Abstract
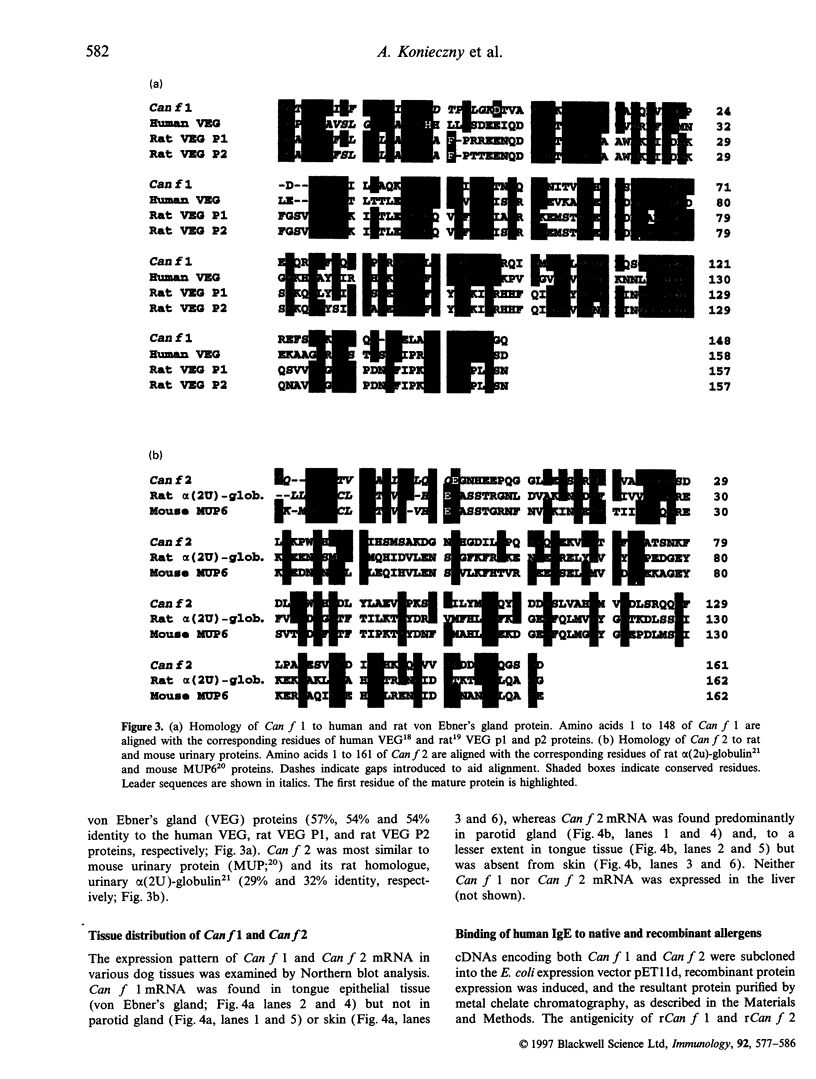
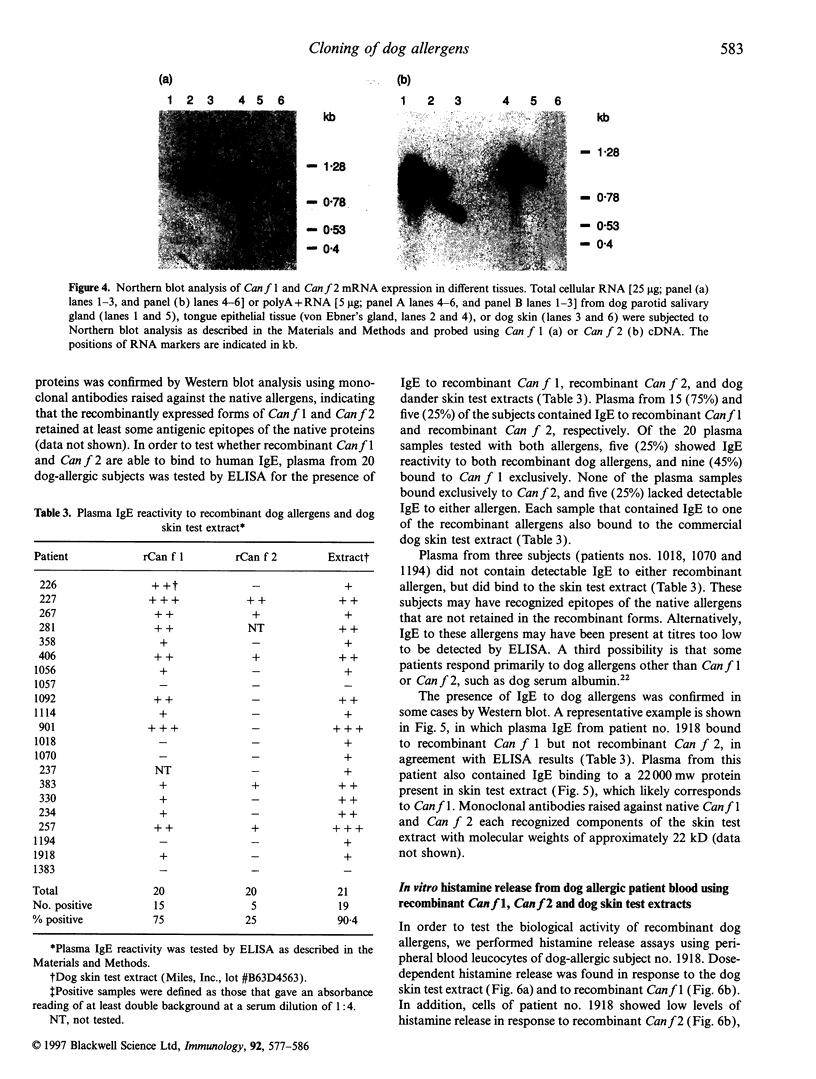
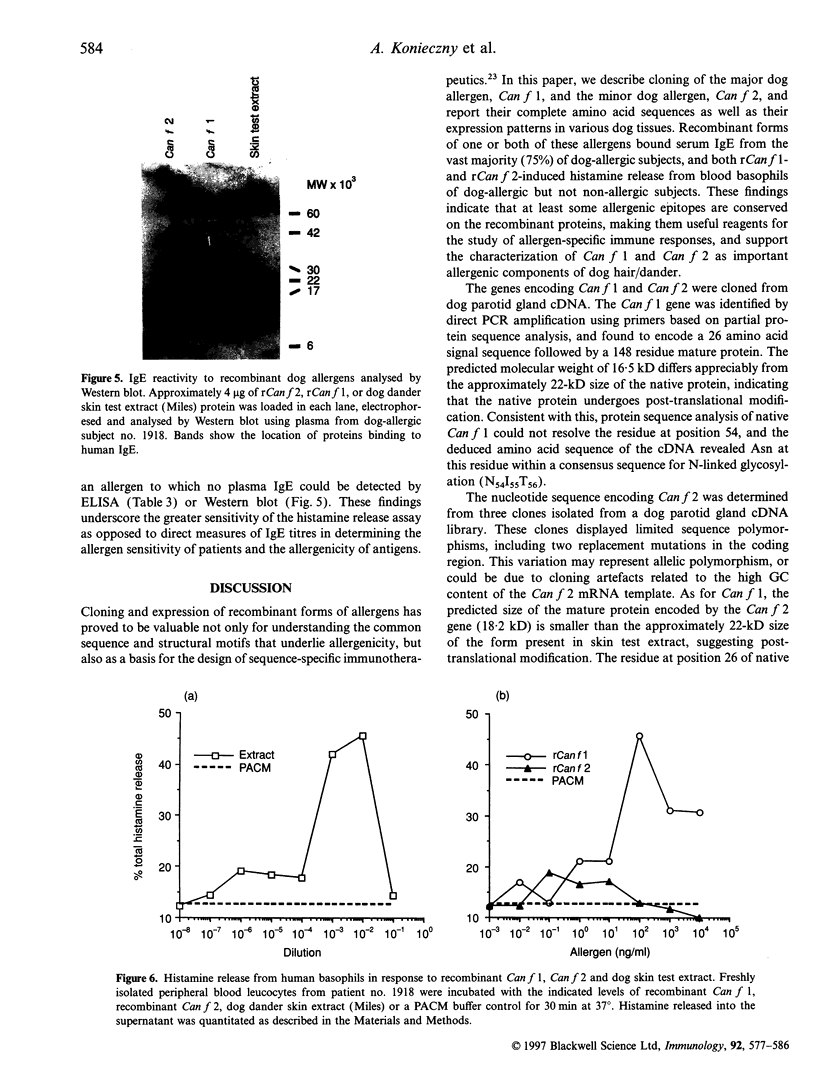
Canis familiaris allergen 1 (Can f 1) and Canis familiaris allergen 2 (Can f 2) are the two major allergens present in dog dander extracts. We now report the isolation of cDNAs encoding both proteins and present their nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences. Can f 1, produced by tongue epithelial tissue, has homology with the von Ebner's gland (VEG) protein, a salivary protein not previously thought to have allergenic properties. Can f 2, produced by tongue and parotid gland, has homology with mouse urinary protein (MUP), a known allergen. Both VEG protein and MUP are members of the lipocalin family of small ligand-binding proteins. Recombinant forms of Can f 1 and Can f 2 were produced and tested for immunoglobulin E (IgE) reactivity. Among dog-allergic subjects, 45% had IgE directed exclusively to rCan f 1, and 25% had IgE to both rCan f 1 and rCan f 2. In addition, both recombinant proteins were able to cross-link IgE and elicit histamine release from peripheral blood leucocytes in vitro. These findings confirm that Can f 1 and Can f 2 are major and minor dog allergens, respectively, and demonstrate that recombinant forms of dog allergens retain at least some IgE-binding epitopes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayard C., Holmquist L., Vesterberg O. Purification and identification of allergenic alpha (2u)-globulin species of rat urine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1996 Jun 4;1290(2):129–134. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(96)00006-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bläker M., Kock K., Ahlers C., Buck F., Schmale H. Molecular cloning of human von Ebner's gland protein, a member of the lipocalin superfamily highly expressed in lingual salivary glands. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Feb 20;1172(1-2):131–137. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(93)90279-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boutin Y., Hébert H., Vrancken E. R., Mourad W. Allergenicity and cross-reactivity of cat and dog allergenic extracts. Clin Allergy. 1988 May;18(3):287–293. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1988.tb02871.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brauer A. W., Oman C. L., Margolies M. N. Use of o-phthalaldehyde to reduce background during automated Edman degradation. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):134–142. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90359-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. R., Leitermann K., Ohman J. L., Jr Distribution of cat allergen 1 in cat tissues and fluids. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1984;74(1):67–70. doi: 10.1159/000233518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böcskei Z., Groom C. R., Flower D. R., Wright C. E., Phillips S. E., Cavaggioni A., Findlay J. B., North A. C. Pheromone binding to two rodent urinary proteins revealed by X-ray crystallography. Nature. 