. S., Whitlow M. Single-chain antigen-binding proteins. Science. 1988 Oct 21;242(4877):423–426. doi: 10.1126/science.3140379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blancher A., Socha W. W., Roubinet F., Rowe A. W., Broly H., Byrne P., Holuigue M., Bouzidi A., Huart J. J., Ruffié J. Human monoclonal anti-D-induced clearance of human D-positive red cells in a chimpanzee model. Vox Sang. 1993;65(1):47–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1993.tb04524.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulianne G. L., Hozumi N., Shulman M. J. Production of functional chimaeric mouse/human antibody. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):643–646. doi: 10.1038/312643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman J. M. Suppression of Rh isoimmunization. A review. Obstet Gynecol. 1978 Oct;52(4):385–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bron D., Feinberg M. B., Teng N. N., Kaplan H. S. Production of human monoclonal IgG antibodies against Rhesus (D) antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3214–3217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brüggemann M., Williams G. T., Bindon C. I., Clark M. R., Walker M. R., Jefferis R., Waldmann H., Neuberger M. S. Comparison of the effector functions of human immunoglobulins using a matched set of chimeric antibodies. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1351–1361. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brüggemann M., Winter G., Waldmann H., Neuberger M. S. The immunogenicity of chimeric antibodies. J Exp Med. 1989 Dec 1;170(6):2153–2157. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.6.2153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butters T. D., Hughes R. C., Vischer P. Steps in the biosynthesis of mosquito cell membrane glycoproteins and the effects of tunicamycin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Feb 6;640(3):672–686. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90097-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carayannopoulos L., Max E. E., Capra J. D. Recombinant human IgA expressed in insect cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 30;91(18):8348–8352. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.18.8348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaabihi H., Ogliastro M. H., Martin M., Giraud C., Devauchelle G., Cerutti M. Competition between baculovirus polyhedrin and p10 gene expression during infection of insect cells. J Virol. 1993 May;67(5):2664–2671. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.5.2664-2671.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson D. J., Fraser M. J., Castellino F. J. Oligosaccharide processing in the expression of human plasminogen cDNA by lepidopteran insect (Spodoptera frugiperda) cells. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 12;29(23):5584–5590. doi: 10.1021/bi00475a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dziegiel M., Nielsen L. K., Andersen P. S., Blancher A., Dickmeiss E., Engberg J. Phage display used for gene cloning of human recombinant antibody against the erythrocyte surface antigen, rhesus D. J Immunol Methods. 1995 May 11;182(1):7–19. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(95)00013-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelfriet C. P. The immune destruction of red cells. Transfus Med. 1992 Mar;2(1):1–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3148.1992.tb00128.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godeau F., Saucier C., Kourilsky P. Replication inhibition by nucleoside analogues of a recombinant Autographa californica multicapsid nuclear polyhedrosis virus harboring the herpes thymidine kinase gene driven by the IE-1(0) promoter: a new way to select recombinant baculoviruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Dec 11;20(23):6239–6246. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.23.6239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasemann C. A., Capra J. D. High-level production of a functional immunoglobulin heterodimer in a baculovirus expression system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3942–3946. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis D. L., Summers M. D. Glycosylation and secretion of human tissue plasminogen activator in recombinant baculovirus-infected insect cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):214–223. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumpel B. M., Goodrick M. J., Pamphilon D. H., Fraser I. D., Poole G. D., Morse C., Standen G. R., Chapman G. E., Thomas D. P., Anstee D. J. Human Rh D monoclonal antibodies (BRAD-3 and BRAD-5) cause accelerated clearance of Rh D+ red blood cells and suppression of Rh D immunization in Rh D- volunteers. Blood. 1995 Sep 1;86(5):1701–1709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroda K., Geyer H., Geyer R., Doerfler W., Klenk H. D. The oligosaccharides of influenza virus hemagglutinin expressed in insect cells by a baculovirus vector. Virology. 1990 Feb;174(2):418–429. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90095-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy R., Miller R. A. Biological and clinical implications of lymphocyte hybridomas: tumor therapy with monoclonal antibodies. Annu Rev Med. 1983;34:107–116. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.34.020183.000543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LoBuglio A. F., Wheeler R. H., Trang J., Haynes A., Rogers K., Harvey E. B., Sun L., Ghrayeb J., Khazaeli M. B. Mouse/human chimeric monoclonal antibody in man: kinetics and immune response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4220–4224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks J. D., Ouwehand W. H., Bye J. M., Finnern R., Gorick B. D., Voak D., Thorpe S. J., Hughes-Jones N. C., Winter G. Human antibody fragments specific for human blood group antigens from a phage display library. Biotechnology (N Y) 1993 Oct;11(10):1145–1149. doi: 10.1038/nbt1093-1145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. A., Oseroff A. R., Stratte P. T., Levy R. Monoclonal antibody therapeutic trials in seven patients with T-cell lymphoma. Blood. 1983 Nov;62(5):988–995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesbit M., Fu Z. F., McDonald-Smith J., Steplewski Z., Curtis P. J. Production of a functional monoclonal antibody recognizing human colorectal carcinoma cells from a baculovirus expression system. J Immunol Methods. 1992 Jul 6;151(1-2):201–208. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(92)90118-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oi V. T., Morrison S. L., Herzenberg L. A., Berg P. Immunoglobulin gene expression in transformed lymphoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):825–829. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poul M. A., Cerutti M., Chaabihi H., Devauchelle G., Kaczorek M., Lefranc M. P. Design of cassette baculovirus vectors for the production of therapeutic antibodies in insect cells. Immunotechnology. 1995 Dec;1(3-4):189–196. doi: 10.1016/1380-2933(95)00019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice D., Baltimore D. Regulated expression of an immunoglobulin kappa gene introduced into a mouse lymphoid cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7862–7865. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. E., Ju G., Ericson B. L., Moschera J., Lahm H. W., Chizzonite R., Summers M. D. Modification and secretion of human interleukin 2 produced in insect cells by a baculovirus expression vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8404–8408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. E., Summers M. D., Fraser M. J. Production of human beta interferon in insect cells infected with a baculovirus expression vector. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;3(12):2156–2165. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.12.2156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson K. M., Melamed M. D., Eagle K., Gorick B. D., Gibson T., Holburn A. M., Hughes-Jones N. C. Production of human monoclonal IgG and IgM antibodies with anti-D (rhesus) specificity using heterohybridomas. Immunology. 1986 May;58(1):157–160. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson R. A., Persson M. A., Burton D. R. Expression of a human monoclonal anti-(rhesus D) Fab fragment in Escherichia coli with the use of bacteriophage lambda vectors. Biochem J. 1991 Jul 15;277(Pt 2):561–563. doi: 10.1042/bj2770561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zu Putlitz J., Kubasek W. L., Duchêne M., Marget M., von Specht B. U., Domdey H. Antibody production in baculovirus-infected insect cells. Biotechnology (N Y) 1990 Jul;8(7):651–654. doi: 10.1038/nbt0790-651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]