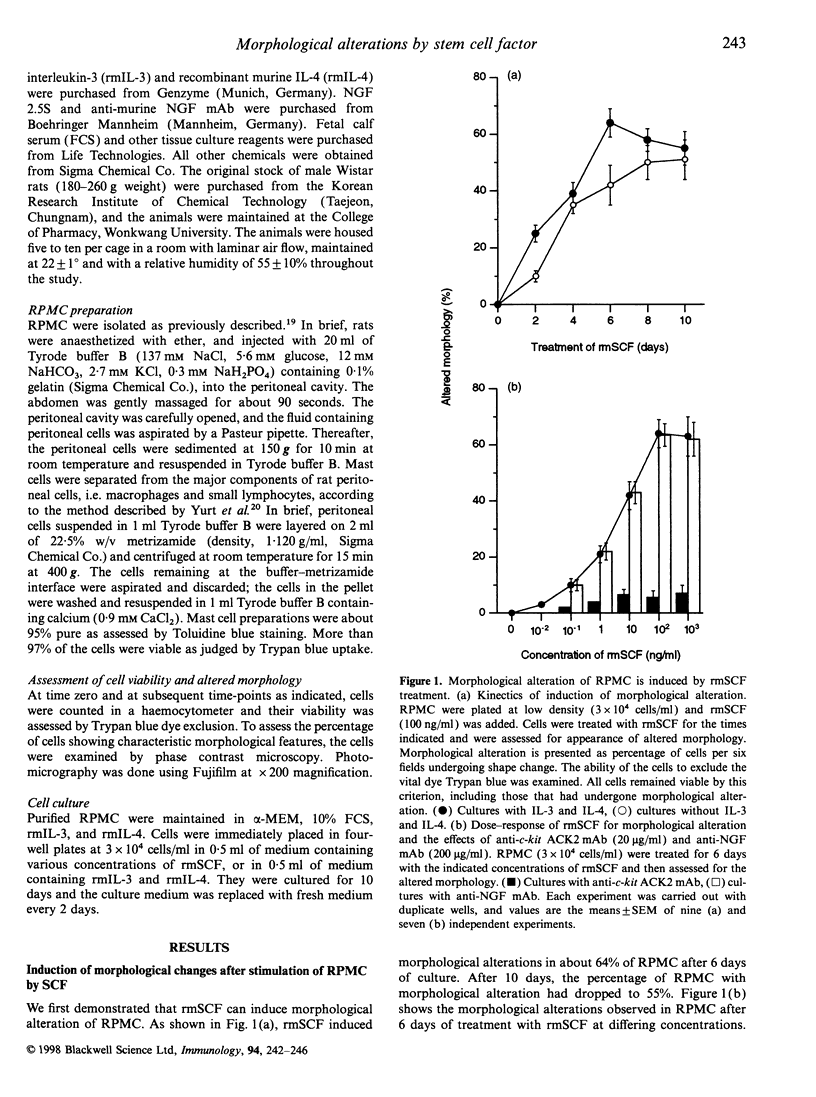
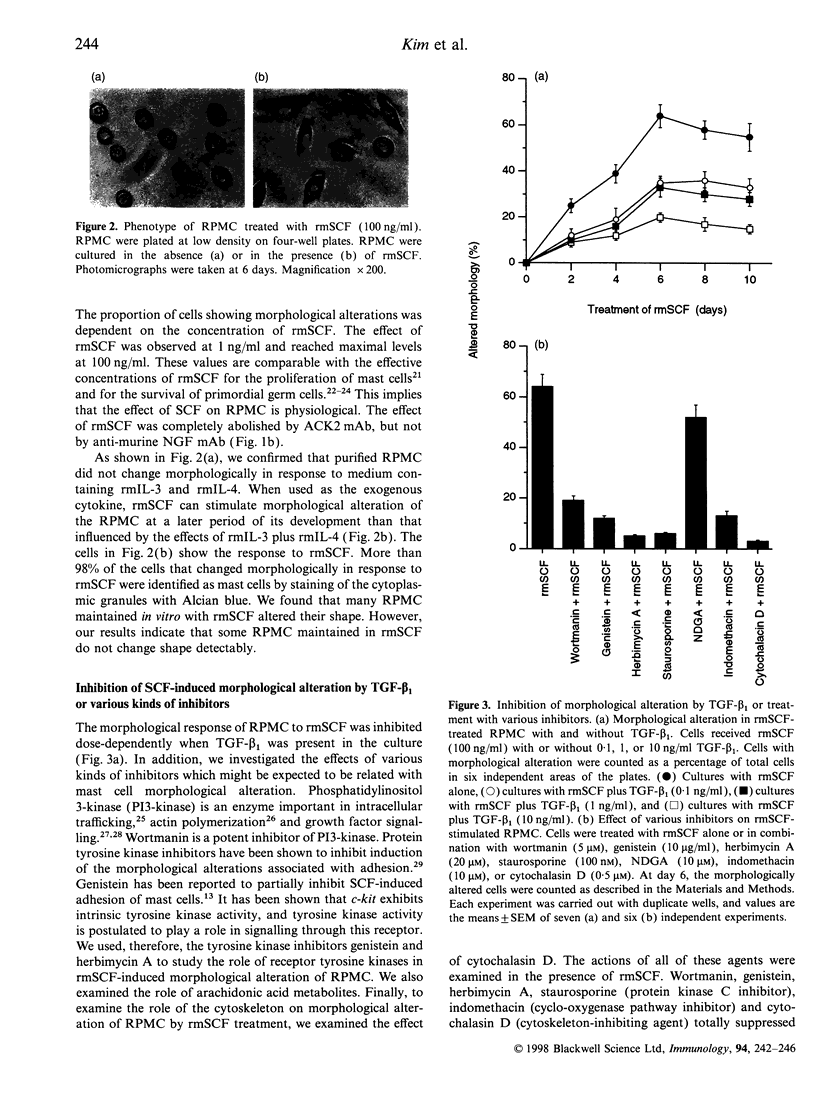
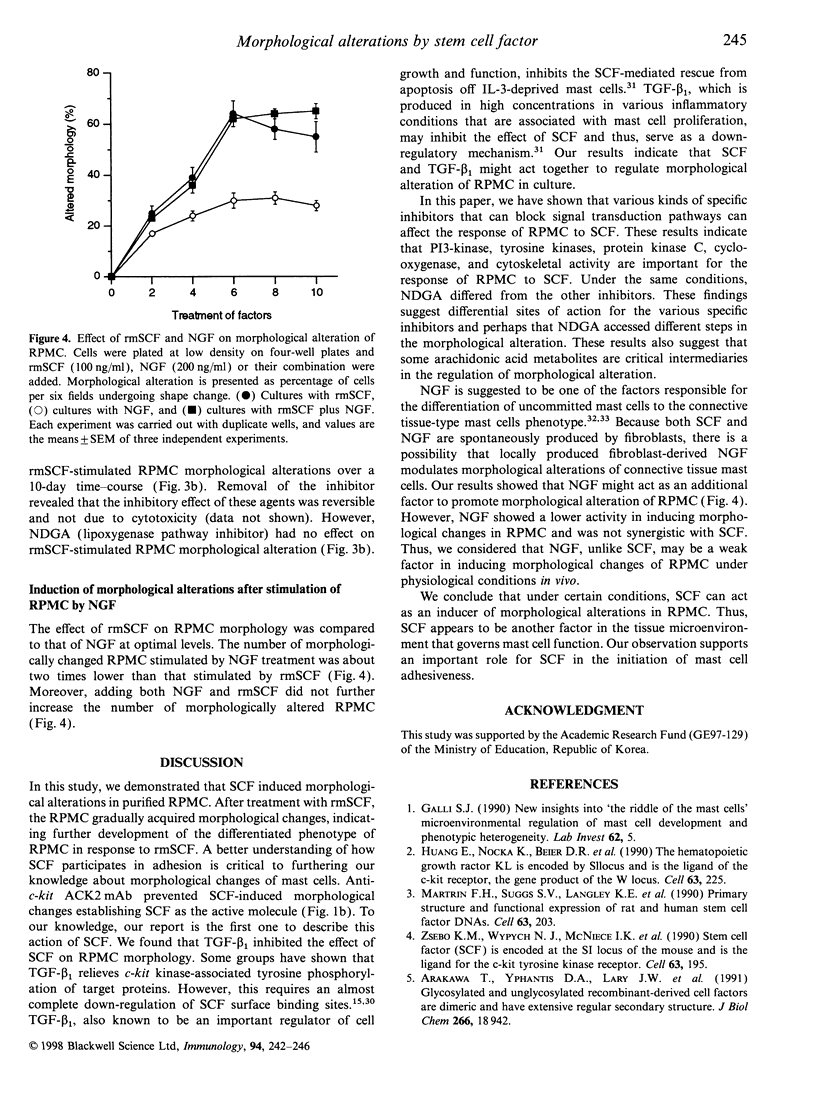
Abstract
Stem cell factor (SCF) stimulates mast cell adhesion and, because SCF is produced normally in tissues, it may be a major factor responsible for the adhesion of mast cells to connective tissue matrix. We found that the morphology of rat peritoneal mast cells (RPMC) altered after the addition of recombinant murine SCF (rmSCF) in vitro. The ability of rmSCF to enhance morphological alteration was dose dependent and completely abolished by anti-c-kit ACK2 monoclonal antibody. Exposure of RPMC to transforming growth factor-beta 1, wortmannin, genistein, herbimycin A, staurosporine, indomethacin and cytochalasin D before the addition of rmSCF antagonized rmSCF-induced morphological alteration. However, nordihydroguiaretic acid had no effect. Many RPMC appeared to respond also to nerve growth factor (NGF) but the total number of cells with altered morphology was much greater when the culture was stimulated by rmSCF than by NGF. We suggest that morphological alterations of mast cells by rmSCF is an important step for the participation in adhesion to tissue under resident physiological conditions.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axelrad A. A. Some hemopoietic negative regulators. Exp Hematol. 1990 Feb;18(2):143–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruni A., Bigon E., Boarato E., Mietto L., Leon A., Toffano G. Interaction between nerve growth factor and lysophosphatidylserine on rat peritoneal mast cells. FEBS Lett. 1982 Feb 22;138(2):190–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80438-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler Y. X., Tibbetts S. A., Chirathaworn C., Benedict S. H. Modulation of T cell morphology and induction of homotypic adhesion by a protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Cell Immunol. 1995 Jun;163(1):129–138. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1995.1107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen B., Liu Y. X., Druker B., Roberts T. M., Schaffhausen B. S. Characterization of pp85, a target of oncogenes and growth factor receptors. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2909–2915. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Columbo M., Horowitz E. M., Botana L. M., MacGlashan D. W., Jr, Bochner B. S., Gillis S., Zsebo K. M., Galli S. J., Lichtenstein L. M. The human recombinant c-kit receptor ligand, rhSCF, induces mediator release from human cutaneous mast cells and enhances IgE-dependent mediator release from both skin mast cells and peripheral blood basophils. J Immunol. 1992 Jul 15;149(2):599–608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dastych J., Metcalfe D. D. Stem cell factor induces mast cell adhesion to fibronectin. J Immunol. 1994 Jan 1;152(1):213–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolci S., Williams D. E., Ernst M. K., Resnick J. L., Brannan C. I., Lock L. F., Lyman S. D., Boswell H. S., Donovan P. J. Requirement for mast cell growth factor for primordial germ cell survival in culture. Nature. 1991 Aug 29;352(6338):809–811. doi: 10.1038/352809a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli S. J. New insights into "the riddle of the mast cells": microenvironmental regulation of mast cell development and phenotypic heterogeneity. Lab Invest. 1990 Jan;62(1):5–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli S. J., Zsebo K. M., Geissler E. N. The kit ligand, stem cell factor. Adv Immunol. 1994;55:1–96. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60508-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godin I., Deed R., Cooke J., Zsebo K., Dexter M., Wylie C. C. Effects of the steel gene product on mouse primordial germ cells in culture. Nature. 1991 Aug 29;352(6338):807–809. doi: 10.1038/352807a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham G. J., Pragnell I. B. Negative regulators of haemopoiesis--current advances. Prog Growth Factor Res. 1990;2(3):181–192. doi: 10.1016/0955-2235(90)90004-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E., Nocka K., Beier D. R., Chu T. Y., Buck J., Lahm H. W., Wellner D., Leder P., Besmer P. The hematopoietic growth factor KL is encoded by the Sl locus and is the ligand of the c-kit receptor, the gene product of the W locus. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90303-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iemura A., Tsai M., Ando A., Wershil B. K., Galli S. J. The c-kit ligand, stem cell factor, promotes mast cell survival by suppressing apoptosis. Am J Pathol. 1994 Feb;144(2):321–328. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jippo-Kanemoto T., Kasugai T., Yamatodani A., Ushio H., Mochizuki T., Tohya K., Kimura M., Nishimura M., Kitamura Y. Supernormal histamine release and normal cytotoxic activity of beige (Chédiak-Higashi syndrome) rat mast cells with giant granules. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1993;100(2):99–106. doi: 10.1159/000236395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura Y., Go S. Decreased production of mast cells in S1/S1d anemic mice. Blood. 1979 Mar;53(3):492–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura Y., Go S., Hatanaka K. Decrease of mast cells in W/Wv mice and their increase by bone marrow transplantation. Blood. 1978 Aug;52(2):447–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kundra V., Escobedo J. A., Kazlauskas A., Kim H. K., Rhee S. G., Williams L. T., Zetter B. R. Regulation of chemotaxis by the platelet-derived growth factor receptor-beta. Nature. 1994 Feb 3;367(6462):474–476. doi: 10.1038/367474a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin F. H., Suggs S. V., Langley K. E., Lu H. S., Ting J., Okino K. H., Morris C. F., McNiece I. K., Jacobsen F. W., Mendiaz E. A. Primary structure and functional expression of rat and human stem cell factor DNAs. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):203–211. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90301-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda H., Kannan Y., Ushio H., Kiso Y., Kanemoto T., Suzuki H., Kitamura Y. Nerve growth factor induces development of connective tissue-type mast cells in vitro from murine bone marrow cells. J Exp Med. 1991 Jul 1;174(1):7–14. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui Y., Toksoz D., Nishikawa S., Nishikawa S., Williams D., Zsebo K., Hogan B. L. Effect of Steel factor and leukaemia inhibitory factor on murine primordial germ cells in culture. Nature. 1991 Oct 24;353(6346):750–752. doi: 10.1038/353750a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meininger C. J., Yano H., Rottapel R., Bernstein A., Zsebo K. M., Zetter B. R. The c-kit receptor ligand functions as a mast cell chemoattractant. Blood. 1992 Feb 15;79(4):958–963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekori Y. A., Metcalfe D. D. Transforming growth factor-beta prevents stem cell factor-mediated rescue of mast cells from apoptosis after IL-3 deprivation. J Immunol. 1994 Sep 1;153(5):2194–2203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce F. L., Thompson H. L. Some characteristics of histamine secretion from rat peritoneal mast cells stimulated with nerve growth factor. J Physiol. 