1992 Nov 12;360(6400):186–188. doi: 10.1038/360186a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derman E. Isolation of a cDNA clone for mouse urinary proteins: age- and sex-related expression of mouse urinary protein genes is transcriptionally controlled. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5425–5429. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flower D. R. The lipocalin protein family: structure and function. Biochem J. 1996 Aug 15;318(Pt 1):1–14. doi: 10.1042/bj3180001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford A. W., Alterman L., Kemeny D. M. The allergens of dog. I. Identification using crossed radio-immunoelectrophoresis. Clin Exp Allergy. 1989 Mar;19(2):183–190. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1989.tb02362.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford A. W., Kemeny D. M. The allergens of dog. II. Identification and partial purification of a major dander allergen. Clin Exp Allergy. 1992 Aug;22(8):793–803. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1992.tb02820.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haugaard L., Dahl R. Immunotherapy in patients allergic to cat and dog dander. I. Clinical results. Allergy. 1992 Jun;47(3):249–254. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1992.tb00658.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedlin G., Graff-Lonnevig V., Heilborn H., Lilja G., Norrlind K., Pegelow K., Sundin B., Lowenstein H. Immunotherapy with cat- and dog-dander extracts. V. Effects of 3 years of treatment. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1991 May;87(5):955–964. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(91)90417-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedlin G., Heilborn H., Lilja G., Norrlind K., Pegelow K. O., Schou C., Løwenstein H. Long-term follow-up of patients treated with a three-year course of cat or dog immunotherapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1995 Dec;96(6 Pt 1):879–885. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(95)70223-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura H., Odani S., Nishi S., Sato H., Arakawa M., Ono T. Primary structure and cellular distribution of two fatty acid-binding proteins in adult rat kidneys. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 25;266(9):5963–5972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjellman B., Pettersson R. The problem of furred pets in childhood atopic disease. Failure of an information program. Allergy. 1983 Jan;38(1):65–73. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1983.tb00858.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kock K., Ahlers C., Schmale H. Structural organization of the genes for rat von Ebner's gland proteins 1 and 2 reveals their close relationship to lipocalins. Eur J Biochem. 1994 May 1;221(3):905–916. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb18806.