Abstract
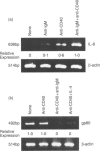
We have examined the contribution of endogenous interleukin-6 (IL-6) to the differentiation of murine B-cell hybridomas. AT73 was established by somatic hybridization between BALB/c mice B cells and 2.52M, a hypoxanthine-aminopterine-thymidine (HAT) medium-sensitive B-cell line mutant. It spontaneously secreted IgM, and addition of exogenous IL-6 augmented IgM secretion. Triggering of CD40 led to an augmentation of IL-6 expression and IgM secretion. Blocking the binding of IL-6 to its cellular receptor through the use of inhibitory monoclonal antibodies inhibited CD40-induced IgM secretion, suggesting a possible autocrine role of IL-6 for the differentiation of a CD40-activated B-cell hybridoma. Co-triggering with CD40 and B-cell receptor or activation through CD40 and IL-4 led to a synergistic augmentation of IL-6 expression as well as additive IgM secretion; this was followed by a marked decrease in the expression of B-cell surface markers on the cell membrane. Furthermore, under conditions where IL-6 expression was augmented, gp80 expression was down-regulated, suggesting a negative feedback mechanism in this B-cell hybridoma. These findings provide a role by which T-cell-dependent activation through CD40 regulates an IL-6 autocrine loop, controlling B-cell differentiation.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axcrona K., Gray D., Leanderson T. Regulation of B cell growth and differentiation via CD21 and CD40. Eur J Immunol. 1996 Sep;26(9):2203–2207. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830260936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballagi-Pordány A., Ballagi-Pordány A., Funa K. Quantitative determination of mRNA phenotypes by the polymerase chain reaction. Anal Biochem. 1991 Jul;196(1):89–94. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(91)90122-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker S., Quay J., Soukup J. Cytokine (tumor necrosis factor, IL-6, and IL-8) production by respiratory syncytial virus-infected human alveolar macrophages. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 15;147(12):4307–4312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berberich I., Shu G. L., Clark E. A. Cross-linking CD40 on B cells rapidly activates nuclear factor-kappa B. J Immunol. 1994 Nov 15;153(10):4357–4366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman M. C., Attrep J. F., Grammer A. C., Lipsky P. E. Ligation of CD40 influences the function of human Ig-secreting B cell hybridomas both positively and negatively. J Immunol. 1996 May 1;156(9):3118–3132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burdin N., Van Kooten C., Galibert L., Abrams J. S., Wijdenes J., Banchereau J., Rousset F. Endogenous IL-6 and IL-10 contribute to the differentiation of CD40-activated human B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1995 Mar 15;154(6):2533–2544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi M. S., Brines R. D., Holman M. J., Klaus G. G. Induction of NF-AT in normal B lymphocytes by anti-immunoglobulin or CD40 ligand in conjunction with IL-4. Immunity. 1994 Jun;1(3):179–187. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(94)90096-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark E. A., Shu G. Association between IL-6 and CD40 signaling. IL-6 induces phosphorylation of CD40 receptors. J Immunol. 1990 Sep 1;145(5):1400–1406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford R. J., Tamayo A., Ambrus J. L., Jr The role of growth factors in human lymphomas. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1992;182:341–347. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-77633-5_44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronowicz E., Coutinho A., Melchers F. A plaque assay for all cells secreting Ig of a given type or class. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Aug;6(8):588–590. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamano T., Kim K. J., Leiserson W. M., Asofsky R. Establishment of B cell hybridomas with B cell surface antigens. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1403–1406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamano T., Murata Y., Yamasaki T., Yasuda Y., Iwasaki T., Nagai K. Establishment of an antigen-specific B cell clone by somatic hybridization. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 15;139(8):2556–2561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasbold J., Johnson-Léger C., Atkins C. J., Clark E. A., Klaus G. G. Properties of mouse CD40: cellular distribution of CD40 and B cell activation by monoclonal anti-mouse CD40 antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Aug;24(8):1835–1842. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibi M., Murakami M., Saito M., Hirano T., Taga T., Kishimoto T. Molecular cloning and expression of an IL-6 signal transducer, gp130. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1149–1157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90411-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata Y., Taga T., Hibi M., Nakano N., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. Characterization of IL-6 receptor expression by monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 1;143(9):2900–2906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki T., Hamano T., Hase K., Murata Y., Yamasaki T., Kakishita E. Functional role of self IA molecules in polyclonal B cell activation using an autoreactive B cell clone derived from (NZB X NZW) F1 mice. Cell Immunol. 1992 Feb;139(2):386–398. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(92)90080-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki T., Hamano T., Murata Y., Yamasaki T., Nagai K. Establishment of a bromelain-treated isologous red blood cell reactive B cell clone by somatic hybridization. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1989 Oct;53(1):78–86. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(89)90103-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabara H. H., Fu S. M., Geha R. S., Vercelli D. CD40 and IgE: synergism between anti-CD40 monoclonal antibody and interleukin 4 in the induction of IgE synthesis by highly purified human B cells. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1861–1864. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaus G. G., Holman M., Hasbold J. Properties of mouse CD40: the role of homotypic adhesion in the activation of B cells via CD40. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Nov;24(11):2714–2719. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830241121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi I., Matsuda T., Saito T., Yasukawa K., Kikutani H., Hirano T., Taga T., Kishimoto T. Abnormal distribution of IL-6 receptor in aged MRL/lpr mice: elevated expression on B cells and absence on CD4+ cells. Int Immunol. 1992 Dec;4(12):1407–1412. doi: 10.1093/intimm/4.12.1407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanzavecchia A. Antigen-specific interaction between T and B cells. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):537–539. doi: 10.1038/314537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagafuchi H., Suzuki N., Mizushima Y., Sakane T. Constitutive expression of IL-6 receptors and their role in the excessive B cell function in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1993 Dec 1;151(11):6525–6534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieckmann P., D'Alessandro F., Nordan R. P., Fauci A. S., Kehrl J. H. IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Autocrine and paracrine cytokines involved in B cell function. J Immunol. 1991 May 15;146(10):3462–3468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronchese F., Hausmann B. B lymphocytes in vivo fail to prime naive T cells but can stimulate antigen-experienced T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1993 Mar 1;177(3):679–690. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.3.679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothe M., Sarma V., Dixit V. M., Goeddel D. V. TRAF2-mediated activation of NF-kappa B by TNF receptor 2 and CD40. Science. 1995 Sep 8;269(5229):1424–1427. doi: 10.1126/science.7544915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito M., Yoshida K., Hibi M., Taga T., Kishimoto T. Molecular cloning of a murine IL-6 receptor-associated signal transducer, gp130, and its regulated expression in vivo. J Immunol. 1992 Jun 15;148(12):4066–4071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taga T., Kawanishi Y., Hardy R. R., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. Receptors for B cell stimulatory factor 2. Quantitation, specificity, distribution, and regulation of their expression. J Exp Med. 1987 Oct 1;166(4):967–981. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.4.967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang B., Matsuda T., Akira S., Nagata N., Ikehara S., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. Age-associated increase in interleukin 6 in MRL/lpr mice. Int Immunol. 1991 Mar;3(3):273–278. doi: 10.1093/intimm/3.3.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vercelli D., Jabara H. H., Arai K., Yokota T., Geha R. S. Endogenous interleukin 6 plays an obligatory role in interleukin 4-dependent human IgE synthesis. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Aug;19(8):1419–1424. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]