1986 Mar;372:379–393. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruderman N. B., Kapeller R., White M. F., Cantley L. C. Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase by insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1411–1415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider W. D., Johnson E. M., Jr Neurotrophic molecules. Ann Neurol. 1989 Oct;26(4):489–506. doi: 10.1002/ana.410260402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai M., Takeishi T., Thompson H., Langley K. E., Zsebo K. M., Metcalfe D. D., Geissler E. N., Galli S. J. Induction of mast cell proliferation, maturation, and heparin synthesis by the rat c-kit ligand, stem cell factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6382–6386. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valent P., Sillaber C., Bettelheim P. The growth and differentiation of mast cells. Prog Growth Factor Res. 1991;3(1):27–41. doi: 10.1016/0955-2235(91)90011-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. E., de Vries P., Namen A. E., Widmer M. B., Lyman S. D. The Steel factor. Dev Biol. 1992 Jun;151(2):368–376. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90176-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yurt R. W., Leid R. W., Jr, Austen K. F. Native heparin from rat peritoneal mast cells. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 25;252(2):518–521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zsebo K. M., Wypych J., McNiece I. K., Lu H. S., Smith K. A., Karkare S. B., Sachdev R. K., Yuschenkoff V. N., Birkett N. C., Williams L. R. Identification, purification, and biological characterization of hematopoietic stem cell factor from buffalo rat liver--conditioned medium. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):195–201. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90300-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vos S., Brach M. A., Asano Y., Ludwig W. D., Bettelheim P., Gruss H. J., Herrmann F. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 interferes with the proliferation-inducing activity of stem cell factor in myelogenous leukemia blasts through functional down-regulation of the c-kit proto-oncogene product. Cancer Res. 1993 Aug 1;53(15):3638–3642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