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kock K., Bläker M., Schmale H. Postnatal development of von Ebner's glands: accumulation of a protein of the lipocalin superfamily in taste papillae of rat tongue. Cell Tissue Res. 1992 Feb;267(2):313–320. doi: 10.1007/BF00302970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorusso J. R., Moffat S., Ohman J. L., Jr Immunologic and biochemical properties of the major mouse urinary allergen (Mus m 1). J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1986 Nov;78(5 Pt 1):928–937. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(86)90242-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco H. L., Zanotti G. Three-dimensional structure and active site of three hydrophobic molecule-binding proteins with significant amino acid sequence similarity. Biopolymers. 1992 Apr;32(4):457–465. doi: 10.1002/bip.360320425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgenstern J. P., Griffith I. J., Brauer A. W., Rogers B. L., Bond J. F., Chapman M. D., Kuo M. C. Amino acid sequence of Fel dI, the major allergen of the domestic cat: protein sequence analysis and cDNA cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9690–9694. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munir A. K., Einarsson R., Dreborg S. K. Mite (Der p I, Der f I), cat (Fel d I) and dog (Can f I) allergens in dust from Swedish day-care centres. Clin Exp Allergy. 1995 Feb;25(2):119–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1995.tb01016.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munir A. K., Einarsson R., Schou C., Dreborg S. K. Allergens in school dust. I. The amount of the major cat (Fel d I) and dog (Can f I) allergens in dust from Swedish schools is high enough to probably cause perennial symptoms in most children with asthma who are sensitized to cat and dog. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1993 May;91(5):1067–1074. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(93)90221-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolte H., Schiøtz O., Skov P. S. A new glass microfibre-based histamine analysis for allergy testing in children. Results compared with conventional leukocyte histamine release assay, skin prick test, bronchial provocation test and RAST. Allergy. 1987 Jul;42(5):366–373. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1987.tb02223.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers B. L., Morgenstern J. P., Garman R. D., Bond J. F., Kuo M. C. Recombinant Fel d.I: Expression, purification, IgE binding and reaction with cat-allergic human T cells. Mol Immunol. 1993 Apr;30(6):559–568. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(93)90030-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakaguchi M., Inouye S., Irie T., Miyazawa H., Watanabe M., Yasueda H., Shida T., Nitta H., Chapman M. D., Schou C. Airborne cat (Fel d I), dog (Can f I), and mite (Der I and Der II) allergen levels in the homes of Japan. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1993 Dec;92(6):797–802. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(93)90056-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schou C., Svendsen U. G., Løwenstein H. Purification and characterization of the major dog allergen, Can f I. Clin Exp Allergy. 1991 May;21(3):321–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1991.tb01663.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitzauer S., Pandjaitan B., Mühl S., Ebner C., Kraft D., Valenta R., Rumpold H. Major cat and dog allergens share IgE epitopes. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997 Jan;99(1 Pt 1):100–106. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(97)70306-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitzauer S., Schweiger C., Sperr W. R., Pandjaitan B., Valent P., Mühl S., Ebner C., Scheiner O., Kraft D., Rumpold H. Molecular characterization of dog albumin as a cross-reactive allergen. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1994 Mar;93(3):614–627. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(94)70073-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unterman R. D., Lynch K. R., Nakhasi H. L., Dolan K. P., Hamilton J. W., Cohn D. V., Feigelson P. Cloning and sequence of several alpha 2u-globulin cDNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3478–3482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viander M., Valovirta E., Vanto T., Koivikko A. Cross-reactivity of cat and dog allergen extracts. RAST inhibition studies with special reference to the allergenic activity in saliva and urine. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1983;71(3):252–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallner B. P., Gefter M. L. Peptide therapy for treatment of allergic diseases. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1996 Aug;80(2):105–109. doi: 10.1006/clin.1996.0102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wüthrich B., Guerin B., Hewitt B. E. Cross-allergenicity between extracts of hair from different dog breeds and cat fur. Clin Allergy. 1985 Mar;15(2):87–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1985.tb02260.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Andrade A. D., Charpin D., Birnbaum J., Lanteaume A., Chapman M., Vervloet D. Indoor allergen levels in day nurseries. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1995 Jun;95(6):1158–1163. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(95)70071-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groot H., Goei K. G., van Swieten P., Aalberse R. C. Affinity purification of a major and a minor allergen from dog extract: serologic activity of affinity-purified Can f I and of Can f I-depleted extract. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1991 Jun;87(6):1056–1065. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(91)92150-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Milligen F. J., Vroom T. M., Aalberse R. C. Presence of Felis domesticus allergen I in the cat's salivary and lacrimal glands. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1990;92(4):375–378. doi: 10.1159/000235168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van't Hof W., Blankenvoorde M. F., Veerman E. C., Amerongen A. V. The salivary lipocalin von Ebner's gland protein is a cysteine proteinase inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1997 Jan 17;272(3):1837–1841. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.3.1837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]